Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Head and Spine Injuries
Uploaded by
KIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Head and Spine Injuries
Uploaded by
KIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDCopyright:
Available Formats
HEAD AND SPINE INJURIES A hematoma may not appear for a day or as
long as several weeks.
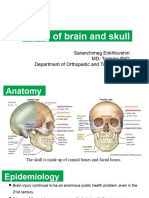
- The brain is a soft and delicate organ. A
hard blow to the head can injure the
brain or spinal cord even when there
CAUSES OF HEAD INJURY
are no visible signs of trauma to the
scalp or face. That’s why all head • Falls (most common cause);
injuries are considered serious and
should be assessed by your doctor or • Exercising and sports-related accidents;
the nearest hospital emergency • Physical assaults;
department.
• Traffic accidents.
HEAD INJURY
- Head injury is a common injury
suffered by people of all age groups, WHO HAS THE HIGHEST RISK
especially children. Fortunately, most • Children;
head injuries are mild, temporary, and
curable without persisting health • The elderly;
problems. Some head injuries may,
• Drug and alcohol users.
however, affect the brain or the tissue
surrounding it, resulting in long-term
complications.
First aid when the injured person is conscious
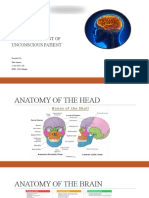
- A head injury is any sort of injury to the
brain, skull, or scalp. This can range - Encourage the injured person to
from a mild bump or bruise to a minimise any movement of their head
traumatic brain injury. or neck. Scalp injuries can bleed
profusely, so control any significant
TYPES OF HEAD INJURIES
blood loss from head wounds with
• Concussion: This is a jarring injury to your direct pressure and a dressing. While
brain. Most of the time, people remain examining the wound, avoid disturbing
blood clots forming in the hair.
conscious. They may feel dazed and lose
Reassure the person and try to keep
balance for a brief time.
them calm.
• Brain contusion: This is a bruise of your brain.
Minor bleeding in your brain
First aid when the injured person is
causes swelling.
unconscious
• Skull fracture: This is a crack in the skull.
- The person should not be moved unless
Sometimes, the broken skull bones can
they are in immediate danger. Any
cut into the brain. unnecessary movement may cause
greater complications to the head injury
• Hematoma: This is bleeding in your brain that itself, the spine or other associated
collects and clots, forming a bump. injuries. A good rule is that if the head is
injured, the neck may be injured too.
Your role is to protect the injured person from SPINAL INJURY
any potential dangers at the scene. You should
- A spinal cord injury damages the spinal
also monitor their airway and breathing until
cord itself or nearby tissues and bones.
the arrival of an ambulance. If the person’s
Depending on the severity of the injury,
breathing becomes impaired due to a problem
you may lose function or mobility in
with their airway, you may need to very
different parts of your body.
carefully tilt their head back (and support it)
Treatments include surgery, medication
until normal breathing returns. If the person
and physical therapy. A newer approach
stops breathing or has no pulse,
looks to tap working nerves.
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) may be
required. Is a spinal cord injury the same as a back
injury?
CONCUSSION
A spinal cord injury isn’t the same as a back
- A concussion is a type of traumatic
injury. Back injuries may damage bones or soft
brain injury—or TBI—caused by a
tissues in the spine, but they don’t affect the
bump, blow, or jolt to the head or by a
spinal cord.
hit to the body that causes the head
and brain to move rapidly back and TYPES OF SPINAL CORD INJURY
forth. Balance problems or dizziness, or
double or blurry vision. Bothered by Spinal cord injuries can be complete or
light or noise. Feeling sluggish, hazy, incomplete (partial):
foggy, or groggy. Confusion, or • Complete: A complete injury causes total
concentration or memory problems. paralysis (loss of function) below the level of
the injury. It affects both sides of the body. A
complete injury may cause paralysis of all four
Treatment of concussion limbs (quadriplegia) or the lower half of the
body (paraplegia).
- Concussion is a mild traumatic brain
injury that follows some trauma to the • Incomplete: After an incomplete injury, some
head. It is a diagnosis made by a doctor function remains on one or both sides of the
when it is certain a more serious head body. The body and brain can still communicate
injury has not occurred. Symptoms of along certain pathways.
concussion can persist for up to three
weeks after trauma. Your doctor or SPINAL INJURY
hospital will provide advice for yourself - A person who has sustained a head injury may
and your family regarding your ongoing have also injured their spine. In elderly people,
care when being discharged for home. the force required to cause neck injuries is
Most importantly, be alert for any much less than in younger people. It can even
danger signs over the next one or two occur from a standing height fall in the elderly.
days, such as persistent vomiting, loss
of coordination, or bad or worsening -It is important to keep the injured person’s
headaches despite analgesia (pain- head in line with their neck. Avoid twisting their
relieving medication). Seek medical head or allowing their head to roll to the side. If
attention immediately. you can, roll a t- shirt, towel or similar soft item
and place it around their neck to keep their
head straight. Don’t try to move them unless • Closed Fracture: A fracture that does not
there is an urgent need to. break the skin. This is also called a simple
fracture.
• Partial Fracture: An incomplete break of the
HOW DO SPINAL INJURIES HAPPEN?
bone
Some possible causes of spinal cord injuries
• Complete Fracture: A complete break of the
(from most to least common) include:
bone causing it to be separated into two or
• Motor vehicle accidents. more pieces
• Falls. • Stable Fracture: The broken ends of the bone
line up and have not moved out of place.
• Gunshot wounds.
• Displaced Fracture: There is a gap between
• Sports injuries. the broken ends of the bone. Repairing a
• Surgical complications. displaced fracture may require surgery.
BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLE INJURY TYPES OF BONE FRACTURE
A fracture is a broken bone. 1. Transverse Fracture- Transverse fractures are
breaks that are in a straight line across the
A potential complication is compartment bone. This type of fracture may be caused by
syndrome. traumatic events like falls or automobile
Fractures are usually caused by traumas like accidents.
falls, car accidents or sports injuries. But some 2. Spiral Fracture-, this is a kind of fracture that
medical conditions and repetitive forces (like spirals around the bone. Spiral fractures occur
running) can increase your risk for experiencing in long bones in the body, usually in the femur,
certain types of fractures. tibia, or fibula in the legs. However, they can
If you break a bone, you might need surgery occur in the long bones of the arms. Spiral
to repair it. Some people only need a splint, fractures are caused by twisting injuries
cast, brace or sling for their bone to heal. How sustained during sports, during a physical
long it takes to recover fully depends on which attack, or in an accident.
of your bones are fractured, where the fracture 3. Greenstick Fracture- This is a partial fracture
is and what caused it. that occurs mostly in children. The bone bends
and breaks but does not separate into two
separate pieces. Children are most likely to
BONE FRACTURE BASICS experience this type of fracture because their
bones are softer and more flexible.
• Open Fracture: A fracture in which the bone
breaks through the skin and can be seen 4. Stress Fracture- Stress fractures are also
outside the leg. Or there is a deep wound that called hairline fractures. This type of fracture
exposes the bone through the skin. This is also looks like a crack and can be difficult to
called a compound fracture. diagnose with a regular X-rays. Stress fractures
are often caused by repetitive motions such as
running.
A dislocation is a disruption of a joint in which
5. Compression Fracture- When bones are the bone ends are no longer in contact.
crushed it is called a compression fracture. The
Trauma that forces a joint out of place causes
broken bone will be wider and flatter in
a dislocation. Car accidents, falls, and contact
appearance than it was before the injury.
sports such as football are common causes of
Compression fractures occur most often in the
this injury.
spine and can cause your vertebrae to collapse.
A type of bone loss called osteoporosis is the Dislocations also occur during regular
most common cause of compression fractures. activities when the muscles and tendons
surrounding the joint are weak. These injuries
6. Oblique Fracture- An oblique fracture is
happen more often in older people who have
when the break is diagonal across the bone.
weaker muscles and balance issues.
This kind of fracture occurs most often in long
bones. Oblique fractures may be the result of a A sprain is an injury to ligaments, articular
sharp blow that comes from an angle due to a capsule, synovial membrane, and tendons
fall or other trauma. crossing the joint.
7. Impacted Fracture- An impacted fracture A strain is a stretching or tearing of the muscle,
occurs when the broken ends of the bone are causing:
driven together. The pieces are jammed
together by the force of the injury that caused Pain
the fracture. Swelling
8. Segmental Fracture- The same bone is Bruising
fractured in two places, leaving a “floating”
segment of bone between the two breaks. AMPUTATIONS
These fractures usually occur in long bones such Can occur as a result of trauma or a surgical
as those in the legs. This type of bone fracture intervention
may take longer to heal or cause complications.
You must control bleeding and treat for shock.
9. Comminuted Fracture- A comminuted
fracture is one in which the bone is broken into Be aware of the victim’s emotional stress.
3 or more pieces. There are also bone
Emergency Medical Care
fragments present at the fracture site. These
types of bone fractures occur when there is a Perform a primary assessment.
high-impact trauma, such as an automobile
Stabilize the patient’s ABCs.
accident.
Perform a rapid scan or focus on a specific
10. Avulsion Fracture- An avulsion fracture
injury.
occurs when a fragment is pulled off the bone
by a tendon or ligament. These types of bone Follow standard precautions.
fractures are more common in children than
adults. Sometimes a child’s ligaments can pull Suspect internal bleeding.
hard enough to cause a growth plate to
fracture.
SPLINTING PELVIC BINDER
A splint is a flexible or rigid device that is used Used to splint the bony pelvis to reduce
to protect and maintain the position of an hemorrhage from bone ends, venous
injured extremity. disruption, and pain
Rigid Splints Meant to provide temporary stabilization
Made from firm material Should be light, made of soft material, easily
applied by one person, and should allow access
Applied to the sides, front, and/or back of an
to the abdomen, perineum, anus, and groin
injured extremity
HOW TO APPLY A SPLINT
Prevent motion at the injury site
1. Follow DRABC
Takes two EMTs to apply
2. Check for other injuries such as open, closed
Follow the steps in Skill Drill 29-3.
and complicated fractures
3. If there is an open wound; apply gauze,
Formable Splints pressure and cover to control bleeding
Most commonly used formable splint is the 4. Ask the casualty to refrain from moving
precontoured, inflatable, clear plastic air splint
5. Handle casualty with care
Comfortable
6. Immobilise fracture with broad bandages to
Provides uniform contact prevent movement at the joints above and
below the fracture by: 1. Supporting the limb –
Applies firm pressure to a bleeding wound gently wrap bandages around the natural
Used to stabilize injuries below the elbow or hollows of the limb.2. Position a padded splint
knee along the injured limb 3. Place padding between
the splint and the natural formation of the limb
Traction Splints and secure firmly with bandages 4. If a leg
Used primarily to secure fractures of the shaft fracture, also immobilise foot and ankle
of the femur Check that bandages are not too tight or too
Several different types: loose every 15 minutes (too tight – the skin is
bulging outside the bandage, too loose – you
Hare splint Sager splint can get multiple fingers underneath the
bandage)
Reel splint Kendrick splint
7. Watch for signs of loss of circulation to foot
(if leg injury) or hand (if arm injury)
8. Observe the casualty closely
9. Seek medical assistance
You might also like
- Head InjuryDocument7 pagesHead InjuryRoshan Ghimire100% (1)
- Neck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNeck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Injury: Presented By: George Michael S. MalunesDocument18 pagesHead Trauma Injury: Presented By: George Michael S. Malunesneil0229No ratings yet
- Head Injury - ConcussionDocument1 pageHead Injury - ConcussionSamarth VaijanapurkarNo ratings yet
- Injury of Brain and SkullDocument50 pagesInjury of Brain and SkullTselmeg TselmegNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Trauma: AKA Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument15 pagesCerebral Trauma: AKA Traumatic Brain InjuryAlison ThorpeNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument7 pagesHead InjurySariiNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument66 pagesHead Injurynur muizzah afifah hussinNo ratings yet
- Self-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IIDocument21 pagesSelf-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IICharmae NaveaNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument54 pagesHead TraumaAbishek PrinceNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument2 pagesHead TraumaAa AaNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument3 pagesHead InjuriesArlene Grace Fortus PalmaNo ratings yet
- PE-TBI Brain InjuryDocument7 pagesPE-TBI Brain InjuryjordaoNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Lesions: Head Injuries: Delano, Alexandra Julianne Duran, Fatima MedrizaDocument31 pagesTraumatic Lesions: Head Injuries: Delano, Alexandra Julianne Duran, Fatima MedrizaFatima Medriza Duran100% (1)
- CCN Lecture Altered PerceptionDocument4 pagesCCN Lecture Altered PerceptionPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- (Klasifikasi) Mild HeadDocument44 pages(Klasifikasi) Mild HeadAfdalNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury1439scribdDocument3 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury1439scribdAllen DavisNo ratings yet
- Head Injury....Document47 pagesHead Injury....nikowareNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Lesions: Head Injuries: Delano, Alexandra Julianne Duran, Fatima MedrizaDocument31 pagesTraumatic Lesions: Head Injuries: Delano, Alexandra Julianne Duran, Fatima MedrizaFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries Injuries To The ScalpDocument6 pagesHead Injuries Injuries To The Scalpashythegreat93No ratings yet
- Brain Swelling Hemorrhaging of The Brain Overlooked or Misdiagnosed Rollover AccidentsDocument6 pagesBrain Swelling Hemorrhaging of The Brain Overlooked or Misdiagnosed Rollover AccidentsNICOLE RAFAEL TACDERASNo ratings yet
- First Aid:: Head and Spine InjuryDocument14 pagesFirst Aid:: Head and Spine InjuryJulia FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Concussion 19Document6 pagesConcussion 19Marcelo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Introduccion: Traumatismo de CráneoDocument18 pagesIntroduccion: Traumatismo de CráneoSamsung j2No ratings yet
- Head Injury Classification: Head Injuries/Head Trauma 1 - Closed (Blunt) Brain InjuryDocument4 pagesHead Injury Classification: Head Injuries/Head Trauma 1 - Closed (Blunt) Brain InjuryClarisse Biagtan CerameNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument5 pagesHead InjuryJames Jayson Liberto100% (3)
- Basic Life Support 2Document12 pagesBasic Life Support 2Fritz CanawayNo ratings yet
- 3 NeurologicalDocument57 pages3 NeurologicalrakeshghonasagiNo ratings yet
- Head N Spinal InjuryDocument34 pagesHead N Spinal InjuryGG WPNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument55 pagesHead InjuryDakaNo ratings yet
- How The Brain Recovers2Document94 pagesHow The Brain Recovers2Anonymous x75qV3lGNo ratings yet
- Legal Med. Report-QueenDocument61 pagesLegal Med. Report-QueenQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- How Bad Your Balance Problem Is Depends On Many FactorsDocument8 pagesHow Bad Your Balance Problem Is Depends On Many FactorsRobert Ross DulayNo ratings yet
- Head Injury - HandoutDocument10 pagesHead Injury - HandoutMohd Hisyamuddin SaharudinNo ratings yet
- Head INJURIES SruthyDocument27 pagesHead INJURIES SruthySreenath SukumaranNo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument12 pagesNeuroAlishaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Head Injury: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument23 pagesSeminar On Head Injury: Submitted To: Submitted byMr. FakeacNo ratings yet
- RU - Trauma and Emergency CareDocument32 pagesRU - Trauma and Emergency CareryanNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument7 pagesHead Injuriesapi-3822433100% (1)
- Amity Institute of Occupational TherapyDocument45 pagesAmity Institute of Occupational Therapyamandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument63 pagesHead Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- DEFTACTDocument10 pagesDEFTACTGermaine RojasNo ratings yet
- Module 56 - Group 4Document27 pagesModule 56 - Group 4Katherine May F. LloritoNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument31 pagesHead InjuryZawawi Ibnu Rosyid0% (1)
- Trauma Head InjuriesDocument13 pagesTrauma Head InjuriesHtet HtinNo ratings yet
- Seminar 5 MG IIDocument6 pagesSeminar 5 MG IIrussianangelNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries - Engie LeeDocument20 pagesHead Injuries - Engie LeeSheena Grace CocamasNo ratings yet
- NCM118 Finals NotesDocument10 pagesNCM118 Finals NotesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Trauma Head InjuriesDocument13 pagesTrauma Head InjuriesRITA SOFIA PINTO LOURENÇONo ratings yet
- ETIOLOGY Head InjuryDocument6 pagesETIOLOGY Head InjuryCresty EstalillaNo ratings yet
- ETIOLOGY Head InjuryDocument6 pagesETIOLOGY Head InjuryCresty EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Deficits-Lecture 1 and 2Document33 pagesNeurologic Deficits-Lecture 1 and 2Israel AgrisNo ratings yet
- Brain Function PDFDocument8 pagesBrain Function PDFGenieyung Faranindia Sakanti Topan 10CNo ratings yet
- Seizures: Pharmaceutical Care 1 // 1D-PHDocument3 pagesSeizures: Pharmaceutical Care 1 // 1D-PHJeanneNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Assessing Head & NeckDocument9 pages2 - Assessing Head & NeckFrancine Julia MorilloNo ratings yet
- United Sataes Army FM 21-11-27 October 1988 - Part03Document44 pagesUnited Sataes Army FM 21-11-27 October 1988 - Part03Darryl RheaNo ratings yet
- 2 What Is Brain InjuryDocument4 pages2 What Is Brain Injuryaditya100% (1)
- WWW - Stroke.nih - Gov: Stroke Strikes Fast. You Should TooDocument4 pagesWWW - Stroke.nih - Gov: Stroke Strikes Fast. You Should Toosatyagraha84No ratings yet
- Ridge CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesRidge CharacteristicsKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- People Vs AsilanDocument2 pagesPeople Vs AsilanAnonymous IYfyCEe50% (2)
- Balindong Vs CADocument9 pagesBalindong Vs CAMarianne SerranoNo ratings yet
- ALTITUDEDocument2 pagesALTITUDEKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- Identifying ConstellationsDocument2 pagesIdentifying ConstellationsKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- BleedingDocument12 pagesBleedingbernard arcigaNo ratings yet
- Accident Incident Report Form - 0Document2 pagesAccident Incident Report Form - 0Francis Hans B. GauranoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10. Medico-Legal Aspect of WoundsDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 10. Medico-Legal Aspect of WoundsMay ChanNo ratings yet
- Swollen ScalpDocument2 pagesSwollen ScalpDaru KristiyonoNo ratings yet
- ContusionsDocument35 pagesContusionsSARVESH MAWALE100% (1)
- Midterm Long Quiz 1 CDI 2Document3 pagesMidterm Long Quiz 1 CDI 2Ronic SolmayorNo ratings yet
- First Aid: Benito, Ira Serrano, EllyzaDocument40 pagesFirst Aid: Benito, Ira Serrano, EllyzaEllyza SerranoNo ratings yet
- Medico-Legal Aspect of InjuryDocument25 pagesMedico-Legal Aspect of InjuryShahriar Shaon100% (1)
- 2023 HandbookDocument113 pages2023 HandbookRj PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Medical Writing A Police StatementDocument4 pagesMedical Writing A Police Statementkenc12No ratings yet
- Dr. Moez - @medicine - WayDocument82 pagesDr. Moez - @medicine - WayAdel AdelNo ratings yet
- Management of Sports InjuriesDocument35 pagesManagement of Sports InjuriesabdulazizmochammadNo ratings yet
- Medico-Legal Aspects of Physical InjuriesDocument9 pagesMedico-Legal Aspects of Physical InjuriesRhem Rick Corpuz100% (1)
- Tarea 2.: Ingles 5.1 Fernano Boluda Del PinoDocument2 pagesTarea 2.: Ingles 5.1 Fernano Boluda Del PinoFernando Boluda Del PinoNo ratings yet
- Angelmar F. Cordova, RN Jofred M. Martinez, Man, RNDocument27 pagesAngelmar F. Cordova, RN Jofred M. Martinez, Man, RNAngeline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Herbalist Class - GM BinderDocument6 pagesHerbalist Class - GM BinderAnthNo ratings yet
- PU Grading ChartDocument1 pagePU Grading ChartvanessapriscilliaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioNo ratings yet
- T2 Laboratories Explosion Damage AssessmentDocument43 pagesT2 Laboratories Explosion Damage AssessmentMPhamNo ratings yet
- Physical Abuse in ChildrenDocument113 pagesPhysical Abuse in ChildrenDan Matthew BuriasNo ratings yet
- TCM External and Internal Pathogenic Causes of DiseaseDocument9 pagesTCM External and Internal Pathogenic Causes of Diseasealbar ismuNo ratings yet
- Life Adv Wordlist Final Alphabetised Unit 6Document7 pagesLife Adv Wordlist Final Alphabetised Unit 6Calixthenx CalixthenxNo ratings yet
- CHANGES After Death (Part Two) 2011 GC - 2Document18 pagesCHANGES After Death (Part Two) 2011 GC - 2HassanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Physiology & Injuries in Sports 2022-23Document10 pagesUNIT 7 Physiology & Injuries in Sports 2022-23xxjksvddukebNo ratings yet
- Physical Education SbaDocument46 pagesPhysical Education SbaDaniel Dowding80% (5)
- FUNDAMENTALS OF TACTICAL COMBAT CASUALTY CARE For PPSCDocument80 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF TACTICAL COMBAT CASUALTY CARE For PPSColiver garcianoNo ratings yet
- Specialized Crime Investigation: With Legal MedicineDocument9 pagesSpecialized Crime Investigation: With Legal MedicineApple AsneNo ratings yet
- Medicolegal Aspects of Physical Injuries: Emil Josef B. Almazan MD Pcom MhcaDocument26 pagesMedicolegal Aspects of Physical Injuries: Emil Josef B. Almazan MD Pcom Mhcaxeileen08No ratings yet
- Refrat Forensic Asphyxia (DR - Wahyu)Document112 pagesRefrat Forensic Asphyxia (DR - Wahyu)Andre PrawiradinataNo ratings yet
- Manual - HALODocument42 pagesManual - HALOsanthigiNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingFrom EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)