Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accumulator
Uploaded by
Shalom GosainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accumulator
Uploaded by
Shalom GosainCopyright:
Available Formats
Accumulator
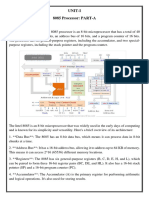
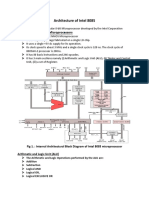
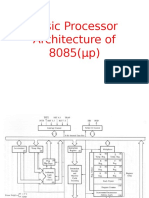
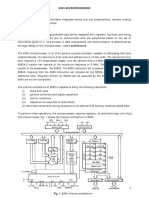
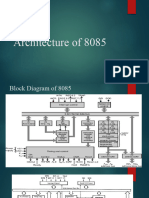
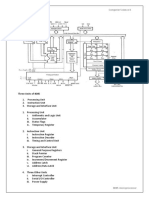
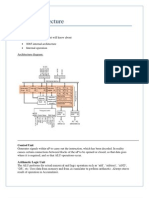
It is an 8-bit register used to perform arithmetic, logical, I/O & LOAD/STORE operations. It is connected to internal data bus &
ALU.
Arithmetic and logic unit
As the name suggests, it performs arithmetic and logical operations like Addition, Subtraction, AND, OR, etc. on 8-bit data.
General purpose register
There are 6 general purpose registers in 8085 processor, i.e. B, C, D, E, H & L. Each register can hold 8-bit data.
These registers can work in pair to hold 16-bit data and their pairing combination is like B-C, D-E & H-L.
Program counter
It is a 16-bit register used to store the memory address location of the next instruction to be executed. Microprocessor
increments the program whenever an instruction is being executed, so that the program counter points to the memory address
of the next instruction that is going to be executed.
Stack pointer
It is also a 16-bit register works like stack, which is always incremented/decremented by 2 during push & pop operation
Temporary register
It is an 8-bit register, which holds the temporary data of arithmetic and logical operations.
Instruction register and decoder
It is an 8-bit register. When an instruction is fetched from memory then it is stored in the Instruction register. Instruction decoder
decodes the information present in the Instruction register.
Timing and control unit
It provides timing and control signal to the microprocessor to perform operations. Following are the timing and control signals,
which control external and internal circuits −
Control Signals: READY, RD’, WR’, ALE
Status Signals: S0, S1, IO/M’ Interrupt control
As the name suggests it controls the interrupts during a process. When a microprocessor is executing a main program and
whenever an interrupt occurs, the microprocessor shifts the control from the main program to process the incoming request.
After the request is completed, the control goes back to the main program.
There are 5 interrupt signals in 8085 microprocessor: INTR, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5, TRAP.
Serial Input/output control
It controls the serial data communication by using these two instructions: SID (Serial input data) and SOD (Serial output data).
Address buffer and address-data buffer
The content stored in the stack pointer and program counter is loaded into the address buffer and address-data buffer to
communicate with the CPU. The memory and I/O chips are connected to these buses; the CPU can exchange the desired data
with the memory and I/O chips.
Address bus and data bus
Data bus carries the data to be stored. It is bidirectional, whereas address bus carries the location to where it should be stored
and it is unidirectional. It is used to transfer the data & Address I/O devices.
You might also like
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument3 pages8085 Microprocessor Architecturetguna21No ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureLithika RameshNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument3 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorANKIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointRajat RajNo ratings yet
- MPC 2Document29 pagesMPC 2rohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- FMM Unit-1Document28 pagesFMM Unit-1CS ENo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument25 pages8085 Microprocessorprofessor2062No ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureAlok AnkitNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20Document26 pagesUnit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20GopinathNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureN.D.SurendharNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 1Document25 pagesNotes Unit 1Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 4 SemesterDocument6 pagesExperiment 1 4 Semesteraman YadavNo ratings yet
- MPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureDocument17 pagesMPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureWickNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument17 pages8085 ArchitectureSamaira Shahnoor ParvinNo ratings yet
- 8085 Is Pronounced AsDocument9 pages8085 Is Pronounced AsArbaaz khan786No ratings yet
- Intel 8085 ArchitectureDocument8 pagesIntel 8085 ArchitectureAravind VJNo ratings yet
- Micro Processor DineshDocument9 pagesMicro Processor DineshsandyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointAmith DhageNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument13 pages8085 MicroprocessorSajid Akram100% (1)
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDocument19 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNo ratings yet
- Unit I The 8086 MicroprocessorDocument21 pagesUnit I The 8086 Microprocessor16211a0470100% (1)
- MPD e ContentsDocument112 pagesMPD e Contentsmeera joshiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors - II: Yashar HajiyevDocument62 pagesMicroprocessors - II: Yashar HajiyevMurad QəhramanovNo ratings yet
- MCT Unit 2Document26 pagesMCT Unit 2Aravind RajNo ratings yet
- 8085 MaterialDocument12 pages8085 MaterialsameerNo ratings yet
- Ii Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDocument6 pagesIi Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureYohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- 1-Architecture of 8085Document34 pages1-Architecture of 8085Pinki KumariNo ratings yet
- MICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualDocument53 pagesMICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualAjay PatilNo ratings yet
- M4 Yash AllabadiDocument6 pagesM4 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- Micrprocessor Notes 2023Document18 pagesMicrprocessor Notes 2023GautamNo ratings yet
- Micro U1Document43 pagesMicro U1Avinash SharmaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Block DiagramDocument5 pages8085 Microprocessor - Block DiagramShreyash ShindeNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument5 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDeep KambleNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document10 pagesIntel 8085venkatesh.mNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - SGDocument15 pagesMicroprocessor - SGSugata Ghosh0% (1)
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument20 pages8085 Microprocessorjeravi84No ratings yet
- Programming With 8085 MicroprocessorDocument33 pagesProgramming With 8085 MicroprocessorBlackk SpydoNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor June29Document9 pages8085 Microprocessor June29Mworozi DicksonNo ratings yet
- MC8085Document7 pagesMC8085Bhavani BhavanNo ratings yet
- MPMC Assignment-1Document7 pagesMPMC Assignment-113Panya CSE2No ratings yet
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument22 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers6012 ANILNo ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorAnonymous zaMNkL100% (1)
- Unit 1: Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDocument5 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorNehaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Department of Electronics & Comm - EnggDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 1: Department of Electronics & Comm - EnggJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Question: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionDocument9 pagesQuestion: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionSidh SinghNo ratings yet
- MPDocument34 pagesMPAbhinandan JainNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesDocument293 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesKumar ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- The 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument12 pagesThe 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureBernard MunyithyaNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument30 pages8085 ArchitecturegokulchandruNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument69 pagesArchitecture of 8085 Microprocessornamrata puranikNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument25 pagesUnit I PDFSomnath2014No ratings yet
- MPA UNIT 1 and 2Document48 pagesMPA UNIT 1 and 2Shiva Krishna KamjulaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Architecture: AccumulatorDocument6 pagesIntel 8085 Architecture: AccumulatorDipesh YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument7 pages1 8085 Microprocessor Architecturejosrichman75No ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - III 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - III 8051 MicrocontrollerAnonymous 4u5XkWGONo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument20 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorCarlnagum 123456789No ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument38 pages8085 Microprocessor Architectureashley panganNo ratings yet
- Prepared by NITHIN JOHN: Module-1Document15 pagesPrepared by NITHIN JOHN: Module-1Nithin JohnNo ratings yet
- 8085 Architecture: Control UnitDocument10 pages8085 Architecture: Control UnitsweetmemoriesneverdiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor EmulatorDocument10 pagesLab 1 - Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor EmulatorSaif Ullah100% (3)
- Class Notes 1 Microprocessor InterfacingDocument44 pagesClass Notes 1 Microprocessor InterfacingChol WelNo ratings yet
- Ec8691 MPMC Question BankDocument41 pagesEc8691 MPMC Question BankManimegalaiNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 S.Y. B.sc. ElectronicsDocument14 pages2023-24 S.Y. B.sc. Electronicsanil sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Concrete Textures v1 Catalog WebDocument42 pagesConcrete Textures v1 Catalog WebakashNo ratings yet
- 3 MicroprocessorDocument45 pages3 MicroprocessorKamran SaifNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesMicroprocessorReenaNo ratings yet
- Timing Diagram MP 8085Document45 pagesTiming Diagram MP 8085shubham kumarNo ratings yet
- 1981 Motorola Microprocessors Data ManualDocument1,182 pages1981 Motorola Microprocessors Data ManualBapeNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 8085 MicroprocessorDocument14 pagesCase Study - 8085 MicroprocessorChat MateNo ratings yet
- Buses: Transfer Bits Between Microprocessor and Other ComponentsDocument36 pagesBuses: Transfer Bits Between Microprocessor and Other ComponentsMd. Jabed AlamNo ratings yet
- Single Board InstructionsDocument121 pagesSingle Board InstructionsAlfredo MeurerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE and O Level Computer Science Computer Systems Workbook by David Watson, Helen WilliamsDocument97 pagesCambridge IGCSE and O Level Computer Science Computer Systems Workbook by David Watson, Helen WilliamsBluedenWave60% (5)
- 8051 Microcontroller DataDocument17 pages8051 Microcontroller DataTechqualcerNo ratings yet
- Assignment I - Winter Semester 2021-22Document10 pagesAssignment I - Winter Semester 2021-22HARDIK PANPALIYANo ratings yet
- ProcessorDocument22 pagesProcessorVishal ChetalNo ratings yet
- 352ccs - Lab ManualDocument48 pages352ccs - Lab ManualGaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Pic MicrocontrollerDocument68 pagesUnit Iv Pic MicrocontrollerShubham MadneNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Applications Syllabus For B.C.A. Under Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) For Candidates Admitted From 2019 - 2020Document39 pagesDepartment of Computer Applications Syllabus For B.C.A. Under Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) For Candidates Admitted From 2019 - 2020Saran VNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document12 pagesUnit 1Pallavi MNo ratings yet
- Cs3691 EmbeddedDocument30 pagesCs3691 EmbeddedSelva PriyaNo ratings yet
- 8085 ExptsDocument25 pages8085 Exptsnetij75375No ratings yet
- Embedded QB New 4Document23 pagesEmbedded QB New 4Sumithra IyappanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors (Bcst601)Document61 pagesMicroprocessors (Bcst601)surbhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 8051Document45 pagesUnit 2 8051KESSAVAN.M ECE20No ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument667 pagesComputer Architecturevishalchaurasiya360001No ratings yet
- 8051 MaterialDocument198 pages8051 Materialsupreetp555No ratings yet
- Course Title: Microcontroller and Interfacing Course Code:4214Document51 pagesCourse Title: Microcontroller and Interfacing Course Code:4214sreejith KBNo ratings yet
- Instruction Groups: The 8051 Has 255 Instructions - Every 8-Bit Opcode From 00 To FF Is Used Except For A5.Document30 pagesInstruction Groups: The 8051 Has 255 Instructions - Every 8-Bit Opcode From 00 To FF Is Used Except For A5.VLC350ZNo ratings yet
- Iso 14229 2 2021Document15 pagesIso 14229 2 2021Amine GRADANo ratings yet