100% found this document useful (2 votes)
476 views59 pagesGas Chromatograph System Overview
The document describes the basic components of a gas chromatograph system, including:
1. A carrier gas system that transports sample components through the chromatographic column at a constant flow rate.
2. A sampling system that extracts, conditions, and transports the sample gas to the detector.
3. A chromatographic column that separates the sample into individual components.
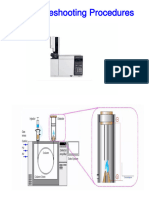
4. A temperature-controlled chamber housing the column and detector.
5. A detector, such as a thermal conductivity detector, that detects eluted components in the carrier gas.
6. An integrator or controller that measures component concentrations.
Uploaded by
Balaji SabanayagamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
476 views59 pagesGas Chromatograph System Overview
The document describes the basic components of a gas chromatograph system, including:
1. A carrier gas system that transports sample components through the chromatographic column at a constant flow rate.
2. A sampling system that extracts, conditions, and transports the sample gas to the detector.
3. A chromatographic column that separates the sample into individual components.
4. A temperature-controlled chamber housing the column and detector.
5. A detector, such as a thermal conductivity detector, that detects eluted components in the carrier gas.
6. An integrator or controller that measures component concentrations.
Uploaded by
Balaji SabanayagamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Basic Chromatograph System: Explains the fundamental components and structure of a gas chromatograph system including sample flow, detectors, and data processing.
- GC System Elements: Describes key elements of gas chromatograph systems such as carrier gas, sampling system, and detectors essential for operation.
- Carrier Gas System: Outlines the purpose, requirements, characteristics, and types of gases used as carriers in chromatography.
- Sampling System: Focuses on the sampling subsystem, discussing regulation, flow rates, and valve types used for introducing samples into the chromatograph.
- Chromatographic Column: Discusses the function and structure of chromatographic columns, emphasizing the separation processes performed.
- Temperature-Controlled Chamber: Explores the role of temperature-controlled chambers, or ovens, in controlling the chromatographic environment.
- Detector: Examines various types of detectors used in gas chromatography and their applications in analyzing different compounds.
- Controller: Describes the role of the chromatograph controller in system operation, diagnostics, and data management.
- Chromatograms & Calculations: Details the process of reading chromatograms and the calculations involved in determining concentrations from raw data.
- Maintenance: Provides a checklist for routine maintenance and operational checks to ensure system performance and longevity.
- Troubleshooting: Offers troubleshooting guidance and checklists for resolving common issues with chromatograph operations.