Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Medicine Physics: Sujit Nilagaonkar
Uploaded by
Ashish Mohan BhattaraiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Medicine Physics: Sujit Nilagaonkar
Uploaded by
Ashish Mohan BhattaraiCopyright:
Available Formats
24
Nuclear Medicine Physics
Sujit Nilagaonkar
BASIC ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS The term X-ray is used for the emission of photons
from outside the nucleus and gamma ray is used for
The atom is considered to be the basic building photons originating in the nucleus.
block of all matter. It represents the physical and From nuclear medicine point of view; gamma
chemical characteristics of that material. It consists rays, beta particles, positrons and alpha particles are
of two components: a nucleus and orbiting electrons important.
which surround the nucleus. The nucleus is said to
be positively charged and the electrons negatively
charged. The nuclei are composed of protons and Methods of Radioactive Decay
neutrons, collectively called nucleons. Protons are
Alpha Decay
positively charge, neutrons are electrically neutral and
orbiting electrons are negatively charged. Alpha decay is common in the higher atomic number
Notation of an atom: range of the periodic table.
A
ZXN In this decay process alpha particles are essentially
Where, A - is atomic mass number (Z + N), X- is the helium nuclei with a +2 charge and an atomic mass
element, Z - Atomic number (i.e. number of protons) number of 4.
and N- is number of neutrons. Alpha particles are undesirable in diagnostic
Isotopes: Isotopes are the radionuclides with the same application, but favorable therapeutic agents have
number of protons (z). These are the same elements been designed.
but with different number of neutrons. e.g. I123, I125, I131. e.g. Uranium238 nucleus.
92 U → 90 U + He
238 234 42
In classical Bohr’s model of atom, the electrons are
described as arranged in well-defined orbits around The uranium-238 nucleus emits a helium-4
the nucleus. Electrons are basic elementary particles. nucleus (the alpha particle) and the parent nucleus
Orbital electrons are the electrons in orbits in an atom. becomes thorium-234.
Orbital electrons in each atom are equal to the number
of protons in the nucleus. The closest orbit to the
Beta Decay
nucleus is referred as K-shell and next one is referred
to as L, M and N so forth. The maximum number of Beta decay is also called as negatron decay. There are
electrons in the K-shell is 2 and in the L shell is 8, in M three common forms of beta decay. In beta decay the
shell is 18 and in N-shell is 32. Outer most orbit cannot conversion of a neutron into a proton, an electron and
have more than 8 electrons. Valence electrons are the a subatomic particle called antineutrino. The electron
electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. These is ejected from the atomic nucleus.
electrons are responsible for defining the chemical
properties of the element.
Gamma Decay
Gamma decay involves the emission of energy from
RADIOACTIVE DECAY
an unstable nucleus in the form of electromagnetic
The term radioactivity refers to the emission of particles radiation. Gamma rays are emitted almost immediately
and/or energy from unstable isotopes. Because of after the primary decay process whether it is alpha
physical properties, certain atoms are unstable and decay, negatron decay.
radioactive decay is a process used by unstable atoms The radioactive decay equation and half-life concept:
to achieve a more stable situation. The decay process is dependent upon the initial
24.indd 124 1/15/2016 6:06:06 PM
Nuclear Medicine Physics 125
Interaction of Radiation with Matter
During radioactive decay, two types of radiation are
emitted.
a. Charged particles such as alpha particles and beta
particles
b. Electromagnetic radiation such as gamma rays and
X-rays.
These radiations transfer their energy to the matter
by ionization and excitation of atoms and molecules as
they pass through it.
The charged particles when passed through matter
cause ionization by transforming energy to the matter,
therefore, they are important for radiation dosimetry
as well.
RADIATION DETECTORS
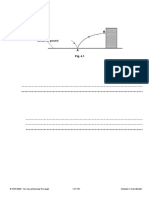
Fig. 24.1 Graphical representation of half-life
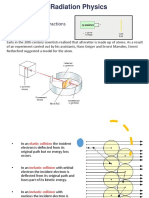
Basic Principle
number of nuclei present, i.e. N and on the time period. When a photon strikes a detector material, it causes
Suppose initial number of nuclei is N at time T0. Let us ionization and excitation by photoelectric and
assume that dN is the number of nuclei decayed over Compton scatter methods. When the ionized atoms
a period dT. undergo de-excitation, energy is released. Most of the
Half-life: It is the time required for a radionuclide to energy is released as thermal energy, but some energy
decay to 50% of the initial activity level. Note that the is released as visible light.
half-life does not express how long a material will Scintillators: These are the materials which produce
remain radioactive but simply the length of time for its visible light after interaction of photons with the
radioactivity to halve of initial activity (Fig. 24.1). matter. And the detectors made from such scintillators
Biological half-life: This term is used to describe are called scintillation detectors.
biological clearance of a radionuclide from a particular There are two types of detector materials one is
tissue or organ. The term biological half-life is useful in detectors made up of organic substances and other are
anticipating about the amount of exposure the patient detectors made up of inorganic substances.
actually receives during a nuclear medicine procedure.
Effective half-life: It is the actual half-life of a
Photomultiplier Tubes
radiopharmaceutical in a biological system.
It is dependent on both the physical half-life and Photomultiplier tube (PMT) is an electronic device
biological half-life. which produces a pulse of electric current when
stimulated by weak light signal and multiplies it to
several folds thus converting a relatively small light
Units of Radioactivity
signal into a large pulse of current. PMTs are available
The SI or metric unit of radioactivity is named in various size and shapes like round, hexagonal,
after Henri Becquerel, in honor of his discovery of square, etc. PMT is basically tubes sealed in glass and
radioactivity, and is called the Becquerel with the evacuated tubes wrapped in metal foil for magnetic
symbol “Bq”. shielding. PMTs are maintained at high voltage
The Becquerel is defined as the quantity of levels. PMTs made up of multiple dynodes which
radioactive substance that gives rise to a decay rate of are maintained at higher voltage levels than another
1 decay per second (1dps). (Fig. 24.2). The PMT has a glass entrance window.
The traditional unit of radioactivity is named after The surface of the glass window is covered by a photo
Marie Curie and is called the curie, with the symbol Ci. emissive substance. This photo emissive surface is
The curie is defined as the amount of radioactive called photocathode. When the photo emissive surface
substance which gives rise to a decay rate of is struck by visible light, it emits electrons. These
3.7 × 1010 decays per second. electrons are called photoelectrons. Focusing grid is
24.indd 125 1/15/2016 6:06:06 PM
126 Textbook of Radiology: Physics
NUCLEAR MEDICINE
IMAGING SYSTEM
Basic Principle of Gamma Camera
Components of gamma camera are collimator, NaI (Tl)
crystal, photomultiplier tube, position logic circuit,
pulse height analyzer and display monitor.
Collimator
Gamma rays cannot be focused. The gamma rays
originating from the patient must be focused on
the camera system to form an image. In nuclear
medicine, patient itself is a source of gamma rays. The
rays coming out from the patient are distributed in all
directions.
Fig. 24.2 Basic structure and working photomultiplier tube This includes gamma rays which are having
significant clinical information and those gamma
rays which are distorted and do not travel in expected
placed between dynodes and photo emissive surface. direction.
This grid directs the photoelectrons towards dynodes. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent gamma rays
which are not traveling in proper direction.
Collimators, here play role of absorptive collimation
Inorganic Scintillators
by absorbing the unwanted gamma rays before they
These are the solid state materials which scintillate reach detector. The image is produced by allowing only
in crystal form. The most commonly used scintillator those rays which are traveling in certain direction to
in nuclear medicine is NaI (Tl) crystal. The crystal is reach detector.
doped with Thallium impurity to make them operable Collimators are formed of metals having high
at room temperature. density and high atomic number. Lead with atomic
number 82 and density 11.3 g/cm cube is most
Characteristics of NaI (Tl) Crystal commonly used for collimator.
Holes are drilled in lead. The lead walls between the
Advantages septa are called collimator septa. The septal thickness,
zz It is relatively dense and with high atomic number— diameter of hole and length of septa are characteristics
therefore it is good absorber and efficient detector. for a particular collimator.
zz It gives good light output—i.e. efficient scintillators
producing one visible light photon per 30 eV of
Detector System and Electronics
radiation.
zz It is transparent to its own radiation-therefore little The gamma camera is formed by a large NaI (Tl)
loss of scintillation light. detector crystal, usually 6 mm to 12 mm thickness and
zz Crystals of large size can be grown in ovens at 35 to 50 cm in diameter. Because of hygroscopic nature
relatively small costs. of the crystal material, the detector crystal is completely
zz Wavelength well matched to peak response to PMT. sealed with thin aluminum casing. The front surface
of crystal is surrounded by a highly reflective material
TiO2 to maximize light output. An optical glass window
Disadvantages
is kept on back surface of the casing for permitting the
zz Fragile and easily fracturable crystal scintillation light to reach the PM tube. All detector
zz Hygroscopic in nature—if absorbs moisture, light electronics such as preamplifier, pulse height analyzer,
transmission from detector to PMT is hampered. automatic gain control and pulse pileup rejection
zz For higher energy gamma rays detection, larger circuits are directly employed on the individual PM
volumes of detector are required. tube bases.
24.indd 126 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
Nuclear Medicine Physics 127
Event Analysis and Positioning
When an event occurs and it is analyzed by pulse
height analyzer. If it falls within the acceptable energy
window, the event is labeled as X and Y co-ordinates
and it is binned in pixels. Each pixel should have
sufficient number of counts detected so as to form an
interpretable image.
In modern gamma cameras, the output from a PMT
is directly digitalized by analog to digital converter and
the event position is calculated in software.
Only those gamma rays whose energy fall within
acceptable energy window 130 Kev to 150 Kev are
selected for the counting. Therefore energy selection
becomes important to improve image resolution.
PRODUCTION OF RADIOISOTOPES
Fig. 24.3 Mo99- Tc99m column generator system
Most of the radioisotopes found in nature have
relatively long half-lives. As a result medical
applications generally require the use of radioisotopes by lead shielding for radiation protection purposes. In
which are produced artificially. addition all components are produced and need to be
A stable nucleus is converted into an unstable maintained in a sterile condition.
nucleus by bombarding the nuclei by protons or
neutrons.
CYCLOTRON
A cyclotron (Fig. 24.4) is a type of charged particle
The Production Methods
accelerator in which electrically charged subnuclear
zz Reactor produced: Nuclear reactors have been a particles as protons, deuterons and alpha particles
source of radioisotope production since a long accelerate outwards from the center along a spiral
period of time. path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by
The production mainly takes place by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly
—— Nuclear fission varying (radio frequency) electric field. The energy
—— Nuclear bombardment of the particle increases as the velocity of the particle
zz Accelerator produced: increases. The cyclotron utilizes this fact to produce
—— Positive ion cyclotron particles of reasonably high energy in a relatively
—— Negative ion cyclotron confined space. When the accelerated beam reaches
its maximum energy it can be directed onto a target
material causing nuclear reactions to occur that result
Radioisotope Generator
in the formation of radionuclides.
Radioisotope generator consists of a relatively long- Cyclotrons were the best source of high-
lived radioisotope (parent) which decays into the short- energy beams for nuclear physics experiments in
lived isotope of interest (daughter). A good example is past. Cyclotrons can be used in particle therapy to
99m
Tc which is the most widely used radioisotope in treat cancer. Ion beams from cyclotrons can be used, as
nuclear medicine today. The 99Mo is called the parent in proton therapy, to penetrate the body and kill tumors
isotope. This isotope has a half-life of six hours. by radiation damage, while minimizing damage to
The chemical separation device is called, in this healthy tissue along their path. Cyclotron beams can
example, a 99mTc Generator. Column Generator System be used to bombard other atoms to produce short-
consists of a ceramic column with 99Mo adsorbed onto lived positron-emitting isotopes (18FDG glucose)
its top surface (Fig. 24.3). A solution called an eluent suitable for PET imaging.
is passed through the column, reacts chemically with
any 99mTc and emerges in a chemical form which
TECHNETIUM-99M
is suitable for combining with a pharmaceutical
to produce a radiopharmaceutical. The ceramic Technetium-99m is a metastable radioactive tracer
column and collection vials need to be surrounded which emits gamma rays from within the body to
24.indd 127 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
128 Textbook of Radiology: Physics
Radionuclides Used for Scanning of Lungs
Perfusion agent are 99mTechnetium -MAA (macro
aggregated albumin) and 99mTechnetium (human
albumin microspheres).
Ventilation agents are 133Xenon and 99mTechnetium
–DTPA (diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid).
Various Techniques for
Isotope Imaging of Lung
Radioactive gases
133
zz Xe: Ventilation studies with Xe-133 are ordinarily
performed first during combined V/Q imaging.
Fig. 24.4 Cyclotron A large field of view gamma camera with a low
energy all purpose collimator is used. The usual
provide information about the functioning of a adult dose of Xe-133 is 10 to 20 mCi. The patient is
person’s specific organs, symbolized as 99mTc. It is the seated (if possible) with the camera positioned in
most commonly-used medical radioisotope. the posterior view.
Technetium-99m when used as a radioactive zz First breath: The patient exhales fully and is asked
tracer can be detected in the body by gamma cameras. to take a maximal inspiration and hold it long
It is well suited to the role because it emits readily enough, if possible, to obtain 100k counts.
detectable 140 keV gamma rays which are about the zz Equilibrium: Obtain two sequential 45 sec poster
same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray images while the patient breathes normally.
diagnostic equipment. The half-life for gamma emission zz Washout: Obtain three sequential 45 sec posterior
is about 6.0058 hours. The “short” physical half- images and then left and right posterior oblique
life and its biological half-life of 1 day allows rapid data images and a final posterior image.
collection, but keep total patient radiation exposure Radio aerosols: For studies with radio aerosols the
low. The same characteristics make the isotope radiopharmaceutical is placed in a special nebulizer
suitable only for diagnostic but never therapeutic use. system. The patient is asked to breathe through the
Molybdenum-99 is used commercially as the easily- mouth piece of the delivery system until sufficient
transportable source of medically used Tc-99m. radio aerosol is delivered to the lungs. 25 to 30 mCi
It is used for imaging and functional studies of 99mTc -DTPA (diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid)
of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, is used. The views obtained in radio aerosol studies
gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. should be the same as those obtained for the perfusion
Diagnostic treatment involving technetium-99m phase in anterior, posterior, right and left lateral and
will result in radiation exposure to technicians, patients, both posterior 45 degree oblique views. 99mTc-DTPA
and passers-by. The doses used in scintigraphy result in aerosols remain in the lung, with a biological half-life
radiation exposures to the patient around 10 mSv, the approaching 1 hour.
equivalent of about 500 chests X-ray exposures. This Perfusion imaging: 99mTc MAA, 4 mCi adult dose is
level of radiation exposure carries a 1 in 1000 lifetime injected intravenously over several respiratory cycles
risk of developing a solid cancer or leukemia in the with the patient in supine position. A large field of view
patient. The risk is higher in younger patients, and gamma camera with a low energy high resolution or
lower in older ones. The radiation source is inside all purpose collimator and a 20% window centered at
the patient and will be carried around for a few days, 140 Kev is used. The views obtained phase in anterior,
exposing others to second-hand radiation. posterior, right and left lateral and both posterior 45°
oblique views. The right and left 45° anterior oblique
views. Obtain 500 k to 750 k counts per image.
RADIONUCLIDE SCANNING
Lungs Clinical Implication
Radionuclide scanning of the lungs is performed zz Ventilation perfusion mismatch: Abnormal
for detection of pulmonary embolism, preoperative perfusion in an area of normal ventilation or much
evaluation of regional pulmonary function, detection larger perfusion abnormality than ventilation
of venous thrombosis and fat embolism. defect.
24.indd 128 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
Nuclear Medicine Physics 129
zz Ventilation perfusion match: Both scintigrams are visualized within 60 minutes and most of the patients
abnormal in the same area: defects of equal size. show it within 90 minutes. If activity is seen within the
zz Segmental defect: Caused by occlusion of a branch gallbladder, but not in the small bowel by 90 minutes
of the pulmonary artery, typical wedge shaped and of the study, Sincalide may be used to expedite small
pleural based. Conforms to segmental anatomy of bowel visualization and measure gallbladder ejection
lung. fraction.
Diagnostic Criteria Cholecystokinin in Hepatobiliary Imaging
The multi institutional modified PIOPED (Prospective Cholecystokinin (CCK) is released endogenously
Investigation of Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis) by the duodenal mucosa in response to a fatty meal.
criteria for combined study interpretation: Gallbladder contraction is initiated when the serum
zz High probability (80–100%) CCK concentration reaches a threshold. CCK also acts
zz Intermediate probability (20–80%) to relax the sphincter of Oddi allowing bile to empty
zz Low probability (<20%) into the small bowel.
zz Normal study. Sincalide (synthetic CCK) reproduces the active
For high probability criteria, the likely hood portion of CCK, the C-terminal octapeptide fragment.
of pulmonary embolism is >80%. The hallmark is The most commonly administered dose is 0.02 ug/kg
a perfusion defect corresponding to a broncho given by slow I.V. infusion typically over 4 to 5 minutes,
pulmonary segment with normal ventilation and Gallbladder contraction begins rapidly following
normal chest radiograph. sincalide infusion, with a maximal effect within 15
When the perfusion study is completely normal minutes.
without a segmental defect, the likelihood of PE is less Indications for the use of Sincalide include
than 5%. The likelyhood of significant morbidity or patient fasting for more than 20 to 24 hours and the
mortality from PE is probably less than 1%. determination of gall bladder ejection fraction (GBEF).
Hepatobiliary Scanning Morphine Augmented Cholescintigraphy
Radioisotopes used in hepatobiliary scanning are Morphine can be used to decrease the time required
analogs of 99m Tc IDA (Iminodiacetic acid) to confirm acute cholecystitis. Dose: 0.04 mg/kg (Max.
zz HIDA: Hydroxy iminodiacetic acid 2–3 mg) given over a 3 minute infusion. Morphine
85% excreted by the liver, 15% by the kidneys may be administered after 45 minutes to 1 hour if the
Good visualization at bilirubin levels of 5–7 mg/dL gallbladder is not visualized, and there is:
zz Disofenin (Mebrofenin) zz No evidence of CBD obstruction, and
It has greatest resistance to displacement by zz Sufficient activity remains within the liver to allow
bilirubin. Over 80% of the administered activity is for subsequent imaging.
cleared from the blood by liver hepatocytes within Morphine can produce up to a 10 fold increase
10 minutes. in the resting pressure of the common bile duct by
Half-life (T1/2) of uptake is about 6 minutes, and causing contraction of the sphincter of Oddi.
the T1/2 of excretion is about 14 minutes. If GB has not filled by 30 minutesafter morphine
injection the exam is diagnostic of acute cholecystitis.
Technique Visualization of the gallbladder 5 to 30 minutes after
morphine is indicative of chronic cholecystitis.
Standard Examination Overall, the sensitivity (96 to 100%) and specificity (81
The patient should be fasting for 4 to 8 hrs; Narcotics to 100%).
that act on the sphincter of Oddi should be stopped
6 to 12 hours prior to the examination.
Indications
Normal examination reveals the liver activity
exceeds cardiac blood pool by 5 minutes and by zz Cholecystitis
10 minutes the cardiac blood pool activity gets zz Bile leak
diminished. Persistent blood pool activity indicates zz Biliary dyskinesia
hepatocellular dysfunction. Biliary activity is typically zz Hepatic arterial perfusion scintigraphy
seen by 15 minutes and over 90% of normal studies zz Biliary atresia
the gallbladder is visualized within 30 minutes. zz Neonatal hepatitis
About 80% of normal patients small bowel activity is zz Choledocal cyst.
24.indd 129 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
130 Textbook of Radiology: Physics
Renal Scanning zz Primary megaureter
Clinical application
In renal scan different agents are used for assessing —— To exclude refluxing or nonrefluxing system
various parameters of renal functions. obstructive or nonobstructive excretory
Agents used to quantify glomerular function is system.
99m
Technetium DTPA. —— Postsurgery to see the success of surgery and
Agents used to quantify effective renal plasma to pick up postoperative complication.
flow are 131I orthoidohippurate and 99mTechnetium For example, stenosis at vesicouretic
mercaptoacetyltriglycine. junction.
Agents used for renal cortical scintigraphy are 99mTc —— In cases where conservative approach is used
DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid) and 99mTc gluco renography is used to monitor progress.
heptonate (GHA). zz Urinary calculi
—— Acute obstruction—diagnosed by IVU and USG
Clinical implication of renography-
Techniques Gives information regarding function of
Quantitative evaluation of clearance the kidneys
zz Under steady state conditions Gives information regarding degree of
—— Constant infusion method obstruction and reduction in ipsilateral
—— Feedback controlled infusion method function which helps to decide urgency of
zz During slope (single injection) intervention and provides a baseline
—— Multiple blood sampling —— Monitoring of progress
Two compartment model Clinical implication
Single compartment model Need of accurate and reliable means of
Stewart-Hamilton principle measuring and monitoring progress
—— Single sample method To monitor increasing obstruction or
—— External counting method deterioration of split function which needs
Diuretic renography. intervention.
—— Bilateral calculus disease:
Clinical implication: Split renal function
Indications of Renography
analysis may influence the decision regarding
zz Obstructive uropathy the type and timing of operation.
Clinical applications In deciding which kidney to operate first.
—— Need of intervention—in cases of equivocal —— Borderline function
obstruction diagnosis the intervention Clinical implication: The management
decision depends upon presence or absence decision depends between removing the
of obstruction and relative function of the calculus or performing a nephrectomy.
kidney. Relative function measurement is essential
Renography contributed to decision making in decision making.
process how to intervene Repeat scan after nephrostomy may
—— Type of intervention—by determination of be necessary to determine the amount
split function, relative function of each kidney of recoverable function before a final
can be determined. This helps surgeons to decision is made.
decide up to what extent function must be zz Renal transplant evaluation
preserved. zz VUR—Methods
In cases of obstructive kidney, it helps surgeons —— Direct radionuclide cystogram
to determine the amount of recoverable —— Indirect radionuclide cystogram
function Advantages: High sensitivity, low radiation
zz Idiopathic hydronephrosis burden to the child
Clinical application—In conditions in which zz Renovascular hypertension evaluation.
dilatation is apparent but no cause is demonstrated,
the key to management is distinguishing between Indications of Renal Cortical Imaging Agents
stasis and obstruction. Diuretic renography plays
important role in decision making. zz To detect focal areas of renal parenchymal defects
zz Acute pyelonephritis
24.indd 130 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
Nuclear Medicine Physics 131
zz Renovascular disease SPECT Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy
zz To evaluate renal scars
zz Complex duplex systems Brain SPECT imaging provides complementary
zz Ectopic kidney evaluation functional information to anatomic imaging exams.
zz Evaluation of poorly functioning kidneys. SPECT agents such as Tc-HMPAO and Tc-ECD reflect
cerebral perfusion.
RADIONUCLIDE AGENTS USED
IN NEUROIMAGING Brain SPECT Imaging in Dementia
zz Conventional brain scintigraphy Dementias produce deficits in perfusion, in part
99m
—— Tc- glucoheptonate (GH) reflecting decreased metabolic needs. Characteristic
99m
—— Tc-diethylene-triamine-pentaacetic acid patterns have a predictive value of over 80% for
(DTPA) the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. A correlation
zz Brain perfusion scintigraphy has also been described between the severity
123
—— I iodoamphetamine (IMP) of these defects, and the severity of the patient’s
99m
—— Tc Tc-Hexamethylpropyleneamine Oxime dementia.
(HMPAO)
99m
Tc- methyl cycteinate dimer (ECD)
Brain SPECT in Psychiatric Disorders
——
zz Brian tumor imaging
201
—— Thallium Tc99m-HMPAO may be more useful than EEG in
99m
—— Tc sestamibi determining response to therapy in patients with
zz Cisternography psychiatric disorders.
111
—— Indium –DTPA
zz Positron emission tomography
Brain SPECT for the Detection
Compound Application
18 of a Seizure Focus
Flurine -fluorodeoxy- glucose utilization
glucose Epilepsy is one of the most prevalent neurological
15Oxygen O2 oxygen metabolism disorders—affecting about 1% of the general
15Oxygen H2O blood flow population. The most common pathologic finding in
11Carbon methionine amino acid these patients is mesial temporal sclerosis which is
metabolism thought to represent a gliotic scar. Excision of this focus
11Carbon methylspiperone dopamine receptor can lead to elimination of the seizures or significantly
activity improved pharmacologic control in 80% of patients. CT
11Carbon carfentanil opiate receptor and MRI have low sensitivity for seizure foci detection,
activity 17% and 34% respectively. The role of brain SPECT is to
11Carbon flunitrazepam benzodiazepine localize the seizure focus.
receptor activity The ictal exam requires that the patient be placed
11Carbon scopolamine muscarinic in a special room with continuous video and EEG
cholinergic receptor monitoring. The patients medication is usually tapered
18 Flurine fluoro-L-DOPA Presynaptic off or discontinued to increase the likelihood of a
dopaminergic seizure episode. The tracer to be injected at the time
system of ictal phase and imaging is done after 40 minutes
11Carbon ephedrine adrenergic of injection. Inter ictal study is conducted and
terminals both images sets are compared to localize seizure
11Carbon or 15Oxygen blood volume focus.
carboxyhemoglobin
CNS Vascular Imaging
Conventional Brain Scintigraphy
Tc99m-cerebral perfusion studies can be used to
Diseases of the brain cause a breakdown in the confirm the presence of cerebral infarction, monitor
blood brain barrier which permits the uptake of the effects of acute thrombolytic therapy and to predict
conventional brain imaging agents. Other than for stroke outcome.
brain death, conventional brain scintigraphy is no
longer routinely performed.
24.indd 131 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
132 Textbook of Radiology: Physics
CSF Flow Studies Brain Tumors
CSF flow studies are performed using either In-111 Viable areas within CNS neoplasms are generally
(DTPA) or Tc99mDTPA. Indications for the exam expected to demonstrate increased metabolism, while
include suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus, areas of necrosis show no metabolic activity.
occult CSF rhinorrhea/otorrhea and ventricular shunt
evaluation.
24.indd 132 1/15/2016 6:06:07 PM
You might also like
- Radioactive Decay ExplainedDocument14 pagesRadioactive Decay ExplainedrenneNo ratings yet
- UCE Physics Modern PhysicsDocument28 pagesUCE Physics Modern PhysicsHasifa KonsoNo ratings yet
- Radio Activity and ParticlesDocument34 pagesRadio Activity and ParticlesKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Atom N RadioactivityDocument91 pagesNuclear Atom N RadioactivityLinaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Application of Flame PhotometerDocument37 pagesInstrumentation and Application of Flame PhotometerVishal Singh100% (4)
- Lecture On Nuclear ChemistryDocument58 pagesLecture On Nuclear Chemistrysadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1479 Describing and Specifying Inductively-Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometers (ICP操作)Document14 pagesASTM E1479 Describing and Specifying Inductively-Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometers (ICP操作)Tu Ngo MinhNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay and Half LifeDocument30 pagesRadioactive Decay and Half LifeM Imran SheikhNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Study NotesDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity - Uses, Dangers and SafetyDocument48 pagesRadioactivity - Uses, Dangers and SafetyChahinese FahsiNo ratings yet
- Radiation Detection & Measurement I: Types of DetectorsDocument35 pagesRadiation Detection & Measurement I: Types of Detectorssnoobper100% (1)
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityDocument70 pagesBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- IARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021Document125 pagesIARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021DHARMENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsDocument145 pagesQuantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsVedant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Photomultiplier Tubes: Photon Is Our BusinessDocument323 pagesPhotomultiplier Tubes: Photon Is Our Businessico haydNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry Basics GuideDocument56 pagesFlow Cytometry Basics GuideRaboisa15No ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and RadioactivityDocument48 pagesNuclear Chemistry and RadioactivityAdityaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1: Negative Charge of Electricity. Positive Charge of Electricity Not Electrically ChargedDocument3 pagesEngineering Utilities 1: Negative Charge of Electricity. Positive Charge of Electricity Not Electrically ChargedE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Principios de Radiacion Goaz 1Document15 pagesPrincipios de Radiacion Goaz 1Alejo UrreaNo ratings yet
- 4.7 RadioactivityDocument14 pages4.7 Radioactivitygabrielsuva6No ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry EditedDocument19 pagesNuclear Chemistry EditedGaichuingamPanmeiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument17 pagesNuclear ChemistryGaichuingamPanmeiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminaryDocument86 pagesRadioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminarySalehe TobaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Basic Chemistry ConceptsDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Basic Chemistry ConceptsMalak RabieNo ratings yet
- Atoms and RadioactivityDocument35 pagesAtoms and Radioactivityrahayuutami30No ratings yet
- Radiation Chemistry Notes EditedDocument15 pagesRadiation Chemistry Notes Editedkiama kariithiNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 4Document9 pagesPDF Document 4harbhjans911No ratings yet
- Notes and Exercise Oxford PDFDocument5 pagesNotes and Exercise Oxford PDFIna DinNo ratings yet
- MODELS OF THE ATOM EXPLAINEDDocument2 pagesMODELS OF THE ATOM EXPLAINEDJohn Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- Interactionofradiation Drvandana 110828021807 Phpapp01Document47 pagesInteractionofradiation Drvandana 110828021807 Phpapp01Kumkumo Kussia KossaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lecture 1Document9 pagesChemistry Lecture 1adithyakrishnahn007No ratings yet
- Chm524 4 RadiochemistryDocument67 pagesChm524 4 Radiochemistryasyraf azlan99No ratings yet
- Basic Radiation Physics: 1.3. Electron InteractionsDocument13 pagesBasic Radiation Physics: 1.3. Electron InteractionsGabriel OrtegaNo ratings yet
- STEM - Rutherford - Baldago, Joanna G.Document23 pagesSTEM - Rutherford - Baldago, Joanna G.Joanna BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Physics - The Physics of The AtomDocument8 pagesPhysics - The Physics of The AtomNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 12 RadioactivityDocument62 pages12 RadioactivityAMRA IQBALNo ratings yet
- S.4. Modern Physics-1 - Read and PracticeDocument13 pagesS.4. Modern Physics-1 - Read and PracticeKEIFER SUTHERLANDNo ratings yet
- X-ray Production, Properties and InteractionsDocument14 pagesX-ray Production, Properties and Interactionsroma ulinaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument13 pagesRevisionrajayush67780No ratings yet
- Nuclear and Radiochemistry NotesDocument74 pagesNuclear and Radiochemistry Notesosolobrandon2No ratings yet
- GCE PHYSICS: Particles, Quantum Phenomena and ElectricityDocument34 pagesGCE PHYSICS: Particles, Quantum Phenomena and ElectricityJames ChongNo ratings yet
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument26 pagesRADIOACTIVITYHarIsh SangwanNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Chapter 4 Nuclear PhysicsDocument14 pagesGroup 5 Chapter 4 Nuclear PhysicsAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Nuclear Atom: Rutherford's ExperimentDocument9 pages2.1 The Nuclear Atom: Rutherford's ExperimentUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Atomic Structure - pdf-98Document12 pagesJEE Main Atomic Structure - pdf-98Zameer AnsariNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - : ElectronDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure - : ElectronAinne Joy DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Dr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopDocument31 pagesDr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Radiation & Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument27 pagesRadiation & Radioactivity and Half LifedwyphyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Radiation: Understanding the AtomDocument58 pagesNuclear Fission and Radiation: Understanding the AtomJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- Radioactive EmmissionDocument15 pagesRadioactive Emmissioneshabennie1No ratings yet
- Atoms Nucleus and Radiation - To Be Filled inDocument15 pagesAtoms Nucleus and Radiation - To Be Filled inNick RandazzoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesNuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureShelly AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Radiation Oncology PresentationDocument47 pagesRadiation Oncology PresentationAriful Islam PrantoNo ratings yet
- Detecting Biological Effects of Radioactive MaterialsDocument37 pagesDetecting Biological Effects of Radioactive MaterialsAlyssaMaeCubillaNo ratings yet
- Neutrons Are Not Fundamental ParticlesDocument8 pagesNeutrons Are Not Fundamental ParticlesKeith D. FooteNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TransformationDocument16 pagesNuclear TransformationAnsel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Untitled Notebook PDFDocument28 pagesUntitled Notebook PDF石上 優No ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument20 pagesGeneral ChemistryEd Ryan RualesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Particle PhysicsDocument9 pagesChapter 11 Particle PhysicsLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics: J.Jeyasugiththan PHD Department of Nuclear Science University of ColomboDocument21 pagesMedical Physics: J.Jeyasugiththan PHD Department of Nuclear Science University of ColombopumaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesGAMING IN MOODNo ratings yet
- Topic 24. RadioactivityDocument25 pagesTopic 24. Radioactivitynotphoenix972No ratings yet
- Gamma Ray LogDocument52 pagesGamma Ray LogPrithiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Document24 pagesUnit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Akshay UdayNo ratings yet
- UV Visible SpectrosDocument21 pagesUV Visible SpectrosShar anilNo ratings yet
- Radiocarbon DatingDocument13 pagesRadiocarbon DatingFabiana MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Detection in UV-visible Spectrophotometry: Detectors, Detection Systems, and Detection StrategiesDocument10 pagesDetection in UV-visible Spectrophotometry: Detectors, Detection Systems, and Detection StrategiesPujhii100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Analytical MethodsDocument104 pagesChapter 4 Analytical MethodsCL SanchezNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry GuideDocument60 pagesSpectrophotometry GuideAarav MahajanNo ratings yet
- LP980 BrochureDocument9 pagesLP980 Brochurezubairkp7No ratings yet
- Laser Induced Fluorescence of Quinine Sulfate and The Kinetics of CL Induced Quenching of The FluorescenceDocument14 pagesLaser Induced Fluorescence of Quinine Sulfate and The Kinetics of CL Induced Quenching of The Fluorescenceglen-576661No ratings yet
- RCAPhotomultiplierHandbook PDFDocument179 pagesRCAPhotomultiplierHandbook PDFPhewNo ratings yet
- SiPM Analog Front-End Electronics for Space ApplicationsDocument7 pagesSiPM Analog Front-End Electronics for Space ApplicationsMasonNo ratings yet
- Gamma Spectrometer (Single Channel Analyzer)Document7 pagesGamma Spectrometer (Single Channel Analyzer)Harsh Purwar100% (7)
- Enhancing The Sensitivity of The LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Dark Matter Experiment To Low Energy SignalsDocument14 pagesEnhancing The Sensitivity of The LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Dark Matter Experiment To Low Energy SignalsCrainlyNo ratings yet
- EPS ETA High-Voltage Generator: Product SpecificationDocument30 pagesEPS ETA High-Voltage Generator: Product Specificationmohamed hanouacheNo ratings yet
- UV-VIS Absorption SpectroscopyDocument63 pagesUV-VIS Absorption SpectroscopyMiftahAinulMardiahNo ratings yet
- ARL Ispark SeriesDocument12 pagesARL Ispark SeriesNikola RanđelovićNo ratings yet
- UV/VIS Spectroscopy Guide for Analyzing Organic & Inorganic SamplesDocument7 pagesUV/VIS Spectroscopy Guide for Analyzing Organic & Inorganic SamplesAnonymous xpYo0nR0No ratings yet
- High Sensitivity Photodetector For Photon-Counting ApplicationsDocument24 pagesHigh Sensitivity Photodetector For Photon-Counting ApplicationsLong HoàngNo ratings yet
- SHCC 1718 Phy Mock 2 PDFDocument12 pagesSHCC 1718 Phy Mock 2 PDFVincent haNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Radionuclides PDFDocument25 pagesIdentification of Unknown Radionuclides PDFindonesian publication center ipcNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray LogDocument13 pagesGamma Ray LogMehsen OsamaNo ratings yet
- ICP OESAReview PDFDocument11 pagesICP OESAReview PDFAlfiah tul NuimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecDocument12 pagesChapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Preamplifiers: Matching The Preamplifier To The Detector and The ApplicationDocument8 pagesPreamplifiers: Matching The Preamplifier To The Detector and The ApplicationsuryaNo ratings yet