Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acmcr v10 1930
Uploaded by
Annals of Clinical and Medical Case ReportsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acmcr v10 1930
Uploaded by
Annals of Clinical and Medical Case ReportsCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Paper
Annals of Clinical and Medical Case Reports
The mass of the Milky Way galaxy
Yanbikov Vildan Shavkyatovich, Vildyan Yanbikov energy incident on a proton p within a solid angle of 4π in one second.
The number of protons in one cubic meter of the Sun’s matter is equal
Russian Federation, Volgograd, 400064, Bibliotechnaya Street, House 14, to n = p/m = M/(V*m) where p is the density of the Sun’s matter, M is
Apartament 95 the mass of the Sun, V is the volume of the Sun, m is the rest mass of
the proton. Let us isolate an elementary volume dV inside the surface of
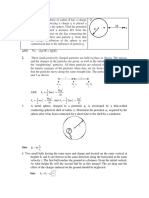
*Corresponding author: the Sun at a distance R from the proton p . With d V = R2 dθdφd
Yanbikov Vil’dyan Shavkyatovich, R Fig. 1). The number of protons in the volume d V is equal to d N = n
Russian Federation, Volgograd, 400064, Bibliotechnaya street, house 14, dV= R2 d θ d φ d R. In one second, the volume d V re-emits
apartament 95, gravitational energy in the amount of Δε*d N = R2 dθdφd
Tel: 8-909-391-34-70; R ; where π = 3.14. The energy incident on the proton p from the entire
E-Mail: vildyanyanbikov@yandex.ru volume of the Sun in one second εр = ;
where 0 ≤ R ≤ R0 ; 0 ≤ θ ≤ π ; 0 ≤ φ ≤ 2π ; R0 - is the radius of the Sun.
Received Date: 01 Apr 2023 The volume of the Sun V = π R03 . r- is the radius of the proton. or εр =
Accepted date: 25 Apr 2023 After solving the integral , we
Published Date: 02 May 2023 get εр = ; Select a small region in the vicinity of the proton p
space free from the matter of the sun. Let’s put two protons p1 and p2 in
1. Abstract this cavity at a distance R from each other. Each of the protons p1 and p2 in
one second, it re-emits of gravitational energy within a solid angle of 4π.
On the Basis of tabular values of the gravitational constant. The calculated Energy gets from proton p1 to proton p2 ε = = ; m
mass of the nucleus of the milky way galaxy. The numerical value of the is the rest mass of the proton. In the last
gravitational constant is determined by the mass of the nucleus of the
milky way galaxy Abstract: Based on the tabular value of the gravitational expression R is the distance between the test protons p1 and p2. The pulse
constant, the mass of the Milky Way galaxy is calculated. Based on the received by the proton p1 in one second
physical meaning the gravitational constant, and the coincidence with the Δр = = ; where c is the speed of light in vacuum. The
calculated on the surface Of the Sun, the mass of the Milky Way galaxy force of attraction between protons p1 and p2 is defined as F = Δр . ( Δt
is calculated. gravitational constant on the surface of the Sun, the mass of =0 ). Substitute =γ ; where γ is the gravitational
the galaxy The Milky Way. constant at the center the Sun. Hence γ = ; Substitute
the values of the quantities, we get the coefficient of gravity in the center
2. Keywords: of the Sun γ = 2.9256* 10 – 10 н*м2*кг – 2 Let’s calculate the coefficient
Gravitational constant, The core of the galaxy, The core mass of the of gravity on the surface of the Sun. Let the center of the Sun S be located
Galaxy, Physical meaning of the gravitational constant, Gravitational on the OZ axis of the spherical coordinate system at a distance R0 from
constant on the surface of the Sun, The mass of the galaxy The Milky Way. its origin (Fig.2). R0 is the radius the Sun, M is the mass of the Sun. Let’s
put a test proton at the beginning a spherical coordinate system on the
3. Gravity in the center and on the surface of the Sun surface of the Sun . Select inside The elementary volume of the Sun dV
= R2 d θ d φ d R The number of protons in one cubic meter of the
Let the Sun be in the empty space of the universe (on the “edge“The Sun n = = ; where p is the density of the substance the Sun, M
universe). In the center of the Sun we introduce a spherical coordinate is the mass of the Sun, V is the volume of the Sun, m is the rest mass of
system At the beginning of the coordinate system, we place the proton p. the proton. The number of protons in the dV volume is equal to d N = n
Wave fronts of a high-frequency gravitational field re-emitted by matter dV= R2 d θ d φ d R In one second, the volume d V re-emits
The suns fall on the proton p within the solid angle of 4π.When the gravitational energy in the amount of Δε*d N = R2 dθdφd
wave front interacts with a proton p, the energy of the proton p becomes R ; where π = 3.14. Where Δε is taken from the Heisenberg uncertainty
indeterminate for some time, according to the principle Heisenberg ratio Δε*Δt ≥ h/( 2π) ; where h is Planck’s constant, Δε is the uncertainty
uncertainties Δε*Δt ≥ h/( 2π) ; where h is Planck’s constant, Δε is the of the proton energy over time Δt . At Δt = 1 sec. we take Δε = h/( 2π).
uncertainty of the The energy incident on the test proton in one second from the volume d V
is equal to The energy incident on the proton p from the entire
proton energy over time Δt . When a wave front passes through a proton, volume of the Sun in one second εр =
it re-emits excess energy into the surrounding space in the form of a ; where 0 ≤ R ≤ 2R0 ; 0 ≤ θ ≤ ; 0 ≤ φ ≤ 2π ; After calculating the
spherically symmetric gravitational wave. Calculate the gravitational integral, we get εр = (1 - ) Now let there be two test
http://acmcasereports.com/ Volume 10 Issue 17 Page 01
Technical Paper
Annals of Clinical and Medical Case Reports
protons on the surface of the Sun with the re-emission energies of εр. The 5. The Basic Part
energy incident on proton p2 from the side of proton p1 will be defined as
ε= = (1 - ) ; In the last expression , R is the Let the center of the nucleus of the galaxy О. The radius of the ball
distance between the trial protons p1 and p2 Pulse received by proton p2 region of the galaxy is R0. The mass of a galaxy M. The Solar system is
in one second Δр = = ; where c is the at a distance H from the center of the galaxy (fig.1.1.). We introduce
speed of light in vacuum. The force of attraction between protons p1 and a coordinate system. To the center of the kernel was on the z axis at a
p2 is defined as F = Δр. Or =γ ; where distance H from the beginning of the coordinate system. Place a test
γ is the gravitational constant on the surface of the Sun. Hence proton in the origin of the coordinate system at point p. In inside the ball
γ= ; (1) volume. dV = R2 d θ d φ d R . The number of protons in one cubic
Substitute the values of the quantities, we get the gravity coefficient meter inside the ball n = = ; where V – the volume of a sphere
(gravitational constant) on the surface of the Sun (r- is the radius of the of radius R0, m is the mass of a proton, ρ is the density substance inside the
proton). γ = 8.572* 10 – 11 н*м2*кг – 2 ball, M – mass of the substance inside the bowl. The number of protons
inside the volume dV is equal to dN = R2 d θ d φ d R The
4. Calculate The Mass Of The Milky Way Galaxy
volume dV in one second, emits gravitational energy in the amount of Δε
* dN = R2 d θ d φ d R ; where Δε taken from Heisenberg’s
Formula (1) is good with a tabular value γ = 6.672*10 – 11 нм2кг – 2. From
uncertainty principle: Δε * Δt = ; Take Δt = 1 second, then Δε = .
here, mentally, the Milky Way galaxy can be represented as a homogeneous
huge star with a radius of Н. The density of which is equal to the density
of the Sun. Let About the center of the core of the Milky Way galaxy. R0
is the radius of the globular region of the galaxy centered at point O and
mass M. The solar system is located at a distance of H + R from the center
of the galaxy (Fig. 1). We introduce the system coordinates so that the
center of the core O is on the z axis at a distance H from the origin of the
coordinate system. Let’s put a test proton at the beginning of the system
coordinates to the point o. The galactic core determines the distribution of
the gravitational constant within the galaxy. The gravitational constant is
no longer constant inside the galaxy. The farther away from the center of
the galaxy, the smaller it is. The mass of the Galactic core is determined
in terms of the gravitational constant inside the Solar system (table value).
Figure 1
Figure 1.1
http://acmcasereports.com/ Volume 10 Issue 17 Page 02
Technical Paper
Annals of Clinical and Medical Case Reports
The energy of the incident proton p per second from the Volume dV is
equal to Δε * dN ; where r – the radius of the proton ( r = 1.5 *10 –
15
m); π = 3.14. R – the distance from the volume dV before the beginning
of the coordinate system. The energy of the incident proton p. 1 second of
the entire volume of a sphere
εp = ; where 0 ≤ θ ≤ arctg θ , 0 ≤ ≤ 2π ;
H – R0 ≤ R ≤ H + R0 ; tg θ = . In view of the smallness of the angle
θ we write arctg θ = θ = ; After calculating the integral get εp =
Let on the edge of the Solar system. Far away from massive objects.
There are two protons at a distance R from each other. Energy falling on
the p2 proton from the proton p1 is equal to ε = εp =
The impulse received by the proton p2 in one second is equal to Δp =
The force of attraction between the protons p1 and p2 is equal to
F = Δp = γ = ; where с – the speed of light in vacuum.
Hence the weight of the Central region of the milky way galaxy M =
γ ; where γ the table value of the gravitational constant (γ =
6.672*10 – 11 н m2кг – 2). Take Н = 2.65*1020 м. then М = 1.3*1053 кг.
Figure 3: R the radius of the Sun. H +R the distance from the center of
the Sun to the center of the galactic core.
Figure 2
6. Conclusion:
The galactic core in the weight specifies a numeric value the gravitational
constant inside the Solar system.
http://acmcasereports.com/ Volume 10 Issue 17 Page 03
You might also like
- Alkali SpectraDocument8 pagesAlkali SpectraVivek DewanganNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Document8 pagesProblem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Gravitation Field TheoryDocument62 pagesNuclear Gravitation Field TheoryKen WrightNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument39 pagesNuclear Physicsredowan.hoque1No ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument9 pagesFinal ProjectAronNo ratings yet
- Natural and Laboratory Plasmas II - Example Sheet 1: (Z) B (1+ (Z/L) ) - HowDocument2 pagesNatural and Laboratory Plasmas II - Example Sheet 1: (Z) B (1+ (Z/L) ) - Howalteru4No ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument39 pagesNuclear Physicsnakib mdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 8 PDFRG RAJNo ratings yet
- Bgu 6 CapacitorDocument4 pagesBgu 6 CapacitorÃmrit SRNo ratings yet
- Limesi FormuleDocument54 pagesLimesi Formulecasejc.justinNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument12 pagesAtomsmidhunesh41No ratings yet
- Atomic NucleusDocument24 pagesAtomic Nucleussudha24_7No ratings yet
- hw01 SolDocument5 pageshw01 Solvincent.savignac11No ratings yet
- Atoms PDFDocument24 pagesAtoms PDFAdinarayanaNo ratings yet
- Life As A Natural Property of The UniverseDocument38 pagesLife As A Natural Property of The UniverseIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 3 IITK /ynm March 31, 2021Document2 pagesPHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 3 IITK /ynm March 31, 2021RAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Grhw1: 1 D 1 D 1 1 D DDocument8 pagesGrhw1: 1 D 1 D 1 1 D DMatejaBoskovicNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Gravitation:: F F R F RDocument7 pagesNewton's Law of Gravitation:: F F R F RSabit Islam BhuiyaNo ratings yet
- The Structures and Evolution of StarsDocument14 pagesThe Structures and Evolution of StarsmmrmathsiubdNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: Lecture Notes OnDocument145 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Waves: Lecture Notes OnSaswat RaysamantNo ratings yet
- Mechanics-Probs4 2017Document5 pagesMechanics-Probs4 2017Diego ForeroNo ratings yet
- Ii Puc: Trinity Pu CollegeDocument10 pagesIi Puc: Trinity Pu CollegeAnsha NasarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4Document5 pagesProblem Set 4James ConnaughtonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Wavesabhishek_modemNo ratings yet
- Em Questions 2019Document20 pagesEm Questions 2019MartinaGmizaNo ratings yet
- Atom and NecluiDocument11 pagesAtom and NecluithinkiitNo ratings yet
- ATOMS NUCLEI (Cbseworldonline - Blogspot.com)Document24 pagesATOMS NUCLEI (Cbseworldonline - Blogspot.com)Sagar VermaNo ratings yet
- Ed Pgs F9-13, 4 Ed Pgs F10-13) - Force and Ed Pgs F15-17, 4 Ed Pgs F15-18) - Elements and Atoms, Edand4 Ed Pgs 1-3) - The Nuclear Atom. Ed)Document7 pagesEd Pgs F9-13, 4 Ed Pgs F10-13) - Force and Ed Pgs F15-17, 4 Ed Pgs F15-18) - Elements and Atoms, Edand4 Ed Pgs 1-3) - The Nuclear Atom. Ed)Daffa AlexNo ratings yet
- Baao 2018Document11 pagesBaao 2018physicsolympiad19No ratings yet
- Models of Stellar Atmospheres: Department of Astronomy Vienna UniversityDocument46 pagesModels of Stellar Atmospheres: Department of Astronomy Vienna UniversityGloria Evelin Vargas SirpaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Physics Study Package 3 SolutionsDocument218 pagesAakash Physics Study Package 3 Solutionsfociwe100% (1)
- Ii Pu Physics Key Answers PDFDocument17 pagesIi Pu Physics Key Answers PDFVeeranna M SabaradaNo ratings yet
- Problem As GradoDocument10 pagesProblem As GradoAntonio Jesus Escalante DiazNo ratings yet
- Brem SST Rah LungDocument43 pagesBrem SST Rah LungDiego FernandezNo ratings yet
- Energetics of The Kerr-Newman Black Hole by The Penrose ProcessDocument16 pagesEnergetics of The Kerr-Newman Black Hole by The Penrose ProcessMichael WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Electrostaic and MagnetismDocument12 pagesElectrostaic and MagnetismDavid Hinostroza VargasNo ratings yet
- Two Body Problems PDFDocument37 pagesTwo Body Problems PDFSantosh SahuNo ratings yet
- Basic Ideas History (Background Material) : Fi - DecaysDocument5 pagesBasic Ideas History (Background Material) : Fi - DecaysRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- PY4A03 Lecture1n2 Properties PDFDocument30 pagesPY4A03 Lecture1n2 Properties PDFRowina PantiloNo ratings yet
- Cap 2013 ExamDocument23 pagesCap 2013 Examhkalloli@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Unit - 8 AtomsDocument9 pagesUnit - 8 AtomsSahil Chawla100% (1)
- Solar System Constraints On R GravityDocument10 pagesSolar System Constraints On R GravitypsistNo ratings yet
- Atoms - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesAtoms - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024shivam.iit2024No ratings yet
- BSC VI Sem Physics Paper-I Unit-III Nuclear PhysicsDocument34 pagesBSC VI Sem Physics Paper-I Unit-III Nuclear PhysicsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Week6 Homework4 PulsarsDocument5 pagesWeek6 Homework4 PulsarsastodudeNo ratings yet
- Ps 9Document2 pagesPs 9endapallikartheeNo ratings yet
- Linköping University Post PrintDocument9 pagesLinköping University Post PrintwhoNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Science of Possible Hollow-Moon SpacecraftDocument40 pagesPredicting The Science of Possible Hollow-Moon SpacecraftIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument54 pagesNuclear PhysicsNarayan VarmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture18 GalacticDynamics&Evolution2019 PDFDocument24 pagesLecture18 GalacticDynamics&Evolution2019 PDFSagar RawalNo ratings yet
- @aakashallen: Estimation of closest distance of approach (derivation) of α - particleDocument25 pages@aakashallen: Estimation of closest distance of approach (derivation) of α - particleYashasvi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Physics Olympiad 2016Document9 pagesBangladesh Physics Olympiad 2016Science Olympiad Blog88% (8)
- Intermediate Electromagnetism, UP 203: Problem Set IIIDocument1 pageIntermediate Electromagnetism, UP 203: Problem Set IIIarjun__123No ratings yet
- Cmi 2 17 PDFDocument2 pagesCmi 2 17 PDFjeremyNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics: Assignment - 2 September 12, 2017Document2 pagesNewtonian Mechanics: Assignment - 2 September 12, 2017jeremyNo ratings yet
- Elementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryFrom EverandElementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryNo ratings yet
- Zero Point Energy Per Stereo Radian and the Distribution of Gravitational Acceleration of Planets Throughout the Solar System.: The Origin and Cause of GravitationFrom EverandZero Point Energy Per Stereo Radian and the Distribution of Gravitational Acceleration of Planets Throughout the Solar System.: The Origin and Cause of GravitationNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsFrom EverandEssentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsNo ratings yet