Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOCHEMAcids and Bases Notes
Uploaded by
Ian MermalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMAcids and Bases Notes
Uploaded by
Ian MermalCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY
Acid and Bases – the most important concentration of the solvent anion
solutes in a solution. This are (OH-).
compounds which have common - The free hydrogen ion H+ cannot
characteristic properties. exist in an aqueous solution
because of its high ratio of
ACIDS WHEN DISSOLVED IN WATER charge in radius it is always
Forms solution that conducts associated with water molecule to
electricity form the hydronium ion (H3O+).
Reacts with metals to produce Spectroscopy - a technology that is
salt and gas used to study surfaces and analyze
Taste sour the vibration of molecules.
Reacts with carbonates to
produce C2O Dissociation in Water – Pure
non-electrolyte water does contain a
BASES WHEN DISSOLVED IN WATER very low concentration of hydronium
Yields solutions that also conduct ion (H3O+) hydroxide (OH-) ions,
electric current formed by the dissociation.
Feels slippery or soapy on the
2 H2O ------ H3O + OH-
skin
Taste bitter - Dissociation constant of water
Turn red litmus paper to blue
Reacts with acids to form salt and concentration of H3O ions x concentration of OH- ions
water Concentration of H2O molecules
ACID BASE THEORIES Kw = concentration of H3O ions x concentration of OH- ions
55.6
Arrhenius Theory - Svante August = 1.8 x 10-16
Arrhenius (1859-1927), a Swedish
chemist is the first one to explain the This can be re written as
Concentration of H3O ions x concentration of OH- ions
behavior of acids and bases.
= (1.8 x 10 -16) x 56 = 1 x 10-14
- This theory states that upon the
dissociation of water, the acids This is called the ionic product of
yield positive hydrogen ions water, K and is the product of the
(H+) while the bases yield H3O and the OH- ion
negative hydrogen ions (H-) concentration in any dilute
- The acid substance upon with the aqueous solution.
reaction with water, causes an
increase in the concentration of
the solvent cation (H3O+) while
the base substance upon
dissolution in or reacting with
water causes an increase in the
Bronsted_Lowry Theory - two other non-metal is called
Johannes Bronsted (1879-1947), ternary acids.
a Danish chemist, and
ThomasLowry (1874-1936), an
Naming Oxyacids of Sulfur
English chemist. Formula Name Formula and
- Theory that considerate the Name of
behavior of hydrogen ions. Oxyanion
Formed
- In this theory, acids donate upon
proton in another substance Reaction
while the base accepts proton with Water
from the other substance. H2SO3 Sulfurous SO3-2, sulfite
- In any acid-base reaction, acid
regardless of the solvent, the H2SO4 SO4-2, sulfate
Sulfuric
donating and accepting the
proton is all that takes place.
acid
Lewis Theory - Gilbert Lewis Naming Oxyacids of Chlorine
- chemical reactions involve the
arrangement of the valence Scheme Formula Name Formula and
electrons or the outermost for Name of
Naming Oxyanion
electrons of an atom the Acids Formed
- This theory states that the acid is upon
the electron pair acceptor and Reaction
the base in the electron pair with Water
donor.
- Lewis defined an acid-base
reaction as the sharing of an increasin Hypo___ous HClO Hypochlorous ClO-,
acid
electron pair, forming a g hypochlorite
coordinate covalent bond ( a number __ous HClO2 Chlorous acid ClO2- ,
of chlorite
covalent bond in which the
Oxygen __ic HClO3 Chloric acid ClO3-,
shared electrons are donated by chlorate
one of the atoms involved). Atoms Per_____ic HClO4 Perchloric ClO4-,
acid
perchlorate
FORMULAS AND NAMES OF ACIDS AND BASES
Naming Acids
- Substance that is composed of
only two elements, hydrogen and
non-metal are called binary
acids.
- Substance that is composed of
three elements, hydrogen and
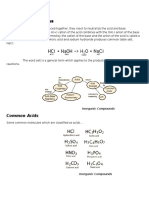
Common Acids and Their Uses - They dissociate into these ions
when dissolves in water.
Name Uses - Bases are named just like binary
Acetic acid Acid in vinegar acids in pure form; the ions are
used to season and named, then combined.
preserve food;
cleans and Common bases and Their uses
deodorizes
Hydrochloric Aids in digestion Name Uses
acid (0.1 M HCl); used Sodium Used in making
as toilet-bowl soaps and (caustic
hydroxide soda or lye)
cleaner and for
detergents; a drain
cleaning metal
and oven cleaner
surfaces
Lithium Used in removing
Sulfuric acid Used in automobile carbon dioxide from
batteries and in hydroxide air in confined areas
making dyes and such as submarines
plastics; a and spaceships
dehydrating agent Magnesium Used as an antacid
Nitric acid Used in making hydroxide (in milk in small dosages
explosives and and laxative in large
fertilizers
of Magnesia) amounts
Phosphoric Removes hard Aluminum Used as an antacid
with no dosage
acid water deposits; hydroxide restriction
used in making
Calcium Used in the
fertilizers; used in preparation of
soft drinks (in hydroxide plaster and mortar
dilute form)
Carbonic acid Used in the
manufacture of THE pH CONCEPT
carbonated drinks
Acetylsalicylic Reduces pain and Changes in the acidity or basidity of some
acid (aspirin) inflammation solutions can be critical in some systems
Hydrofluoric Used in glass such as the following:
acid etching
A body of water supporting aquatic
Citric acid Occurs naturally in
plants and animals
some fruits; used in
flavoring Our stomach digesting ingested food
carbonated drinks Cells of living organisms where vital
Naming Bases life processes are carried out
Some industrial processes where
- Bases are compounds consisting
reactions take place at a desired rate
of a metal and a hydroxide ion.
In 1909, a Danish biochemist,
-Soren Sorensen ( 1868-1939), proposed acid (designated as the
the pH scale as a more convenient way conjugate acid) has one
of expressing hydronium ion
color and its conjugate base
concentration. The symbol, pH, stands
for some German words which literally has another color.
means “the power of the hydrogen ion.” - A conjugate acid-base
system involves a Bronsted
pH of Common Substances
acid (a proton donoe) and
Substance pH its resulting base (a proton
1.0 M HCl 0 acceptor) when the acid
Battery acid 1
(H2SO4)
loses a proton. Some
Gastric juice 1.6- indicators like
1.8 phenolphthalein are usually
Calamansi juice 2.2 used in solution, while
Vinegar 2.8
others like litmus and
Apple juice 3.0
Carbonated 3.1 universal indicator are
drink usually impregnated on
Orange juice 3.5 paper strips.
Tomato juice 4.2
Urine 6.1
Milk 6.5
Saliva 6.5
Pure water 7
Blood 7.4
Seawater 8.4
Milk of 10.5
magnesia
1.0 M NaOH 14
INDICATORS
- Indicators are chemical dyes
which are acids and bases
that change color at certain
hydronium ion
concentrations.
- Indicators is an acid-base
system in which the weak
You might also like
- Elements of ArtDocument1 pageElements of Artsamson8cindy8louNo ratings yet
- Ib History Command Term PostersDocument6 pagesIb History Command Term Postersapi-263601302100% (4)
- 3 Acids & BasesDocument24 pages3 Acids & BasesAbdul Quddus100% (1)
- Theories of Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesTheories of Acids and BasesDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Role of Personal Finance Towards Managing of Money - DraftaDocument35 pagesRole of Personal Finance Towards Managing of Money - DraftaAndrea Denise Lion100% (1)
- Habib Public School Chemistry Class-X Unit: 10 Acids Bases and Salts Name of StudentDocument31 pagesHabib Public School Chemistry Class-X Unit: 10 Acids Bases and Salts Name of Studentmehwish razaNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base TheoryDocument25 pagesAcid and Base TheoryPtrick MahnyNo ratings yet
- Oracle - Prep4sure.1z0 068.v2016!07!12.by - Lana.60qDocument49 pagesOracle - Prep4sure.1z0 068.v2016!07!12.by - Lana.60qLuis AlfredoNo ratings yet
- Famous Russian PianoDocument10 pagesFamous Russian PianoClara-Schumann-198550% (2)
- Origami Oso HormigueroDocument9 pagesOrigami Oso HormigueroRogelio CerdaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsDocument15 pagesMethods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsYossr MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Mcom Sem 4 Project FinalDocument70 pagesMcom Sem 4 Project Finallaxmi iyer75% (4)
- Nirav Sir: 2 + - (S) + (Aq) - (Aq)Document19 pagesNirav Sir: 2 + - (S) + (Aq) - (Aq)api-233404189No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ChemistryDocument24 pagesChapter 8 ChemistrySasukeNo ratings yet
- Acidity and BasicityDocument89 pagesAcidity and Basicityjzllfrncsc100% (4)
- Acids and Bases Module 1Document7 pagesAcids and Bases Module 1EPHRAIM JOSHUA SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Acids, Base and SaltDocument31 pagesAcids, Base and SaltAhsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base - DefinitionsDocument3 pagesAcid and Base - DefinitionsFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- On. EQUILIBRIUM-2 (2) .PPTMDocument47 pagesOn. EQUILIBRIUM-2 (2) .PPTMrithanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Reactions: Common AcidsDocument7 pagesAcid-Base Reactions: Common AcidsSheervine FalconNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry - Acids and BaseDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry - Acids and BasePaul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and Basesroku shinNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TheoriesDocument12 pagesAcid Base TheoriesJuan TamadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Acid and BaseDocument18 pagesChemistry Acid and BaseKabwe LeonardNo ratings yet
- Theories of Acid and BaseDocument17 pagesTheories of Acid and BaseCedrick LaurenioNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument43 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionsKhara TeanoTanNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibraDocument16 pagesIonic EquilibraPankaj JindamNo ratings yet
- Metal and Its Effective Feature in Organic CatalysisDocument6 pagesMetal and Its Effective Feature in Organic CatalysisMehwish AfreenNo ratings yet
- Fulltext 007Document33 pagesFulltext 007Agus SurahmanNo ratings yet
- Bronsted Lewry TheoriesDocument27 pagesBronsted Lewry TheoriesSagita AfifNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium-2Document13 pagesChemical Equilibrium-2MUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- Wa0099.Document48 pagesWa0099.nm.ananya2008No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument42 pagesAcid BaseBon PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Lewis TheoryDocument6 pagesLewis TheoryDesireal TattaoNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 (Asam Basa)Document40 pagesModul 2 (Asam Basa)Seo HerinNo ratings yet
- The Arrhenius Theory of Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesThe Arrhenius Theory of Acids and BasesRohini SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases and Solubility EquilibriaDocument43 pagesAcids and Bases and Solubility EquilibriaGienet MaeNo ratings yet
- Acidity and BasicityDocument89 pagesAcidity and BasicityAria IsipNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BuffersDocument52 pagesAcid Base Buffersdinesh111180No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Faculty: LH 171 Course Code: CHEM 1101Document11 pagesAcids and Bases: Faculty: LH 171 Course Code: CHEM 1101Md KhanNo ratings yet
- Arrhenius Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesArrhenius Acids and BasesMight RamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4-Part-1Document65 pagesUnit - 4-Part-1sc21fs301017No ratings yet
- Chapter 08Document4 pagesChapter 08zahidNo ratings yet
- Topic 8.1 IB ChemistryDocument36 pagesTopic 8.1 IB ChemistryFrank AlfanoNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesGaayathiriNo ratings yet
- Acid and Bases: Arrhenius HypothesisDocument26 pagesAcid and Bases: Arrhenius HypothesisBackup AccountNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 10 Note - Week FiveDocument18 pagesChemistry Grade 10 Note - Week FiveKolade Fatai OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Theories of Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesTheories of Acids and BasesEllen LabradorNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument36 pagesAcid Baseবিল গেটসNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- Brønsted Lowry Acids and Bases 14Document10 pagesBrønsted Lowry Acids and Bases 14Suvromoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Acids and BasesDocument10 pagesTheories of Acids and BasesPraveen SubrahmanianNo ratings yet
- 04awater and Acid-Base SystemDocument27 pages04awater and Acid-Base SystemAtirahNo ratings yet
- LAcids and BasesDocument37 pagesLAcids and BasesAnonymous rFIshYy100% (1)
- محاضرة 6 (ن)Document22 pagesمحاضرة 6 (ن)انمي العراقNo ratings yet
- A Level Acid-Base Theory, Lewis Acids and Bases, Bronsted-Lowry Proton Theory GCDocument7 pagesA Level Acid-Base Theory, Lewis Acids and Bases, Bronsted-Lowry Proton Theory GCvarunvijay89No ratings yet
- Biochem Act 1Document31 pagesBiochem Act 1Irene Orzame - VizonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Skol Project!Document11 pagesChemistry Skol Project!Chetan GhodkeNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Grade 11 Term 4 Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Sciences Grade 11 Term 4 Week 2Sphenathi NgaphiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts Week 16 Learning Objectives: 8.1 Acids and Base TheoriesDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts Week 16 Learning Objectives: 8.1 Acids and Base TheoriesReygemae Quitoras-ObsidNo ratings yet
- Ionic EqDocument53 pagesIonic EqNurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- M3 - L1 - Acids and Bases - A Brief ReviewDocument5 pagesM3 - L1 - Acids and Bases - A Brief ReviewKevinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1000 Lecture 19: The Halogens: Marc R. RousselDocument18 pagesChemistry 1000 Lecture 19: The Halogens: Marc R. RousselMahmoud AbdAllahNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesAcids and BasesAletheaNo ratings yet
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974From EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannNo ratings yet
- RSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Document79 pagesRSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Gigi's DelightNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and The Role of Manageme PDFDocument20 pagesDecision Making and The Role of Manageme PDFRaadmaan RadNo ratings yet
- CEE Annual Report 2018Document100 pagesCEE Annual Report 2018BusinessTech100% (1)
- ISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Document8 pagesISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Tamo Kim ChowNo ratings yet
- Objective & Scope of ProjectDocument8 pagesObjective & Scope of ProjectPraveen SehgalNo ratings yet
- Biological Beneficiation of Kaolin: A Review On Iron RemovalDocument8 pagesBiological Beneficiation of Kaolin: A Review On Iron RemovalValentin GnoumouNo ratings yet
- PLC Laboratory Activity 2Document3 pagesPLC Laboratory Activity 2Kate AlindajaoNo ratings yet
- Retailing in IndiaDocument11 pagesRetailing in IndiaVinod MalkarNo ratings yet
- Post Appraisal InterviewDocument3 pagesPost Appraisal InterviewNidhi D100% (1)
- Agco Serie 800 PDFDocument24 pagesAgco Serie 800 PDFJohnny VargasNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Allan WatsonDocument29 pagesUnit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Allan WatsonLuqman OsmanNo ratings yet
- Test ScienceDocument2 pagesTest Sciencejam syNo ratings yet
- BMOM5203 Full Version Study GuideDocument57 pagesBMOM5203 Full Version Study GuideZaid ChelseaNo ratings yet
- Making Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Document18 pagesMaking Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Mariam TchkoidzeNo ratings yet
- Application Activity Based Costing (Abc) System As An Alternative For Improving Accuracy of Production CostDocument19 pagesApplication Activity Based Costing (Abc) System As An Alternative For Improving Accuracy of Production CostM Agus SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Companyprofil E: Erfanconstructionsolut IonDocument14 pagesCompanyprofil E: Erfanconstructionsolut IonNurin AleesyaNo ratings yet
- CX Programmer Operation ManualDocument536 pagesCX Programmer Operation ManualVefik KaraegeNo ratings yet
- 8.ZXSDR B8200 (L200) Principle and Hardware Structure Training Manual-45Document45 pages8.ZXSDR B8200 (L200) Principle and Hardware Structure Training Manual-45mehdi_mehdiNo ratings yet
- Lecturenotes Data MiningDocument23 pagesLecturenotes Data Miningtanyah LloydNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Elasticity and ForecastingDocument25 pagesChapter3 Elasticity and ForecastingGee JoeNo ratings yet
- Law of EvidenceDocument14 pagesLaw of EvidenceIsha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Electro Fashion Sewable LED Kits WebDocument10 pagesElectro Fashion Sewable LED Kits WebAndrei VasileNo ratings yet