Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apeco Reviewer
Apeco Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kate LlanetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Apeco Reviewer
Apeco Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kate LlanetaCopyright:
Available Formats
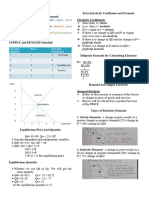
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
SUPPLY
➔ willingness of sellers to offer a given
quantity of good or service for a
given price
➔ sellers normally sell more at a
higher price than at a lower price
➔ to maximize their profit, they will
increase their supply (produce
more products)
QUANTITY SUPPLIED
- amount of good a seller supply
THE LAW OF SUPPLY
- as the price increases/decreases
quantity of the product also
increases/decreases
- ceteris paribus (direct relationship)
MARKET PRICE CONTROL
- a venue where consumers and - when company experienced
suppliers of goods transact on surplus, there is a possibility that
buying or selling of any items producers will lose
- sets the amount of good or service - when market is encountering
to be rendered and most shortage, there is a likelihood that
importantly the price that the consumers will be abused
output is going to be sold or - the price may be fixed at a level
bought below the market equilibrium price
or above the market equilibrium
MARKET EQUILIBRIUM price
- price agreed by the seller to offer its
good or service for sale and for the FLOOR PRICE
buyer to pay for it
- price at which quantity demanded ● above the equilibrium
● legal minimum price imposed by
of a good is exactly equal to the
the government on certain goods
quantity supplied and services
- state of balance between demand ● undertaken by government if a
and supply surplus in the economy persists
- D=S ● form of assistance to producers
by the government for them to
survive in their business
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
PRICE CEILING
● usually below the equilibrium
price
● the legal maximum price
imposed by the government
● undertaken by government if
there is a persistent shortage of
goods
● imposed by the government to
protect consumers from abusive INTERPRETATION OF THE
producers or sellers who take COEFFICIENT PED
advantage of situations such as
occurrence of a calamity 1. ELASTIC
➔ PED is greater than 1 = PED
>1
➔ the good is non-essential
➔ buyers are sensitive to its
price
2. INELASTIC
➔ PED is less than 1 = PED < 1
➔ the product is an essential
or important good
➔ buyers show little response
to the change in its price
SOLVING THE EQUILIBRIUM 3. UNITARY ELASTIC
➔ coefficient of price elasticity
DEMAND - 𝑄𝐷=𝑎−𝑏𝑃
is equal to 1 = PED = 1
SUPPLY - 𝑄𝑠=c+𝑑𝑃
➔ there is proportional
EQUILIBRIUM CONDITION - 𝑄𝐷=𝑄𝑠 variation or change in the
Qd and the price of the
product
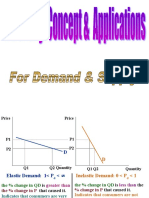
ELASTICITIES
4. PERFECTLY ELASTIC
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (PED) ➔ PED is = ∞
- measures the sensitivity of ➔ this signifies when seller
response of the quantity demand increases the prices of his
to the change in price of the good product, no one will buy
or service from him
𝐸𝑑=(𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑄𝑑)/𝑄1 𝑥100 5. PERFECTLY INELASTIC
(𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒)/𝑃1 𝑥100 ➔ PED is = 0
➔ It means that consumers
Change in Qty= Q2-Q1 still buy the exact quantity
Q1= “original Qd” of the product regardless of
Q2= “new Qd” the price
Change in price= P2-P1
P1= original price of the good
P2= new price of the good
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY (PES) percentage change in price
- how the suppliers respond to the in absolute value
variation of products’ price in the 4. PERFECTLY ELASTIC
market ➔ PES is = ∞
𝐸𝑆=(𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑄𝑠)/𝑄1 𝑥100 ➔ quantity supplied does not
(𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒)/𝑃1 𝑥100 respond at all to a change in
price
5. PERFECTLY INELASTIC
Change in Qty= Q2-Q1
➔ PES is = 0
Q1= “original Qd”
➔ quantity supplied is
Q2= “new Qd”
unlimited at a given price,
Change in price= P2-P1
but no quantity can be
P1= original price of the good
supplied at any other price
P2= new price of the good
INCOME ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
- sensitivity of quantity demanded to
the % change in income of the
consumers
INTERPRETATION OF THE
COEFFICIENT PES
1. ELASTIC
➔ PES is greater than 1 = PES >
1
➔ producers can increase
output without a rise in
cost or a time delay
2. INELASTIC
➔ PES is less than 1 = PES < 1
➔ Firms find it hard to change
production in a given time
period. Supply is relatively
unresponsive to a change in
demand. Producers may
find it easier to put up prices
3. UNITARY ELASTIC
➔ coefficient of price elasticity
is equal to 1 = PES = 1
➔ percentage change in
quantity of a quantity
supplied is the same as the
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
1. NUMBER & SIZE OF BUYERS &
CROSS PRICE ELASTICITY OF
DEMAND SELLERS
- determines the market
➔ how the demand quantity of a
concentration
certain product changes as the
- more suppliers and sellers in the
price of a related good changes
market signifies less concentrated
market
- fewer producers indicates a more
concentrated market
MARKET CONCENTRATION
LESS MORE
Concentration Concentration
More suppliers Less suppliers
Less market More market
power power
2. TYPE OF PRODUCT
MARKET STRUCTURES - making the product unique
- Homogenous – undifferentiated or
same products
FACTORS DETERMINING THE
- Niche – differentiated or unique
DEGREE OF COMPETITION AND
products
MARKET POWER:
● Number and size of buyers and TYPE OF PRODUCT
sellers
● Type of products
● Entry and exit of firms in the
market Undifferentiated Differentiated
● Pricing power
Homogeneous Unique
● Degree of knowledge of
economic agents regarding
Horizontal Inelastic demand
prices, costs, demand and supply
demand
condition
Very responsive to Not responding to
price change price change
Huge costs Huge profits
Low market High market
power power
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
3. ENTRY OR EXIT OF FIRMS IN
CLASSIFICATION OF MARKET
THE MARKET STRUCTURES
- strength of barriers that may hinder
the entry of firms or suppliers in the
market PERFECT COMPETITION
- inherent features of the industry
and different methods 1. lot of customers and suppliers in
specific market, but they only
show a very little or no impact on
KINDS OF BARRIERS TO ENTRY the prices of items
2. highly similar products or
● SCALE BARRIERS homogenous products are sold
- requirements for a large by the sellers in perfect
production plant for a competition
feasible operation in the 3. sellers have ease of entry or exit
industry from the markets as there are no
barriers to enter into or exit from
● LEGAL BARRIERS the industry
- proprietary rights and 4. in a perfectly competitive
their corresponding legal environment, the market players
protection extended to are price takers
existing market players in 5. buyers and suppliers are
the production and well-informed of the pricing,
distribution of products costs, and other relevant
information for them to come up
with their economic decision
4. PRICING POWER
- market power of the firm or the
ability to set or control the price of IMPERFECT COMPETITION
products in the market
➔ exists when there are concepts of
- level of pricing power depends on perfectly competitive
whether the firm can regulate the environment that are not met
level of demand and supply of the ● Monopoly
products - when a single or one seller
- price-setters - can manipulate the has control of entire
level of supply or demand supply of raw materials
- no close substitute or no
- price-takers - cannot control the
alternative store or firm for
level of supply or demand the monopolist
● Monopolistic Competition
5. DEGREE OF KNOWLEDGE OF - many firms offer similar
ECONOMIC AGENTS items in the market but
may have different brands
- availability or limitation of
- sell heterogenous or
economic information to the differentiated products
players in the market ● Oligopoly
- firms interact with each
other and
interdependence among
them exists
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
5. INTEREST RATES
MARKET STRUCTURES &
IMPLICATIONS FOR ● The price you pay to borrow
ENTREPRENEURS money
● Cost of borrowing
1. INVESTMENT (borrower’s point of view)
- involves employment of ● Reward for lending (lender’s
funds with the aim of point of view)
achieving additional income
2. RETURN - When interest rates rise,
Depends on: banks charge more for
● Nature of investment business loans
● Maturity period - When interest rates are low,
● Other factors businesses can borrow more
Received in the form of: readily
Yield{dividend or interest] + capital
appreciation [difference between
sales price and purchase price]
3. RISK
● Inherent in any investment
● Risk and return of an
investment are related
● The higher the risk, the
higher is the return THE GOAL OF A FIRM
Risks may be: ➔ to maximize shareholder’s wealth
● Loss of capital or firm’s long-run value
● Delay in repayment
● Non-payment of interest
FORMS OF BUSINESS
● Variability in returns
ORGANIZATIONS
4. SAFETY 1. PROPRIETORSHIP
- every investor expects to get - unincorporated business
back his capital on maturity owned by one individual
without loss and without 2. PARTNERSHIP
delay - unincorporated business
- another feature an investor owned by two or more
desires for investments people
- certainty of return of capital 3. CORPORATION
without loss of money or - legal entity created by state
time
IMPORTANT BUSINESS TRENDS
1. Globalization
2. Improving information
technology
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
TAXATION APPROACHES TO TAXATION
➔ inherent power of the state to 1. The ability to pay principle states
demand enforced contributions that taxation should be levied
from the people for public purposes according to an individual’s ability
to pay. This approach to taxation is
usually the basis for progressive
TAX
taxation
➔ levy imposed by government on 2. The benefit approach proposes
the income, wealth and capital that taxation should be levied
gains of persons or businesses, on broadly in relation to the benefits
spending on goods and services, that people receive in public
and on properties services
3. The tax incidence approach
WHY IS TAXATION NECESSARY? proposes that the major duty of a
tax system is to analyze the effect of
➔ for the government to be able to
a particular tax on the distribution
finance its expenditures
of tax welfare
PURPOSES OF TAXATION MINIMUM WAGE
➔ Taxes are used by the government
● Statutory Monetary Benefits are
for a variety of purposes:
employee benefits required by law
1. to raise revenue for the government
to be given to the employees
to cover its own expenditure
● The ones giving the benefits are:
2. instrument of fiscal policy in
The employer or the government
regulating the level of total
spending (or aggregate demand) in
the economy so as to stabilize the REGIONAL WAGE ORDERS
economy ➔ the daily minimum wage rates per
3. to alter the distribution of income industry per locality within the
and wealth region and in some instances
4. to control the volume of imports depending on the number of
workers and capitalization of
MAJOR DIVISION OF TAXES enterprises
➔ The basis of the minimum wage
DIRECT TAXES rates prescribed by law shall be the
- taxes levied by government on the normal working hours of eight
income and wealth received by hours a day
households and businesses in order
to raise government revenue and as
an instrument of fiscal policy
INDIRECT TAXES
- taxes levied by government on
goods and services in order to raise
revenue and as an instrument of
fiscal policy
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
APECO 084 : FINALS COVERAGE
EXEMPT FROM INCOME TAX
● Statutory Minimum Wage (SMW)
inclusive of COLA (Cost of Living
Allowance)
● Holiday pay
● Overtime pay
● Night shift differential pay
● Hazard pay
SWOT ANALYSIS
STRENGTH
1. What advantages do they have
that others don’t?
2. What do they do better?
3. What personal resources do
they have access to?
4. What do other people see as
their strengths?
WEAKNESSES
1. What should they avoid?
2. What could the employees
improve?
3. What things do other people
see as weaknesses?
OPPORTUNITIES
1. Do co-workers out-perform in
key areas?
2. Employees’ strengths and see
opportunities there
THREATS
1. What obstacles do they face?
2. Is their job (demand) changing?
3. Is changing technology
threatening their position?
4. Could their weaknesses
threaten them?
K8’S (do not resell if u want to pass the finals ><)
You might also like
- Toward A Comparative Institutional AnalysisDocument482 pagesToward A Comparative Institutional Analysisbtkazemi100% (1)
- Apeco SemisDocument6 pagesApeco SemisAthena Francine LangiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Demand ElasticitiesDocument23 pagesChapter 4 - Demand ElasticitiesMohammad Yunus SalehiNo ratings yet
- Elasticities Applications of Supply Demand AnalysisDocument30 pagesElasticities Applications of Supply Demand AnalysisHafiz bbaNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics Reviewer FinalsDocument3 pagesBasic Microeconomics Reviewer FinalsDearlyne AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument5 pagesApplied Economics ReviewervillajuanalleahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Elasticities (Economics)Document14 pagesChapter-3 Elasticities (Economics)tychrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Iness KyapwanyamaNo ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument5 pagesELASTICITYRaymark Raymundo MejiaNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument5 pagesElasticityricardo mollaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 3-2 4Document28 pagesLesson-2 3-2 4Diana BendanilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6Document6 pagesChapter 5 & 6Safirah LaelatiNo ratings yet
- DEMAND - ConceptsDocument30 pagesDEMAND - ConceptsSebin Sara SolomonNo ratings yet
- Elasticities: Gce A-Level & Ib EconomicsDocument37 pagesElasticities: Gce A-Level & Ib EconomicsingeNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply and Prices: Week 2Document32 pagesDemand, Supply and Prices: Week 2Don D DadaNo ratings yet
- Elasticities RevisionDocument1 pageElasticities RevisionAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply PDFDocument37 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply PDFJeanew TheFoxNo ratings yet
- IB Econ Notes Chapter 3Document13 pagesIB Econ Notes Chapter 3Yiyun HanNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 PDFDocument3 pagesChap 8 PDFKoi CallejaNo ratings yet
- L5 ElasticityDocument23 pagesL5 ElasticityAhmed HishamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elasticity of DemandDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Elasticity of DemandAvi JhaNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument43 pagesElasticityɴᴜʀ sʏᴀᴢᴡᴀɴᴀNo ratings yet
- Utility and Elasticity SummaryDocument2 pagesUtility and Elasticity Summaryshafa anisa ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Elstacity 11Document23 pagesElstacity 11Nourine GadNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument39 pagesElasticitymd sitab aliNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument26 pages3.1. Elasticity and Its ApplicationSamantha Cinco100% (2)
- T4 Applications of Supply and Demand SummaryDocument4 pagesT4 Applications of Supply and Demand Summarycassandra evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Econs Unit 2 Chap 8-9-11Document72 pagesEcons Unit 2 Chap 8-9-11b972xmny46No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Priscilla T Baffour, PHDDocument47 pagesElasticity of Demand: Priscilla T Baffour, PHDDavidNo ratings yet
- Application of Elasticity PDFDocument26 pagesApplication of Elasticity PDFvibhuNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Elasticity of Demand & Supply: Mba/Pgdm (2009-2011) New Delhi Institute of ManagementDocument32 pagesProject Report ON Elasticity of Demand & Supply: Mba/Pgdm (2009-2011) New Delhi Institute of ManagementNitin Rana71% (7)
- Price Elasticity of Demand (Autosaved) - 1Document5 pagesPrice Elasticity of Demand (Autosaved) - 1Raphinos VakachaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 3Document11 pagesUnit 2 Part 3FeelipeferrerNo ratings yet
- 3 ElasticitiesDocument9 pages3 ElasticitiesshriyaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument31 pagesEconomicsdipu jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Midterms Econ Reviewer (Less The Written On Board)Document6 pagesMidterms Econ Reviewer (Less The Written On Board)Agatha B. AcostaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Applications OF Supply and DemandDocument10 pagesTopic 4 Applications OF Supply and DemandShannen MarriNo ratings yet
- Elastic I TiesDocument19 pagesElastic I TiesArooj FatimaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Application of Supply & Demand, Demand and Consumer BehaviorDocument78 pagesUnit-2: Application of Supply & Demand, Demand and Consumer BehaviorRodel Carreon CandelariaNo ratings yet
- 106 Managerial EconomicsDocument9 pages106 Managerial EconomicspratsondasNo ratings yet
- ECON1101 Microeconomics 1 CheatsheetDocument4 pagesECON1101 Microeconomics 1 CheatsheetYeung Chak LamNo ratings yet
- (DONE) Econ 201 Final Notes 2Document76 pages(DONE) Econ 201 Final Notes 2Vaga boundedNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Demand, and SupplyDocument37 pagesThe Theory of Demand, and SupplyWaaqoo Guutuu Waaqoo GuutuuNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its Applications - 5 - 6 - 920220823223838Document26 pagesElasticity and Its Applications - 5 - 6 - 920220823223838Aditi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cape Econ RevisionsDocument6 pagesCape Econ RevisionsSristi LallNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument3 pagesEconomics Notescim5046No ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument22 pagesElasticity of DemandRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Utility and ElasticityDocument2 pagesUtility and ElasticityJayNo ratings yet
- DEMANDDocument2 pagesDEMANDMary Ann BalocaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument61 pagesLecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyJoanne FerrerNo ratings yet
- Demand Notes1Document25 pagesDemand Notes1Jada CallisteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To EconomicsDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To EconomicsMaynardFroyC.NeryNo ratings yet
- Friday Prelim MKTG 214-Pricing Strategy ReDocument5 pagesFriday Prelim MKTG 214-Pricing Strategy ReJoferlyn Mai Marabillo VillarNo ratings yet
- 5 - Concepts of Elasticity (Notes)Document10 pages5 - Concepts of Elasticity (Notes)ML CreationsNo ratings yet
- Ayaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1Document12 pagesAyaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1AzharNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Elasticity - Measure of ResonsivenessDocument2 pages2.3. Elasticity - Measure of ResonsivenessgebreNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterDocument29 pagesCh. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterSpencer AlexanderNo ratings yet
- EC120 CheatSheetMidtermDocument3 pagesEC120 CheatSheetMidtermdylan8939No ratings yet
- Demand Schedule and Demand Curve Supply Schedule and The Supply Curve Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument31 pagesDemand Schedule and Demand Curve Supply Schedule and The Supply Curve Elasticity of Demand and SupplyBhavana ChavanNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument14 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandSergioNo ratings yet
- Summative Notes of GlobalizationDocument7 pagesSummative Notes of GlobalizationKate LlanetaNo ratings yet
- BMATH - Salary Wage IncomeDocument3 pagesBMATH - Salary Wage IncomeKate LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Bsfin FinalsDocument5 pagesBsfin FinalsKate LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Besor FinalsDocument3 pagesBesor FinalsKate LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: Krugman/Wells EconomicsDocument42 pagesSupply and Demand: Krugman/Wells EconomicsSaral DesaiNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument11 pagesFINALMinh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument56 pagesEconomicsAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics 2Document152 pagesMicro Economics 2Criss JasonNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Monetary Approach ToDocument54 pages1 - The Monetary Approach TohalhoshanNo ratings yet
- 13 Chapter 9 Zakat in Mainstream Economic ModelDocument17 pages13 Chapter 9 Zakat in Mainstream Economic Modelapi-292047125No ratings yet
- Price Floor CeilingDocument31 pagesPrice Floor CeilingRashmeet AroraNo ratings yet
- Macro TS1Document2 pagesMacro TS1Katunga MwiyaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument21 pagesAggregate Demand and SupplypoojanpandyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 PowerPointsDocument68 pagesChapter 17 PowerPointsBryant CansecoNo ratings yet
- Rationality: Lawrence E. Blume and David EasleyDocument19 pagesRationality: Lawrence E. Blume and David EasleyGabriel RoblesNo ratings yet
- Theories of International Migration - A Review and AppraisalDocument37 pagesTheories of International Migration - A Review and AppraisalThaysa AndréiaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Foeign Exchange DeterminationDocument57 pagesTheories of Foeign Exchange DeterminationPakki Harika MeghanaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Money and Interest RatesDocument115 pagesIntroducing Money and Interest RatesRojohn ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Final Proposal 4Document15 pagesFinal Proposal 4eyob yohannesNo ratings yet
- 기말 기출 모음Document13 pages기말 기출 모음누텔라냐암No ratings yet
- DEB Annexures 1608-2019Document412 pagesDEB Annexures 1608-2019Logesh WarNo ratings yet
- Lipsey and Christo Economics 14Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesLipsey and Christo Economics 14Th Edition Full Chapterjamie.gardner403100% (22)
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument34 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityMD Shakil KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Micro Ultimate Cheat Sheet KeyDocument3 pagesAP Micro Ultimate Cheat Sheet KeyAndra IuliaNo ratings yet
- Ac 2203 Long Exam CompilationDocument31 pagesAc 2203 Long Exam CompilationSyraChiaraDumaguingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Macro SolutionDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Macro Solutionsaurabhsaurs100% (1)
- Exam1 Practice Exam SolutionsDocument37 pagesExam1 Practice Exam SolutionsSheehan T Khan100% (3)
- SEBI Question Paper Phase I Paper 2 2022Document8 pagesSEBI Question Paper Phase I Paper 2 2022venom0003fNo ratings yet
- ECN 211 QuestionsDocument84 pagesECN 211 QuestionsDaniel AdegboyeNo ratings yet
- EC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesEC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsR and R wweNo ratings yet
- ST - Joseph College of Engineering Department of Management Studies Ba5101 Economic Analysis For Business - I Part - ADocument23 pagesST - Joseph College of Engineering Department of Management Studies Ba5101 Economic Analysis For Business - I Part - Ajsc nazeerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Labour Markets & Labour Market InstitutionDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Labour Markets & Labour Market InstitutionakashdeepjoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Supply DemandDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Supply Demandapi-428447569No ratings yet