Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Engine Block
What Is Engine Block
Uploaded by
ruth akoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Engine Block
What Is Engine Block
Uploaded by
ruth akoCopyright:
Available Formats
Prepared by Mr.
Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 1 of 7
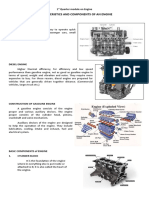
What Is Engine Block? Definition, Function and Uses
Components of an engine block
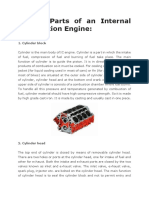
Parts of an Engine The main structure of an engine typically consists of cylinders, coolant
passages, oil galleries, crankcase, and cylinder head(s).
Car engines are designed around sealed, resilient metal cylinders. Most
modern vehicles have between four and eight cylinders, though some 1. Cylinder Blocks
vehicles can have as many as sixteen! The cylinders are made to open and
close at precisely the correct time to bring in fuel to combine with the A cylinder block is a structure that contains the cylinder, plus any cylinder
spark for burning internally and to release the exhaust gases produced. sleeves and coolant passages. In the earliest decades of internal
combustion engine development, cylinders were usually cast individually.
While many of us think of the engine as one major component, it’s made Cylinder blocks were usually produced individually for each cylinder.
up of several individual components working simultaneously. You may
have heard of some of these car engine parts’ names but it’s important to Following that, engines began to combine two or three cylinders into a
know what their role is and how they relate to other components within the single-cylinder block, with an engine combining several of these cylinder
engine. blocks combined.
There are the various parts of a car engine consist of: the engine block In early engines with multiple cylinder banks such as a V6, V8, or flat-6
(cylinder block), combustion chamber, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, engine each bank was typically a separate cylinder block (or multiple
camshaft, timing chain, valves, rocker arms, pushrods/lifters, injectors, blocks per bank). Since the 1930s, mass production methods have
spark plugs, oil pan, distributor, connecting rods, piston ring, and developed to allow both banks of cylinders to be integrated into the same
flywheels. cylinder block.
2. Cylinder Liners
1. Engine Block Wet liner cylinder blocks use cylinder walls that are entirely removable,
which fit into the block by means of special gaskets. They are referred to
as “wet liners” because their outer sides come in direct contact with the
engine’s coolant. In other words, the liner is the entire wall, rather than
being merely a sleeve.
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 2 of 7
3. Cylinders.
These are the spaces where pistons travel. They are large in size and have
Advantages of wet liners are a lower mass, a reduced space requirement,
precisely formed holes to create a seal with the piston. The size and
and that the coolant liquid is heated faster from a cold start, which reduces
number of cylinders measure the power and size of an engine.
start-up fuel consumption and provides heating for the car cabin sooner.
Dry liner cylinder blocks use either the block’s material or a discrete liner 4. Oil Passages or Galleries.
inserted into the block to form the backbone of the cylinder wall. These allow oil to reach the cylinder head and the crankshaft.
Additional sleeves are inserted within, which remain “dry” on their
outside, surrounded by the block’s material.
For either wet or dry liner designs, the liners (or sleeves) can be replaced,
potentially allowing overhaul or rebuild without replacement of the block
itself, although that is often not a practical repair option.
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 3 of 7
attached. It is a mechanical part able to perform a conversion between
reciprocating motion and rotational motion.
5. Deck.
This is the top surface of the block where the head of the cylinder sits. The main purpose of this connecting rod is to absorb the reciprocating
motion of the piston and pass it on to the crankshaft. When the crankshaft
is moved by the connecting rod, it converts that movement into rotary
6. Crankcase.
This houses the crankshaft and is found at the bottom of modern engine motion and turns the flywheel, which continues to move the vehicle
blocks. Other components include engine mounts, core plugs, coolant, wheels.
ancillary mountings, and faults.
Without a crank, a reciprocating piston engine is not able to transmit the
piston reciprocating movement to the drive shaft. In simple terms, a
reciprocating engine cannot move a vehicle without a crankshaft.
Various engines go through a power cycle with different numbers of
crankshaft revolutions. For example, a 2-stroke engine completes a power
cycle after one revolution of the crankshaft, while a 4-stroke engine
completes a power cycle after the completion of two revolutions of the
crankshaft.
Crankshafts can be welded, semi-integrated, or one-piece. This component
of the engine connects the output section of the engine to the input section.
The crank acts as a link that supplies the output power in the form of
rotational kinetic energy – the piston is connected to the center of the
crank via a connecting rod. The crank arm allows the piston to rotate the
crankshaft to generate force to move the vehicle.
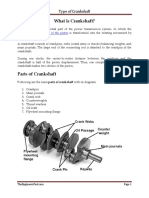
What is crankshaft?
A crankshaft is a shaft driven by a crank mechanism, consisting of a series
of cranks and crankpins to which the connecting rods of an engine are
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 4 of 7
What is connecting rod?
A connecting rod is the part of a piston engine that connects the piston to the crankshaft.
Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston
into the rotation of the crankshaft.
Small End: The end at which the connecting rod is attached to the face of the piston pin is
The connecting rod is required to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the known as the small end of the connecting rod.
piston. In its most common form, in an internal combustion engine, it allows pivoting on
Big End: The end at which the connecting rod is attached to the side of the crank pin is
the piston end and rotation on the shaft end.
known as big end of the connecting rod.
The predecessor to the connecting rod is a mechanical linkage used by water mills to
Bush Bearing: Both ends of the connecting rod are fixed with a bush bearing. A phosphor
convert the rotating motion of the water wheel into reciprocating motion. The most
bronze bush is fitted with the solid eye is attached to the small end of the connecting rod.
common usage of connecting rods is in internal combustion engines or on steam engines.
The Big end is attached to the crankpin. The end is divided into two parts and is supported
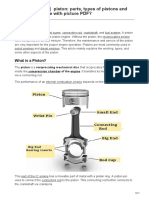
Parts of Connecting rods over the crank bearing shell.
Following are the parts of connecting rod: Bearing Insert: In the big end of the connecting rod, there is a bearing insert that is
connected to the bearing cap, it is known as a bearing insert These are made in two parts
that fit together on the crankshaft. This is the position where the connecting rod travels
along the reverse direction.
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 5 of 7
Bolt and Nut: After the connecting rod is fitted with the crank at the bottom, both sides of
the big ends are fastened by some bolts and nuts. Thus, by combining these all components
the connecting rod is ready to use.
Shank: Furthermore, each of the bolt and nuts are employed to connect both the connecting
rod and bearing cap. And a section beam is applied it is known as shank. The section of the
rod may be rectangular, tubular, and a circular section.
Wrist Pin: The engine piston is connected to the connecting rod with the help of a hollow
hardened steel tube called wrist pin. It is also known as gudgeon pin. Wrist pin goes
through the short end of the connecting rod and pivots on the engaged piston.
Piston: The piston is connected to the crankshaft with the help of a connecting rod, which
is usually shortened to the rod or Conrod. The purpose of the piston is to work as a movable
plug in the cylinder, which forms the bottom of the combustion chamber.
Bearing Cap: Shell bearings have an adjustment for wear, but it controls the running and
the side clearance allows the bearing cap to be tightened correctly
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 6 of 7
Prepared by Mr. Kupesan UOG trainee term 3, 2023 Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Specification Sheets-Mechanical PartsDocument4 pagesSpecification Sheets-Mechanical PartsSheena BejasaNo ratings yet
- What Is Crankshaf1Document9 pagesWhat Is Crankshaf1Dhananjay NagareNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 CrankshaftDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 2 CrankshaftAUNG0% (1)
- MCE 4780: Mechanical Engineering Lab 1: Fahim Shahrier, 160011052, MCE 16, Group B 2nd February 2020Document19 pagesMCE 4780: Mechanical Engineering Lab 1: Fahim Shahrier, 160011052, MCE 16, Group B 2nd February 2020Fahim ShahrierNo ratings yet
- Types of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesTypes of Internal Combustion EnginesMoayadNo ratings yet
- ME 314, Internal Combustion Engine Sessional 1 2Document42 pagesME 314, Internal Combustion Engine Sessional 1 2Imam Arefin SwadhinNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Components of An EngineDocument3 pagesCharacteristics and Components of An EngineKalayaan EscoteroNo ratings yet
- Engine Parts: Laboratory Exercise 3Document5 pagesEngine Parts: Laboratory Exercise 3Milx Jyms AvilaNo ratings yet
- Give Examples of Internal Combustion Engine That Is Commonly Used in Engineering FieldDocument11 pagesGive Examples of Internal Combustion Engine That Is Commonly Used in Engineering Fieldaruna MoonNo ratings yet
- Parts of Gas & Diesel EnginesDocument45 pagesParts of Gas & Diesel Enginesmichael beljanoNo ratings yet
- To Study The Stationary and Moving Automobile Parts PDFDocument16 pagesTo Study The Stationary and Moving Automobile Parts PDFTAHIR QAMAR100% (2)
- Pimsat Colleges Engineering Materials 1Document8 pagesPimsat Colleges Engineering Materials 1Sev Anne T. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engg. Lab: ManualDocument42 pagesAutomobile Engg. Lab: ManualAjankya Singhania100% (1)
- Part OneDocument9 pagesPart OneJesson Jade PahitNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document4 pagesAssignment #1Usman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- TUGASDocument2 pagesTUGASselviana safitriNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of An Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesMain Parts of An Internal Combustion EngineVenkatNo ratings yet
- Mar Power Week 1Document15 pagesMar Power Week 1DarkxeiDNo ratings yet
- Components or Parts of IC Engine With Its Function PDFDocument9 pagesComponents or Parts of IC Engine With Its Function PDFMilbert Vaz AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Tugas DeckyDocument2 pagesTugas Deckyselviana safitriNo ratings yet
- Engine Design and Components: Crank ShaftDocument17 pagesEngine Design and Components: Crank Shaftanjali sharmaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockMr. Jerome Nithin GladsonNo ratings yet
- What Is Flywheel?Document7 pagesWhat Is Flywheel?Ronnie Macharia MwangiNo ratings yet
- Exp No - Docx Gaurav Kr.Document13 pagesExp No - Docx Gaurav Kr.Prashant KashyapNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 PDFDocument11 pagesExercise 5 PDFErica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Engines & Its ComponentsDocument33 pagesClassification of Engines & Its ComponentsSunil DhankharNo ratings yet
- Final Engine ProjectDocument38 pagesFinal Engine Projectvinayharish02002No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document32 pagesUnit 1Rakeshkumarceg100% (1)
- Chapter-II Internal Combustion Engine: A. CylinderDocument16 pagesChapter-II Internal Combustion Engine: A. CylinderSajeet KarkeeNo ratings yet
- English Task 6: Machine and Motors: Author: Nazhmi FadhilaDocument4 pagesEnglish Task 6: Machine and Motors: Author: Nazhmi FadhilaNazhmi FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Auto MechanicDocument106 pagesAuto Mechanicamigoscribd100% (1)
- Reciprocating Engine Parts Design: G.T.U. B.E. (Mech) Sem-Viii 2011-12Document61 pagesReciprocating Engine Parts Design: G.T.U. B.E. (Mech) Sem-Viii 2011-12Divyraj JadejaNo ratings yet
- Types of EngineDocument11 pagesTypes of Enginejoshua jan allawanNo ratings yet
- Study of Working Mechanisms of Important Components of Automobile EngineDocument5 pagesStudy of Working Mechanisms of Important Components of Automobile EngineNiranjana KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering-2 PracticalDocument35 pagesThermal Engineering-2 PracticalAlok Anand100% (1)
- Main Parts of An EngineDocument5 pagesMain Parts of An EngineLuriz CadeliñaNo ratings yet
- Final Engine Report.Document28 pagesFinal Engine Report.Chethu ChethuNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2: I. C. Engines Working Principles of I.C. Engines Study of Different Components of I.C. EnginesDocument29 pagesLecture - 2: I. C. Engines Working Principles of I.C. Engines Study of Different Components of I.C. EnginesViknesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Vehicle EngineDocument31 pagesVehicle EnginenoahNo ratings yet
- Components of Ic Engine T613010Document9 pagesComponents of Ic Engine T613010Kolte RushikeshNo ratings yet
- What Is CamshaftDocument6 pagesWhat Is CamshaftJa Phe TiNo ratings yet
- How Many Small Engines Do You Have at Home?Document67 pagesHow Many Small Engines Do You Have at Home?Rajkumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Razo, Alvin T - BSME3B - ME110 - RESEARCHDocument5 pagesRazo, Alvin T - BSME3B - ME110 - RESEARCHAlvin RazoNo ratings yet
- Both Internal Combustion Engines and External Combustion Engines Are Known As Heat EnginesDocument70 pagesBoth Internal Combustion Engines and External Combustion Engines Are Known As Heat EnginesBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Assignmnt No 1 AutoDocument18 pagesAssignmnt No 1 AutoAtul Kuttal AŤűNo ratings yet
- Block Del MotorDocument11 pagesBlock Del MotorLuwīsi Karikamo RomaniNo ratings yet
- Pusa Institute of Technology Industrial Visit At: WectinDocument17 pagesPusa Institute of Technology Industrial Visit At: WectinNavneet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- SI ENGINE and BASIC IGNITION SYSTEMDocument41 pagesSI ENGINE and BASIC IGNITION SYSTEMShrvan HirdeNo ratings yet
- Marine EngineDocument26 pagesMarine EngineNeil Stephen GuiaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automobile EngineeringDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Automobile EngineeringSaurabh AwacharNo ratings yet
- Journal PowerGenwithDynamo ARPNDocument5 pagesJournal PowerGenwithDynamo ARPNShotech EngineeringNo ratings yet
- What Is Piston How Does A Piston WorkDocument15 pagesWhat Is Piston How Does A Piston WorkRony henneryNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4.Document7 pagesLab Report 4.Usman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of EngineDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of EngineJerome BalatbatNo ratings yet
- Automotive Brake System (Summary)Document6 pagesAutomotive Brake System (Summary)Rhenz MagnoNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Cycle Engine OperationsDocument32 pages4 Stroke Cycle Engine Operationsreymart tabelismaNo ratings yet
- Design of IC Engine ComponentsDocument52 pagesDesign of IC Engine Componentsmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Powerplant LabDocument35 pagesSpreadsheet Powerplant LabSan Jose, Kyla Mae M.No ratings yet
- Block - ConrodDocument22 pagesBlock - ConrodArnold ChafewaNo ratings yet
- A Power Primer - An Introduction to the Internal Combustion EngineFrom EverandA Power Primer - An Introduction to the Internal Combustion EngineNo ratings yet