Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trial WatchTrends in Clinical Trial Design Complexity
Uploaded by
SophiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trial WatchTrends in Clinical Trial Design Complexity
Uploaded by
SophiaCopyright:
Available Formats
N E W S & A N A LY S I S
BIOBUSINESS BRIEFS
T R I A L WAT C H of excessive and unnecessary clinical data
may also compromise data integrity and
Trends in clinical trial design complexity analysis, lead to higher error rates, drive
longer study durations and delay submissions
to regulatory agencies.
The challenges of measuring the safety and Phase I protocols were the most complex, A growing number of pharmaceutical and
efficacy of investigational drugs that target with the highest mean number of distinct biotechnology companies and contract
chronic, difficult-to-treat or rare diseases procedures (36) and total procedures (253) research organizations have taken steps to
in more narrowly defined patient carried out in the 2011–2015 period. Phase III optimize their protocol designs in order
subpopulations have increased the scope protocols saw the highest relative growth in to improve feasibility, ease site and subject
of clinical trials and the burden to execute total procedures carried out, increasing by participation burden, reduce the number of
them in the past 15 years. Other factors 70% from a mean of 110 procedures in unplanned and unbudgeted protocol
affecting protocol design include capturing 2001–2005 to 187 in 2011–2015 (FIG. 1a). amendments, and gather more meaningful
more patient-reported outcome measures, A mean of 22 distinct procedures were carried clinical data. These initiatives include protocol
and the collection of comparative out for each phase III protocol in 2001–2005, review committees, protocol-authoring
effectiveness and biomarker data. Here, compared with 35 in 2011–2015 — a 59% practices connecting procedures to primary
we provide new benchmark data on trial increase. The mean number of planned study and key secondary end points, common
complexity with the aim of enabling drug volunteer visits increased by 25%, from 12 protocol-authoring templates, and soliciting
development sponsors to compare against visits per protocol in 2001–2005 to 15 visits feedback on draft protocol designs from
their own organizational practices and per protocol in 2011–2015. patients and investigative site staff before
informing clinical research practitioners of The work required to administer phase I, II approval and execution. Studies at the Tufts
evolving protocol design practices. and III protocols at investigative sites also Center for the Study of Drug Development
The analysis is based on 9,737 clinical trial increased substantially over the 10‑year time have not yet detected a measurable
protocols that received ethics review board period (Supplementary information S1 (box)), industry-wide impact from these initiatives,
approval between 2001 and 2015, drawn from as did the mean total cost per study volunteer although early anecdotal reports indicate
Medidata’s PICAS database, which contains per visit (FIG. 1b). Although the costs for many that these initiatives are beginning to yield
detailed protocol and investigative site procedures such as blood tests have come reductions in the number of protocol
contract data from more than 170 global down during the past decade, the total cost amendments and in the burden on
pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies per volunteer visit has grown considerably investigative site administration (Ther. Innov.
(76% of the protocols were provided by large because of the increase in the total number of Regul. Sci. 47, 651–655; 2013).
companies and 24% by mid-sized and smaller procedures carried out. Phase II studies saw Kenneth A. Getz is at the Tufts Center for the Study of
companies (see Supplementary information S1 the highest increase in the mean nominal cost Drug Development, Tufts University, 75 Kneeland
(box) for details)). Design elements associated per study volunteer visit (61%), followed Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02111, USA.
with executional feasibility — including the closely by phase I (49%) studies. Phase III Rafael A. Campo is at Medidata Solutions,
number of procedures performed, the number studies showed more modest growth in mean 350 Hudson Street, New York, New York 10014, USA.
of planned study volunteer visits, the work cost per visit, with an increase of 34% over the Correspondence to K.A.G.
kenneth.getz@tufts.edu
effort to administer procedures and the cost 10-year period.
per study volunteer visit — were evaluated These study findings are striking given doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.65
Published online 18 Apr 2017
and compared across two time periods — research linking protocol complexity to longer The authors declare no competing interests.
2001–2005 and 2011–2015 — separated by cycle times, higher numbers of protocol
10 years to characterize trends. This approach amendments and lower patient recruitment SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
See online article: S1 (box)
was used to allow longer time horizons in and retention rates (for example, Contemp.
ALL LINKS ARE ACTIVE IN THE ONLINE PDF
which to gather more meaningful insights Clin. Trials 28, 583–592; 2007). The collection
while reducing any outlier effects in any
given year.
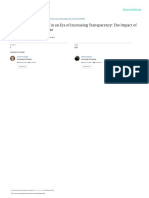
The results of this analysis show that a 100 b 2.0
protocol design elements associated with 90 Phase I protocols 2001–2005
1,873
Mean cost (nominal US$)
80 Phase II protocols 2011–2015
protocol execution have grown rapidly. Phase III protocols 1.5
The mean number of distinct procedures 70
67 70
Growth (%)
1,386
carried out per protocol increased significantly 60
1,259
50
59 1.0
for phases I, II and III, most notably among 54 53
978
40 44
phase II and III protocols (FIG. 1a). The
862
30
728
frequency with which each distinct procedure 29 0.5
was performed grew at an even faster rate,
20 23 25
10
leading to a higher growth in the mean number
0 0
of total procedures. During this period, Number of distinct Number of total Number of planned study Phase I Phase II Phase III
however, the mean number of planned visits procedures procedures performed volunteer visits protocols protocols protocols
per study volunteer grew at a far more modest Figure 1 | Trends in the complexity and costs of clinical trials. a | Growth rates for protocol
rate, resulting in more procedures performed design metrics between 2001–2005 and 2011–2015. b | Cost perNature Reviews
volunteer | Drug
visit for Discovery
the same two
per study volunteer visit and a greater burden periods. Increases in protocol complexity have offset cost savings from procedural efficiencies
on volunteer participation. and technology improvements. See Supplementary information S1 (box) for details.
NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION | 1
©
2
0
1
7
M
a
c
m
i
l
l
a
n
P
u
b
l
i
s
h
e
r
s
L
i
m
i
t
e
d
,
p
a
r
t
o
f
S
p
r
i
n
g
e
r
N
a
t
u
r
e
.
A
l
l
r
i
g
h
t
s
r
e
s
e
r
v
e
d
.
You might also like
- Qualidade Lin Infect DisDocument6 pagesQualidade Lin Infect DisBen-Hur AlbergariaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Research PaperDocument10 pagesQuality Control Research PaperwesayNo ratings yet
- 2) Use of Environmental Scans in Health Services Delivery Research A Scoping ReviewDocument12 pages2) Use of Environmental Scans in Health Services Delivery Research A Scoping ReviewMahnooshNo ratings yet
- Biemer 2010 Total Survey Error Design, Implementation, and EvaluationDocument32 pagesBiemer 2010 Total Survey Error Design, Implementation, and EvaluationJohannes SpencerNo ratings yet
- 2012 ChienDocument7 pages2012 ChienKiều Lê Nhật ĐôngNo ratings yet
- Using Process Tracing To Improve Policy Making: The (Negative) Case of The 2003 Intervention in Iraq by Andrew Bennett, 2015Document13 pagesUsing Process Tracing To Improve Policy Making: The (Negative) Case of The 2003 Intervention in Iraq by Andrew Bennett, 2015Ian Niccolo Vizcarra TobiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Value of Information of Precisi - 2019 - NJAS - Wageningen JouDocument9 pagesAssessment of The Value of Information of Precisi - 2019 - NJAS - Wageningen Joueri addharuNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach To Measuring Effi Ciency of Scientifi C Research Projects: Data Envelopment AnalysisDocument7 pagesA Novel Approach To Measuring Effi Ciency of Scientifi C Research Projects: Data Envelopment AnalysisAnna DestrianaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0190740913003083 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0190740913003083 MainMas SahidNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Practice and Information SharingDocument18 pagesSupply Chain Practice and Information SharingUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Earned Value 2Document8 pagesEarned Value 2gedefayeNo ratings yet
- Gauge R&R Studies That Incorporate Baseline InformationDocument11 pagesGauge R&R Studies That Incorporate Baseline InformationDARIO HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- AuthorPreparedVersion JQTHistoryPaperRevisionDocument24 pagesAuthorPreparedVersion JQTHistoryPaperRevisionCASTILLO CARBAJAL ARIELNo ratings yet
- Research Into Telehealth Applications in Speech-Language PathologyDocument10 pagesResearch Into Telehealth Applications in Speech-Language PathologyJose Alonso Aguilar ValeraNo ratings yet
- Application of Design of Experiment (DOE) Techniques To Process Validation in Medical Device ManufactureDocument10 pagesApplication of Design of Experiment (DOE) Techniques To Process Validation in Medical Device ManufactureCamila MatheusNo ratings yet
- Leading The Implementation of ICT InnovationsDocument40 pagesLeading The Implementation of ICT InnovationsSabah BelgachaNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Weekly Data Collection Js SamDocument22 pagesModeling The Weekly Data Collection Js SamJonathan RougierNo ratings yet
- The Antecedents of The Use of Continuous Auditing in The Internal Auditing ContextDocument15 pagesThe Antecedents of The Use of Continuous Auditing in The Internal Auditing ContextSari HendriastutiNo ratings yet
- Convergent Parallel Mixed-Methods Study To UnderstDocument11 pagesConvergent Parallel Mixed-Methods Study To UnderstFerdinand BulusanNo ratings yet
- Toward Understanding Outcomes Associated With Data Quality ImprovementDocument12 pagesToward Understanding Outcomes Associated With Data Quality ImprovementNurul Pratiwi KarimNo ratings yet
- Biemer Total Survey ErrorDocument32 pagesBiemer Total Survey ErrorGeorge MiticaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Systems Engineering and Project Success in Commercial-Focused Versus Government-Focused ProjectsDocument9 pagesComparing Systems Engineering and Project Success in Commercial-Focused Versus Government-Focused ProjectsRajini GuttiNo ratings yet
- Crawford JEM 2008Document11 pagesCrawford JEM 2008Prashant Singh SankhalaNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Good Evaluation Practice in Health Informatics (GEP-HI)Document13 pagesGuideline For Good Evaluation Practice in Health Informatics (GEP-HI)Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Ten Simple Rules On How To Write A Standard Operating ProcedureDocument10 pagesTen Simple Rules On How To Write A Standard Operating ProcedureHarold Sanhueza100% (1)
- Examiner Alignment and Assessment in Clinical Periodontal Researchhefti - Et - Al-2012-Periodontology - 2000Document20 pagesExaminer Alignment and Assessment in Clinical Periodontal Researchhefti - Et - Al-2012-Periodontology - 2000Dr. DeeptiNo ratings yet
- How Effect Size Practical Significance Misleads Clinical Practice The Case For Switching To Practical Benefit To Assess Applied Research FindingsDocument13 pagesHow Effect Size Practical Significance Misleads Clinical Practice The Case For Switching To Practical Benefit To Assess Applied Research FindingsDami TepedeNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Safeguarding Examiner Objectivity and Evidence Reliability During Digital Forensic InvestigationsDocument9 pagesStrategies For Safeguarding Examiner Objectivity and Evidence Reliability During Digital Forensic Investigationshenu wigastaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Pilot StudiesDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Pilot Studieskumar21189No ratings yet
- WHO Digital HealthDocument16 pagesWHO Digital HealthDjaloeGWiwahaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3148904 PDFDocument38 pagesSSRN Id3148904 PDFErnaNo ratings yet
- Very Good One For Existing ResearchDocument13 pagesVery Good One For Existing Researchtimi20032000No ratings yet
- Feature: Does Process Excellence Handcuff Drug Development?Document5 pagesFeature: Does Process Excellence Handcuff Drug Development?Tom TompsonNo ratings yet
- Delone FrameworkDocument23 pagesDelone FrameworkSaniNo ratings yet
- Pucher 2018Document9 pagesPucher 2018Felipe NunesNo ratings yet
- CRR 01344Document440 pagesCRR 01344Vikas Krishnavihar KalisseryNo ratings yet
- Curran, 2012 - Effectiveness-Implementation Hybrid DesignsDocument10 pagesCurran, 2012 - Effectiveness-Implementation Hybrid DesignsThuane SalesNo ratings yet
- David Eddy Health Technology Assessment and Evidence-Based Medicine What Are We Talking AboutDocument2 pagesDavid Eddy Health Technology Assessment and Evidence-Based Medicine What Are We Talking AboutStavros TheodoridisNo ratings yet
- Accounting, Organizations and Society: Leslie Eldenburg, Naomi Soderstrom, Veronda Willis, Anne WuDocument16 pagesAccounting, Organizations and Society: Leslie Eldenburg, Naomi Soderstrom, Veronda Willis, Anne WuLestari Suryaningsih StepanusNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Pilot StudiesDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Pilot Studiesnyan hein aungNo ratings yet
- Patient Journey Modelling 04462857Document6 pagesPatient Journey Modelling 04462857AasdNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Accounting Information Systems: Dichapong Pongpattrachai, Paul Cragg, Richard FisherDocument21 pagesInternational Journal of Accounting Information Systems: Dichapong Pongpattrachai, Paul Cragg, Richard FisherBragi Vidar UllNo ratings yet
- Description: Tags: rV165-NIDRR-0412Document5 pagesDescription: Tags: rV165-NIDRR-0412anon-894286No ratings yet
- 2007 Comparability Exam Standards o Chapter11Document25 pages2007 Comparability Exam Standards o Chapter11Christopher CurranNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Impact of Organizational Practices On The Relative Productivity of University Technology Transfer Offices: An Exploratory StudyDocument22 pagesAssessing The Impact of Organizational Practices On The Relative Productivity of University Technology Transfer Offices: An Exploratory StudyHazel Jael HernandezNo ratings yet
- HQ Vol20 No3-MaxwellDocument8 pagesHQ Vol20 No3-MaxwellJordi Vinyals ParcerissaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Open Data and Software Is Energy Research LaggingDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Open Data and Software Is Energy Research LaggingaKNo ratings yet
- Spotfire ClinicalDocument14 pagesSpotfire Clinicalamir1290No ratings yet
- Multi-Level Verification of Clinical Protocols: April 1999Document11 pagesMulti-Level Verification of Clinical Protocols: April 1999Аня РыбинаNo ratings yet
- FMR No 4Document7 pagesFMR No 4Dwi RatihNo ratings yet
- 'Lean' On Digital PathologyDocument6 pages'Lean' On Digital PathologyIT LicensingNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Manajemen Patient SafetyDocument7 pagesJurnal Manajemen Patient SafetyfarizkaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation Information Systems-70-80Document11 pagesDesign and Implementation Information Systems-70-80ZulkifliWalangadiNo ratings yet
- Lot-To-Lot Variation and Verification - cclm-2022-1126Document8 pagesLot-To-Lot Variation and Verification - cclm-2022-1126Georgiana Daniela DragomirNo ratings yet
- Marosszeky Et Al. 2004 - Lessons Learnt in Developing Effective Performance Measures For Construction Safety ManagementDocument12 pagesMarosszeky Et Al. 2004 - Lessons Learnt in Developing Effective Performance Measures For Construction Safety ManagementMurugan RaNo ratings yet
- Scoring System As An Alternative Audit Method in FDocument11 pagesScoring System As An Alternative Audit Method in FYesica Marcelina SinagaNo ratings yet
- Increasing Project Flexibility: The Response Capacity of Complex ProjectsFrom EverandIncreasing Project Flexibility: The Response Capacity of Complex ProjectsNo ratings yet
- New sanitation techniques in the development cooperation: An economical reflectionFrom EverandNew sanitation techniques in the development cooperation: An economical reflectionNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Practices by Corporates in India PPTDocument13 pagesCapital Budgeting Practices by Corporates in India PPTRVijaySai0% (1)
- EPON OLT Operation Manual V1.2 20211102Document484 pagesEPON OLT Operation Manual V1.2 20211102MfahmifauzanNo ratings yet
- Banking Financial InstitutionsDocument252 pagesBanking Financial Institutionspraise ferrerNo ratings yet
- Anichol 60 For Broilers ReferencesDocument5 pagesAnichol 60 For Broilers Referencesjimlee2jimleeNo ratings yet
- 1st PUC BLUE PRINT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTDocument1 page1st PUC BLUE PRINT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTthakursingh14367% (3)
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument12 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementvionysusgoghNo ratings yet
- Taxation (Malawi) : Tuesday 4 June 2013Document10 pagesTaxation (Malawi) : Tuesday 4 June 2013angaNo ratings yet
- Veolia Case StudyDocument15 pagesVeolia Case StudyKanakarao MalappareddyNo ratings yet
- Fermentación BatchDocument8 pagesFermentación BatchJennifer A. PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Activity 15 - Compass ErrorDocument3 pagesActivity 15 - Compass ErrorzeynNo ratings yet
- SUD Life Elite Assure PlusDocument4 pagesSUD Life Elite Assure Plussourav agarwalNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optic Cable SplicingDocument33 pagesFibre Optic Cable SplicingAmax TeckNo ratings yet
- LTE Throughput Troubleshooting GuidlelineDocument15 pagesLTE Throughput Troubleshooting GuidlelineTourchianNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Principles of Virology Ebook PDF FREEDocument11 pagesInstant Download Principles of Virology Ebook PDF FREEwalter.penn362100% (51)
- List of RAs UpdatedDocument12 pagesList of RAs UpdatedThe SuperstarNo ratings yet
- BSMS Drexel ScheduleDocument4 pagesBSMS Drexel ScheduleAmy ZhiNo ratings yet
- Masoneilan 31000 Series Rotary Control ValvesDocument12 pagesMasoneilan 31000 Series Rotary Control ValvesJuan Manuel AcebedoNo ratings yet
- 4 Fundamental Principles of Traffic FlowDocument141 pages4 Fundamental Principles of Traffic FlowKaye Dabu100% (1)
- Human Resource Recruitment IN Aneja Training and Placement ServicesDocument25 pagesHuman Resource Recruitment IN Aneja Training and Placement ServicesHarnitNo ratings yet
- On Campus BA - Consultant JDDocument2 pagesOn Campus BA - Consultant JDSivaramakrishna SobhaNo ratings yet
- Blitzscales 14Document72 pagesBlitzscales 14Andrej Bašić100% (3)
- Persentasi Luwak CoffeeDocument36 pagesPersentasi Luwak CoffeeMukti LestariNo ratings yet
- Cs Supply ChainDocument7 pagesCs Supply ChainJoy MartinezNo ratings yet
- MILLER Testable ConceptsDocument109 pagesMILLER Testable ConceptsMohammedGooda100% (1)
- Cot On Theoretical and Experimental ProbabilityDocument8 pagesCot On Theoretical and Experimental ProbabilityNoemie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Azam in 30 DuaDocument3 pagesAzam in 30 DuafaizaninNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Mathematics 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in General Mathematics 2nd QuarterDominic Dalton CalingNo ratings yet
- White Lily - Ship's ParticularDocument1 pageWhite Lily - Ship's ParticularAYA ALHADITHEYNo ratings yet
- Code For VirtualboxDocument1 pageCode For VirtualboxAnonymous 4m8ueTNo ratings yet
- CLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseDocument5 pagesCLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseJhalen Shaq CarrascoNo ratings yet