Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BAM101 Chapter 1 - 8 Glossary
BAM101 Chapter 1 - 8 Glossary
Uploaded by
BE K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views40 pagesThis document defines key economic terms in order of appearance across chapters 1-8. It provides the term, definition, chapter, and page number for over 50 terms related to businesses, goods, services, economic systems, unemployment, inflation, and more. Key terms include business, goods, services, profit, loss, capitalism, communism, gross domestic product, recession, unemployment, inflation, and consumer price index. The document serves as a glossary to define important vocabulary for understanding introductory economics and business concepts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key economic terms in order of appearance across chapters 1-8. It provides the term, definition, chapter, and page number for over 50 terms related to businesses, goods, services, economic systems, unemployment, inflation, and more. Key terms include business, goods, services, profit, loss, capitalism, communism, gross domestic product, recession, unemployment, inflation, and consumer price index. The document serves as a glossary to define important vocabulary for understanding introductory economics and business concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views40 pagesBAM101 Chapter 1 - 8 Glossary
BAM101 Chapter 1 - 8 Glossary
Uploaded by
BE KThis document defines key economic terms in order of appearance across chapters 1-8. It provides the term, definition, chapter, and page number for over 50 terms related to businesses, goods, services, economic systems, unemployment, inflation, and more. Key terms include business, goods, services, profit, loss, capitalism, communism, gross domestic product, recession, unemployment, inflation, and consumer price index. The document serves as a glossary to define important vocabulary for understanding introductory economics and business concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 40
Key Terms in Order of Appearance
Term Definition Chpt Page
business An organization that strives for a profit 1 5.01
by providing goods and services desired
by its customers.
goods Tangible items manufactured by 1 5.02
businesses.
services Intangible offerings of businesses that 1 5.03
can’t be held, touched, or stored.
standard of living A country’s output of goods and 1 5.04
services that people can buy with the
money they have.
quality of life The general level of human happiness 1 5.05
based on such things as life expectancy,
educational standards, health,
sanitation, and leisure time.
risk The potential to lose time and money 1 5.06
or otherwise not be able to accomplish
an organization’s goals.
revenue The money a company receives by 1 5.07
providing services or selling goods to
customers.
costs Expenses incurred from creating and 1 5.08
selling goods and services.
profit The money left over after all costs are 1 5.09
paid.
loss What a company shows when costs are 1 5.10
greater than revenues
not-for-profit organization An organization that exists to achieve 1 6.1
some goal other than the usual
business goal of profit.
factors of production The resources used to create goods 1 7.1
and services.
knowledge The combined talents and skills of the 1 7.2
workforce.
capital The inputs, such as tools, machinery, 1 8.1
equipment, and buildings, used to
produce goods and services and get
them to the customer.
entrepreneurs People who combine the inputs of 1 8.2
natural resources, labor, and capital to
produce goods or services with the
intention of making a profit or
accomplishing a not-for-profit goal.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 1
Term Definition Chpt Page
demography The study of people’s vital statistics, 1 10.1
such as their age, gender, race and
ethnicity, and location.
technology The application of science and 1 11.1
engineering skills and knowledge to
solve production and organizational
problems.
productivity The amount of goods and services one 1 11.2
worker can produce.
economic system The combination of policies, laws, and 1 12.1
choices made by a nation’s government
to establish the systems that determine
what goods and services are produced
and how they are allocated.
economics The study of how a society uses scarce 1 12.2
resources to produce and distribute
goods and services.
capitalism An economic system based on 1 14.1
competition in the marketplace and
private ownership of the factors of
production (resources); also known as
the private enterprise system.
communism An economic system characterized by 1 15.1
government ownership of virtually all
resources, government control of all
markets, and economic decision-
making by central government
planning.
socialism An economic system in which the basic 1 15.2
industries are owned either by the
government itself or by the private
sector under strong government
control.
mixed economies Economies that combine several 1 16.1
economic systems; for example, an
economy where the government owns
certain industries but others are owned
by the private sector.
macroeconomics The subarea of economics that focuses 1 17.1
on the economy as a whole by looking
at aggregate data for large groups of
people, companies, or products.
microeconomics The subarea of economics that focuses 1 17.2
on individual parts of the economy,
such as households or firms.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 2
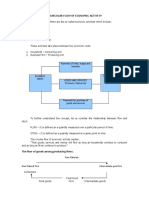
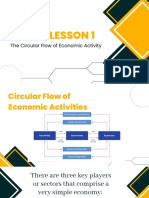
Term Definition Chpt Page
circular flow The movement of inputs and outputs 1 17.3
among households, businesses, and
governments; a way of showing how
the sectors of the economy interact.
economic growth An increase in a nation’s output of 1 18.1
goods and services.
gross domestic product The total market value of all final goods 1 19.1
(GDP) and services produced within a nation’s
borders each year.
business cycles Upward and downward changes in the 1 19.2
level of economic activity.
recession A decline in GDP that lasts for at least 1 19.3
two consecutive quarters.
full employment The condition when all people who 1 20.1
want to work and can work have jobs.
unemployment rate The percentage of the total labor force 1 20.2
that is not working but is actively
looking for work.
frictional unemployment Short-term unemployment that is not 1 20.3
related to the business cycle.
structural unemployment Unemployment that is caused by a 1 20.4
mismatch between available jobs and
the skills of available workers in an
industry or region; not related to the
business cycle.
cyclical unemployment Unemployment that occurs when a 1 20.5
downturn in the business cycle reduces
the demand for labor throughout the
economy.
seasonal unemployment Unemployment that occurs during 1 21.1
specific seasons in certain industries.
inflation The situation in which the average of 1 21.2
all prices of goods and services is rising.
demand-pull inflation Inflation that occurs when the demand 1 22.1
for goods and services is greater than
the supply.
cost-push inflation Inflation that occurs when increases in 1 22.2
production costs push up the prices of
final goods and services.
purchasing power The value of what money can buy. 1 22.2
consumer price index (CPI) An index of the prices of a “market 1 23.1
basket” of goods and services
purchased by typical urban consumers.
producer price index (PPI) An index of the prices paid by 1 23.2
producers and wholesalers for various
commodities, such as raw materials,
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 3
Term Definition Chpt Page
partially finished goods, and finished
products.
national debt The accumulated total of all of the 1 23.3
federal government’s annual budget
deficits.
monetary policy A government’s programs for 1 24.1
controlling the amount of money
circulating in the economy and interest
rates.
fiscal policy The government’s use of taxation and 1 24.2
spending to affect the economy.
expansionary policy The use of monetary policy by the Fed 1 24.3
to increase, or loosen, the growth of
the money supply.
contractionary policy The use of monetary policy by the Fed 1 24.4
to tighten the money supply by selling
government securities or raising
interest rates.
budget surplus When the government takes in more 1 25.1
money than it spends
budget deficit When the government spends more 1 25.2
money than it takes in
federal budget deficit The condition that occurs when the 1 25.3
federal government spends more for
programs than it collects in taxes.
demand The quantity of a good or service that 1 26.1
people are willing to buy at various
prices.
demand curve A graph showing the quantity of a good 1 26.2
or service that people are willing to buy
at various prices.
supply The quantity of a good or service that 1 27.1
businesses will make available at
various prices.
supply curve A graph showing the quantity of a good 1 27.2
or service that businesses will make
available at various prices.
equilibrium The point at which quantity demanded 1 28.1
equals quantity supplied.
market structure The number of suppliers in a market. 1 29.1
perfect (pure) competition A market structure in which a large 1 30.1
number of small firms sell similar
products, buyers and sellers have good
information, and businesses can be
easily opened or closed.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 4
Term Definition Chpt Page
pure monopoly A market structure in which a single 1 31.1
firm accounts for all industry sales of a
particular good or service and in which
there are barriers to entry.
barriers to entry Factors, such as technological or legal 1 31.2
conditions, that prevent new firms
from competing equally with an
existing firm.
monopolistic competition A market structure in which many firms 1 31.3
offer products that are close
substitutes and in which entry is
relatively easy.
oligopoly A market structure in which a few firms 1 31.4
produce most or all of the output and
in which large capital requirements or
other factors limit the number of firms.
ethics A set of moral standards for judging 2 39.1
whether something is right or
wrong.
ethical issue A situation where a person must 2 39.2
choose from a set of actions that may
be ethical or unethical.
justice What is considered fair according to 2 42.1
the prevailing standards of society;
an equitable distribution of the
burdens and rewards that society
has to offer.
Human Rights Certain rights – to life, freedom, to the 2 43.1
pursuit of happiness – are bestowed at
birth and cannot be taken away
Legal Rights Certain rights guaranteed by the 2 43.2
government and its laws
code of ethics A set of guidelines prepared by a firm 2 44
to provide its employees with the
knowledge of what the firm expects
in terms of their responsibilities and
behavior toward fellow employees,
customers, and suppliers.
corporate social The concern of businesses for the 2 48
responsibility (CSR) welfare of society as a whole;
consists of obligations beyond
those required by law or contracts.
Stakeholders Individuals or groups to whom a 2 50
business has a responsibility; include
employees, customers, the general
public, and investors.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 5
Term Definition Chpt Page
social investing The practice of limiting investments 2 53
to securities of companies that
behave in accordance with the
investor’s beliefs about ethical and
social responsibility to encourage
businesses to be more socially
responsible.
corporate philanthropy The practice of charitable giving by 2 54.1
corporations; includes contributing
cash, donating equipment and
products, and supporting the
volunteer efforts of company
employees.
strategic giving The practice of tying philanthropy 2 54.2
and corporate social responsibility
efforts closely to a company’s
mission or goals and targeting
donations to the communities
where a company does business.
global vision The ability to recognize and react to 3 61.1
international business
opportunities, be aware of threats
from foreign competition, and
effectively use international
distribution networks to obtain raw
materials and move finished
products to customers.
Exports Goods and services produced in one 3 62.2
country and sold to other countries.
balance of trade The difference between the value 3 62.3
of a country’s exports and the value
of its imports during a specific time.
Imports Goods and services that are bought 3 62.3
from other countries.
trade surplus A favorable balance of trade that 3 62.4
occurs when a country exports
more than it imports.
trade deficit An unfavorable balance of trade 3 62.5
that occurs when a country imports
more than it exports.
balance of payments A summary of a country’s 3 62.6
international financial transactions
showing the difference between
the country’s total payments to and
its total receipts from other
countries.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 6
Term Definition Chpt Page
floating exchange rates A system in which prices of 3 63.1
currencies move up and down
based upon the demand for and
supply of the various currencies.
Devaluation A lowering of the value of a nation’s 3 63.2
currency relative to other
currencies.
absolute advantage The situation when a country can 3 63.4
produce and sell a product at a
lower cost than any other country
or when it is the only country that
can provide the product.
comparative advantage The concept that each country 3 64.1
should specialize in the products
that it can produce most readily
and cheaply and trade those
products for those that other
countries can produce more readily
and cheaply.
free trade The policy of permitting the people 3 64.2
and businesses of a country to buy
and sell where they please without
restrictions.
Protectionism The policy of protecting home 3 64.3
industries from outside competition
by establishing artificial barriers
such as tariffs and quotas.
Outsourcing Sending work functions to another 3 64.4
country, resulting in domestic
workers losing their jobs.
G20 Informal group that brings together 3 65.1
19 countries and the European
Union—the 20 leading economies
in the world.
Tariff A tax imposed on imported goods. 3 65.2
protective tariffs Tariffs that are imposed in order to 3 65.3
make imports less attractive to
buyers than domestic products are.
import quota A limit on the quantity of a certain 3 66.1
good that can be imported.
Embargo A total ban on imports or exports of 3 66.2
a product.
Dumping The practice of charging a lower 3 66.3
price for a product in foreign
markets than in the firm’s home
market.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 7
Term Definition Chpt Page
Uruguay Round A 1994 agreement originally signed 3 67.1
by 117 nations to lower trade
barriers worldwide.
WTO - World Trade An organization established by the 3 67.2
Organization Uruguay Round in 1994 to oversee
international trade, reduce trade
barriers, and resolve disputes
among member nations.
World Bank An international bank that offers 3 68.1
low-interest loans, as well as advice
and information, to developing
nations.
IMF - International An international organization, 3 68.2
Monetary Fund founded in 1945, that promotes
trade, makes short-term loans to
member nations, and acts as a
lender of last resort for troubled
nations.
preferential tariff A tariff that is lower for some 3 69.1
nations than for others.
free-trade zone An area where the nations allow 3 69.2
free, or almost free, trade among
each other while imposing tariffs on
goods of nations outside the zone.
NAFTA - North American A 1993 agreement creating a free- 3 69.3
Free Trade Agreement trade zone including Canada,
Mexico, and the United States.
Mercosur Trade agreement between Peru, 3 70.1
Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and
Paraguay.
European Union Trade agreement among 28 3 71.1
European nations.
European integration The delegation of limited 3 72.1
sovereignty by European Union
member states to the EU so that
common laws and policies can be
created at the European level.
Exporting The practice of selling domestically 3 74.1
produced goods to buyers in
another country.
Licensing The legal process whereby a firm 3 74.2
agrees to allow another firm to use
a manufacturing process,
trademark, patent, trade secret, or
other proprietary knowledge in
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 8
Term Definition Chpt Page
exchange for the payment of a
royalty.
contract manufacturing The practice in which a foreign firm 3 75.1
manufactures private-label goods
under a domestic firm’s brand
name.
joint venture An agreement in which a domestic 3 75.1
firm buys part of a foreign firm or
joins with a foreign firm to create a
new entity.
joint venture When a domestic company buys 3 75.2
part of a foreign company or joins
with a foreign company to create a
new entity
direct foreign Active ownership of a foreign 3 76.1
investment company or of manufacturing or
marketing facilities in a foreign
country.
countertrade A form of international trade in 3 77.1
which part or all of the payment for
goods or services is in the form of
other goods and services.
Nationalism A sense of national consciousness 3 77.2
that boosts the culture and
interests of one country over those
of all other countries.
Infrastructure The basic institutions and public 3 79.1
facilities upon which an economy’s
development depends.
multinational Corporations that move resources, 3 80.1
corporations goods, services, and skills across
national boundaries without regard
to the country in which their
headquarters are located.
sole proprietorship A business that is established, owned, 4 90.1
operated, and often financed by one
person.
partnership An association of two or more 4 92.1
individuals who agree to operate a
business together for profit.
general partnership Each partner can act on behalf of the 4 92.2
firm and has unlimited liability for all its
business obligations.
limited partnership A partnership with one or more general 4 92.3
partners, who have unlimited liability,
and one or more limited partners,
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 9
Term Definition Chpt Page
whose liability is limited to the amount
of their investment in the company.
general partners Partners who have unlimited liability 4 92.4
for all of the firm’s business obligations
and who control its operations.
limited partners Partners whose liability for the firm’s 4 92.5
business obligations is limited to the
amount of their investment. They help
to finance the business but do not
participate in the firm’s operations.
Corporation A legal entity with an existence and life 4 95.1
separate from its owners, who are not
personally liable for the entity’s debts.
A corporation is chartered by the state
in which it is formed and can own
property, enter into contracts, sue and
be sued, and engage in business
operations under the terms of its
charter.
stockholders (or The owners of a corporation who hold 4 96.1
shareholders) shares of stock that carry certain rights.
shareholders (or The owners of a corporation who hold 4 96.2
stockholders) shares of stock that carry certain rights.
board of directors A group of people elected by the 4 96.3
stockholders to handle the overall
management of a corporation, such as
setting major corporate goals and
policies, hiring corporate officers, and
overseeing the firm’s operations and
finances.
Cooperative A legal entity typically formed by 4 100.1
people with similar interests, such as
suppliers or customers, to reduce costs
and gain economic power. A
cooperative has limited liability, an
unlimited life span, an elected board of
directors, and an administrative staff;
all profits are distributed to the
member-owners in proportion to their
contributions.
joint venture Two or more companies that form an 4 101.1
alliance to pursue a specific project,
usually for a specified time period.
franchising A form of business organization based 4 102.1
on a business arrangement between a
franchisor, which supplies the product
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 10
Term Definition Chpt Page
or service concept, and the franchisee,
who sells the goods or services of the
franchisor in a certain geographic area.
franchisor In a franchising arrangement, the 4 102.2
company that supplies the product or
service concept to the franchisee.
franchisee In a franchising arrangement, the 4 102.3
individual or company that sells the
goods or services of the franchisor in a
certain geographic area.
franchise agreement A contract setting out the terms of a 4 102.4
franchising arrangement, including the
rules for running the franchise, the
services provided by the franchisor,
and the financial terms. Under the
contract, the franchisee is allowed to
use the franchisor’s business name,
trademark, and logo.
merger The combination of two or more firms 4 106.1
to form one new company.
Acquisition The purchase of a target company by 4 106.2
another corporation or by an investor
group typically negotiated with the
target company board of directors.
horizontal merger A merger of companies at the same 4 107.1
stage in the same industry; done to
reduce costs, expand product offerings,
or reduce competition.
vertical merger A merger of companies at different 4 107.2
stages in the same industry; done to
gain control over supplies of resources
or to gain access to different markets.
conglomerate merger A merger of companies in unrelated 4 108.1
businesses; done to reduce risk.
small business A business with under 500 employees 5 116.1
that is independently managed, is
owned by an individual or a small
group of investors, is based locally, and
is not a dominant company in its
industry.
entrepreneurs People with vision, drive, and creativity 5 116.2
who are willing to take the risk of
starting and managing a business to
make a profit, or greatly changing the
scope and direction of an existing firm.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 11
Term Definition Chpt Page
intrapreneurs Entrepreneurs who apply their 5 119.1
creativity, vision, and risk-taking within
a large corporation, rather than
starting a company of their own.
business plan A formal written statement that 5 125.1
describes in detail the idea for a new
business and how it will be carried out;
includes a general description of the
company, the qualifications of the
owner(s), a description of the product
or service, an analysis of the market,
and a financial plan.
debt A form of business financing consisting 5 129.1
of borrowed funds that must be repaid
with interest over a stated time period.
equity A form of business financing consisting 5 129.2
of funds raised through the sale of
stock (i.e., ownership) in a business.
Angel Investors individual investors or groups of 5 129.3
experienced investors who provide
financing for start-up businesses by
investing their own
money, often referred to as “seed
capital.”
venture capital Financing obtained from venture 5 130.1
capitalists, investment firms that
specialize in financing small, high-
growth companies and receive an
ownership interest and a voice in
management in return for their money.
management The process of guiding the 6 138.1
development, maintenance, and
allocation of resources to attain
organizational goals.
efficiency Using the least amount of resources to 6 139.1
accomplish the organization’s goals.
effectiveness The ability to produce the desired 6 139.2
result or good.
planning The process of deciding what needs to 6 141.1
be done to achieve organizational
objectives; identifying when and how it
will be done; and determining who
should do it.
strategic planning The process of creating long-range (one 6 141.2
to five years), broad goals for the
organization and determining what
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 12
Term Definition Chpt Page
resources will be needed to accomplish
those goals.
mission An organization’s purpose and reason 6 142.1
for existing; its long-term goals.
mission statement A formal document that states an 6 142.2
organization’s purpose and reason for
existing and describes its basic
philosophy.
tactical planning The process of beginning to implement 6 143.1
a strategic plan by addressing issues of
coordination and allocating resources
to different parts of the organization;
has a shorter time frame (less than one
year) and more specific objectives than
strategic planning.
operational planning The process of creating specific 6 144.1
standards, methods, policies, and
procedures that are used in specific
functional areas of the organization;
helps guide and control the
implementation of tactical plans.
contingency plans Plans that identify alternative courses 6 144.2
of action for very unusual or crisis
situations; typically stipulate the chain
of command, standard operating
procedures, and communication
channels the organization will use
during an emergency.
organizing The process of coordinating and 6 144.3
allocating a firm’s resources in order to
carry out its plans.
top management The highest level of managers; includes 6 145.1
CEOs, presidents, and vice presidents,
who develop strategic plans.
middle management Managers who design and carry out 6 145.3
tactical plans in specific areas of the
company.
supervisory (first-line) Managers who design and carry out 6 145.3
management operation plans for the ongoing daily
activities of the firm.
first-line / front-line Managers who design and carry out 6 145.4
(supervisory) management operation plans for the ongoing daily
activities of the firm.
leadership The process of guiding and motivating 6 146.1
others toward the achievement of
organizational goals.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 13
Term Definition Chpt Page
power The ability to influence others to 6 146.2
behave in a particular way.
legitimate power Power that is derived from an 6 146.3
individual’s position in an organization.
reward power Power that is derived from an 6 146.4
individual’s control over rewards.
coercive power Power that is derived from an 6 146.5
individual’s ability to threaten negative
outcomes.
expert power Power that is derived from an 6 146.6
individual’s extensive knowledge in one
or more areas.
referent power Power that is derived from an 6 146.7
individual’s personal charisma and the
respect and/or admiration the
individual inspires.
leadership style The relatively consistent way that 6 147.1
individuals in leadership positions
attempt to influence the behavior of
others.
autocratic leaders Directive leaders who prefer to make 6 147.2
decisions and solve problems on their
own with little input from subordinates
participative leaders Leaders who share decision-making 6 147.3
with group members and encourage
discussion of issues and alternatives;
includes democratic, consensual, and
consultative styles.
democratic leaders Leaders who solicit input from all 6 148.1
members of the group and then allow
the members to make the final decision
through a vote.
consensual leaders Leaders who encourage discussion 6 148.2
about issues and then require that all
parties involved agree to the final
decision.
consultative leaders Leaders who confer with subordinates 6 149.1
before making a decision but who
retain the final decision-making
authority.
free-rein (laissez-faire) A leadership style in which the leader 6 149.3
leadership turns over all authority and control to
subordinates.
situational leadership Selecting a leadership style based on 6 149.4
the maturity and competency level of
those who will complete the task.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 14
Term Definition Chpt Page
free-rein (laissez-faire) A leadership style in which the leader 6 149.4
leadership turns over all authority and control to
subordinates.
empowerment The process of giving employees 6 149.5
increased autonomy and discretion to
make decisions, as well as control over
the resources needed to implement
those decisions.
corporate culture The set of attitudes, values, and 6 150.1
standards that distinguishes one
organization from another.
controlling The process of assessing the 6 151.1
organization’s progress toward
accomplishing its goals; includes
monitoring the implementation of a
plan and correcting deviations from the
plan.
informational roles A manager’s activities as an 6 152.1
information gatherer, an information
disseminator, or a spokesperson for the
company.
interpersonal roles A manager’s activities as a figurehead, 6 152.2
company leader, or liaison.
decisional roles A manager’s activities as an 6 152.3
entrepreneur, resource allocator,
conflict resolver, or negotiator.
programmed decisions Decisions made in response to 6 152.4
frequently occurring routine situations.
nonprogrammed decisions Responses to infrequent, unforeseen, 6 153.1
or very unusual problems and
opportunities where the manager does
not have a precedent to follow in
decision-making.
technical skills A manager’s specialized areas of 6 155.1
knowledge and expertise, as well as the
ability to apply that knowledge.
human relations skills A manager’s interpersonal skills that 6 156.1
are used to accomplish goals through
the use of human resources.
conceptual skills A manager’s ability to view the 6 156.2
organization as a whole, understand
how the various parts are
interdependent, and assess how the
organization relates to its external
environment.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 15
Term Definition Chpt Page
global management skills A manager’s ability to operate in 6 160.1
diverse cultural environments.
M1 The total amount of readily available 7 166.0.1
money in the system; includes currency
and demand deposits.
money Anything that is acceptable as payment 7 166.1
for goods and services.
M2 A term used by economists to describe 7 166.0.2
the monetary supply. Includes all M1
monies plus time deposits and other
money that is not immediately
accessible.
currency Cash held in the form of coins and 7 167.1
paper money.
demand deposits Money kept in checking accounts that 7 167.2
can be withdrawn by depositors on
demand.
time deposits Deposits at a bank or other financial 7 167.3
institution that pay interest but cannot
be withdrawn on demand.
open market operations The purchase or sale of Canadian 7 168.1
government bonds by the Bank of
Canada to stimulate or slow down the
economy.
discount rate The interest rate that the Federal 7 169.1
Reserve charges its member banks.
financial intermediation The process in which financial 7 169.2
institutions act as intermediaries
between the suppliers and demanders
of funds.
chartered bank Financial institution licensed by the 7 170.0
federal government to operate in
Canada
commercial banks Profit-oriented financial institutions 7 170.1
that accept deposits, make business
and consumer loans, invest in
government and corporate securities,
and provide other financial services.
credit unions Not-for-profit, member-owned 7 170.2
financial cooperatives.
cash flows The inflow and outflow of cash for a 8 171.1
firm.
pension funds Large pools of money set aside by 7 172.1
corporations, unions, and governments
for later use in paying retirement
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 16
Term Definition Chpt Page
benefits to their employees or
members.
brokerage firm A financial institution that buys and 7 173
sells securities (stocks and bonds) for
its clients
finance company A financial institution specializing in 7 173.2
short-term loans for which the
borrower pus up tangible assets as
security.
Canada Deposit Insurance An independent, quasi-public 7 173.3
Corporation (CDIC) corporation backed by the full faith and
credit of the Canadian government that
insures deposits in commercial banks
and thrift institutions for up to a ceiling
of $100,000 per account.
financial management The art and science of managing a 8 180.1
firm’s money so that it can meet its
goals.
return The opportunity for profit. 8 182.1
Risk The potential for loss or the chance 8 182.2
that an investment will not achieve the
expected level of return.
risk-return trade-off A basic principle in finance that holds 8 182.3
that the higher the risk, the greater the
return that is required.
cash management The process of making sure that a firm 8 183.1
has enough cash on hand to pay bills as
they come due and to meet
unexpected expenses.
marketable securities Short-term investments that are easily 8 183.2
converted into cash.
commercial paper Unsecured short-term debt—an IOU— 8 183.4
issued by a financially strong
corporation.
accounts receivable Sales for which a firm has not yet been 8 184.1
paid.
capital expenditures Investments in long-lived assets, such 8 185.1
as land, buildings, machinery,
equipment, and information services,
that are expected to provide benefits
over a period longer than one year.
capital budgeting The process of analyzing long-term 8 186.1
projects and selecting those that offer
the best returns while maximizing the
firm’s value.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 17
Term Definition Chpt Page
unsecured loans Loans for which the borrower does not 8 186.1
have to pledge specific assets as
security.
trade credit The extension of credit by the seller to 8 186.2
the buyer between the time the buyer
receives the goods or services and
when it pays for them.
accounts payable Purchases for which a buyer has not 8 186.3
yet paid the seller.
line of credit An agreement between a bank and a 8 187.1
business that specifies the maximum
amount of unsecured short-term
borrowing the bank will allow the firm
over a given period, typically one year.
revolving credit agreement A guaranteed line of credit whereby a 8 187.2
bank agrees that a certain amount of
funds will be available for a business to
borrow over a given period, typically
two to five years.
secured loans Loans for which the borrower is 8 187.3
required to pledge specific assets as
collateral, or security.
factoring A form of short-term financing in which 8 187.4
a firm sells its accounts receivable
outright at a discount to a factor.
financial risk The chance that a firm will be unable to 8 188.1
make scheduled interest and principal
payments on its debt.
term loan A business loan with a maturity of 8 189.1
more than one year; can be unsecured
or secured.
bonds Long-term debt obligations (liabilities) 8 189.2
issued by corporations and
governments.
interest A fixed amount of money paid by the 8 189.3
issuer of a bond to the bondholder on a
regular schedule, typically every six
months; stated as the coupon rate.
principal The amount borrowed by the issuer of 8 189.4
a bond; also called par value.
mortgage loan A long-term loan made against real 8 190.1
estate as collateral.
common stock A security that represents an 8 190.2
ownership interest in a corporation.
IPO (Initial Public Offering) The first sale of a company’s stock to 8 190.3
the public
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 18
Term Definition Chpt Page
dividends Payments to stockholders from a 8 191.1
corporation’s profits.
stock dividends Payments to stockholders in the form 8 191.2
of more stock; may replace or
supplement cash dividends.
retained earnings Profits that have been reinvested in a 8 191.3
firm.
preferred stock An equity security for which the 8 192.1
dividend amount is set at the time the
stock is issued and the dividend must
be paid before the company can pay
dividends to common stockholders.
securities corporations or governments that 8 192.1
represent either equity or debt.
institutional investors Investment professionals who are paid 8 193.2
to manage other people’s money.
primary market The securities market where new 8 193.3
securities are sold to the public.
secondary market The securities market where old 8 193.4
(already issued) securities are bought
and sold, or traded, among investors;
includes broker markets, dealer
markets, the over-the-counter market,
and the commodities exchanges.
investment bankers Firms that act as intermediaries, buying 8 193.5
securities from corporations and
governments and reselling them to the
public.
underwriting The process of buying securities from 8 193.6
corporations and governments and
reselling them to the public; the main
activity of investment bankers.
Stockbroker A person who is licensed to buy and 8 194.1
sell securities on behalf of clients.
municipal bonds Bonds issued by states, cities, counties, 8 196.1
and other state and local government
agencies.
mutual fund A financial-service company that pools 8 196.3
investors’ funds to buy a selection of
securities that meet its stated
investment goals.
bond ratings Letter grades assigned to bond issues 8 196.2
to indicate their quality or level of risk;
assigned by rating agencies such as
Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s (S&P).
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 19
Term Definition Chpt Page
exchange traded fund A security similar to a mutual fund; 8 197.1
(ETF) holds a broad basket of stocks with a
common theme but trades on a stock
exchange so that its price changes
throughout the day.
broker markets National and regional securities 8 198.1
exchanges that bring buyers and sellers
together through brokers on a
centralized trading floor.
National Association of The first and largest electronic stock 8 200.1
Securities Dealers market, which is a sophisticated
Automated Quotation telecommunications network that links
(NASDAQ) system dealers throughout the United States.
over-the-counter (OTC) Markets, other than the exchanges, on 8 201.1
market which small companies trade; includes
the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board
(OTCBB) and the Pink Sheets.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 20
Key Terms Alphabetically
Term Definition Chpt Page
absolute advantage The situation when a country can 3 63.4
produce and sell a product at a
lower cost than any other country
or when it is the only country that
can provide the product.
accounts payable Purchases for which a buyer has not 8 186.3
yet paid the seller.
accounts receivable Sales for which a firm has not yet been 8 184.1
paid.
Acquisition The purchase of a target company by 4 106.2
another corporation or by an investor
group typically negotiated with the
target company board of directors.
Angel Investors individual investors or groups of 5 129.3
experienced investors who provide
financing for start-up businesses by
investing their own
money, often referred to as “seed
capital.”
autocratic leaders Directive leaders who prefer to make 6 147.2
decisions and solve problems on their
own with little input from subordinates
balance of payments A summary of a country’s 3 62.6
international financial transactions
showing the difference between
the country’s total payments to and
its total receipts from other
countries.
balance of trade The difference between the value 3 62.3
of a country’s exports and the value
of its imports during a specific time.
barriers to entry Factors, such as technological or legal 1 31.2
conditions, that prevent new firms
from competing equally with an
existing firm.
board of directors A group of people elected by the 4 96.3
stockholders to handle the overall
management of a corporation, such as
setting major corporate goals and
policies, hiring corporate officers, and
overseeing the firm’s operations and
finances.
bond ratings Letter grades assigned to bond issues 8 196.2
to indicate their quality or level of risk;
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 21
Term Definition Chpt Page
assigned by rating agencies such as
Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s (S&P).
bonds Long-term debt obligations (liabilities) 8 189.2
issued by corporations and
governments.
broker markets National and regional securities 8 198.1
exchanges that bring buyers and sellers
together through brokers on a
centralized trading floor.
brokerage firm A financial institution that buys and 7 173
sells securities (stocks and bonds) for
its clients
budget deficit When the government spends more 1 25.2
money than it takes in
budget surplus When the government takes in more 1 25.1
money than it spends
business An organization that strives for a profit 1 5.01
by providing goods and services desired
by its customers.
business cycles Upward and downward changes in the 1 19.2
level of economic activity.
business plan A formal written statement that 5 125.1
describes in detail the idea for a new
business and how it will be carried out;
includes a general description of the
company, the qualifications of the
owner(s), a description of the product
or service, an analysis of the market,
and a financial plan.
Canada Deposit Insurance An independent, quasi-public 7 173.3
Corporation (CDIC) corporation backed by the full faith and
credit of the Canadian government that
insures deposits in commercial banks
and thrift institutions for up to a ceiling
of $100,000 per account.
capital The inputs, such as tools, machinery, 1 8.1
equipment, and buildings, used to
produce goods and services and get
them to the customer.
capital budgeting The process of analyzing long-term 8 186.1
projects and selecting those that offer
the best returns while maximizing the
firm’s value.
capital expenditures Investments in long-lived assets, such 8 185.1
as land, buildings, machinery,
equipment, and information services,
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 22
Term Definition Chpt Page
that are expected to provide benefits
over a period longer than one year.
capitalism An economic system based on 1 14.1
competition in the marketplace and
private ownership of the factors of
production (resources); also known as
the private enterprise system.
cash flows The inflow and outflow of cash for a 8 171.1
firm.
cash management The process of making sure that a firm 8 183.1
has enough cash on hand to pay bills as
they come due and to meet
unexpected expenses.
chartered bank Financial institution licensed by the 7 170.0
federal government to operate in
Canada
circular flow The movement of inputs and outputs 1 17.3
among households, businesses, and
governments; a way of showing how
the sectors of the economy interact.
code of ethics A set of guidelines prepared by a firm 2 44
to provide its employees with the
knowledge of what the firm expects
in terms of their responsibilities and
behavior toward fellow employees,
customers, and suppliers.
coercive power Power that is derived from an 6 146.5
individual’s ability to threaten negative
outcomes.
commercial banks Profit-oriented financial institutions 7 170.1
that accept deposits, make business
and consumer loans, invest in
government and corporate securities,
and provide other financial services.
commercial paper Unsecured short-term debt—an IOU— 8 183.4
issued by a financially strong
corporation.
common stock A security that represents an 8 190.2
ownership interest in a corporation.
communism An economic system characterized by 1 15.1
government ownership of virtually all
resources, government control of all
markets, and economic decision-
making by central government
planning.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 23
Term Definition Chpt Page
comparative advantage The concept that each country 3 64.1
should specialize in the products
that it can produce most readily
and cheaply and trade those
products for those that other
countries can produce more readily
and cheaply.
conceptual skills A manager’s ability to view the 6 156.2
organization as a whole, understand
how the various parts are
interdependent, and assess how the
organization relates to its external
environment.
conglomerate merger A merger of companies in unrelated 4 108.1
businesses; done to reduce risk.
consensual leaders Leaders who encourage discussion 6 148.2
about issues and then require that all
parties involved agree to the final
decision.
consultative leaders Leaders who confer with subordinates 6 149.1
before making a decision but who
retain the final decision-making
authority.
consumer price index (CPI) An index of the prices of a “market 1 23.1
basket” of goods and services
purchased by typical urban consumers.
contingency plans Plans that identify alternative courses 6 144.2
of action for very unusual or crisis
situations; typically stipulate the chain
of command, standard operating
procedures, and communication
channels the organization will use
during an emergency.
contract manufacturing The practice in which a foreign firm 3 75.1
manufactures private-label goods
under a domestic firm’s brand
name.
contractionary policy The use of monetary policy by the Fed 1 24.4
to tighten the money supply by selling
government securities or raising
interest rates.
controlling The process of assessing the 6 151.1
organization’s progress toward
accomplishing its goals; includes
monitoring the implementation of a
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 24
Term Definition Chpt Page
plan and correcting deviations from the
plan.
Cooperative A legal entity typically formed by 4 100.1
people with similar interests, such as
suppliers or customers, to reduce costs
and gain economic power. A
cooperative has limited liability, an
unlimited life span, an elected board of
directors, and an administrative staff;
all profits are distributed to the
member-owners in proportion to their
contributions.
corporate culture The set of attitudes, values, and 6 150.1
standards that distinguishes one
organization from another.
corporate philanthropy The practice of charitable giving by 2 54.1
corporations; includes contributing
cash, donating equipment and
products, and supporting the
volunteer efforts of company
employees.
corporate social The concern of businesses for the 2 48
responsibility (CSR) welfare of society as a whole;
consists of obligations beyond
those required by law or contracts.
Corporation A legal entity with an existence and life 4 95.1
separate from its owners, who are not
personally liable for the entity’s debts.
A corporation is chartered by the state
in which it is formed and can own
property, enter into contracts, sue and
be sued, and engage in business
operations under the terms of its
charter.
cost-push inflation Inflation that occurs when increases in 1 22.2
production costs push up the prices of
final goods and services.
costs Expenses incurred from creating and 1 5.08
selling goods and services.
countertrade A form of international trade in 3 77.1
which part or all of the payment for
goods or services is in the form of
other goods and services.
credit unions Not-for-profit, member-owned 7 170.2
financial cooperatives.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 25
Term Definition Chpt Page
currency Cash held in the form of coins and 7 167.1
paper money.
cyclical unemployment Unemployment that occurs when a 1 20.5
downturn in the business cycle reduces
the demand for labor throughout the
economy.
debt A form of business financing consisting 5 129.1
of borrowed funds that must be repaid
with interest over a stated time period.
decisional roles A manager’s activities as an 6 152.3
entrepreneur, resource allocator,
conflict resolver, or negotiator.
demand The quantity of a good or service that 1 26.1
people are willing to buy at various
prices.
demand curve A graph showing the quantity of a good 1 26.2
or service that people are willing to buy
at various prices.
demand deposits Money kept in checking accounts that 7 167.2
can be withdrawn by depositors on
demand.
demand-pull inflation Inflation that occurs when the demand 1 22.1
for goods and services is greater than
the supply.
democratic leaders Leaders who solicit input from all 6 148.1
members of the group and then allow
the members to make the final decision
through a vote.
demography The study of people’s vital statistics, 1 10.1
such as their age, gender, race and
ethnicity, and location.
Devaluation A lowering of the value of a nation’s 3 63.2
currency relative to other
currencies.
direct foreign Active ownership of a foreign 3 76.1
investment company or of manufacturing or
marketing facilities in a foreign
country.
discount rate The interest rate that the Federal 7 169.1
Reserve charges its member banks.
dividends Payments to stockholders from a 8 191.1
corporation’s profits.
Dumping The practice of charging a lower 3 66.3
price for a product in foreign
markets than in the firm’s home
market.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 26
Term Definition Chpt Page
economic growth An increase in a nation’s output of 1 18.1
goods and services.
economic system The combination of policies, laws, and 1 12.1
choices made by a nation’s government
to establish the systems that determine
what goods and services are produced
and how they are allocated.
economics The study of how a society uses scarce 1 12.2
resources to produce and distribute
goods and services.
effectiveness The ability to produce the desired 6 139.2
result or good.
efficiency Using the least amount of resources to 6 139.1
accomplish the organization’s goals.
Embargo A total ban on imports or exports of 3 66.2
a product.
empowerment The process of giving employees 6 149.5
increased autonomy and discretion to
make decisions, as well as control over
the resources needed to implement
those decisions.
entrepreneurs People who combine the inputs of 1 8.2
natural resources, labor, and capital to
produce goods or services with the
intention of making a profit or
accomplishing a not-for-profit goal.
entrepreneurs People with vision, drive, and creativity 5 116.2
who are willing to take the risk of
starting and managing a business to
make a profit, or greatly changing the
scope and direction of an existing firm.
equilibrium The point at which quantity demanded 1 28.1
equals quantity supplied.
equity A form of business financing consisting 5 129.2
of funds raised through the sale of
stock (i.e., ownership) in a business.
ethical issue A situation where a person must 2 39.2
choose from a set of actions that may
be ethical or unethical.
ethics A set of moral standards for judging 2 39.1
whether something is right or
wrong.
European integration The delegation of limited 3 72.1
sovereignty by European Union
member states to the EU so that
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 27
Term Definition Chpt Page
common laws and policies can be
created at the European level.
European Union Trade agreement among 28 3 71.1
European nations.
exchange traded fund A security similar to a mutual fund; 8 197.1
(ETF) holds a broad basket of stocks with a
common theme but trades on a stock
exchange so that its price changes
throughout the day.
expansionary policy The use of monetary policy by the Fed 1 24.3
to increase, or loosen, the growth of
the money supply.
expert power Power that is derived from an 6 146.6
individual’s extensive knowledge in one
or more areas.
Exporting The practice of selling domestically 3 74.1
produced goods to buyers in
another country.
Exports Goods and services produced in one 3 62.2
country and sold to other countries.
factoring A form of short-term financing in which 8 187.4
a firm sells its accounts receivable
outright at a discount to a factor.
factors of production The resources used to create goods 1 7.1
and services.
federal budget deficit The condition that occurs when the 1 25.3
federal government spends more for
programs than it collects in taxes.
finance company A financial institution specializing in 7 173.2
short-term loans for which the
borrower pus up tangible assets as
security.
financial intermediation The process in which financial 7 169.2
institutions act as intermediaries
between the suppliers and demanders
of funds.
financial management The art and science of managing a 8 180.1
firm’s money so that it can meet its
goals.
financial risk The chance that a firm will be unable to 8 188.1
make scheduled interest and principal
payments on its debt.
first-line / front-line Managers who design and carry out 6 145.4
(supervisory) management operation plans for the ongoing daily
activities of the firm.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 28
Term Definition Chpt Page
fiscal policy The government’s use of taxation and 1 24.2
spending to affect the economy.
floating exchange rates A system in which prices of 3 63.1
currencies move up and down
based upon the demand for and
supply of the various currencies.
franchise agreement A contract setting out the terms of a 4 102.4
franchising arrangement, including the
rules for running the franchise, the
services provided by the franchisor,
and the financial terms. Under the
contract, the franchisee is allowed to
use the franchisor’s business name,
trademark, and logo.
franchisee In a franchising arrangement, the 4 102.3
individual or company that sells the
goods or services of the franchisor in a
certain geographic area.
franchising A form of business organization based 4 102.1
on a business arrangement between a
franchisor, which supplies the product
or service concept, and the franchisee,
who sells the goods or services of the
franchisor in a certain geographic area.
franchisor In a franchising arrangement, the 4 102.2
company that supplies the product or
service concept to the franchisee.
free trade The policy of permitting the people 3 64.2
and businesses of a country to buy
and sell where they please without
restrictions.
free-rein (laissez-faire) A leadership style in which the leader 6 149.3
leadership turns over all authority and control to
subordinates.
free-rein (laissez-faire) A leadership style in which the leader 6 149.4
leadership turns over all authority and control to
subordinates.
free-trade zone An area where the nations allow 3 69.2
free, or almost free, trade among
each other while imposing tariffs on
goods of nations outside the zone.
frictional unemployment Short-term unemployment that is not 1 20.3
related to the business cycle.
full employment The condition when all people who 1 20.1
want to work and can work have jobs.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 29
Term Definition Chpt Page
G20 Informal group that brings together 3 65.1
19 countries and the European
Union—the 20 leading economies
in the world.
general partners Partners who have unlimited liability 4 92.4
for all of the firm’s business obligations
and who control its operations.
general partnership Each partner can act on behalf of the 4 92.2
firm and has unlimited liability for all its
business obligations.
global management skills A manager’s ability to operate in 6 160.1
diverse cultural environments.
global vision The ability to recognize and react to 3 61.1
international business
opportunities, be aware of threats
from foreign competition, and
effectively use international
distribution networks to obtain raw
materials and move finished
products to customers.
goods Tangible items manufactured by 1 5.02
businesses.
gross domestic product The total market value of all final goods 1 19.1
(GDP) and services produced within a nation’s
borders each year.
horizontal merger A merger of companies at the same 4 107.1
stage in the same industry; done to
reduce costs, expand product offerings,
or reduce competition.
human relations skills A manager’s interpersonal skills that 6 156.1
are used to accomplish goals through
the use of human resources.
Human Rights Certain rights – to life, freedom, to the 2 43.1
pursuit of happiness – are bestowed at
birth and cannot be taken away
IMF - International An international organization, 3 68.2
Monetary Fund founded in 1945, that promotes
trade, makes short-term loans to
member nations, and acts as a
lender of last resort for troubled
nations.
import quota A limit on the quantity of a certain 3 66.1
good that can be imported.
Imports Goods and services that are bought 3 62.3
from other countries.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 30
Term Definition Chpt Page
inflation The situation in which the average of 1 21.2
all prices of goods and services is rising.
informational roles A manager’s activities as an 6 152.1
information gatherer, an information
disseminator, or a spokesperson for the
company.
Infrastructure The basic institutions and public 3 79.1
facilities upon which an economy’s
development depends.
institutional investors Investment professionals who are paid 8 193.2
to manage other people’s money.
interest A fixed amount of money paid by the 8 189.3
issuer of a bond to the bondholder on a
regular schedule, typically every six
months; stated as the coupon rate.
interpersonal roles A manager’s activities as a figurehead, 6 152.2
company leader, or liaison.
intrapreneurs Entrepreneurs who apply their 5 119.1
creativity, vision, and risk-taking within
a large corporation, rather than
starting a company of their own.
investment bankers Firms that act as intermediaries, buying 8 193.5
securities from corporations and
governments and reselling them to the
public.
IPO (Initial Public Offering) The first sale of a company’s stock to 8 190.3
the public
joint venture An agreement in which a domestic 3 75.1
firm buys part of a foreign firm or
joins with a foreign firm to create a
new entity.
joint venture When a domestic company buys 3 75.2
part of a foreign company or joins
with a foreign company to create a
new entity
joint venture Two or more companies that form an 4 101.1
alliance to pursue a specific project,
usually for a specified time period.
justice What is considered fair according to 2 42.1
the prevailing standards of society;
an equitable distribution of the
burdens and rewards that society
has to offer.
knowledge The combined talents and skills of the 1 7.2
workforce.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 31
Term Definition Chpt Page
leadership The process of guiding and motivating 6 146.1
others toward the achievement of
organizational goals.
leadership style The relatively consistent way that 6 147.1
individuals in leadership positions
attempt to influence the behavior of
others.
Legal Rights Certain rights guaranteed by the 2 43.2
government and its laws
legitimate power Power that is derived from an 6 146.3
individual’s position in an organization.
Licensing The legal process whereby a firm 3 74.2
agrees to allow another firm to use
a manufacturing process,
trademark, patent, trade secret, or
other proprietary knowledge in
exchange for the payment of a
royalty.
limited partners Partners whose liability for the firm’s 4 92.5
business obligations is limited to the
amount of their investment. They help
to finance the business but do not
participate in the firm’s operations.
limited partnership A partnership with one or more general 4 92.3
partners, who have unlimited liability,
and one or more limited partners,
whose liability is limited to the amount
of their investment in the company.
line of credit An agreement between a bank and a 8 187.1
business that specifies the maximum
amount of unsecured short-term
borrowing the bank will allow the firm
over a given period, typically one year.
loss What a company shows when costs are 1 5.10
greater than revenues
M1 The total amount of readily available 7 166.0.1
money in the system; includes currency
and demand deposits.
M2 A term used by economists to describe 7 166.0.2
the monetary supply. Includes all M1
monies plus time deposits and other
money that is not immediately
accessible.
macroeconomics The subarea of economics that focuses 1 17.1
on the economy as a whole by looking
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 32
Term Definition Chpt Page
at aggregate data for large groups of
people, companies, or products.
management The process of guiding the 6 138.1
development, maintenance, and
allocation of resources to attain
organizational goals.
market structure The number of suppliers in a market. 1 29.1
marketable securities Short-term investments that are easily 8 183.2
converted into cash.
Mercosur Trade agreement between Peru, 3 70.1
Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and
Paraguay.
merger The combination of two or more firms 4 106.1
to form one new company.
microeconomics The subarea of economics that focuses 1 17.2
on individual parts of the economy,
such as households or firms.
middle management Managers who design and carry out 6 145.3
tactical plans in specific areas of the
company.
mission An organization’s purpose and reason 6 142.1
for existing; its long-term goals.
mission statement A formal document that states an 6 142.2
organization’s purpose and reason for
existing and describes its basic
philosophy.
mixed economies Economies that combine several 1 16.1
economic systems; for example, an
economy where the government owns
certain industries but others are owned
by the private sector.
monetary policy A government’s programs for 1 24.1
controlling the amount of money
circulating in the economy and interest
rates.
money Anything that is acceptable as payment 7 166.1
for goods and services.
monopolistic competition A market structure in which many firms 1 31.3
offer products that are close
substitutes and in which entry is
relatively easy.
mortgage loan A long-term loan made against real 8 190.1
estate as collateral.
multinational Corporations that move resources, 3 80.1
corporations goods, services, and skills across
national boundaries without regard
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 33
Term Definition Chpt Page
to the country in which their
headquarters are located.
municipal bonds Bonds issued by states, cities, counties, 8 196.1
and other state and local government
agencies.
mutual fund A financial-service company that pools 8 196.3
investors’ funds to buy a selection of
securities that meet its stated
investment goals.
NAFTA - North American A 1993 agreement creating a free- 3 69.3
Free Trade Agreement trade zone including Canada,
Mexico, and the United States.
National Association of The first and largest electronic stock 8 200.1
Securities Dealers market, which is a sophisticated
Automated Quotation telecommunications network that links
(NASDAQ) system dealers throughout the United States.
national debt The accumulated total of all of the 1 23.3
federal government’s annual budget
deficits.
Nationalism A sense of national consciousness 3 77.2
that boosts the culture and
interests of one country over those
of all other countries.
nonprogrammed decisions Responses to infrequent, unforeseen, 6 153.1
or very unusual problems and
opportunities where the manager does
not have a precedent to follow in
decision-making.
not-for-profit organization An organization that exists to achieve 1 6.1
some goal other than the usual
business goal of profit.
oligopoly A market structure in which a few firms 1 31.4
produce most or all of the output and
in which large capital requirements or
other factors limit the number of firms.
open market operations The purchase or sale of Canadian 7 168.1
government bonds by the Bank of
Canada to stimulate or slow down the
economy.
operational planning The process of creating specific 6 144.1
standards, methods, policies, and
procedures that are used in specific
functional areas of the organization;
helps guide and control the
implementation of tactical plans.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 34
Term Definition Chpt Page
organizing The process of coordinating and 6 144.3
allocating a firm’s resources in order to
carry out its plans.
Outsourcing Sending work functions to another 3 64.4
country, resulting in domestic
workers losing their jobs.
over-the-counter (OTC) Markets, other than the exchanges, on 8 201.1
market which small companies trade; includes
the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board
(OTCBB) and the Pink Sheets.
participative leaders Leaders who share decision-making 6 147.3
with group members and encourage
discussion of issues and alternatives;
includes democratic, consensual, and
consultative styles.
partnership An association of two or more 4 92.1
individuals who agree to operate a
business together for profit.
pension funds Large pools of money set aside by 7 172.1
corporations, unions, and governments
for later use in paying retirement
benefits to their employees or
members.
perfect (pure) competition A market structure in which a large 1 30.1
number of small firms sell similar
products, buyers and sellers have good
information, and businesses can be
easily opened or closed.
planning The process of deciding what needs to 6 141.1
be done to achieve organizational
objectives; identifying when and how it
will be done; and determining who
should do it.
power The ability to influence others to 6 146.2
behave in a particular way.
preferential tariff A tariff that is lower for some 3 69.1
nations than for others.
preferred stock An equity security for which the 8 192.1
dividend amount is set at the time the
stock is issued and the dividend must
be paid before the company can pay
dividends to common stockholders.
primary market The securities market where new 8 193.3
securities are sold to the public.
principal The amount borrowed by the issuer of 8 189.4
a bond; also called par value.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 35
Term Definition Chpt Page
producer price index (PPI) An index of the prices paid by 1 23.2
producers and wholesalers for various
commodities, such as raw materials,
partially finished goods, and finished
products.
productivity The amount of goods and services one 1 11.2
worker can produce.
profit The money left over after all costs are 1 5.09
paid.
programmed decisions Decisions made in response to 6 152.4
frequently occurring routine situations.
Protectionism The policy of protecting home 3 64.3
industries from outside competition
by establishing artificial barriers
such as tariffs and quotas.
protective tariffs Tariffs that are imposed in order to 3 65.3
make imports less attractive to
buyers than domestic products are.
purchasing power The value of what money can buy. 1 22.2
pure monopoly A market structure in which a single 1 31.1
firm accounts for all industry sales of a
particular good or service and in which
there are barriers to entry.
quality of life The general level of human happiness 1 5.05
based on such things as life expectancy,
educational standards, health,
sanitation, and leisure time.
recession A decline in GDP that lasts for at least 1 19.3
two consecutive quarters.
referent power Power that is derived from an 6 146.7
individual’s personal charisma and the
respect and/or admiration the
individual inspires.
retained earnings Profits that have been reinvested in a 8 191.3
firm.
return The opportunity for profit. 8 182.1
revenue The money a company receives by 1 5.07
providing services or selling goods to
customers.
revolving credit agreement A guaranteed line of credit whereby a 8 187.2
bank agrees that a certain amount of
funds will be available for a business to
borrow over a given period, typically
two to five years.
reward power Power that is derived from an 6 146.4
individual’s control over rewards.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 36
Term Definition Chpt Page
risk The potential to lose time and money 1 5.06
or otherwise not be able to accomplish
an organization’s goals.
Risk The potential for loss or the chance 8 182.2
that an investment will not achieve the
expected level of return.
risk-return trade-off A basic principle in finance that holds 8 182.3
that the higher the risk, the greater the
return that is required.
seasonal unemployment Unemployment that occurs during 1 21.1
specific seasons in certain industries.
secondary market The securities market where old 8 193.4
(already issued) securities are bought
and sold, or traded, among investors;
includes broker markets, dealer
markets, the over-the-counter market,
and the commodities exchanges.
secured loans Loans for which the borrower is 8 187.3
required to pledge specific assets as
collateral, or security.
securities corporations or governments that 8 192.1
represent either equity or debt.
services Intangible offerings of businesses that 1 5.03
can’t be held, touched, or stored.
shareholders (or The owners of a corporation who hold 4 96.2
stockholders) shares of stock that carry certain rights.
situational leadership Selecting a leadership style based on 6 149.4
the maturity and competency level of
those who will complete the task.
small business A business with under 500 employees 5 116.1
that is independently managed, is
owned by an individual or a small
group of investors, is based locally, and
is not a dominant company in its
industry.
social investing The practice of limiting investments 2 53
to securities of companies that
behave in accordance with the
investor’s beliefs about ethical and
social responsibility to encourage
businesses to be more socially
responsible.
socialism An economic system in which the basic 1 15.2
industries are owned either by the
government itself or by the private
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 37
Term Definition Chpt Page
sector under strong government
control.
sole proprietorship A business that is established, owned, 4 90.1
operated, and often financed by one
person.
Stakeholders Individuals or groups to whom a 2 50
business has a responsibility; include
employees, customers, the general
public, and investors.
standard of living A country’s output of goods and 1 5.04
services that people can buy with the
money they have.
stock dividends Payments to stockholders in the form 8 191.2
of more stock; may replace or
supplement cash dividends.
Stockbroker A person who is licensed to buy and 8 194.1
sell securities on behalf of clients.
stockholders (or The owners of a corporation who hold 4 96.1
shareholders) shares of stock that carry certain rights.
strategic giving The practice of tying philanthropy 2 54.2
and corporate social responsibility
efforts closely to a company’s
mission or goals and targeting
donations to the communities
where a company does business.
strategic planning The process of creating long-range (one 6 141.2
to five years), broad goals for the
organization and determining what
resources will be needed to accomplish
those goals.
structural unemployment Unemployment that is caused by a 1 20.4
mismatch between available jobs and
the skills of available workers in an
industry or region; not related to the
business cycle.
supervisory (first-line) Managers who design and carry out 6 145.3
management operation plans for the ongoing daily
activities of the firm.
supply The quantity of a good or service that 1 27.1
businesses will make available at
various prices.
supply curve A graph showing the quantity of a good 1 27.2
or service that businesses will make
available at various prices.
tactical planning The process of beginning to implement 6 143.1
a strategic plan by addressing issues of
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 38
Term Definition Chpt Page
coordination and allocating resources
to different parts of the organization;
has a shorter time frame (less than one
year) and more specific objectives than
strategic planning.
Tariff A tax imposed on imported goods. 3 65.2
technical skills A manager’s specialized areas of 6 155.1
knowledge and expertise, as well as the
ability to apply that knowledge.
technology The application of science and 1 11.1
engineering skills and knowledge to
solve production and organizational
problems.
term loan A business loan with a maturity of 8 189.1
more than one year; can be unsecured
or secured.
time deposits Deposits at a bank or other financial 7 167.3
institution that pay interest but cannot
be withdrawn on demand.
top management The highest level of managers; includes 6 145.1
CEOs, presidents, and vice presidents,
who develop strategic plans.
trade credit The extension of credit by the seller to 8 186.2
the buyer between the time the buyer
receives the goods or services and
when it pays for them.
trade deficit An unfavorable balance of trade 3 62.5
that occurs when a country imports
more than it exports.
trade surplus A favorable balance of trade that 3 62.4
occurs when a country exports
more than it imports.
underwriting The process of buying securities from 8 193.6
corporations and governments and
reselling them to the public; the main
activity of investment bankers.
unemployment rate The percentage of the total labor force 1 20.2
that is not working but is actively
looking for work.
unsecured loans Loans for which the borrower does not 8 186.1
have to pledge specific assets as
security.
Uruguay Round A 1994 agreement originally signed 3 67.1
by 117 nations to lower trade
barriers worldwide.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 39
Term Definition Chpt Page
venture capital Financing obtained from venture 5 130.1
capitalists, investment firms that
specialize in financing small, high-
growth companies and receive an
ownership interest and a voice in
management in return for their money.
vertical merger A merger of companies at different 4 107.2
stages in the same industry; done to
gain control over supplies of resources
or to gain access to different markets.
World Bank An international bank that offers 3 68.1
low-interest loans, as well as advice
and information, to developing
nations.
WTO - World Trade An organization established by the 3 67.2
Organization Uruguay Round in 1994 to oversee
international trade, reduce trade
barriers, and resolve disputes
among member nations.
BAM101 (2197) OER Chapter Glossaries Chapters 1 - 8.docx
p. 40
You might also like
- Dwnload Full Business Essentials Canadian 8th Edition Ebert Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Business Essentials Canadian 8th Edition Ebert Solutions Manual PDFtetelcannyr3zpqc100% (15)
- Module 1 The Foundations of Business With Activity and Case StudyDocument8 pagesModule 1 The Foundations of Business With Activity and Case StudyThe PsychoNo ratings yet
- BAM101 Chapter 1 - 4 GlossaryDocument16 pagesBAM101 Chapter 1 - 4 GlossaryBE KNo ratings yet
- BQS406 L2Document19 pagesBQS406 L2Zulkhairy AffandyNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Bisnis EnglishDocument34 pagesPengantar Bisnis Englishderi-aprianto-8032No ratings yet
- Study Material Commercial BankingDocument171 pagesStudy Material Commercial BankingprateekramchandaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document60 pagesChapter 1GadisaNo ratings yet
- Economic ActivityDocument34 pagesEconomic ActivitysantiagoguevaracortezNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics-Unit 6-Lesson 1Document12 pagesApplied Economics-Unit 6-Lesson 1johnNo ratings yet
- LE02-ECO-MA-SP23-Fundamentals of Engineering EconomicsDocument25 pagesLE02-ECO-MA-SP23-Fundamentals of Engineering EconomicsAli NawazNo ratings yet
- McGraw Business Summary Unit1Document6 pagesMcGraw Business Summary Unit1Jimmy gogoNo ratings yet
- By: Instructor Workineh A. (MSC) ToDocument55 pagesBy: Instructor Workineh A. (MSC) ToaregaNo ratings yet
- ECO2211 - The Nature and Method of EconomicsDocument33 pagesECO2211 - The Nature and Method of EconomicsFISH JELLY100% (1)
- Eco 102 (Chapter 2) NewDocument2 pagesEco 102 (Chapter 2) NewMA. FELICITI IGNACIONo ratings yet
- Yunit 1 Mga Pangunahing Konsepto NG EkonDocument8 pagesYunit 1 Mga Pangunahing Konsepto NG EkonHanzel Dy NietesNo ratings yet
- Business Plan PresentationDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan PresentationGwyneth Nicole ValdezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2Document39 pagesChapter 1.2Sherefedin AdemNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Session 1-StudentsDocument17 pagesWeek 4 Session 1-StudentsArianne LucasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 2.1 Economic SystemsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 2.1 Economic SystemsOsvaldo Ola YaniNo ratings yet
- R14 Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic GrowthDocument8 pagesR14 Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growthdar shilNo ratings yet
- TUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicDocument22 pagesTUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicKim Ngọc HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Sheet1: If There Are Images in This Attachment, They Will Not Be DisplayedDocument13 pagesSheet1: If There Are Images in This Attachment, They Will Not Be DisplayedManoj KNo ratings yet
- Business and EconomicsDocument13 pagesBusiness and EconomicsEema AminNo ratings yet
- Advance CH 1Document34 pagesAdvance CH 1zekariyas melleseNo ratings yet
- Econreadings 4Document2 pagesEconreadings 4wilhelmina romanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Glossary Theme1Document13 pagesEdexcel Glossary Theme1Stinkytofu DianaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4Erika Mae SatunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Managerial EconomicsNur DinieNo ratings yet
- Entreprenuerial Management - Entr311: INDUSTRY - A Group of Business Firms Offering Similar Goods orDocument2 pagesEntreprenuerial Management - Entr311: INDUSTRY - A Group of Business Firms Offering Similar Goods orJoanne DawangNo ratings yet
- Business 110 Chapter 2 Flashcards - Quizlet - 1649065419162Document6 pagesBusiness 110 Chapter 2 Flashcards - Quizlet - 1649065419162Emmanuel OdukoyaNo ratings yet
- O.L Business PDFDocument159 pagesO.L Business PDFSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: A. ResourcesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: A. ResourcesGelila TenaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Roles of The Financial System in The Global EconomyDocument10 pagesFunctions and Roles of The Financial System in The Global EconomyMH SahirNo ratings yet
- Economic Systems: Depend On, Based On Appoint, Assign Salaries Define, Make Share In, ParticipateDocument3 pagesEconomic Systems: Depend On, Based On Appoint, Assign Salaries Define, Make Share In, ParticipateBoualem MokademNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document18 pagesChapter 02Maria Joy Oro YatluserNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument28 pagesManagerial Economicsudvasto100% (2)
- Handout For Applied Economics 1st QuarterDocument4 pagesHandout For Applied Economics 1st QuarterNorlie Amor LabradorNo ratings yet
- BOM - Chapter 4 OrganizingDocument6 pagesBOM - Chapter 4 OrganizingEtnad SebastianNo ratings yet
- Micro One Handout PDFDocument89 pagesMicro One Handout PDFtegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- LA EX Economy Ready Reconer 2020Document74 pagesLA EX Economy Ready Reconer 2020Srinivas DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Business Essentials Canadian 7th Edition Ebert Solutions Manual PDFDocument14 pagesDwnload Full Business Essentials Canadian 7th Edition Ebert Solutions Manual PDFtetelcannyr3zpqc100% (14)
- Business in A Changing WorldDocument15 pagesBusiness in A Changing WorldhnyNo ratings yet
- BusinessEthics Lesson 1 7Document14 pagesBusinessEthics Lesson 1 7Zzah SoloNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Economics 0455Document17 pagesCaie Igcse Economics 0455Grade 8A PATEL YASHVI VIPULNo ratings yet
- Let's Begin With A Game!Document35 pagesLet's Begin With A Game!Leonora MisolasNo ratings yet
- 12 Eco Material EngDocument161 pages12 Eco Material EngYASHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Scarcity: Can Produce More Products.Document3 pagesScarcity: Can Produce More Products.ela kikayNo ratings yet
- 01 Economics ReviewerDocument6 pages01 Economics Reviewerortega.johnrhonlieNo ratings yet
- Year10 - Eco - L2 - Mixed EconomiesDocument12 pagesYear10 - Eco - L2 - Mixed EconomiescutekookieoppaNo ratings yet
- Branches of EconomicsDocument3 pagesBranches of EconomicsJuan Paolo OloteoNo ratings yet
- Untitled Section: 8 of 10 PointsDocument28 pagesUntitled Section: 8 of 10 PointsRuby JaneNo ratings yet
- Microeconomic AnalysisDocument32 pagesMicroeconomic AnalysisAbdin AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Social Account and TransactionDocument33 pagesChapter 2 Social Account and TransactionNanye AbichNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and The Economics EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Business and The Economics EnvironmentsM Aqib AnsariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Economic Systems and Market FailureDocument2 pagesWorksheet Economic Systems and Market FailureMuhammad Fareed100% (1)
- Econ 100.2 Reviewer LE 1 (C1-C5)Document14 pagesEcon 100.2 Reviewer LE 1 (C1-C5)DcimasaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Chapter 1 Government Activity in The Modern Mixed EconomyDocument23 pagesOutline: Chapter 1 Government Activity in The Modern Mixed EconomyRiksa D.ANo ratings yet
- Applied Economics All ModuleDocument18 pagesApplied Economics All ModuleSamantha ValienteNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument12 pagesEconomicsRahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Economics and Marketing - Review Exam Set 1 Select The Best AnswerDocument20 pagesAgricultural Economics and Marketing - Review Exam Set 1 Select The Best AnswerSean HooeksNo ratings yet
- Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary BusinessDocument24 pagesEconomic Challenges Facing Contemporary Businessmonel_24671No ratings yet
- Econ6075 Policy1 Assignment2 Fuyun 3035870703Document4 pagesEcon6075 Policy1 Assignment2 Fuyun 3035870703daisyNo ratings yet
- YDocument68 pagesYAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- EMI Songs Australia Pty Limited V Larrikin Music Publishing Pty Limited (2011) FCAFC 47 (31 March 2011)Document68 pagesEMI Songs Australia Pty Limited V Larrikin Music Publishing Pty Limited (2011) FCAFC 47 (31 March 2011)Christopher S. HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Introduction Theory of The FirmDocument6 pagesIntroduction Theory of The FirmFadil Ym100% (2)
- Solved Assume Firms in The Short Run Are Earning Above Normal ProfitsDocument1 pageSolved Assume Firms in The Short Run Are Earning Above Normal ProfitsM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- Ragan: Economics: Fifteenth Canadian EditionDocument26 pagesRagan: Economics: Fifteenth Canadian EditionAmn GillNo ratings yet
- Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony: Chapter OutlineDocument34 pagesMarket Power: Monopoly and Monopsony: Chapter OutlineLolaNo ratings yet
- Zero To OneDocument11 pagesZero To Oneshahdhairya245No ratings yet
- Mcomsem Imangerialeconomicpaper101compressedDocument250 pagesMcomsem Imangerialeconomicpaper101compressedGAGAN BHULLARNo ratings yet
- Bangalore UniversityDocument64 pagesBangalore UniversityNavin TiwariNo ratings yet
- Yandel Bootleggers & Baptists 1983 RegulationDocument5 pagesYandel Bootleggers & Baptists 1983 RegulationMichael ThomasNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument14 pagesBusiness EthicsDaniel DassNo ratings yet
- B - Com - Hons Batch 2018 (15-06-2020)Document55 pagesB - Com - Hons Batch 2018 (15-06-2020)sunandasharma8886456No ratings yet
- CSEET Economics One LinersDocument34 pagesCSEET Economics One LinersAnkit Kumar50% (2)
- FIRST EXAM, Fall 2014 MKT 3013.001, IBC Principles of Marketing Chapters 1, 2, 9, 10 & 14 InstructionsDocument12 pagesFIRST EXAM, Fall 2014 MKT 3013.001, IBC Principles of Marketing Chapters 1, 2, 9, 10 & 14 InstructionsJuan Andres MarquezNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Paper 2019 Set 1Document76 pagesCBSE Class 12 Economics Paper 2019 Set 1NikhilNo ratings yet
- Types of OligopolyDocument3 pagesTypes of OligopolyIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- McKiernan Article - Strategy Past Strategy FuturesDocument10 pagesMcKiernan Article - Strategy Past Strategy FuturesChukwuka EgbuiweNo ratings yet
- The Road We Are TravellingDocument109 pagesThe Road We Are TravellingTCFdotorg100% (3)
- PricingDocument3 pagesPricingcarnivalofpainNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Opportunities in The Changing Market Environment: Basic MarketingDocument34 pagesEvaluating Opportunities in The Changing Market Environment: Basic MarketingKhánh MaiNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Group Summary - Group DDocument3 pagesModule 6 - Group Summary - Group DStuti KariaNo ratings yet
- Economics Revision KitDocument300 pagesEconomics Revision KitKen ChepkwonyNo ratings yet
- Oil and The Economy of Russia From The Late-Tsarist To The Post-Soviet Period by Nat MoserDocument189 pagesOil and The Economy of Russia From The Late-Tsarist To The Post-Soviet Period by Nat MoserMax Oswald-SellsNo ratings yet
- Gios Samar Vs DOTCDocument38 pagesGios Samar Vs DOTCLady Lyn DinerosNo ratings yet
- Pricing Policies:: (I) Competitive SituationDocument9 pagesPricing Policies:: (I) Competitive Situationshivam tiwariNo ratings yet