Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relative
Relative
Uploaded by
bisrat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThe document contains 4 examples involving relative motion between objects in translating reference frames.
1. Cars A and B are both traveling at 100 km/h but car A is accelerating and car B is decelerating, so car B would appear to be accelerating to an observer in car A.
2. A car is traveling at 100 km/h and rain is falling at 6 km/h in the direction of travel, so the velocity of the rain as seen by the driver is 6 km/h.
3. Car A is traveling at 30 mi/h at a constant speed while car B is initially traveling at 20 mi/h and accelerating at 1200 mi/h^2,
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains 4 examples involving relative motion between objects in translating reference frames.
1. Cars A and B are both traveling at 100 km/h but car A is accelerating and car B is decelerating, so car B would appear to be accelerating to an observer in car A.
2. A car is traveling at 100 km/h and rain is falling at 6 km/h in the direction of travel, so the velocity of the rain as seen by the driver is 6 km/h.
3. Car A is traveling at 30 mi/h at a constant speed while car B is initially traveling at 20 mi/h and accelerating at 1200 mi/h^2,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageRelative
Relative
Uploaded by
bisratThe document contains 4 examples involving relative motion between objects in translating reference frames.
1. Cars A and B are both traveling at 100 km/h but car A is accelerating and car B is decelerating, so car B would appear to be accelerating to an observer in car A.
2. A car is traveling at 100 km/h and rain is falling at 6 km/h in the direction of travel, so the velocity of the rain as seen by the driver is 6 km/h.
3. Car A is traveling at 30 mi/h at a constant speed while car B is initially traveling at 20 mi/h and accelerating at 1200 mi/h^2,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
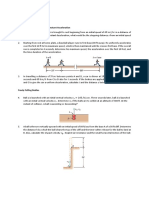
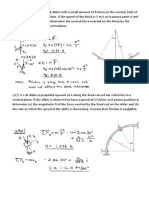
Examples on Relative Motion ( Translating Axes )
1. For the instant represented, car A has a
speed of 100 km/h, which is increasing
at the rate of 8 km/h each second.
Simultaneously, car B also has a speed
of 100 km/h as it rounds the turn and is
slowing down at the rate of 8 km/h each
second. Determine the acceleration that
car B appears to have to an observer in
car A.
2. The car is traveling at a constant speed
of 100km/h. If the rain is falling at 6
km/h in the direction shown, determine
the velocity of the rain as seen by the
driver.
3. At the instant shown, cars A and B travel
at speeds of 30mil/h and 20mi/h
respectively. If B is increasing its speed
by 1200mi/h2 while A maintains a
constant speed, determine the velocity
and acceleration of B with respect to A.
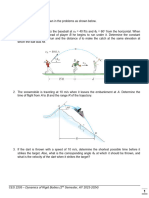
4. A batter hits the baseball A with an initial velocity of Vo = 100 ft/sec directly toward fielder B
at an angle of 300 to the horizontal; the initial position of the ball is 3 ft above ground level.
Fielder B require 1/4 sec to judge where the ball should be caught and begins moving to that
position with constant speed. Because of great experience, fielder B chooses his running speed
so that he arrives at the "catch position" simultaneously with the baseball. The catch position
is the field location at which the ball altitude is 7 ft.
Determine the velocity of the ball relative to the fielder at the instant the catch is made.
Prepared by: Chala A.
You might also like
- Dynamics Sheet 6 2023 2024Document2 pagesDynamics Sheet 6 2023 2024abdoayad1382005No ratings yet
- Assignment #1 MK Kinematika & Dinamika: Kinematics of Particles-Rectilinear MotionsDocument2 pagesAssignment #1 MK Kinematika & Dinamika: Kinematics of Particles-Rectilinear MotionsEGG RiderNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1 Rectilinear Translation Rectilinear Translation With Constant AccelerationDocument1 pageExercise No. 1 Rectilinear Translation Rectilinear Translation With Constant AccelerationRossana AgustinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 Relative MotionDocument7 pagesWorksheet 7 Relative MotionObsinet ObsinetNo ratings yet
- DynaDocument3 pagesDynaKim FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SoalDocument2 pagesSoalAhmad Ridwan SidiqNo ratings yet
- ESC 17 Assignment 2Document1 pageESC 17 Assignment 2200720553No ratings yet
- Problem Set2 DynamicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set2 DynamicsSonrim JunioNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3, From N-T Upto ConstrainedDocument4 pagesWorksheet 3, From N-T Upto Constrainedhemengebeyehu862No ratings yet
- Relative MotionDocument4 pagesRelative MotionHazim OmarNo ratings yet
- PLATES1 Tbes 8Document2 pagesPLATES1 Tbes 8Chris ChanNo ratings yet
- Mec31-1 HW3 4TH Term Sy 14-15Document3 pagesMec31-1 HW3 4TH Term Sy 14-15DiannaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration WorksheetDocument3 pagesAcceleration WorksheetJulia RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Acceleration: Graphs and ProblemsDocument11 pagesAcceleration: Graphs and ProblemsMithilesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Phet Contribution 2818 4963Document18 pagesPhet Contribution 2818 4963Rizwan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Phet Contribution 2818 4940Document18 pagesPhet Contribution 2818 4940Rizwan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Rectilinear MotionDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Rectilinear MotionSpencer Josh RegedorNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Assignment No. 2: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE: Relative Motion, Dependent MotionDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics Assignment No. 2: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE: Relative Motion, Dependent MotionshreyashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Solutions 7th GiancoliDocument30 pagesChapter 02 Solutions 7th GiancoliHetal Gandhi100% (3)
- Mech PsetDocument7 pagesMech PsetJomel JazminNo ratings yet
- Alyza DynamicsDocument2 pagesAlyza DynamicsJayBurdeosNo ratings yet
- Online%2Document6 pagesOnline%2jan12th2004No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Dynamics) Assignment 1Document4 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Dynamics) Assignment 1All in one EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 - Vector Sums: Find, To The Nearest Tenth, The Magnitude and Bearing of Each Resultant VectorDocument2 pages5.4 - Vector Sums: Find, To The Nearest Tenth, The Magnitude and Bearing of Each Resultant VectorJackson NewmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Projectile&Curvilinear Motion)Document2 pagesProblem Set (Projectile&Curvilinear Motion)Mico AndresNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice ProblemsAji no MotoNo ratings yet
- M1 Kinematics TestDocument1 pageM1 Kinematics TestFandy ArdyNo ratings yet
- Acceleration - AnswersDocument2 pagesAcceleration - AnswersMeeta NurkunasegranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Solutions 7th GiancoliDocument30 pagesChapter 02 Solutions 7th GiancoliAce PTNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetJULLIANA VILORIANo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Sec 6Document3 pagesDynamics - Sec 6Ashraf ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesKinematics Worksheet 1Hanh Vo100% (1)
- A Racing Car Traveling With Constant Acceleration Increases Its Speed From 10mDocument2 pagesA Racing Car Traveling With Constant Acceleration Increases Its Speed From 10mTesfaye BelayeNo ratings yet
- HW1 ch12Document1 pageHW1 ch12Rajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- Universidad de La Salle Physics 1: Mechanics Pr. Daniel VarelaDocument2 pagesUniversidad de La Salle Physics 1: Mechanics Pr. Daniel VarelaKaren BeltranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Motion Summative Test 1.0Document1 page3rd Quarter Motion Summative Test 1.0Jan JanNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument2 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBrentNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Motion Summative Test 3.0Document1 page3rd Quarter Motion Summative Test 3.0Jan JanNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument4 pagesSample ProblemsNikka FerrerNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 1Document6 pagesCE222 Problem Set 1Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- Emch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - M - CDocument7 pagesEmch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - M - CRajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- Emch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - MDocument7 pagesEmch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - MRajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- Distance TimeDocument2 pagesDistance TimeSaugato MondalNo ratings yet
- CBSE+9+Umang +motion+ +revision+in+1+shotDocument115 pagesCBSE+9+Umang +motion+ +revision+in+1+shotDushyant SinghNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Fisica IDocument5 pagesTrabajo Fisica IMVAZ233No ratings yet
- AM1100 Worksheet 5 - Kinematics of Rigid Body SystemsDocument1 pageAM1100 Worksheet 5 - Kinematics of Rigid Body Systemsrohith chinna0% (1)
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionlouisadonaldlwrNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Giancoli Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Giancoli Solutions Manual PDFdihedronnozle.39n6i100% (14)
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Tapas+ +Intro+to++Relative+Motion+in+1d+and+2d+Document74 pagesTapas+ +Intro+to++Relative+Motion+in+1d+and+2d+Gmail ManNo ratings yet
- Solve Curvilinear MotionDocument3 pagesSolve Curvilinear Motionصادق سلام محمود شوطNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Circular Motion WorksheetDocument3 pagesCh. 5 Circular Motion WorksheetTreeiciclesNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 de DinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 1 de DinamicaMelany Elizabeth BarriosNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument5 pagesKINEMATICSPhysicsNo ratings yet
- JEE-NEET Imp. ch-2 Amit SirDocument8 pagesJEE-NEET Imp. ch-2 Amit Sirjunejarishit8No ratings yet
- Grade 9 ExamDocument1 pageGrade 9 ExamKC PISONET-1No ratings yet