Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formative Test I (Plus Feedback) NBSS 2020-2021 - Attempt Review
Uploaded by
Alif YusufOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formative Test I (Plus Feedback) NBSS 2020-2021 - Attempt Review
Uploaded by
Alif YusufCopyright:
Available Formats
Portal LiVE Unpad Kategori Kelas English (en)
Dashboard - My courses - Neurobehavior & Special Senses System_131001_genap - General - Formative Test I (plus Feedback) NBSS 2020-2021
Neurobehavior & Special Senses System 2020-2021 Genap
Neurobehavior & Special
Senses System_131001_g
enap
Participants Started on Friday, 9 April 2021, 10:50 PM Quiz navigation
Badges State Finished 1 2 3 4 5 6
Competencies
Completed on Saturday, 10 April 2021, 12:16 AM 7 8 9 10 11 12
Grades
Time taken 1 hour 26 mins 13 14 15 16 17 18
Course sections Marks 70.00/71.00
19 20 21 22 23 24
Grade 98.59 out of 100.00
25 26 27 28 29 30
Dashboard
31 32 33 34 35 36
Site home Question 1
37 38 39 40 41 42
Calendar Correct
43 44 45 46 47 48
Private files
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
49 50 51 52 53 54
My courses
Flag question
55 56 57 58 59 60
A 73 year-old patient with a 15-year history of Parkinsons Disease comes to your office with severe ataxia and a loss of facial
61 62 63 64 65 66
expression. The medication he has been on is no longer effective. You discuss the possibility of treating him with deep brain
stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus.What is the rationale behind this treatment?
67 68 69 70 71
A. Restoration of the output from the substantia nigra
Show one page at a time
B. Increased input to the caudate nucleus
C. Increased inhibition of the thalamus Finish review
D. Increased inhibitory output from the subthalamic nucleus
E. Restoration of tonic firing pattern from the subthalamic nucleus
LO 1: Explain the Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
LO 2: Explain the Contributions of the Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia to Overall Motor Control
LO 3: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 4: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: Restoration of tonic firing pattern from the subthalamic nucleus
Question 2
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient in the neurological ward has been suspected to have an extensive bilateral lesions of the amygdaloid nuclei. Which of
the following sign is the most probable to be found on examination?
A. Hypotonic paralysis in both lower limbs
B. Motor aphasia
C. Loss of proprioceptive sensation in all the four limbs
D. Difficulty in recognition of emotional facial expressions (especially of fear) of other people
E. Difficulty in naming objects presented to the left visual field
LO 1: Explain the Contributions of the Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia to Overall Motor Control
LO 2: Explain the Cerebral Cortex, Intellectual Functions of the Brain, Learning, and Memory
LO 3: Explain the Behavioral and Motivational Mechanisms of the Brain—The Limbic System and the Hypothalamus
The correct answer is: Difficulty in recognition of emotional facial expressions (especially of fear) of other people
Question 3
Incorrect
Mark 0.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A health worker is researching causes of hypertension. He is working on the autonomic nervous system. Which one of the
following five statements about the autonomic nervous system is correct?
A. An anticholinergic medication will give rise to bladder urgency
B. Pupillary dilatation is mediated by the parasympathetic system
C. Secretomotor nerves of the lacrimal gland course with the facial nerve
D. Vascular smooth muscle is innervated by parasympathetic adrenergic neurons
E. Secretomotor nerves of the lacrimal gland course with the facial nerve
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the Autonomic Nervous System
The correct answer is: Secretomotor nerves of the lacrimal gland course with the facial nerve
Question 4
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 21-year-old man has an acute earache. He tells you that he has been swimming and surfing the previous week. His ear is
discharging. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute otitis externa
B. Impacted wisdom tooth
C. Acute mastoiditis
D. Acute otitis media
E. Ear trauma
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Ear - External Ear - Middle Ear - Internal Ear
LO 2: Explain the Sense of Hearing
The correct answer is: Acute otitis externa
Question 5
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 55 year old man presents to your office complaining of vision difficulty. On examination he has been found to have a right
homonymous hemianopia.The lesion of damage is at:
A. Ig DRight lateral geniculate body
B. Left optic tract
C. Right optic radiation
D. Optic chiasma
E. Left optic nerve
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
The correct answer is: Left optic tract
Question 6
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
While playing hockey a boy falls and hits his head on the ice. X-rays reveal a linear fracture from just behind the ear toward the
foramen magnum and involving the jugular foramen.Which of the following might you most likely expect to find?
A. He will have some difficulty swallowing
B. There will be signs attributable to a hemorrhage of the middle meningeal artery
C. The patient has difficulty opening his right eye
D. The patient has lost control of lip movements
E. The patient will be unable to close his jaw properly
LO 1: Explain the basic anatomy of: - Nervous System - Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
LO 2: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve
(CN IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN
VI) - Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
The correct answer is: He will have some difficulty swallowing
Question 7
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
An agitated 24 year old man is brought to the Emergency Room in handcuffs by the police after he was found wandering along
the road in a confused state. The patient becomes mute and appears to be calm.What is the next most appropriate step in
managing this patient?
A. Take a history from the police
B. Remove the handcuffs to make the patient comfortable
C. Talk with the patient about his impulse control
D. Administer a sedative intramuscularly
E. Advise detention under the Mental Health Act
LO 1: Apply the Communication with patients, patients relative and community
LO 2: Apply the Doctor-Patient Communication
The correct answer is: Take a history from the police
Question 8
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Following a lumbar puncture, patients often experience headache. What is the most appropriate primary reason?
A. Irritation of the meningeal arteries
B. Accumulation of fluid in the subdural space
C. Stretching of the dura
D. Distension of the scalp vessels
E. Bleeding in the subarachnoid space
LO 1: Explain the basic anatomy of: - Nervous System - Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
LO 2: Explain the Histology of nerve tissue: neurons, glial cells, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system
The correct answer is: Stretching of the dura
Question 9
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
As a doctor in the Emergency Department, you see an otherwise fit 51 year old man who has a metal fragment embedded in his
left index finger. You plan to remove this under a digital nerve block using local anaesthetic, which prevents normal action
potential conduction. What ion traffic is mostly affected?
A. Potassium
B. Calcium
C. Sodium
D. Magnesium
E. Chloride
LO 1: Explain the Transport of Substances Through Cell Membranes
LO 2: Explain the Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
LO 3: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 4: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: Sodium
Question 10
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Neurons are supported by glial cells. Which ONE of the following cells plays an important role in maintaining the integrity of the
blood brain barrier?
A. Microglia
B. Oligodendrocytes
C. Schwann cells
D. Golgi cells
E. Protoplasmic astrocytes
LO 1: Explain the Histology of nerve tissue: neurons, glial cells, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system
The correct answer is: Protoplasmic astrocytes
Question 11
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 70-year-old woman is brought by her family to the Emergency Room with chief complain difficulty in breathing and feel to
unconsciousness. After fast but thorough examination she needs intubation. What should you do as a physician?
A. Performed intubation immediately
B. Consider refusing the patient because of her unrealistic condition
C. Ask the nurse to do the intubation
D. Refer her to another competence physician
E. Explain the procedure and result to the patients family, but the decision is them
LO 1: Explain about Life Support Technology in the context of End of Life
The correct answer is: Explain the procedure and result to the patients family, but the decision is them
Question 12
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient is receiving local anaesthetic for a root canal treatment in his upper molar. The dentist injects novocaine. This stops
pain by blocking nerve conduction. What is the most appropriate underlying mechanism?
A. This is an all-or-none response for the generator potential
B. A blockade of voltage-gated Na+ channels blocks action potentials
C. Decrease of the signal intensity will decrease the action potential
D. G-protein-coupled mechanisms indirectly influence ion channels
E. It causes the membrane to become refractory
LO 1: Explain the Transport of Substances Through Cell Membranes
LO 2: Explain the Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
LO 3: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 4: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: A blockade of voltage-gated Na+ channels blocks action potentials
Question 13
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 4 year old child has suffered a global neurodevelopmental insult from viral encephalitis in the neonatal period. You are asked
to assess his neurodevelopmental age from the following observations:He drinks from a cup but is unable to wash his hands.He
scribbles but cannot draw a line.He has 3 words.He walks but cannot run.What is the correct neurodevelopmental age?
A. 12 - 18 months
B. 18 - 24 months
C. 24 - 30 months
D. 30 - 36 months
E. 6 - 12 months
LO 1: Explain the Development of nerve tissue
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: 12 - 18 months
Question 14
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Prevention of nutrition-related illness in the population is important to maintain good quality of health. Which of the following is
most correct example of primary prevention?
A. Legislation and enforcement to ban or control the use of hazardous products
B. Oral vaccination against infectious diseases
C. Weight loss programs offered through community agencies
D. Dietary Guidelines
E. Nutritional services for underweight children
LO 1: Explain the Community Nutrition
The correct answer is: Dietary Guidelines
Question 15
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 21-year-old student is admitted to A and E after falling down a flight of stairs at a nightclub. He localises pain, opens his eyes
to pain and utters incomprehensible sounds. When you telephone the neurosurgical registrar he asks you to describe his
Glasgow Coma Scale. Which of the following is correct?
A. Eyes 3, Motor 4, Verbal 3; Total 10/15
B. Eyes 4, Motor 5, Verbal 2; Total 11/15
C. Eyes 1, Motor 2, Verbal 2; Total 5/15
D. Eyes 2, Motor 5, Verbal 2; Total 9/15
E. Eyes 1, Motor 2, Verbal 2; Total 5/15
LO 1: Explain the The Eye: Central Neurophysiology of Vision
LO 2: Explain the Cortical and Brain Stem Control of Motor Function
The correct answer is: Eyes 2, Motor 5, Verbal 2; Total 9/15
Question 16
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Skin has several sensory receptors. Which of the followings is most likely correct?
A. Meissners corpuscles: found in superficial skin layers, slowly adapting
B. Merkels discs: deep in the skin, rapidly adapting
C. Ruffini ending: slowly adapting
D. Free nerve ending: rapidly adaptive and found deep in the skin
E. Pacinian corpuscles: have big receptive fields, slowly adapting
LO 1: Explain the Histology of nerve tissue: neurons, glial cells, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system
LO 2: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 3: Explain the Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
The correct answer is: Ruffini ending: slowly adapting
Question 17
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
The parents of a 2 month old baby girl raise concern about her vision in that she doesnt seem to be able to fixate. Examination
reveals reduced red reflex bilaterally together with some haziness noted over the lens region.What could be the cause of her
problem?
A. Normal variation
B. Squint
C. Hypermetropia
D. Delayed visual maturation
E. Congenital rubella
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Eye - Orbits, Eyelids and Lacrimal Apparatus - Eyeball - Nerves of Orbit - Vasculature of Orbit - Surface
Anatomy of Eye and Lacrimal Apparatus
LO 2: Explain the Histology and development of eye and ear
LO 3: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
LO 4: Explain the The Eye: Central Neurophysiology of Vision
The correct answer is: Congenital rubella
Question 18
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 35 year old man presents with fever, severe headache, drowsiness and a stiff neck. He has also developed a faint rash on his
arms and trunk.A lumbar puncture is performed and shows a large number of the cells shown below.Which of the following
tissue is most likely to be injured?
A. Cerebrum
B. Spinal cord)
C. Nerve
D. Muscle
E. Meninges
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
The correct answer is: Meninges
Question 19
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 10-year-old boy is diagnosed as Acute poliomyelitis.Which following structure of nervous system is most likely damaged?
A. Anterior horn cells at the spinal cord
B. Frontal lobe
C. Posterior column of the spinal cord
D. Cerebral motor cortex
E. White matter of the spinal cord
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Motor Functions of the Spinal Cord; the Cord Reflexes
LO 3: Explain the disorders of Peripheral Nerves and Muscles - Disorders of Peripheral Nerves - Disorders Associated With Peripheral Nerve
Injury - Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction: - Disorders of Skeletal Muscle - Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
LO 4: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Anterior horn cells at the spinal cord
Question 20
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 30-year-old man beliefs that he has headache, photophobia and nausea. What is the correct about the likelihood of his
condition?
A. Perceived benefit
B. Perceived susceptibility
C. Perceived severity
D. Perceived barriers
E. Perceived threat
LO 1: Explain the Theories of health behaviour and health promotion
The correct answer is: Perceived susceptibility
Question 21
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 55-year-old woman, came with chief complain hyper pigmented macula and aging at her face. She wants her face become
white, smooth, and supple without wrinkle and looks younger like a 25-year-old woman, in a month.What should you do as a
physician?
A. Explain the procedure and result to the patient, but the decision is in her hand
B. Refer her to another competence physician
C. Refuse the patient because of her big motivation
D. Consider to refuse the patient because of her unrealistic expectation
E. Performed chemical peeling twice weekly for a month
LO 1: Explain the Medical Ethics: Medical Code of Ethics, Confidentiality, Treatment Refusal and Professional Standard
The correct answer is: Explain the procedure and result to the patient, but the decision is in her hand
Question 22
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
There are many communication methods and media that are used in communicating health messages in community. you are
to give health education to high school students about Sexuality. Which method is most appropriate?
A. Messages in social media
B. School Radio
C. Displays, such as Posters, Wall Magazine, etc
D. Talkshow
E. Small Groups Talk
LO 1: Apply the Communication with patients, patients relative and community
The correct answer is: Small Groups Talk
Question 23
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 60-year-old healthy man is being treated for insomnia with a benzodiazepine (chlordiazepoxide). Now he comes to you
complaining of daytime sleepiness. What is the MOST likely explanation for this recent problem?
A. The development of tolerance
B. A decrease in hepatic blood flow
C. His phase II reactions are suppressed due to kidney failure
D. The chlordiazepoxide is being metabolized to active compounds
E. He has liver disease and his microsomal oxidase system is not functioning well
LO 1: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: The chlordiazepoxide is being metabolized to active compounds
Question 24
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A farm worker inhales a pesticide which blocks acetylcholinesterase in the neuromuscular junction. He presents with
breathlessness. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause of his difficulty in breathing?
A. Decreased amount of acetylcholine in the smooth muscle
B. Reduction in acetylcholine reuptake
C. Rapid breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse
D. Lack of acetylcholine production at the synapse
E. Blockade of the acetylcholine receptors by acetylcholine
LO 1: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 2: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 3: Explain the Autonomic Drugs - Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology - Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs -
Cholinoceptor-Blocking Drugs - Adrenoceptor Agonists & Sympathomimetic Drugs - Adrenoceptor Antagonist Drugs
The correct answer is: Blockade of the acetylcholine receptors by acetylcholine
Question 25
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
In a physiology practical class, when a steel rod was held against an area of skin with a constant force, students noticed that
the firing rate in the related cutaneous sensory nerve decreased. What property of the sensory system most likely indicates this
observation?
A. Adaptation of receptors
B. Recruitment of receptors of a different modality
C. Change in receptive fields
D. Adaptation of the central sensory mechanisms
E. Increasing sensitivity to the stimulus
LO 1: Explain the Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
LO 2: Explain the Somatic Sensations: General Organization, the Tactile and Position Senses
LO 3: Explain the Somatic Sensations: Pain, Headache, and Thermal Sensations
The correct answer is: Adaptation of receptors
Question 26
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You examine an 8 year olds hearing with a tuning fork. She consistently hears the tuning fork applied to her mastoids louder
than when held approximate to both meati. However when the tuning fork is applied to her forehead she hears it louder on the
left. What is the most correct intepreation of the examination?
A. Bilateral sensineural loss greater in R ear
B. Bilateral conductive loss greater on the left
C. Bilateral sensineural loss and R conductive loss
D. Unilateral sensineural and conductive loss
E. Right sensineural loss
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Ear - External Ear - Middle Ear - Internal Ear
LO 2: Explain the Sense of Hearing
The correct answer is: Bilateral conductive loss greater on the left
Question 27
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A right-handed 65-year-woman suddenly feels weakness of her right arm and hand and subsequently finds that she cannot
move them voluntarily. During the examination she has slow and hesitant speech. She can move her legs normally, her vision is
normal, her finger-to-nose test is normal, and there is no sign of disequilibrium.Which of the following arteries is most likely to
have been affected?
A. Middle cerebral artery
B. Anterior cerebral artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Superior cerebellar artery
E. Anterior choroidal artery
LO 1: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
LO 2: Explain the basic anatomy of: - Nervous System - Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
The correct answer is: Middle cerebral artery
Question 28
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Vulnerable subject needs to be reconsidered when they are faced with decision of their health intervention. Which of the
following that is not included ones?
A. poor people
B. children
C. mentally illness
D. elderly people
E. pregnant women
LO 1: Explain about Decision making in vulnerable group
The correct answer is: elderly people
Question 29
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You are a casualty officer. A 43-year-old man is brought in by his wife after a turn at home. He had complained of a nasty taste
and then felt very strange. His wife says he was not answering her and seemed absent and then started to smack his lips and
twitch. The patient cannot remember any of this. He appears confused some two hours after the episode.What type of seizure is
this?
A. Tonic clonic Seizure
B. Myoclonic seizure
C. Myoclonic seizure
D. Absence seizure
E. Complex partial seizure
LO 1: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Complex partial seizure
Question 30
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
According the scheme above, which of the major abnormalities will appear on neurological examination if there is a lesion in
the location indicated by the star?
A. Increase muscle tone and reflex activity for that spinal segment
B. Loss of muscle tone and reflexes for that spinal segment
C. Loss of pain and temperature sensation for that spinal segment
D. Loss of reflexes and tactile sensation for that spinal segment
E. Loss of tactile sensation for that spinal segment
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 3: Explain the Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
LO 4: Explain the Somatic Sensations: General Organization, the Tactile and Position Senses
The correct answer is: Loss of muscle tone and reflexes for that spinal segment
Question 31
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
The benzodiazepines, effective antianxiety medications, are now thought to act by altering the action of which of the following
neurotransmitters?
A. Dopamine
B. Noradrenaline
C. Histamine
D. GABA (gamma amino butyric acid)
E. Substance p
LO 1: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 2: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 3: Explain the disorders of Peripheral Nerves and Muscles - Disorders of Peripheral Nerves - Disorders Associated With Peripheral Nerve
Injury - Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction: - Disorders of Skeletal Muscle - Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
LO 4: Explain the Movement Disorders - Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium - Antidepressant Agents - Opioid Agonists & Antagonists - Drugs of
Abuse
The correct answer is: GABA (gamma amino butyric acid)
Question 32
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 70 year old woman presents with pain in the upper arm after a fall. On examination she has pain, swelling and tenderness
over the distal humerus. In addition she is unable to actively extend her fingers, thumb or wrist. X-rays reveal an oblique
minimally displaced fracture at the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the humerus. What is the most likely site of
neurological injury?
A. T1 nerve root
B. Median nerve
C. Brachial plexus
D. Ulnar nerve
E. Radial nerve
LO 1: Explain the Cortical and Brain Stem Control of Motor Function
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Peripheral Nerves and Muscles - Disorders of Peripheral Nerves - Disorders Associated With Peripheral Nerve
Injury - Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction: - Disorders of Skeletal Muscle - Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
The correct answer is: Radial nerve
Question 33
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 72-year-old woman is referred with progressive memory loss and disturbed night time behaviour. After psychometric
assessment and brain imaging she is diagnosed with Alzheimers disease. What class of drugs would improve the
neurotransmitter deficit?
A. Monoamine-oxidase inhibitors
B. Tricyclic antidepressants
C. Anticholinesterases
D. Antihistamines
E. Anticholinergics
LO 1: Explain the Autonomic Drugs - Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology - Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs -
Cholinoceptor-Blocking Drugs - Adrenoceptor Agonists & Sympathomimetic Drugs - Adrenoceptor Antagonist Drugs
The correct answer is: Anticholinesterases
Question 34
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A child with Down syndrome is referred to a stimulation centre for therapy. The mother is concerned that at the age of three
years the little boy is not yet speaking in sentences. He is running and is starting to undress himself. She would like to know
whether he will develop in the same way as his brother, who does not have the syndrome, if he attends the centre.How will the
little boy develop if he attends the stimulation centre?
A. The main benefit of the centre is that the little boys parents will be relieved of the burden of caring for the child
B. Children with Down syndrome do not live for very long therefore there is no benefit in spending time and money on
stimulating the child
C. The stimulation at the centre will be of no benefit to the child and the mother is wasting her money
D. The extra stimulation will ensure that he develops normally like his sibling who does not have Down syndrome
E. The stimulation will assist the little boy in reaching his own potential but he is unlikely to develop at the same rate as
his sibling
LO 1: Explain the Development of nerve tissue
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Peripheral Nerves and Muscles - Disorders of Peripheral Nerves - Disorders Associated With Peripheral Nerve
Injury - Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction: - Disorders of Skeletal Muscle - Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
LO 3: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: The stimulation will assist the little boy in reaching his own potential but he is unlikely to develop at the same rate as
his sibling
Question 35
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You found out that most of your study group member consumed unhealthy amount of instant noodle. The reason: they did not
like their own cooking. Being an avid cook, you decided to provide free training sessions for your friends on how to prepare
healthy food in simple ways. Within a month, at least some of your friends were more confident to prepare their own healthy
meals. What you have just improved:
A. Self-efficacy
B. Incentive motivation
C. Decisional balance
D. Facilitation
E. Outcome expectation
LO 1: Explain the Principle and concept health promotion
The correct answer is: Self-efficacy
Question 36
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You follow up on a patient who suffered spinal cord trauma 3 months ago. He presents with spastic paralysis of his legs. Which
of the following mechanism is the most correct?
A. Secondary trauma to ascending pathways
B. Axon degeneration of the Alpha motoneuron
C. Demyelination of the peripheral nerves
D. Build-up of lactic acid in the muscle tissue
E. Demyelination of the peripheral nerves
LO 1: Explain the Motor Functions of the Spinal Cord; the Cord Reflexes
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Build-up of lactic acid in the muscle tissue
Question 37
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 18 years old woman came to Hospital to get a treatment. She wanted to get her nose higher because she said that she often
felt difficult to breath. After more anamnesis and physical examination as well as supporting examination, you did not find any
anatomical nor physiological dysfunction. The patient keep said that she really wants to do the measure.Should physicians
perform interventions on this patient?
A. Physician only responsible for proposing a method to achieve the patients goal
B. The medical profession is going to compromised if the measure is not done
C. Because it is to prevent stigmatization, it is compatible with the medical ethic to do such measure
D. The physician should do the measures since the patient have medical indication
E. The physician should avoid the risks as much as he can
LO 1: Apply the Doctor-Patient Communication
The correct answer is: Physician only responsible for proposing a method to achieve the patients goal
Question 38
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
In testing pupillary function, light is shone into the LEFT eye and only the right pupil constricts.This indicates dysfunction of which
cranial nerve?
A. Right optic (cranial nerve II)
B. Left optic (cranial nerve II)
C. Right oculomotor (cranial nerve III)
D. Sympathetic nervous system (Horners syndrome)
E. Left oculomotor (cranial nerve III)
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
The correct answer is: Right oculomotor (cranial nerve III)
Question 39
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
One of health education within communities is making a Health Campaign. What is the most correct thing should be
considered when organizing one?
A. Getting leader involved
B. Campaign can be planned to promote knowledge and skills of particular health issue.
C. Campaign should have as many as health issues possible in order to gain interest of the community
D. Campaign is a long term activities so we need to plan carefully
E. The campaign should have short and catchy theme
LO 1: Explain Health education with communities
The correct answer is: The campaign should have short and catchy theme
Question 40
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient has the following signs and symptoms: Parkinsonlike tremor; dermatitis and slight jaundice; mild hypertension with
tachycardia; oculogyric crisis. Which of the following drugs most likely produced the syndrome?
A. A monoamine oxidase inhibitor
B. Reserpine
C. Guanethidine
D. Mephenesin
E. Chlorpromazine
LO 1: Explain the Movement Disorders - Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium - Antidepressant Agents - Opioid Agonists & Antagonists - Drugs of
Abuse
The correct answer is: Chlorpromazine
Question 41
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
The ophthalmologist diagnoes Mrs. HO that she suffered from diabetic retinopathy and advised her to undergo surgery. Which
of the followings is the origin of the altered structure?
A. Optic vesicle
B. Otic vesicle
C. Mesenchyme cells
D. Lens vesicle
E. Surface ectoderm
LO 1: Explain the Histology and development of eye and ear
The correct answer is: Optic vesicle
Question 42
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Ozone depletion as the result of increased CFC from industries or technology devices such as refrigerator and air conditioner
potentially causes the following health problems:
A. Malnutrition
B. Respiratory diseases
C. Skin cancer
D. Skin burn
E. Degenerative diseases
LO 1: Explain the Environmental Health: Air and Noise Pollution
The correct answer is: Skin cancer
Question 43
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 72 year old man trips over an uneven pavement and strikes his forehead on the ground. He states that his arms were
immediately too weak to push himself up off the ground. When brought in to the hospital he has grade 2 dorsiflexion of the
wrists, grade 2 weakness of elbow extension and no movement of the intrinsic hand muscles. He has a partial sensory level to
light touch and pinprick to C7. His biceps and supinator reflexes are normal but the triceps reflexes are absent. He has grade 4+
power in the lower limbs and brisk reflexes the morning after admission. He can weight bear, but only with assistance. Sphincter
control appears to be retained. What is the most likely site of neurological damage?
A. Medulla
B. Frontal lobe
C. Brachial plexus
D. Cervical nerve roots
E. Cervical cord
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Peripheral Nerves and Muscles - Disorders of Peripheral Nerves - Disorders Associated With Peripheral Nerve
Injury - Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction: - Disorders of Skeletal Muscle - Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
The correct answer is: Cervical cord
Question 44
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A subject is rotated clockwise in a swivel chair for one minute then suddenly stopped. Which directions of the fast phases of
nystagmic eye movements is the most correct?
A. Both clockwise
B. No change in eye movement
C. Clockwise and anticlockwise respectively
D. Both anticlockwise
E. Anticlockwise and clockwise respectively
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the Histology and development of eye and ear
LO 3: Explain the The Eye: Central Neurophysiology of Vision
The correct answer is: Clockwise and anticlockwise respectively
Question 45
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient presents with involuntary, continuous but irregular movements that go from side to side. He has a positive family
history of similar conditions.Which part of the CNS is most likely affected in this patient?
A. Primary motor cortex
B. Basal ganglia
C. Sensory cortex
D. Cerebellum
LO 1: Explain the Contributions of the Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia to Overall Motor Control
The correct answer is: Basal ganglia
Question 46
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 26 year old accountant visits his GP complaining of extreme fatigue and nightmares. On direct questioning, he admits to
abusing crystal meth (metamphetamine) over the past month, but now he is trying to quit. What is the most appropriate
mechanism of action in yielding the chief compliant?
A. Antagonism of NMDA-type glutamate receptors
B. Stimulation of GABA
C. Stimulation of the enzyme monoamine oxidase
D. Stimulation of presynaptic serotonin receptors
E. Increased release of monoaminergic neurotransmitters
LO 1: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 2: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 3: Explain the Autonomic Drugs - Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology - Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs -
Cholinoceptor-Blocking Drugs - Adrenoceptor Agonists & Sympathomimetic Drugs - Adrenoceptor Antagonist Drugs
The correct answer is: Increased release of monoaminergic neurotransmitters
Question 47
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Dana had implicit (non-declarative) memory loss. Which ONE of the following is TRUE regarding Dana?
A. She forgot the details of the wedding of her friend which she attended last summer
B. She always had difficulty in remembering geographical facts
C. She had difficulty in learning tasks with motor skills
D. She most probably had a lesion in the amygdala
E. Dana forgot her own name
LO 1: Explain the Cortical and Brain Stem Control of Motor Function
LO 2: Explain the Contributions of the Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia to Overall Motor Control
LO 3: Explain the Cerebral Cortex, Intellectual Functions of the Brain, Learning, and Memory
The correct answer is: She had difficulty in learning tasks with motor skills
Question 48
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
One of the challanges when organize health education in community is to obtain the participation of every members, even in
small groups. Which one of the statement below is NOT the way to encourage participation of community member in
community project?
A. Give explanation about how important their job to the success of whole project
B. Keep people informed about the activities being planned
C. Encourage them to give suggestions
D. Pick national holiday for meeting time
E. Set out specific tasks and jobs for everyone
LO 1: Explain Health education with groups
The correct answer is: Pick national holiday for meeting time
Question 49
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A seven year-old, unimmunized boy was brought to Emergency with history of fever, loss of weight and vomiting for the last two
weeks. He lives in a two bedroom house along with his grandfather, who had a history of chronic cough. On examination the
child had neck stiffness and was constantly fitting. A lumbar puncture was done on this child after excluding signs of raised
intracranial pressure.Which of the following findings is expected to be seen in his cerebrospinal fluid?
A. A low protein count
B. Increased number of polymorphs
C. Numerous red blood cells
D. A high sugar count
E. A low sugar count
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
The correct answer is: A low sugar count
Question 50
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient presents with loss of pain and temperature sensation in both hands, weakness and wasting of the small muscles of
the left hand, loss of pain and temperature sensibility in the right leg and a spastic paralysis of the left leg.Where is the lesion
most likely located?
A. Right internal capsule involving the thalamus
B. Right cerebral cortex involving the pre- and post-central gyri
C. Left half of the cord at both lower cervical and upper lumbar levels
D. Ventral lateral part of the right half of the medulla
E. Left half of the lower cervical and upper thoracic spinal cord
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Somatic Sensations: General Organization, the Tactile and Position Senses
The correct answer is: Left half of the lower cervical and upper thoracic spinal cord
Question 51
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 50-year-old man felt tingling and mild pain in his left leg. Four weeks later, the symptoms extended to the lower left quadrant
of the abdomen. Pain sensation on the right side was normal.Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
A. Stenosis of the intervertebral foramina
B. Compression of the spinal cord by tumor
C. Demyelination of peripheral nerves
D. Herniation of intervertebral discs
E. Viral infection of the spinal ganglia
LO 1: Explain the basic anatomy of: - Nervous System - Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
LO 2: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 3: Explain the Somatic Sensations: Pain, Headache, and Thermal Sensations
LO 4: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Compression of the spinal cord by tumor
Question 52
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
An 8-year-old child presents with complete left facial palsy and complete failure of abduction of the left eye.What is the most
likely anatomical site of the lesion?
A. Thalamus
B. Brain stem
C. Temporal lobe
D. Cerebellum
E. Parietal lobe
LO 1: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
LO 2: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve
(CN IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN
VI) - Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
The correct answer is: Brain stem
Question 53
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Lack of knowledge people in the community about the danger of COVID-19 cases among villagers can cause spreading.Which
of the following sentence is the most correct concept an ecological perspectives related to behaviour theories that educators
use in COVID-19 case.
A. Interpersonal capacity
B. Public policy
C. Community factors
D. Interpersonal support
E. Institutional factors
LO 1: Explain Health education with individuals
The correct answer is: Interpersonal capacity
Question 54
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are used to treat Parkinsons disease in which there is a loss of dopaminergic neurons
from the substantia nigra in the brain. Which mechanism of action is the most appropriate to be used?
A. Block breakdown of dopamine
B. Promote dopamine synthesis
C. Promote re-uptake of dopamine
D. Block autoreceptors for feedback regulation on the terminal
E. Block autoreceptors for feedback regulation on the terminal
LO 1: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 2: Explain the Contributions of the Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia to Overall Motor Control
LO 3: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 4: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: Block breakdown of dopamine
Question 55
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You are on duty in the Emergency Department and are called to see a woman of 31 who has been brought in having developed
a very severe headache whilst shopping 2 hours earlier, saying, I felt I had been hit by a hammer. A witness to the episode said
she collapsed to the ground at the time and was unconscious for about a minute. She vomited shortly after the episode, and
the headache is still severe though slightly easier. She is normally on no treatment and has no relevant medical history. On
examination she is drowsy, though responds to commands, and is orientated in time and place. Her blood pressure is 165/95
mmHg and heart rate 55/min. There are no focal neurological abnormalities. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage
B. Extradural haematoma
C. Meningitis
D. Cerebral artery thrombosis
E. Migraine
LO 1: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
LO 2: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage
Question 56
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A one year old girl is diagnosed as having congenital deafness. This abnormality may be caused by abnormal development of
the tympanic cavity. The development of the ear begins with the development of which one of these parts?
A. Auricle
B. Otocyst
C. Meatal plug
D. Utricle
E. Mesoderm layer
LO 1: Explain the Histology and development of eye and ear
The correct answer is: Otocyst
Question 57
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A fit 60 year old man develops shingles in the distribution of the right T8 dermatome. Four weeks later he has persistent severe
dermatomal pain disrupting his daytime activities despite regular paracetamol and codeine tablets. Amitriptyline is added to
his therapy.What is the most important mechanism of pain relief by this agent?
A. Relief of associated depression
B. Promotion of normal sleep
C. Peripheral anticholinergic activity
D. Stimulation of afferent C fibres
E. Enhancement of descending spinal inhibitory nerve activity
LO 1: Explain the Movement Disorders - Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium - Antidepressant Agents - Opioid Agonists & Antagonists - Drugs of
Abuse
The correct answer is: Enhancement of descending spinal inhibitory nerve activity
Question 58
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 63-year-old man complains of burning numbness in his feet and weakness of his legs. Examination shows reduction of the
tendon reflexes and superficial sensation in the legs. The muscles are weak and tender.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Peripheral neuropathy.
B. Hypokalemia.
C. Polymyositis
D. Multiple sclerosis.
E. Lumbar disc prolapse.
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
LO 3: Explain the Somatic Sensations: General Organization, the Tactile and Position Senses
LO 4: Explain the Somatic Sensations: Pain, Headache, and Thermal Sensations
The correct answer is: Peripheral neuropathy.
Question 59
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
You are a general practitioner seeing a 65 year old man who had recently been to see his optician for a routine eye check
where he was found to have intraocular pressures of 33 and 35 mm Hg (Normal value: 11-21 mmHg). He was started on
treatment and has now come to see you for a repeat prescription. You referred him to hospital for further management, and
after an outpatient consultation the diagnosis of chronic glaucoma was confirmed.What is the most appropriate mechanism
for the disease development ?
A. Excessive production of aqueous humour
B. Loss of inhibition to the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye
C. Development of post vitreous attachment
D. Micro-haemorrhages in the vitreous humour
E. Blocked drainage of aqueous humour
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Eye - Orbits, Eyelids and Lacrimal Apparatus - Eyeball - Nerves of Orbit - Vasculature of Orbit - Surface
Anatomy of Eye and Lacrimal Apparatus
LO 2: Explain the Histology and development of eye and ear
LO 3: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
LO 4: Explain the The Eye: Central Neurophysiology of Vision
The correct answer is: Blocked drainage of aqueous humour
Question 60
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A child with having nightmare as a chief complaint was referred to the sleep laboratory and was diagnosed to have a sleep
disturbance. Which of the following statements is most correct appear in anamnesis?
A. Her condition is very common in young children
B. Her sleep disturbance occurred mostly during the first two hours of sleep
C. Her nightmares usually happened during REM sleep
D. She could not be awakened easily from her nightmare attack, and she remembered nothing afterwards
E. Her sleep disturbance occurred mostly during sleep stage II
LO 1: Explain the States of Brain Activity—Sleep, Brain Waves, Epilepsy, Psychoses, and Dementia
The correct answer is: Her nightmares usually happened during REM sleep
Question 61
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Mother takes her child to Primary Health Centre for BCG immunization. Which of the following statement is the most correct
example for type of health related behaviour:
A. Illness behaviour
B. Preventive health behavior
C. Health behavior
D. Bad behavior
E. Sick role behavior
LO 1: Explain the Concept of behaviour and Determinant of Health
The correct answer is: Preventive health behavior
Question 62
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Which of the following conditions requires the most enabling factor in the case to prevent COVID-19 spread?
A. Disinfectants fluid not available in the every village
B. Lack of information from village officer about reporting systems related to sudden death of the poultry
C. Many poultries died during rainy season is normal for community
D. People`s believe that consume the sick poultry is safe
E. People remove the used mask to the river
LO 1: Explain the Prevention of diseases
The correct answer is: Disinfectants fluid not available in the every village
Question 63
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 72-year-old woman has experienced progressive memory problems for several years. For the past year, she has gotten lost
while walking around her own neighborhood and has been unable to find the bathroom in her own house or recognize family
members. What would be the most likely neuropathology findings?
A. Oligodendroglial cytoplasmic inclusion
B. Numerous neocortical senile plaques.
C. Atrophy and gliosis of the caudate nuclei.
D. Neocortical neuronal Pick bodies.
E. Many Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra.
LO 1: Explain the Cranial Meninges - Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces Explain the anatomy of the Brain - Parts of
Brain Ventricular System of Brain Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
LO 2: Explain the Cerebral Cortex, Intellectual Functions of the Brain, Learning, and Memory
LO 3: Explain the disorders of Central Nervous System - Edema, Herniation, and Hydrocephalus - Cerebrovascular Diseases - Central Nervous
System Trauma Traumatic Parenchymal Injuries Traumatic Vascular Injury - Congenital Malformations and Perinatal Brain Injury - Infections
of the Nervous System Epidural and Subdural Infections Meningitis - Diseases of Myelin - Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer Disease -
Tumors - Genetic Metabolic Diseases Acquired Metabolic and Toxic Disturbances
The correct answer is: Numerous neocortical senile plaques.
Question 64
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
In testing pupillary function, light is shone into the LEFT eye and both left and right pupils constrict. As the light is swung to the
RIGHT eye and shone into the RIGHT eye, both pupils dilate and remain dilated (swinging flashlight test). The pupils again
constrict when the light is swung over to the LEFT eye.Which cranial nerves is most likely altered?
A. Right oculomotor (cranial nerve III)
B. Right optic (cranial nerve II)
C. Sympathetic nervous system (Horners syndrome)
D. Left oculomotor (cranial nerve III)
E. Left optic (cranial nerve II)
LO 1: Explain the anatomy of the Cranial Nerves - Olfactory Nerve (CN I) - Optic Nerve (CN II) - Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) - Trochlear Nerve (CN
IV) - Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) - Maxillary Nerve (CN V2) - Mandibular Nerve (CN V3) - Abducent Nerve (CN VI) -
Facial Nerve (CN VII) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic (General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) -
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) Somatic (Branchial) Motor Visceral (Parasympathetic) Motor Somatic
(General) Sensory Special Sensory (Taste) Visceral Sensory - Vagus Nerve (CN X) - Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) - Hypoglossal Nerve (CN
XII)
LO 2: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
The correct answer is: Right optic (cranial nerve II)
Question 65
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Before the surgeon cut the tissue in one operation, he injected a Local anesthetic. What is the most appropriate mechanism of
action of this drug?
A. Inhibiting the specific increase in sodium conductance
B. Raising the firing threshold
C. Increasing the level of cholinesterase
D. Depolarizing the nerve above the critical firing level
E. Preventing repolarization of the nerve
LO 1: Explain the Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
LO 2: Explain the Organization of the Nervous System, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters
LO 3: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
LO 4: Explain the Drugs That Act In The Central Nervous System - Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs - Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs -
The Alcohols - Antiseizure Drugs - General Anaesthetics - Local Anaesthetics - Skeletal Muscle Relaxants - Pharmacologic Management of
Parkinsonism & Other
The correct answer is: Inhibiting the specific increase in sodium conductance
Question 66
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Neurotransmitter metabolism involves physiologically active amines that are derived from amino acids are further
metabolized to carboxylic acids. Which of the following enzymes is involved in this process?
A. Amino acid decarboxylase
B. Catechol-O-methyltransferase
C. MoAmino acid
D. Amino acid oxidase
E. Dopamine beta-oxidase
LO 1: Explain the Transmembrane potential in neurons, neuron interaction through synapses, neurotransmitters, and synaptic junctions
The correct answer is: MoAmino acid
Question 67
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient had been confirmed to a vessel obstruction of the anterior spinal artery. The doctor need further evidence by
planning several exam such as motoric and sensoric examinations. Which ONE of the following features will most likely be
found on examination of this patient?
A. Bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensations below the site of the lesion
B. Loss of tactile discrimination bilaterally below the site of the lesion
C. Muscle wasting in all the four limbs
D. Normal reflexes in all four limbs
E. Muscle weakness in both left limbs but the right limbs are normal
LO 1: Explain the contents of Vertebral Canal - Spinal Cord - Spinal Nerves and Nerve Roots - Spinal Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Vasculature of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots
LO 2: Explain the Somatic Sensations: Pain, Headache, and Thermal Sensations
The correct answer is: Bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensations below the site of the lesion
Question 68
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 22 year old man presents at your surgery, very upset. His girlfriend has just walked out following an argument. As a
consequence of this type of stress several hormones can be shown to be elevated. What part of the brain mediates this neuro-
hormonal response?
A. Pituitary Gland
B. Thalamus
C. Hypothalamus
D. Cortex
E. Pineal Gland
LO 1: Explain the Cranial Meninges
- Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Meningeal Spaces
Explain the anatomy of the Brain
- Parts of Brain
Ventricular System of Brain
Arterial Blood Supply to Brain Venous Drainage of Brain
LO 2: Explain the Behavioral and Motivational Mechanisms of the Brain—The Limbic System and the Hypothalamus
The correct answer is: Hypothalamus
Question 69
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earths atmosphere and oceans and its related effects. Which of the
following is the most appropriate for the result of individual empowerment?
A. Transporting exotic fruits and vegetables from one destination to another
B. Turn down, switch off, recycle and walk
C. Using less toxic material and find less toxic alternative or method such as cleaning products
D. Frequent washing with clean water, wash hands, toys, vegetables, fruits, and furnitures
E. Reduce gaseous and volatile exposure via adequate ventilation usage of exhaust fans if necessary
LO 1: Explain the Community Empowerment
The correct answer is: Turn down, switch off, recycle and walk
Question 70
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A patient, aged 70 years and who has high myopia, gives a history of seeing flashes, floaters and loss of partial field of vision in
the right eye. Which of the following methods of fundus examination will be ideal to diagnose and assess the condition?
A. Binocular indirect ophthalmoscopy
B. Direct ophthalmoscopy
C. Distant direct ophthalmoscopy
D. Gonioscopy
E. Biomicroscopy/slit lamp Exam
LO 1: Explain the The Eye: Optics of Vision
LO 2: Explain the The Eye: Central Neurophysiology of Vision
The correct answer is: Binocular indirect ophthalmoscopy
Question 71
Correct
Mark 1.00 out of 1.00
Flag question
A 49 year old man presents to the Emergency Department for the fifth time in a month complaining of atypical chest pain with
radiation into the neck and down both arms. As on previous occasions, his ECG is normal. He is noted to have tachycardia with
rapid shallow breaths.What is the most likely psychiatric diagnosis?
A. Generalised anxiety disorder
B. Bi-polar disorder
C. Major depression
D. Schizophrenia
E. Panic disorder
LO 1: Explain the basic anatomy of: - Nervous System - Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
The correct answer is: Panic disorder
Finish review
Formative Test I NBSS 2020-20… Jump to... Formative Test II NBSS 2020-2…
NAVIGASI KOLABORASI
Tentang kami Magang
Website Unpad
Portal LiVE Unpad
HUBUNGI KAMI
LAYANAN LMS
Telp: 085759314557; 085225999797
LMS LiVE Unpad
Email: elearning@unpad.ac.id
LMS MOOC Unpad
Office: Gedung Grha Kandaga, Lt 4.
SUMBER BELAJAR Kampus Unpad Jatinangor, Sumedang, 45363
Kandaga Unpad
Repositori Unpad
Database Jurnal
© LiVE All rights reserved
Get the mobile app
You might also like
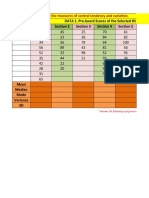
- DATA 1. Pre-Board Scores of The Selected BS Education Students (Per Section) Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5Document10 pagesDATA 1. Pre-Board Scores of The Selected BS Education Students (Per Section) Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5ariane galeno100% (1)
- Del Rosario, A - Section B - Exelcise 4Document14 pagesDel Rosario, A - Section B - Exelcise 4ariane galeno100% (1)
- CUST105: Customer Service: Quiz NavigationDocument1 pageCUST105: Customer Service: Quiz NavigationJeffrey Witty100% (1)
- #Human BrainDocument28 pages#Human BrainDharaa Gupta100% (2)
- Rizal Exam QuestionsDocument1 pageRizal Exam QuestionsRenz Gerard AmorNo ratings yet
- 1st Year JEE-Mains Weekly Test-07 16-08-2021 Attempt ReviewDocument1 page1st Year JEE-Mains Weekly Test-07 16-08-2021 Attempt ReviewKolli BavithaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year JEE-Mains Weekly Test-11 13-09-2021 Attempt ReviewDocument1 page1st Year JEE-Mains Weekly Test-11 13-09-2021 Attempt ReviewKolli BavithaNo ratings yet
- SECOND QUARTER EXAM - Attempt ReviewDocument1 pageSECOND QUARTER EXAM - Attempt ReviewShelvie Morata (Bebeng)No ratings yet
- Two Short Magnets Placed Along The Same Axis With Their Like Poles Facing Each Other Repel Each Other With A Force Which Varies Inversely AsDocument1 pageTwo Short Magnets Placed Along The Same Axis With Their Like Poles Facing Each Other Repel Each Other With A Force Which Varies Inversely AsaswinNo ratings yet
- Class XI (Mome+Height) Jee Mains Rakhi Ass PDFDocument56 pagesClass XI (Mome+Height) Jee Mains Rakhi Ass PDFprateek amrawanshiNo ratings yet
- TOS FinalDocument1 pageTOS FinalKevan jaymes KatipunanNo ratings yet
- College Success - Certificate Final Exam - Attempt Review (Page 1 of 15) - Saylor AcademyDocument1 pageCollege Success - Certificate Final Exam - Attempt Review (Page 1 of 15) - Saylor AcademyJeffrey WittyNo ratings yet
- TOS in Math 7Document2 pagesTOS in Math 7Mon DilligNo ratings yet
- BAHASA INGGRIS XII PAS T.A. 20212022 (Page 3 of 50)Document1 pageBAHASA INGGRIS XII PAS T.A. 20212022 (Page 3 of 50)Mufida NugraheniNo ratings yet
- Monthly Assessment Test, DNB (Radiotherapy) : Central Nervous System Name: DateDocument3 pagesMonthly Assessment Test, DNB (Radiotherapy) : Central Nervous System Name: DateKiran PaulNo ratings yet
- Earth's magnetic field horizontal componentDocument1 pageEarth's magnetic field horizontal componentaswinNo ratings yet
- Item-Analysis-FINAL Del Q2Document10 pagesItem-Analysis-FINAL Del Q2DELIA GAPUSANNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis Diagnostic Test GANEMEDEDocument25 pagesItem Analysis Diagnostic Test GANEMEDEJacqueline Gapuzan CalilitNo ratings yet
- 第一章 数的开方Document3 pages第一章 数的开方chua cindyNo ratings yet
- 1Q GM Test AnalysisDocument5 pages1Q GM Test AnalysisJoyce BondocNo ratings yet
- UGRD-ACTG421 Practicum With Case Study: Quiz NavigationDocument1 pageUGRD-ACTG421 Practicum With Case Study: Quiz NavigationCamae LamigoNo ratings yet
- Gradesheet Template For AY2020-21, 1st SemDocument2 pagesGradesheet Template For AY2020-21, 1st SemReyan BallasoNo ratings yet
- TOS Link Test Item Analysis More Than 40 ItemsDocument11 pagesTOS Link Test Item Analysis More Than 40 ItemsleogarybonNo ratings yet
- RI Answer FormDocument10 pagesRI Answer FormMangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- Beacon Mock 2020 Conversion TableDocument4 pagesBeacon Mock 2020 Conversion TableMelodyLoNo ratings yet
- Monthly Calendar 615bb64bc41a0Document2 pagesMonthly Calendar 615bb64bc41a0api-568336768No ratings yet
- Christian Colleges Accounting Exam AnswersDocument2 pagesChristian Colleges Accounting Exam AnswersKarlo PalerNo ratings yet
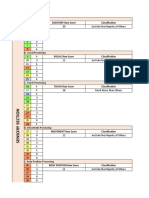
- Auditory, visual and tactile processing scoresDocument7 pagesAuditory, visual and tactile processing scoresJames Remar FajardoNo ratings yet
- NAV-225-FINALS ReviewerDocument1 pageNAV-225-FINALS ReviewerJhun Clyde Dabasol100% (2)
- Assignment - Inclusion-Exclusion Principle1Document2 pagesAssignment - Inclusion-Exclusion Principle1aumkolekar2712No ratings yet
- 18 November - Weekly ET - Grade 12 - JEE PCM - Full Length Mock - Test Paper 2 - Answer Sheet TemplateDocument5 pages18 November - Weekly ET - Grade 12 - JEE PCM - Full Length Mock - Test Paper 2 - Answer Sheet TemplateAmmar AdilNo ratings yet
- 18 November - Weekly ET - Grade 12 - JEE PCM - Full Length Mock - Test Paper 2 - Answer Sheet TemplateDocument5 pages18 November - Weekly ET - Grade 12 - JEE PCM - Full Length Mock - Test Paper 2 - Answer Sheet TemplateAmmar AdilNo ratings yet
- I Put A Spell On YouDocument2 pagesI Put A Spell On YouCouturier100% (1)
- Item Analysis Diagnostic TestDocument31 pagesItem Analysis Diagnostic TestJacqueline Gapuzan CalilitNo ratings yet
- Christian Colleges of Southeast Asia: Auditing Assurance & Concepts & Applications (Assets)Document1 pageChristian Colleges of Southeast Asia: Auditing Assurance & Concepts & Applications (Assets)Karlo PalerNo ratings yet
- TOS Link Test Item Analysis More Than 40 ItemsDocument11 pagesTOS Link Test Item Analysis More Than 40 ItemsAlfielAquinoNo ratings yet
- Msalala and Ushetu Ward, Village, KitongojiDocument46 pagesMsalala and Ushetu Ward, Village, KitongojijosephNo ratings yet
- Analyzing 21st Century Literature ContentDocument3 pagesAnalyzing 21st Century Literature ContentAngelaLomagdongNo ratings yet
- Semester Calendar Spring 2019 1 1Document2 pagesSemester Calendar Spring 2019 1 1api-445758503No ratings yet
- Semester Calendar Fall 2017 1Document2 pagesSemester Calendar Fall 2017 1api-371659761No ratings yet
- Philippines Education Table SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPhilippines Education Table SpecificationsMichael Manipon SegundoNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Scholarship Test Paper 1 First Language and Maths Key PDFDocument1 pageSTD 8 Scholarship Test Paper 1 First Language and Maths Key PDFSwati MahajanNo ratings yet
- Math 141 2021 Fall SyllabusDocument2 pagesMath 141 2021 Fall SyllabusTuran HüseynliNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis TemplateDocument26 pagesItem Analysis TemplateIan Ceasar SipeNo ratings yet
- Calendar Psychological AssessmentDocument1 pageCalendar Psychological AssessmentAlba Alventosa FasNo ratings yet
- My Practice Exam ScoreDocument3 pagesMy Practice Exam ScoreFer FloresNo ratings yet
- Alice in Chains Man in A Box - 1374941869Document2 pagesAlice in Chains Man in A Box - 1374941869Marciel AvelarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet GenerationDocument3 pagesWorksheet GenerationNeha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Filipino and English Reading Skills ReportDocument4 pagesFilipino and English Reading Skills ReportKenneth Winston MoranoNo ratings yet
- Semester Calendar Fall 2017 2Document2 pagesSemester Calendar Fall 2017 2api-371807642No ratings yet
- Frequency of Correct Response: Department of Education Division of RizalDocument24 pagesFrequency of Correct Response: Department of Education Division of RizalEdwin LapatNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument4 pagesTable of SpecificationErwin TabasanNo ratings yet
- Modul Short Course Pusbamulya 2021Document51 pagesModul Short Course Pusbamulya 2021HRP. PardedeNo ratings yet
- TOS and Test Item Analysis-40 Items and AboveDocument11 pagesTOS and Test Item Analysis-40 Items and AboveFloyd MoralesNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Kode Pengawas Xi Dan XiiDocument1 pageJadwal Kode Pengawas Xi Dan XiiInsiyatus NyNo ratings yet
- English 7 Diagnostic TestDocument7 pagesEnglish 7 Diagnostic TestJhay Mhar ANo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6: Mabalbalino EsDocument3 pagesGrade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6: Mabalbalino Esmariatheresa18No ratings yet
- Draft2 - Math2 Tentative Calendar Online and Oncite Version 2021 PDFDocument5 pagesDraft2 - Math2 Tentative Calendar Online and Oncite Version 2021 PDFNuttawut BunlueNo ratings yet
- Modul Short Course Pusbamulya 2021Document52 pagesModul Short Course Pusbamulya 2021Alfia AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Program Enrollment Test Quiz ResultsDocument24 pagesProgram Enrollment Test Quiz ResultsIKECHUKWU SOLOMON ELILINo ratings yet
- 2011 @radproflib D Karthikeyan Step PDFDocument310 pages2011 @radproflib D Karthikeyan Step PDFToma BichirNo ratings yet
- Deskripsi TemanDocument2 pagesDeskripsi TemanTimoriaty MorindaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Review ArticleDocument6 pagesMaxillary Sinus Augmentation: Review ArticlePriliNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesClaudio Antonio MutimucuioNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Medula SpinalisDocument85 pagesKuliah Medula SpinalisMuhamad Thohar ArifinNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Head and NeckDocument75 pagesPhysical Assessment Head and NeckDeeeee100% (2)
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible DeptDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible DeptGopinath Thilak100% (7)
- Respiratory System Organs and FunctionsDocument8 pagesRespiratory System Organs and FunctionsJoselito JardielNo ratings yet
- Norma Frontalis BY DR SHAZIA FAHMIDocument28 pagesNorma Frontalis BY DR SHAZIA FAHMISyeda AlizaNo ratings yet
- Hipo HiperthyroidDocument49 pagesHipo HiperthyroidMuhammad Bilal Bin AmirNo ratings yet
- ThyroidectomyDocument2 pagesThyroidectomykzone2290No ratings yet
- Understanding the Connections and Functions of the Temporal LobesDocument19 pagesUnderstanding the Connections and Functions of the Temporal LobesEdward LinNo ratings yet
- The Theory and Neuroscience of Cerebellar CognitionDocument30 pagesThe Theory and Neuroscience of Cerebellar CognitionIlincaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous SystemlalaNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Spinal Cord: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemDocument64 pagesThe Brain and Spinal Cord: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemMaymay MustradoNo ratings yet
- Ear Nose and Throat QuizDocument6 pagesEar Nose and Throat QuizParsaant SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 04 06 Cerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaDocument53 pages05 04 06 Cerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaiachapraNo ratings yet
- Sialography ExaminationDocument14 pagesSialography ExaminationEkaRahmaNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based NursingDocument9 pagesEvidence-Based NursingKate AbadNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR BELL'S PALSY CASE AT DR. SARDJITO HOSPITAL YOGYAKARTADocument15 pagesPHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR BELL'S PALSY CASE AT DR. SARDJITO HOSPITAL YOGYAKARTAYasudalahNo ratings yet
- Functional Neuroanatomy of Bipolar Disorder: Structure, Function, and Connectivity in An Amygdala-Anterior Paralimbic Neural SystemDocument16 pagesFunctional Neuroanatomy of Bipolar Disorder: Structure, Function, and Connectivity in An Amygdala-Anterior Paralimbic Neural SystemLin FernándezNo ratings yet
- Contouring the Cochlea on T2 MRIDocument10 pagesContouring the Cochlea on T2 MRIAna Paula IoostNo ratings yet
- Robust Pre-Operative Language Mapping in Patients With Brain Tumors: A Feasibility StudyDocument15 pagesRobust Pre-Operative Language Mapping in Patients With Brain Tumors: A Feasibility StudyMohammad FakhriNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentClaudia WinNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Complex Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesUnderstanding the Complex Nervous Systemwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Human Anatomy: Prof. Dr. Med. Petra Köpf-Maier, BerlinDocument14 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy: Prof. Dr. Med. Petra Köpf-Maier, BerlinEspoire LibertéNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of HydrocephalusJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2Document8 pagesPraktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2kuanlins crushNo ratings yet
- New Scientist Essential Guide - No7 - The Human BrainDocument100 pagesNew Scientist Essential Guide - No7 - The Human BrainHieu Trinh100% (4)