Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 10 +11
Lab 10 +11
Uploaded by
عبد اللطيف حبوش0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesPID control is the most common control algorithm used in industry. It determines system behavior based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms where proportional looks at present errors, integral looks at past errors, and derivative looks at future errors. Using only proportional and derivative gains results in a proportional derivative (PD) controller. A PID controller can be reduced to seven different controller types by including or excluding the P, I, and D terms.
Original Description:
Original Title
lab 10 +11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPID control is the most common control algorithm used in industry. It determines system behavior based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms where proportional looks at present errors, integral looks at past errors, and derivative looks at future errors. Using only proportional and derivative gains results in a proportional derivative (PD) controller. A PID controller can be reduced to seven different controller types by including or excluding the P, I, and D terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesLab 10 +11
Lab 10 +11
Uploaded by
عبد اللطيف حبوشPID control is the most common control algorithm used in industry. It determines system behavior based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms where proportional looks at present errors, integral looks at past errors, and derivative looks at future errors. Using only proportional and derivative gains results in a proportional derivative (PD) controller. A PID controller can be reduced to seven different controller types by including or excluding the P, I, and D terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
What PID stands for?
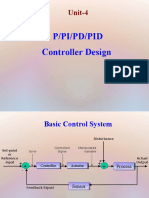
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control is the most common control algorithm used in industry
and has been universally accepted in industrial control.
In PID controller, determine what time does each of the term in the PID controls (circle only) ?
Proportional: present
Integral: past
Derivative: future
What are the drawbacks of P controller?
steady-state error occurs after a set-point change or a sustained disturbance
Lab 11 :
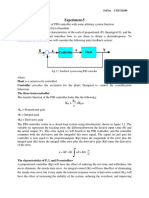
If we only use a proportional and differential gains of the PID controller, what we can call
this controller?
Proportional Derivative Controller (PD Controller)
How many different controllers can we obtain from a PID controller? List them
7 Controllers.
P Controller, I Controller, D Controller, PI Controller, PD Controller, ID Controller,
PID Controller
Closed-Loop Rise Overshoot Settling Steady-State Stability
response Time Time Error
KP Decrease Increase Small Decrease Decrease
change
KI Decrease Increase Increase Decrease Decrease
Significantly
KD Minor Minor Minor No effect Improve
decrease decrease decrease
a. The open-loop system characteristics (Plot)
b. Tune a P controller
overshoot Increase
Rise time Decrease
steady-state error Increase
c. Tune a PD Controller
overshoot Decrease
Rise time no change
steady-state error Decrease
d. Tune a PID controller
rise time Decrease
Overshoot no Decrease
steady-state error Decrease
You might also like
- Pid Controller Without NoiseDocument10 pagesPid Controller Without NoisessleandroNo ratings yet
- 09 PID Control + CompensatorsDocument32 pages09 PID Control + Compensatorsomar hanyNo ratings yet
- Controller 5Document39 pagesController 5DSYMEC224Trupti BagalNo ratings yet
- Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesProportional-Integral-Derivative Control: ObjectivesQuenneBelocuraNo ratings yet
- 英文PID资料Document3 pages英文PID资料Richard LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.5Document8 pagesChapter 1.5Anonymous en5etXfNo ratings yet
- App PIDDocument12 pagesApp PIDP Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 03: (P Controller)Document8 pagesExperiment No. 03: (P Controller)KADUSKAR PALASHNo ratings yet
- Amd Pid ControlDocument12 pagesAmd Pid ControlpfalencarNo ratings yet
- Study On Control of PID and Motor: Let's StartDocument18 pagesStudy On Control of PID and Motor: Let's Startraadhassan02No ratings yet
- 5 PidDocument7 pages5 PidKADUSKAR PALASHNo ratings yet
- 5 - PID IAPC - MergedDocument20 pages5 - PID IAPC - MergedNikita ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- How Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning MethodsDocument12 pagesHow Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning Methodsmurugan1984No ratings yet
- Introduction To PID Controller With Detailed P, PI, PD & PD Control - VivekBose - Com (1) Very Good ThingDocument19 pagesIntroduction To PID Controller With Detailed P, PI, PD & PD Control - VivekBose - Com (1) Very Good Thingahsan.shah7542No ratings yet
- By Group 5: Sintu Kumar Sharma 0017 Avishek Mukherjee 0018 MD Ashraf Alam Khan 0019 Dali Das 0020Document13 pagesBy Group 5: Sintu Kumar Sharma 0017 Avishek Mukherjee 0018 MD Ashraf Alam Khan 0019 Dali Das 0020Sunil SinghNo ratings yet
- PIDtutorialDocument13 pagesPIDtutorialalijnubyNo ratings yet
- P/Pi/Pd/Pid Controller Design: Unit-4Document39 pagesP/Pi/Pd/Pid Controller Design: Unit-4harish9No ratings yet
- The Dark Side of LoopDocument143 pagesThe Dark Side of Loopsongzheng chenNo ratings yet
- Utm Sour6Document3 pagesUtm Sour6JamalAhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Position Control SystemDocument8 pagesLab 12 Position Control SystemCat HowardNo ratings yet
- Experiment-5: Roll No. - 1709721094Document3 pagesExperiment-5: Roll No. - 1709721094shardendu dwivediNo ratings yet
- 4 PiDocument7 pages4 PiKADUSKAR PALASHNo ratings yet
- Controlsystem 5Document8 pagesControlsystem 5sabarivelan sNo ratings yet
- PID Robust Control Using Taguchi MethodDocument6 pagesPID Robust Control Using Taguchi MethodIsra Lemus SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pid Tuning MethodsDocument16 pagesPid Tuning MethodsNirmal sachanNo ratings yet
- Performance of P-Only, PI and PID ControllersDocument21 pagesPerformance of P-Only, PI and PID ControllersRahulMunthaNo ratings yet
- Performance of P-Only, PI and PID ControllersDocument21 pagesPerformance of P-Only, PI and PID ControllersarunNo ratings yet
- PIDDocument32 pagesPIDHani Hasan100% (1)
- Pid PDFDocument22 pagesPid PDFmansoorNo ratings yet
- 4 - Pi IapcDocument7 pages4 - Pi IapcNikita ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 1.4. Lean Six Sigma AbbreviationsDocument6 pages1.4. Lean Six Sigma AbbreviationsEric DesportesNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Lect. 4 PIDDocument65 pagesControl Systems Lect. 4 PIDhmaymadNo ratings yet
- FA17-EEE-037 Control Lab Report 11Document6 pagesFA17-EEE-037 Control Lab Report 11Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- PID ControlDocument32 pagesPID ControlSyamil RahmanNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING EXERCISE 03 Zarelle and CheloDocument4 pagesPROGRAMMING EXERCISE 03 Zarelle and CheloJeremiah PuaNo ratings yet
- Effects of A PID Controller in Closed Loop Feedback SystemDocument4 pagesEffects of A PID Controller in Closed Loop Feedback Systemali.azim1380No ratings yet
- Control Tutorials For MATLAB and Simulink - Introduction - PID Controller DesignDocument17 pagesControl Tutorials For MATLAB and Simulink - Introduction - PID Controller DesignPrashant ChinamalliNo ratings yet
- PidDocument18 pagesPidByron Xavier Lima CedilloNo ratings yet
- The Guide To PID TuningDocument29 pagesThe Guide To PID TuningIvan OxfordNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - Loop TuningDocument41 pagesModule 10 - Loop TuningHtet LwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - PID ControllerDocument62 pagesChapter 4 - PID ControllerHuy Nguyen LuongNo ratings yet
- PID ControllerDocument5 pagesPID ControllerAbhilash MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- PidDocument10 pagesPidarundh93No ratings yet
- Control SystenDocument87 pagesControl SystenKpsingh KalsiNo ratings yet
- PI Controller in The Simulink Model Using MATLABDocument9 pagesPI Controller in The Simulink Model Using MATLABMatlabAsignmentExpertsNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Changes in The Past Twenty YearsDocument8 pagesBusiness Environment Changes in The Past Twenty YearsLowFunctioningSociopathNo ratings yet
- Routh-Hurwitz Stability CriterionDocument37 pagesRouth-Hurwitz Stability CriterionNagajyothiVirivintiNo ratings yet
- Pi Tops DemoDocument54 pagesPi Tops DemoAndres JimenezNo ratings yet
- Traditional PID Control Method: Fundamental of Instruments and Process Course Name: Myo Zaw Oo Student ID: 3122999029Document11 pagesTraditional PID Control Method: Fundamental of Instruments and Process Course Name: Myo Zaw Oo Student ID: 3122999029Myo Zaw OoNo ratings yet
- 05 Introduction PID Controller DesignDocument22 pages05 Introduction PID Controller DesignAhtisham195No ratings yet
- 1.1 Proportional Control Mode (P) : V OimendustegurDocument1 page1.1 Proportional Control Mode (P) : V OimendustegurmsNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 - IntroducaoDocument31 pages1 - 1 - IntroducaoAndré GomesNo ratings yet
- KrishiDocument3 pagesKrishiKrishi ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Breakthrough IT: Supercharging Organizational Value Through TechnologyFrom EverandBreakthrough IT: Supercharging Organizational Value Through TechnologyNo ratings yet