0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views3 pagesUnderstanding Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
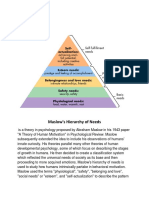
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory that humans are motivated to fulfill basic needs in a specific order. Physiological needs like food, water, shelter must be met first before safety, love, esteem and self-actualization. The first four levels are considered deficiency needs that arise due to deprivation, while self-actualization is a growth need focused on reaching one's full potential. Maslow later updated his theory to clarify that need satisfaction exists on a spectrum rather than an all-or-nothing basis.
Uploaded by
Md Imamul Hasan ArifCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views3 pagesUnderstanding Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory that humans are motivated to fulfill basic needs in a specific order. Physiological needs like food, water, shelter must be met first before safety, love, esteem and self-actualization. The first four levels are considered deficiency needs that arise due to deprivation, while self-actualization is a growth need focused on reaching one's full potential. Maslow later updated his theory to clarify that need satisfaction exists on a spectrum rather than an all-or-nothing basis.
Uploaded by
Md Imamul Hasan ArifCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd