Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MLSCH 103
MLSCH 103
Uploaded by
Hikari TsukkiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MLSCH 103
MLSCH 103
Uploaded by
Hikari TsukkiCopyright:
Available Formats
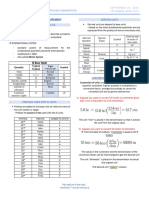
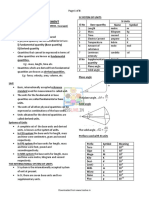
Chapter 2 Prefixes for Units
Important Chemical Concepts and a Basic
Approach to Chemical Equilibrium
tera- (T) 10
12
MEASUREMENT- consists of two parts: a giga- (G) 10
9
number and a unit.
mega- (M) 10
6
● A number without any unit is usually
meaningless. kilo- (k) 2
10
English System - United States, most
measurements are made with old English deci- (d) 10
−1
system units:
- pounds centi- (c) 10
−2
- miles
- gallons milli- (m) −3
10
Metric System - a system originated in
France about 1800 and that has since micro- (µ) 10
−6
spread throughout the world. Use for
convenience, so we won’t have to use long nano- (n) 10
−9
numbers.
pico- (p) 10
−12
International System of Units (SI) - based
on a metric system and uses some metric
units. It is more restrictive. femto- (f) 10
−15
Basic Properties: Base units in atto- (a) 10
−18
Metric System
SI Units
Length meter (m) SI is the acronym for the French "Système
International d'Unités."
Volume liter (L)
The ångstrom unit, Å, is a non-Sl unit of
Mass gram (g) length that is widely used to express the
wavelength of very short radiation such as
Time seconds (s) −10
X-rays (1Å = 0.1 nm = 10 m). Typical
X-radiation lies in the range of 0.1 to 10 Å.
Temperature kelvin (K)
Primary Regions of the
Energy Joule (J)
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Amount of mole (mol)
Substance - Microwave
- Visible Light
Electric Current ampere (A) - Infrared
- Ultraviolet rays
Luminous candela (cd) - X-rays
Intensity - Gamma Rays
- Radio Waves
- Easy to convert one unit to another
- With the use of prefixes
You might also like
- Grade 10 Physics Student's BookDocument142 pagesGrade 10 Physics Student's BookJames Soe89% (19)
- CCTV Training Material-2008Document78 pagesCCTV Training Material-2008KAZIMALI25100% (5)
- Troubleshooting Guide For Capacitor Excited GeneratorsDocument16 pagesTroubleshooting Guide For Capacitor Excited GeneratorstracypearlNo ratings yet
- Bosch Automotive HandbookDocument1,799 pagesBosch Automotive Handbookalperper90% (10)
- Topics in Engineering Logic: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandTopics in Engineering Logic: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Compass 1Document4 pagesMagnetic Compass 1Naman ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsDocument49 pages1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsPunitha Marimuthoo100% (1)
- Minimum Shield Wire Size Fault Current ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesMinimum Shield Wire Size Fault Current ConsiderationsMilagros Mercedes Olmos CervantesNo ratings yet
- Teknik Kendali Digital PDFDocument230 pagesTeknik Kendali Digital PDFWahyu Juliarto100% (3)
- Quantity Unit Abbreviation: SI UnitsDocument2 pagesQuantity Unit Abbreviation: SI UnitsST - Roselyn BellezaNo ratings yet
- VM Apr 30 l2Document9 pagesVM Apr 30 l2SomilNo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerDaligdig, Queen DuqueNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 NotesDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 1 NotesNicole de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- International System of Units (SI)Document14 pagesInternational System of Units (SI)Luka TikveshanskiNo ratings yet
- MAHA ONE SHOT - Units and DimensionsDocument48 pagesMAHA ONE SHOT - Units and DimensionskhokharzinniaNo ratings yet
- Robust H Control of A Scanning Tunneling Microscope Under Parametric UncertaintiesDocument6 pagesRobust H Control of A Scanning Tunneling Microscope Under Parametric UncertaintiesMishaalNo ratings yet
- Reliability Model: Microwave Remote Sensing Based On Small Satellite (MR3S)Document1 pageReliability Model: Microwave Remote Sensing Based On Small Satellite (MR3S)juanNo ratings yet
- Atoms Molecule and Chemical Arithmatic (Final) - 1 - (E)Document29 pagesAtoms Molecule and Chemical Arithmatic (Final) - 1 - (E)Manas OakNo ratings yet
- A-Level-Physics-Chapter 1Document4 pagesA-Level-Physics-Chapter 1natlyn55No ratings yet
- Units and Measurements: PhysicsDocument80 pagesUnits and Measurements: PhysicsAmit Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Anwinder RewinderDocument6 pagesAluminum Anwinder RewinderYESSER SOUISSINo ratings yet
- Chapter One:: Introduction To Measurement SystemsDocument3 pagesChapter One:: Introduction To Measurement SystemsRahman SatarNo ratings yet
- Physics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24Document45 pagesPhysics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24govind_galamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - v4Document29 pagesChapter 1 - v4方包No ratings yet
- Implementation of A Fixed Low Order Controller On STM32 MicrocontrollerDocument8 pagesImplementation of A Fixed Low Order Controller On STM32 Microcontrollerbreismam alfonso rueda diazNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document17 pagesWa0001BORN TO DIENo ratings yet
- Robust Computer Control An Inverted Pendulum: Medrano-CerdaDocument10 pagesRobust Computer Control An Inverted Pendulum: Medrano-CerdaVictor PassosNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1Document66 pagesPhysics - 1Aj EstoleNo ratings yet
- SI Unit EDocument1 pageSI Unit EEvangelin GuardamanoNo ratings yet
- Zerosix Studypoint: Table of SI UnitsDocument1 pageZerosix Studypoint: Table of SI UnitsniteshNo ratings yet
- Pdfcoffeecom Bosch Automotive Handbook 2 PDF Free 240402 221553Document1,391 pagesPdfcoffeecom Bosch Automotive Handbook 2 PDF Free 240402 221553mohamed azarudeenNo ratings yet
- DSP 2 MarksDocument20 pagesDSP 2 MarksSanthosh SandyNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Physics Ayyappan Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementDocument8 pagesHsslive Xi Physics Ayyappan Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementHarish SridharNo ratings yet
- Model Reference Control of Nonlinear Time-Delayed 1-st Order PlantsDocument5 pagesModel Reference Control of Nonlinear Time-Delayed 1-st Order PlantsBodoShowNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and Fault DiagnosisDocument174 pagesElectrical Measurements and Fault Diagnosisjosphat mbathaNo ratings yet
- Furuta 1992Document6 pagesFuruta 1992LÊ ĐẠI HIỆPNo ratings yet
- Robustness of DS-CDMA Multiuser Detectors: Pål Orten and Tony OttossonDocument5 pagesRobustness of DS-CDMA Multiuser Detectors: Pål Orten and Tony OttossonEmraan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Ch1-Units and MeasurementsDocument22 pagesCh1-Units and MeasurementsALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- Digital H Robust Control of Mechanical System With Implicit ObserverDocument6 pagesDigital H Robust Control of Mechanical System With Implicit ObserverGuilherme HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Class11 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument73 pagesClass11 2 Units and MeasurementsDIVYALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- Module 1Document53 pagesModule 1Alias SimounNo ratings yet
- Digital Control: Fundamentals: ENGI 7825: Control Systems II Andrew VardyDocument32 pagesDigital Control: Fundamentals: ENGI 7825: Control Systems II Andrew VardyZhraa NorNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument145 pagesPhysicsSS NDANo ratings yet
- Electronics 08 00221Document13 pagesElectronics 08 00221AMAN GOYALNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementDocument61 pagesUnits of Measurementjustin macabalitaoNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Notes-AyyappanDocument46 pagesHSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Notes-AyyappanDebater DudeNo ratings yet
- Metric System: PhysicsDocument12 pagesMetric System: Physicsnicole bNo ratings yet
- Dy SPAN2010 KimDocument8 pagesDy SPAN2010 Kimzizo1921No ratings yet
- Signal and SystemDocument152 pagesSignal and System22bei001No ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesUnits and MeasurementsKajol HNo ratings yet
- Infrared Thermography: An Introduction ToDocument21 pagesInfrared Thermography: An Introduction ToGabriel DediuNo ratings yet
- Eee Zg512 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Document5 pagesEee Zg512 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Shivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Learning Material - 01Document4 pagesLearning Material - 01Vincent VasquezNo ratings yet
- GuidetoConnectionofSupply Full en PDFDocument323 pagesGuidetoConnectionofSupply Full en PDFESM PNo ratings yet
- Manual Millennium II Multi Channel Transmitters Rosemount en 71578Document70 pagesManual Millennium II Multi Channel Transmitters Rosemount en 71578davidNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Estimation of Hybrid ANFIS-PSO-Based MPPT For PV Grid Integration Under Fluctuating Sun IrradianceDocument12 pagesAn Experimental Estimation of Hybrid ANFIS-PSO-Based MPPT For PV Grid Integration Under Fluctuating Sun Irradiancerasheed ahmed rNo ratings yet
- Cbema and Itic CurveDocument6 pagesCbema and Itic CurveShung Tak ChanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesDatasheet PDFEsteban MaryoryNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection FundamentalsDocument4 pagesPower System Protection FundamentalsMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Order of Half Cells in The Electrochemical SeriesDocument4 pagesOrder of Half Cells in The Electrochemical SeriesJuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1-Electrical System - Question Bank For Energy Managers & Energy AuditorsDocument1 pageChapter 3.1-Electrical System - Question Bank For Energy Managers & Energy Auditorsசீனு அருண்No ratings yet
- File W3G800KS3903 323881 DB ENDocument7 pagesFile W3G800KS3903 323881 DB ENAykut BacakNo ratings yet
- CG Power and Industrial Solutions Limited: Data Sheet of 3 Phase Induction MotorDocument1 pageCG Power and Industrial Solutions Limited: Data Sheet of 3 Phase Induction MotorprasadNo ratings yet
- TCSRDocument16 pagesTCSRscottsawNo ratings yet
- 20160226toronto SscsDocument88 pages20160226toronto SscsMohamed ShehabeldinNo ratings yet
- FlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoTouch LU30 ManualDocument6 pagesFlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoTouch LU30 ManualPromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Galvanostatic Charge-Discharge of A Li-Ion Battery With AutolabDocument2 pagesGalvanostatic Charge-Discharge of A Li-Ion Battery With AutolabShantanu GhoshNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical FileDocument31 pagesPhysics Practical FileAyushNo ratings yet
- An3095 Stevalisv002v1 Stevalisv002v2 3 KW Gridconnected PV System Based On The Stm32f103xx StmicroelectronicsDocument55 pagesAn3095 Stevalisv002v1 Stevalisv002v2 3 KW Gridconnected PV System Based On The Stm32f103xx StmicroelectronicsAhmar Hayat KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 PDFDocument23 pagesLecture 01 PDFAbd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- SPC 6601Document11 pagesSPC 6601ciro_svNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits:: Basic ConceptsDocument20 pagesDC Circuits:: Basic ConceptsJibek NasipbekNo ratings yet
- Remstar Pro 2 and AutoDocument106 pagesRemstar Pro 2 and AutoJohn E FosterNo ratings yet
- DS3 DSheet Flatpack2 System Integrated v5Document2 pagesDS3 DSheet Flatpack2 System Integrated v5Eng M ElseaidyNo ratings yet
- RPT Physics F6 Second Term 2018Document8 pagesRPT Physics F6 Second Term 2018norhazli ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Panel Board: Schedule of LoadsDocument1 pagePanel Board: Schedule of LoadsMary Joy AzonNo ratings yet
- TeleTek CA60PlusDocument44 pagesTeleTek CA60PlusRaimonda ČerekienėNo ratings yet
- Libro Academia Metodos Examen Lampara de Hendidura Clinical Optics 2020-2021Document3 pagesLibro Academia Metodos Examen Lampara de Hendidura Clinical Optics 2020-2021Camila FlorezNo ratings yet
- Ziegler 3490 SS Energy Meter With RS 485Document6 pagesZiegler 3490 SS Energy Meter With RS 485maheshNo ratings yet
- Invendis TechnologiesDocument9 pagesInvendis TechnologiesSudhakar V100% (1)