Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resumen Ingles Proyección 2
Uploaded by
valentinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resumen Ingles Proyección 2
Uploaded by
valentinaCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Information Research and Review, February, 2019
International Journal of Information Research and Review
Vol. 06, Issue, 02, pp.6141-6145, February, 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLE
ESTHETIC AND FUNCTIONAL MANAGEMENT OF INSUFFISANT PROTHETIC SPACE USING A
GUIDED OSTEOPLASTY APPROACH
*Oubbaih, A. and Bellemkhannate, S.
Resident Doctor, Service of Removable Prosthesis, Faculty of Dentistry, Casablanca, Morocco
ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT
Article History: A prominent osteomucosal ridge with a high smile line in the complete edentulous patient should not
th
escape our vigilance during the clinical examination, as it may compromise the aesthetic result of
Received 08 November, 2018
prosthetic rehabilitation. This prominence will create insufficient prosthetic space, which makes it
Received in revised form
11th December, 2018 difficult or even impossible to assemble the anterior teeth. The aesthetic problem becomes even more
Accepted 03rd January, 2019 complicated in the case of asymmetry of the osteomucosal defect. In such a situation, pre-prosthetic
Published online 28th February, 2019 surgery is required. We will illustrate the management of such a similar clinical case, by proposing an
appropriate therapeutic approach for better aesthetic and occlusive-functional result.
Keywords:
Total edentulous,
Pre-prosthetic surgery,
Aesthetic.
Copyright © 2019, Oubbaih and Bellemkhannate. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricte d use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
INTRODUCTION The management of these situation may require pre-prosthetic
surgery which may be more delicate in patients with an altered
The remodeling and resorption process after teeth extraction
general condition (2). Pre-prosthetic surgery will be indicated
load to bone loss (6). The greatest resorption occurs during the
whenever it is likely to improve local structures for total
first year following the loss of teeth. Thereafter, the vertical
prostheses and it requires the application of rigorous protocols
alveolar loss reaches the maxillary alveolar process, it is
to achieve good results. (8)
estimated at 0.1 mm per year and sometimes even 0.5 mm per
year (10). In total edentulous patients, there are large
Clinical Case
individual variations in bone ridges often with irregular
architecture that is either atrophied or enlarged depending on
We report a case of a prominent and asymmetric
the anatomical sites. This makes prosthetic rehabilitation more
anteromaxillary ridge. A 54-year-old patient with balanced
delicate and the upper anterior teeth assembly impossible when
type I diabetes, under insulin treatment, consulted for a
it concerns the anterior maxillary area. These bone changes can
prosthetic rehabilitation. Clinical examination revealed total
be explained first, by uncompensated extractions that induce
edentulous jaw with an irregular and enlarged anterior ridge of
the antagonistic teeth to regress with their periodontium, which
greater vertical height on the left side, adherent mucous
can later create an enlarged ridge that is highly visible in the
fibrosis, shallow palate, conjunctival hypertrophy of the left
patient's smile; or by the asynchronism of dental extractions,
tuberosity and atrophy of the right side (Fig1a, b).
causing delayed, anarchic and asymmetric bone resorption
patterns. This situation is similar to the combined syndrome
A subtotal edentulism at the mandible with 3 residual teeth, 34,
described by Kelley, which is characterized by resorption of
43 and 44, very extruded, with a gingival recession of 3 mm
the alveolar bone in the weakest area of the upper arch, namely
and a mobility degree 2 of both premolars according to the
the region of the anterior teeth, a process accentuated by the
MUHELLMANN classification (Fig1c). Clinical analysis
occlusal stress exerted by the anterior mandibular teeth (7). A
revealed, an extreme difference in the degree of resorption at
highly visible hypertrophied ridge at the patient's smile
the maxillary ridge, which is very accentuated on the side
compromises the management of the occlusion plan and
where the antagonistic teeth 43, 44 persist. The resorption
sometimes the prosthetic space. The treatment of this type of
process is accentuated by the occlusal stress exerted by these
edentulous situation remains a real biological and technical
teeth. During the smile, the anterior osteomucosal ridge is very
challenge.
visible, which disrupts the situation of the future occlusion
*Corresponding author: Oubbaih, A.
plane and reveals an insufficient prosthetic space for successful
Resident Doctor, Service of Removable Prosthesis, Faculty of Dentistry, aesthetic outcomes (Fig3a,b). The radiological examination
Casablanca, Morocco
6142 Oubbaih and Bellemkhannate, Esthetic and functional management of insuffisant prothetic space using a guided osteoplasty approach
completes the clinical one and reveals the presence of an Pre-prosthetic study
impacted canine tooth that is erupting (Fig. 2).
Study impressions were taken, and the models derived from
these impressions were mounted on articulators according to a
clinically validated vertical occlusion dimension. The analysis
of the articulator models confirmed our clinical diagnosis of a
very small prosthetic space requiring surgical intervention to
improve the local conditions of the prosthesis insertion (Fig 4).
(a)
(a)
(b)
(b)
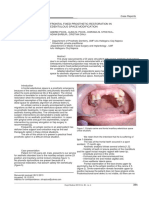
Figure 3. Smile analysis (a: light smile, b: large smile)
(c)
Figure 1. (a,b) : hypertrophy of the maxillary ridge on the left
side c: 34, 44, 43: teeth with gingival recession from 1 to 3 mm
Figure 4. Insufficient prosthetic space for placing
anteromaxillary teeth
Therapeutic decision
To obtain a favourable environment for making a conventional
bimaxillary complete prosthesis, it was decided to perform a
larger resection of the maxillary bone ridge in the left
quadrant. As for the mandible, we considered the extraction of
Figure 2. Radiological examination revealing the presence of an the residual teeth given their unfavourable prognosis; including
impacted mandibular canine tooth the canine tooth impacted, to avoid any subsequent prosthetic
discomfort. The avulsion of the residual teeth and the reduction
of the maxillary alveolar ridge considerably widen the space
6143 International Journal of Information Research and Review, Vol. 06, Issue, 02, pp. 6141-6145, February, 2019
for the adjustment of the new occlusion plan. It remains to cardiovascular diseases, etc.) (5). In the present case, we
determine the osteotomy value necessary for a better aesthetic revealed that the patient is a type I diabetic under insulin
result. For this reason, we have evaluated the quantity of bone treatment. Surgical management of diabetic patients requires a
to be resected using a graduated ruler placed under the upper specific clinical approach to identify the type of diabetes,
lip against the anterior ridge (lips at rest). This height has been evaluate the degree of metabolic control and take into
estimated at 5 mm, this area to be eliminated has been consideration the different precautions in collaboration with a
delimited on the arch model on which a silicone key has been diabetologist. After the extraction of the residual teeth, the
made first to guide its correction (Fig 6, 7). On the corrected patient underwent two time surgical procedures. First, the
model, a transparent resin surgical guide was made to lead the extraction of the impacted tooth, then the maxillary
surgical resection. osteoplasty. Both surgeries were performed in the service of
surgical pathology according to the Protocol:
General precautions
In order to have an appropriate glucose level during the
procedure, the intervention is scheduled in the morning. This
time concords with 2 hours after the insulin injection (the peak
activity). Care was also taken to ensure that the patient ate
properly before the appointment to avoid any risk of
hypoglycemic discomfort.
Precautions regarding stress
Our patient being very anxious, we proceeded with a
premedication with Atarax ®. Indeed, because of the
stimulating effect of stress on the production of adrenaline and
Figure 5. Value assessment of reduction estimated at 5 mm cortisol, which are hyperglycemic, it seems appropriate to
perform sedation if the patient seems anxious. Possibly, a
change in insulin dosage may be considered by the attending
physician in the event of very high physiological and/or
psychological stress (9).
Precautions during anaesthesia
Provided that low concentrations are chosen, the use of
vasoconstrictors in anesthetic products is not contraindicated.
However, it seems desirable to use the lowest dosages so as not
to overly aggravate existing vascular disturbances.
Precautions regarding the risk of infection
The diabetes is an important risk factor in the development of
Figure 6. Delimitation of the area to be reduced on the model infection after surgery. It may delay wound healing, especially
if the pathology is poorly or uncontrolled. Thus, preventive
and therapeutic measures were taken (3). The patient, although
balanced, antibiotic prophylaxis was administered in view of
the planned invasive surgery, which began within one hour
before the procedure and continued for 7 days after the
procedure.
Bone resection controlled by the surgical guide
Bone resection was performed after a scalpel incision and
mucosal elevation flap to provide good visibility of the bone
relief. The excess of bone was first cut with a bone cutter
under abundant irrigation of saline solution and then
regularized with a gouge forceps under the control of the
surgical guide. The finishing is done with bone rape. The
mucosa is brought together edge to edge and any excess was
Figure 7. Silicone key on the model to be corrected removed. Non-resorbable sutures are used due to delayed
healing (Fig 8, 11). Sutures were removed eight days after the
Pre-prosthetic surgery
procedure due to the lack of temporary prostheses; the surgical
Pre-prosthetic surgery must always be preceded by a general guide was used during the healing period to guide it and to
examination properly conducted to identify all the pathological contain post-operative oedema.
processes that may compromise the desired result (diabetes,
6144 Oubbaih and Bellemkhannate, Esthetic and functional management of insuffisant prothetic space using a guided osteoplasty approach
Figure 8. Delimitation of the bone Figure 9. Ridge after reduction Figure10. Regularization with a Figure11. Checking the reduced
block to be removed bone rape height with the surgical guide
Healing and delay phase
Figure 12. Surgical site after Figure 13. Surgical guide filled Figure 14. Surgical site Figure 15. Surgical site after 2
suture with retard resin (Fitt de Kerr) after 1 week weeks
used for healing control
Result of the surgery
Figure 16. a: before surgery, b: after
Figure 17. Maxillary secondary impression with Figure 18. Impregum® mandibular secondary Figure 19. Aesthetic result
Permlastic regular® impression
Prosthetic phase functional impression was taken with Permlastic Regular® on
the maxilla and Impregum® on the mandible (Fig17, 18). The
The final prosthetic treatment is started after 3 weeks of occlusion models from the secondary impression allowed the
provisionalization. This treatment was consisted of a adjustment of an adequate and smooth occlusion plane after
conventional bimaxillary complete prosthesis. After recharging the improvement of anatomical conditions and inter-maxillary
with KERR® maxillary and mandibular paste, an anatomical- relationships. The centric relation is performed appropriately to
6145 International Journal of Information Research and Review, Vol. 06, Issue, 02, pp. 6141-6145, February, 2019
the patient's vertical dimension. Regular follow-up was However, it must always be justified by a pre-prosthetic,
ensured for a better psychological and functional integration of economical study and preceded by a general examination
the new prosthesis (Fig 19). properly conducted in order to adapt the management protocol
to each clinical situation.
DISCUSSION
REFERENCES
The sudden change from a subtotal to a total edentulism
without immediate prosthetic rehabilitation causes a Bassetti R, Bassetti M, Kremer U, Mericske-Stern R: Le
differential in the degree of ridge resorption within the same «syndrome combiné» existe-t-il? Rev Mens Suisse
arch. The duration of uncompensated edentulism influences the Odontostomatol Vol. 120 9/2010
degree of bone resorption. A complete prosthesis that is well Davarpanah M, Rajzbaum P, Demurashvili G, Szmukler-
adjusted and integrated into its anatomical-functional Moncler S: L'édenté total au sourire gingival. Inf Dent
environment through the forces it absorbs generates a bio- 2015; 33: 2-8.
stimulation of bone cells, thus maintaining the balance Drouri S, Lahlou Kh, El Ouazzani A: Diabète et thérapeutiques
between resorption and apposition and preventing asymmetries endodontiques. Le courrier du dentiste. Avril 2014
of osteomucous ridges. According to Tolstunov (2007), Geramipanah F, Sadighpour L, Hendi A: Management of
occlusal pressure exerted by solid teeth on toothless regions of limited Interocclusal Distance With the Aid of the modified
the alveolar ridge could cause small, moderate or even marked Surgical Guide: A clinical Report. J dent (Tehran) Mars
changes (atrophy/hypertrophy) in the toothless region of the 2017; 14(2): 105-108.
alveolar ridge. These bone reactions are in accordance with Jivraj S, Chee W, Corrado P: Treatment planning of the
Wolff's (1892) theory that "bone adapts its external shape and edentulous maxilla. British Dental Journal Sep 2006; 201:
internal structure in response to mechanical stresses" (11). The 261-271
use of osteoplasty after pre-prosthetic analysis, thus allowing Korunoska Stevkovska V, Guguvcevski L, Menceva Z,
an adequate estimate of the amount of bone to be resected, Gigovski N, Mijoska A, Nikolovska J, Bajraktarova-
avoids any unwanted and aggressive surgical procedure that valjakova E : Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Patient with
may sacrifice the patient's bone capital (4). The present case, is anterior hyper function syndrome. Open Access Maced J
a complex situation, explained by the long duration of med Sci 2017; 5(7): 1000-1004
edentulism, more than 3 years without prosthesis. In addition Rajendran S, Baburajan: Combination syndrome (review
the persistence of a few antagonistic mandibular teeth article). (IJOPRD) international journal of prosthodontics
increased the extent bone resorption process asymmetrically. and Restorative Dentistry 2012; 2(4): 156-160.
The effect of daily microtrauma, promoting the regression of Regragui A, Sefrioui A, Merzouk N, Berrada S: Hypertrophie
the anterior mandibular area with hypertrophy of the adjacent osseuse buccale chez l'édenté complet: une fatalité à
maxillary ridge this made the prosthetic environment similar to contourner! AOS 2016; 275: 1-7.
a Kelly's syndrome. Regarding the general conditions of the Taisse. S, Benyahya. I. Diabète et odontologie. Le courrier du
patient, we chose a conservative and codified surgical protocol. dentiste. Novembre 2000
Our therapeutic approach consists of a bone osteotomy at the Tallgren A. The continuing reduction of the residual alveolar
left anteromaxillary ridge using a surgical guide designed after ridges in complete denture wearers: a mixed-longitudinal
a pre-prosthetic study, thus allowing a good aesthetic and study covering 25 years. J Prosth Dent 1972;27(2):120-132.
functional prosthetic integration. Tolstunov L: Combination syndrome: classification and case
report. J Oral Implantol. 2007;33(3):139-51.
Conclusion
The purpose of pre-prosthetic surgery is to give the complete
prosthesis a better fit and to allow patients to adapt faster and
better to their prosthesis.
*******
You might also like
- Physical Therapy Amputee Assessment FormDocument4 pagesPhysical Therapy Amputee Assessment FormTopaz CompanyNo ratings yet
- ADA-RiskForm 6y PDFDocument2 pagesADA-RiskForm 6y PDFvalentina0% (1)
- Alamo Wars by Ray VillarealDocument194 pagesAlamo Wars by Ray VillarealArte Público Press100% (3)
- Decoronation of An Ankylosed Permanent Incisor: Alveolar Ridge Preservation and Rehabilitation by An Implant Supported Porcelain CrownDocument4 pagesDecoronation of An Ankylosed Permanent Incisor: Alveolar Ridge Preservation and Rehabilitation by An Implant Supported Porcelain CrownJuan Carlos MeloNo ratings yet
- 6.preprosthetic Surgery A Review of LiteratureDocument7 pages6.preprosthetic Surgery A Review of Literaturemirah indrianiNo ratings yet
- Articol RJMEDocument4 pagesArticol RJMELaura IosifNo ratings yet
- 2010 Miniscrew Assisted Nonsurgical PalatalDocument10 pages2010 Miniscrew Assisted Nonsurgical PalatalMariana SantosNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Esthetics For Implant Restorations in The Anterior Maxilla: Anatomic and Surgical ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesOptimizing Esthetics For Implant Restorations in The Anterior Maxilla: Anatomic and Surgical ConsiderationsitziamanzNo ratings yet
- Optimizando La EsteticaDocument19 pagesOptimizando La EsteticaGiovanna ChamonNo ratings yet
- Reconstrução de Severa Reabsorção Maxilar Com Distração OsteogenicaDocument7 pagesReconstrução de Severa Reabsorção Maxilar Com Distração OsteogenicaNelson UzunNo ratings yet
- 14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Document6 pages14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- 2020 Article 265Document7 pages2020 Article 265Fabian BarretoNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Residual Mandibular Defect With Fixed Removable Hybrid Prosthesis-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesProsthodontic Rehabilitation of Residual Mandibular Defect With Fixed Removable Hybrid Prosthesis-A Case ReportnastitiiNo ratings yet
- TMP 371 BDocument4 pagesTMP 371 BFrontiersNo ratings yet
- The Fate of The Distal Papilla Around Tooth-Bound Implant-Supported Restorations in Maxillary Central Incisor SitesDocument7 pagesThe Fate of The Distal Papilla Around Tooth-Bound Implant-Supported Restorations in Maxillary Central Incisor SitesValentinaNo ratings yet
- Restoring Soft Tissue Esthetics with Acrylic Gingival EpithesisDocument4 pagesRestoring Soft Tissue Esthetics with Acrylic Gingival EpithesisannysaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document58 pagesChapter 13Yaser JasNo ratings yet
- Implant Reconstruction of The Bone-Grafted Maxilla: Review of The Literature and Presentation of 8 CasesDocument9 pagesImplant Reconstruction of The Bone-Grafted Maxilla: Review of The Literature and Presentation of 8 CasesRohan BhagatNo ratings yet
- Bodnar 2019therapeutic Variants in Complex Clinical Cases of Intercalated EdentationDocument7 pagesBodnar 2019therapeutic Variants in Complex Clinical Cases of Intercalated EdentationAnonymous AyxIccS4aXNo ratings yet
- Australian Dental Journal - 2018 - Spencer - Implant Based Rehabilitation Options For The Atrophic Edentulous JawDocument8 pagesAustralian Dental Journal - 2018 - Spencer - Implant Based Rehabilitation Options For The Atrophic Edentulous JawAswathi RaghuthamanNo ratings yet
- MOLARDocument8 pagesMOLARJuan Carlos MeloNo ratings yet
- 1999 115 1 1 12 Figueroa PDFDocument12 pages1999 115 1 1 12 Figueroa PDFAlla MushkeyNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Symphyseal Distraction Case ReportDocument7 pagesMandibular Symphyseal Distraction Case ReportsebitadesantaNo ratings yet
- 03 Mareque pp15-19Document5 pages03 Mareque pp15-19OMAR NOLBERTO DIAZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Dental CaseDocument4 pagesDental CaseCristi GaidurNo ratings yet
- Guided Bone RegenerationDocument4 pagesGuided Bone Regenerationahmad955mlsNo ratings yet
- Artigo MedeirosDocument6 pagesArtigo MedeirosEugénio MartinsNo ratings yet
- Tooth TtriyionDocument5 pagesTooth TtriyionDhanasriNo ratings yet
- Chung 2009Document19 pagesChung 2009Joshua StalinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Utama ProstoDocument5 pagesJurnal Utama ProstoParlin BrutuNo ratings yet
- Okay 2001Document12 pagesOkay 2001Hema SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 (1) 11 14Document4 pages3 (1) 11 14marcelodentNo ratings yet
- Rosa 2014Document6 pagesRosa 2014Michal PerkowskiNo ratings yet
- Supplement The Base To Complement The Crown: Localized Ridge Augmentation Using Connective Tissue GraftDocument5 pagesSupplement The Base To Complement The Crown: Localized Ridge Augmentation Using Connective Tissue GraftBianca DimofteNo ratings yet
- Intruding Overerupted Molar with MiniscrewsDocument8 pagesIntruding Overerupted Molar with MiniscrewsPanaite TinelaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352587820300693 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2352587820300693 Mainabhishekjha0082No ratings yet
- Resective Osseous Surgery: A Tool in Restoring Smile - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesResective Osseous Surgery: A Tool in Restoring Smile - A Case ReportdoctormallikaNo ratings yet
- Franceschi2018 PDFDocument12 pagesFranceschi2018 PDFMichal PerkowskiNo ratings yet
- GholamiDocument4 pagesGholamiLalaNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedDocument2 pagesProsthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- IPIntJMedPaediatrOncol 9 2 77 82Document6 pagesIPIntJMedPaediatrOncol 9 2 77 82Laraduta AgustiniNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Management of Flabby Tissue by Modified Massad S Technique A Case ReportDocument8 pagesProsthetic Management of Flabby Tissue by Modified Massad S Technique A Case ReportMamta SentaNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Maxillary Buccal Bone Exostosis: Rare Case ReportDocument4 pagesBilateral Maxillary Buccal Bone Exostosis: Rare Case Reportegi007No ratings yet
- Fulltext - Jda v5 Id1107Document3 pagesFulltext - Jda v5 Id1107Sahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Management For Immediate Implant Placement in Sites With Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case ReportDocument6 pagesTherapeutic Management For Immediate Implant Placement in Sites With Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case ReportRaul Alfonsin SanchezNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Edentulous Maxillectomy Patient With Lightweight, Top Open Obturator: A Clinical ReportDocument3 pagesRehabilitation of Edentulous Maxillectomy Patient With Lightweight, Top Open Obturator: A Clinical ReportSaatvik AtriNo ratings yet
- Tanpa Judul PDFDocument7 pagesTanpa Judul PDFnadyashintakasihNo ratings yet
- Managing Missing Mandibular PremolarsDocument4 pagesManaging Missing Mandibular PremolarsKanish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Oh 2010Document5 pagesOh 2010gbaez.88No ratings yet
- Frontal Fixed Prosthetic Restoration in Edentulous Space ModificationDocument3 pagesFrontal Fixed Prosthetic Restoration in Edentulous Space ModificationFlorin UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Rapid Orthodontic Treatment After The Ridge-Splitting TechniqueDocument10 pagesRapid Orthodontic Treatment After The Ridge-Splitting TechniqueEugenioNo ratings yet
- Ankylosed Teeth As Abutments For Maxillary Protraction: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesAnkylosed Teeth As Abutments For Maxillary Protraction: A Case Reportdrgeorgejose7818No ratings yet
- Decoronation For The Management of An Ankylosed Young Permanent ToothDocument5 pagesDecoronation For The Management of An Ankylosed Young Permanent ToothCesar Augusto Rojas MachucaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: The Prosthetic Management of A Case of Epulis Fissuratum by A Novel TechniqueDocument6 pagesCase Report: The Prosthetic Management of A Case of Epulis Fissuratum by A Novel TechniqueMichelle VelezNo ratings yet
- Ams 5 108Document4 pagesAms 5 108Alice EmailsNo ratings yet
- 0718 381X Ijodontos 15 02 479Document5 pages0718 381X Ijodontos 15 02 479Jaime Moncayo PinosNo ratings yet
- 6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothDocument6 pages6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Implant Supported Overdenture As Occlusal Guide, Case ReportDocument5 pagesMandibular Implant Supported Overdenture As Occlusal Guide, Case ReportFrancisca Dinamarca LamaNo ratings yet
- Crid2014 658790Document6 pagesCrid2014 658790paula catanaNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy of Mandibular Incisor PDFDocument4 pagesVital Pulp Therapy of Mandibular Incisor PDFSebastian CastroNo ratings yet
- Mclaurin 2020Document9 pagesMclaurin 2020magus davilaNo ratings yet
- BOPT Technique (2013)Document14 pagesBOPT Technique (2013)Joselyn RodríguezNo ratings yet
- CAMBRA - Best Practices in Dental Caries PDFDocument15 pagesCAMBRA - Best Practices in Dental Caries PDFEm Ery100% (1)
- Accreditation-2013 Pediatric Dentistry PDFDocument411 pagesAccreditation-2013 Pediatric Dentistry PDFadenaNo ratings yet
- Cirugía Periapical Con Remoción de Quiste Periapical: Presentación de Un CasoDocument8 pagesCirugía Periapical Con Remoción de Quiste Periapical: Presentación de Un CasovalentinaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 1 y Psiquiatría PDFDocument8 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Tipo 1 y Psiquiatría PDFvalentinaNo ratings yet
- InTech-Management of Bone Loss in Primary and Revision Knee Replacement SurgeryDocument25 pagesInTech-Management of Bone Loss in Primary and Revision Knee Replacement SurgerySagaram ShashidarNo ratings yet
- Preview PDFDocument91 pagesPreview PDFankita awasthiNo ratings yet
- The Universal Prosthesis - Appendixes 2005-11-18 - A4Document60 pagesThe Universal Prosthesis - Appendixes 2005-11-18 - A4Inne ten HaveNo ratings yet
- Amputation AssignmentDocument19 pagesAmputation Assignmentmushimiyimana jacquelineNo ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Social Welfare RulesDocument8 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Social Welfare RulesJaNo ratings yet
- KDJVol33No4 KeralaDentalJournal 2Document62 pagesKDJVol33No4 KeralaDentalJournal 2Loly SinagaNo ratings yet
- Future Human Evolution Fabienne Goux-BaudimentDocument10 pagesFuture Human Evolution Fabienne Goux-BaudimentandinNo ratings yet
- Exoskeletons and Robotic Prosthetics: A Review of Recent DevelopmentsDocument7 pagesExoskeletons and Robotic Prosthetics: A Review of Recent DevelopmentsOliver Malpartida CustodioNo ratings yet
- Removable Prosthetic Treatment in Children - Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesRemovable Prosthetic Treatment in Children - Literature ReviewNancy Amelia RosaNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument5 pagesCad CamsauriuaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Feet 16 1slideDocument25 pagesProsthetic Feet 16 1slideNolanNo ratings yet
- Durable Medical Equipment Dme Reference List PDFDocument20 pagesDurable Medical Equipment Dme Reference List PDFArias Richard DNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Interd TaskDocument3 pagesRubrics For Interd Taskapi-265986384No ratings yet
- Ac 72Document5 pagesAc 72Giovani TardiniNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb AmputationDocument37 pagesLower Limb AmputationUhuebor David0% (1)
- Iso 14801 2016Document11 pagesIso 14801 2016robonrobertorrsNo ratings yet
- DGTIN Assignment 2020Document15 pagesDGTIN Assignment 2020jadenNo ratings yet
- Cyborg Technology: A Quiet Revolution: Review ArticleDocument4 pagesCyborg Technology: A Quiet Revolution: Review ArticleHemasundar Reddy JolluNo ratings yet
- PCE Written Exam Study GuideDocument117 pagesPCE Written Exam Study GuideShora Jari0% (1)
- Amputation Rehab: Exercises & Stump CareDocument5 pagesAmputation Rehab: Exercises & Stump CareRazelAnneValinoNo ratings yet
- Human Engineering: Prosthetics and Orthotics: Mike NorellDocument39 pagesHuman Engineering: Prosthetics and Orthotics: Mike Norellmuhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- Costumes and Props: General Obligations Concerning Occupational Health and SafetyDocument4 pagesCostumes and Props: General Obligations Concerning Occupational Health and SafetyMariaMaraNo ratings yet
- Prama implant system catalogueDocument104 pagesPrama implant system catalogueGheorgheNo ratings yet
- Robotic Symbionts: Interweaving Human and Machine ActionsDocument10 pagesRobotic Symbionts: Interweaving Human and Machine ActionsEsteban AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Knee Surgery Using Computer Assisted Surgery and Robotics PDFDocument221 pagesKnee Surgery Using Computer Assisted Surgery and Robotics PDFHendra AjahNo ratings yet
- 3D Printed Bionic Prosthetic Hands: Conference PaperDocument7 pages3D Printed Bionic Prosthetic Hands: Conference PaperDaniel BarajasNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Artificial Limb Production CentreDocument5 pagesLightweight Artificial Limb Production Centresahil patelNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life Assessment of Patients Utilizing Orbital Implant Supported ProsthesesDocument6 pagesQuality of Life Assessment of Patients Utilizing Orbital Implant Supported ProsthesesBagis Emre GulNo ratings yet