Professional Documents
Culture Documents
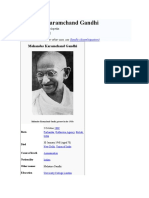
Mahatma Gandhi - Wikipedia
Uploaded by
Mister KantaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mahatma Gandhi - Wikipedia
Uploaded by
Mister KantaCopyright:
Available Formats
20/08/2023, 17:41 Mahatma Gandhi - Wikipedia
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi[pron 1] (2 October
Mahātmā
1869 – 30 January 1948) was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial
nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent Gandhi
resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's
independence from British rule. He inspired movements for
civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific
Mahātmā (from Sanskrit 'great-souled, venerable'), first
applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used
throughout the world.
Born and raised in a Hindu family in coastal Gujarat, Gandhi
trained in the law at the Inner Temple, London, and was
called to the bar at age 22 in June 1891. After two uncertain
years in India, where he was unable to start a successful law
practice, he moved to South Africa in 1893 to represent an
Indian merchant in a lawsuit. He went on to live in South
Africa for 21 years. It was here that Gandhi raised a family
and first employed nonviolent resistance in a campaign for
Gandhi in London, 1931
civil rights. In 1915, aged 45, he returned to India and soon
set about organising peasants, farmers, and urban labourers Born Mohandas
to protest against excessive land-tax and discrimination. Karamchand Gandhi
2 October 1869
Assuming leadership of the Indian National Congress in Porbandar,
1921, Gandhi led nationwide campaigns for easing poverty, Porbandar State,
expanding women's rights, building religious and ethnic
Kathiawar Agency,
amity, ending untouchability, and, above all, achieving
British India
swaraj or self-rule. Gandhi adopted the short dhoti woven
with hand-spun yarn as a mark of identification with India's Died 30 January 1948
rural poor. He began to live in a self-sufficient residential (aged 78)
community, to eat simple food, and undertake long fasts as a New Delhi, Dominion
means of both introspection and political protest. Bringing of India
anti-colonial nationalism to the common Indians, Gandhi led
them in challenging the British-imposed salt tax with the Cause of Assassination
400 km (250 mi) Dandi Salt March in 1930 and in calling for death (gunshot wounds)
the British to quit India in 1942. He was imprisoned many Monuments Raj Ghat
times and for many years in both South Africa and India.
Gandhi Smriti
Gandhi's vision of an independent India based on religious Other names Bapu
pluralism was challenged in the early 1940s by a Muslim
Citizenship British Empire
nationalism which demanded a separate homeland for
Muslims within British India. In August 1947, Britain (1869–1947)
granted independence, but the British Indian Empire was Dominion of India
partitioned into two dominions, a Hindu-majority India and (1947–1948)
a Muslim-majority Pakistan. As many displaced Hindus,
Alma mater Samaldas Arts
Muslims, and Sikhs made their way to their new lands,
religious violence broke out, especially in the Punjab and College[a]
Bengal. Abstaining from the official celebration of
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mahatma_Gandhi 1/55
20/08/2023, 17:41 Mahatma Gandhi - Wikipedia
independence, Gandhi visited the affected areas, attempting University College
to alleviate distress. In the months following, he undertook London[b]
several hunger strikes to stop the religious violence. The last
Inns of Court School
of these was begun in Delhi on 12 January 1948 when he was
of Law
78. The belief that Gandhi had been too resolute in his
defense of both Pakistan and Indian Muslims spread among Occupations Lawyer · anti-
some Hindus in India. Among these was Nathuram Godse, a colonialist · political
militant Hindu nationalist from Pune, western India, who ethicist
assassinated Gandhi by firing three bullets into his chest at
Years active 1893–1948
an interfaith prayer meeting in Delhi on 30 January 1948.
Gandhi's birthday, 2 October, is commemorated in India as Era British Raj
Gandhi Jayanti, a national holiday, and worldwide as the Known for Leadership of the
International Day of Nonviolence. Gandhi is considered to be campaign for
the Father of the Nation in post-colonial India. During
India's
India's nationalist movement and in several decades
independence
immediately after, he was also commonly called Bapu
from British rule
(Gujarati endearment for "father," roughly "papa,"[2]
"daddy."[3]). Nonviolent
resistance
Early life and background Notable work The Story of My
Experiments with
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi[4][5] was born on 2 October Truth
1869[6] into a Gujarati Hindu Modh Bania family[7][8] in Political party Indian National
Porbandar (also known as Sudamapuri), a coastal town on Congress (1920–
the Kathiawar Peninsula and then part of the small princely 1934)
state of Porbandar in the Kathiawar Agency of the British
Raj. His father, Karamchand Uttamchand Gandhi (1822– Movement Indian independence
1885), served as the dewan (chief minister) of Porbandar movement
state.[9][10] His family originated from the then village of Spouse Kasturba Gandhi
Kutiana in what was then Junagadh State.[11]
(m. 1883; died 1944)
Although he only had an elementary education and had Children Harilal · Manilal ·
previously been a clerk in the state administration, Ramdas · Devdas
Karamchand proved a capable chief minister.[12] During his Parents Karamchand Gandhi
tenure, he married four times. His first two wives died young, (father)
after each had given birth to a daughter, and his third
Putlibai Gandhi
marriage was childless. In 1857, he sought his third wife's
permission to remarry; that year, he married Putlibai (1844– (mother)
1891), who also came from Junagadh,[12] and was from a Relatives See Family of
Pranami Vaishnava family.[13] Karamchand and Putlibai had Mahatma Gandhi
three children over the ensuing decade: a son, Laxmidas (c. C. Rajagopalachari
1860–1914); a daughter, Raliatbehn (1862–1960); and (father-in-law of
another son, Karsandas (c. 1866–1913).[14][15] Gandhi's son
Devdas)
On 2 October 1869, Putlibai gave birth to her last child,
Mohandas, in a dark, windowless ground-floor room of the Awards Time Person of the
Gandhi family residence in Porbandar city. As a child, Year (1930)
Gandhi was described by his sister Raliat as "restless as
mercury, either playing or roaming about. One of his President of the Indian National
Congress
favourite pastimes was twisting dogs' ears."[16] The Indian
classics, especially the stories of Shravana and king In office
Harishchandra, had a great impact on Gandhi in his December 1924 – April 1925
childhood. In his autobiography, he states that they left an
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mahatma_Gandhi 2/55
You might also like
- Mahatma Gandhi - WikipediaDocument4 pagesMahatma Gandhi - WikipediaKumud100% (1)
- Mahatma Gandhi - Leader of Indian Independence MovementDocument6 pagesMahatma Gandhi - Leader of Indian Independence MovementMarvin BerrensteinNo ratings yet
- Times 3Document2 pagesTimes 3Thokchom TennysonNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi: "Gandhi" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesMahatma Gandhi: "Gandhi" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeSamir DesaiNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument4 pagesMahatma GandhiSanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument11 pagesMahatma GandhiTawfiqMehranNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument2 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiPalak PathakNo ratings yet
- RRRRRDocument1 pageRRRRRjohnalenonaNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument14 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhinandanaNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument4 pagesMahatma Gandhimishraakash774No ratings yet
- Gandhi - The Father of Indian IndependenceDocument3 pagesGandhi - The Father of Indian IndependenceAnmol SenNo ratings yet
- Bania: Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (PronouncedDocument12 pagesBania: Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (Pronounced2k2j2No ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi: Leader of Indian Independence MovementDocument10 pagesMahatma Gandhi: Leader of Indian Independence MovementMohd ShoabNo ratings yet
- Gandhi's Life and LegacyDocument41 pagesGandhi's Life and LegacyRayudu VVSNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument4 pagesMahatma Gandhisahil_bali86No ratings yet
- MG 01Document1 pageMG 01Navneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Gandhi: Leader of Indian Independence MovementDocument3 pagesGandhi: Leader of Indian Independence MovementPrasad PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Gandhi's Life and Impact as Leader of Indian IndependenceDocument3 pagesGandhi's Life and Impact as Leader of Indian IndependenceRudolph Antony ThomasNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument8 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiRichi SinghNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: Swaraj Dhoti CharkhaDocument1 pageMohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: Swaraj Dhoti CharkhaVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi - Leader of Indian Independence MovementDocument1 pageMahatma Gandhi - Leader of Indian Independence MovementObamaNo ratings yet
- Tamil BooksDocument4 pagesTamil Booksharikr2006No ratings yet
- Gandhi's Life and ImpactDocument1 pageGandhi's Life and Impactsathiya_preeNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument12 pagesMahatma Gandhi32 THAPODHAN REDDY BANDANo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (Pron 1)Document1 pageMohandas Karamchand Gandhi (Pron 1)Manmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- GandhiDocument34 pagesGandhiframesclose100% (2)
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: MahatmaDocument2 pagesMohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: MahatmaAwaludin MohamadNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi: Quit India in 1942. He Was Imprisoned For Many Years, Upon Many Occasions, inDocument2 pagesMahatma Gandhi: Quit India in 1942. He Was Imprisoned For Many Years, Upon Many Occasions, inMuhammad Tri RizkiNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi: "Gandhi" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesMahatma Gandhi: "Gandhi" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeBineet KumarNo ratings yet
- GandhiDocument20 pagesGandhiAnbel LijuNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument7 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiNithin KiranNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument57 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiAnurag BhargavaNo ratings yet
- MAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Document27 pagesMAHATMA GANDHI - ppt1111Patricia JosephNo ratings yet
- Mohandas GandhiDocument38 pagesMohandas GandhiFaizan100% (1)
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument10 pagesMohandas Karamchand Gandhikiranchaudharik2No ratings yet
- Wike Pedia GandhiDocument34 pagesWike Pedia Gandhidoors-and-windowsNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: / Ɡ Ɑ N D I, Ɡ Æ NDocument1 pageMohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: / Ɡ Ɑ N D I, Ɡ Æ NSantosh DineshNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument1 pageMohandas Karamchand GandhiJoshua WacanganNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument78 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiKrishan Kant100% (1)
- Mahatma Gandhi Biography: Quick FactsDocument8 pagesMahatma Gandhi Biography: Quick FactsdsdjdjsdNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument18 pagesMahatma GandhiPritish BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- Biografi Mohandas KaramchandDocument2 pagesBiografi Mohandas KaramchandAsef LiantoNo ratings yet
- Gandhi PDFDocument16 pagesGandhi PDFmadhaviNo ratings yet
- Gandhiji or RathvaDocument16 pagesGandhiji or RathvaDevansu RathvaNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Gandhi Biography: Early YearsDocument16 pagesMohandas Gandhi Biography: Early YearsskalaNo ratings yet
- Gandhi PDFDocument16 pagesGandhi PDFJayalakshimi JayaNo ratings yet
- Ohandas Karamchand Gandhi (: SwarajDocument2 pagesOhandas Karamchand Gandhi (: SwarajPeter KhanNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument27 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiAditya KavuluriNo ratings yet
- Gandhi's Inspiring Leadership of Non-Violence in IndiaDocument5 pagesGandhi's Inspiring Leadership of Non-Violence in IndiaPablo JuarezNo ratings yet
- Mahatma GandhiDocument8 pagesMahatma GandhiPUIN AMEZQUITA MONICA JULIETHNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi: Civil Rights Activist in South Africa (1893-1914)Document3 pagesMahatma Gandhi: Civil Rights Activist in South Africa (1893-1914)Rahul Chandran KarunagappallyNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Freedom FighterDocument27 pagesTop 10 Freedom Fightermunishmalik1No ratings yet
- Mahatmagandhi 141110074418 Conversion Gate02Document19 pagesMahatmagandhi 141110074418 Conversion Gate02JLNo ratings yet
- All About INDIADocument22 pagesAll About INDIAJohn Rey LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Jay - GhandiDocument2 pagesJay - GhandiMary Joyce Bautista SilverioNo ratings yet
- Gandhi's Early Life and Struggles in South AfricaDocument3 pagesGandhi's Early Life and Struggles in South AfricaNikunj ShahNo ratings yet
- Mahatama GandhiDocument31 pagesMahatama Gandhipankaj singhNo ratings yet
- EBook - What Is BlockchainDocument17 pagesEBook - What Is BlockchainMister KantaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 & 5Document8 pagesExperiment 4 & 5Mister KantaNo ratings yet
- C++ Cheat Sheet: SyntaxDocument35 pagesC++ Cheat Sheet: SyntaxVicente BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Python Notes/Cheat Sheet: Operator FunctionalityDocument7 pagesPython Notes/Cheat Sheet: Operator FunctionalityJohnyMacaroniNo ratings yet
- Man Who Sailed Up The Ganges and Died in Nagpur - Times of IndiaDocument4 pagesMan Who Sailed Up The Ganges and Died in Nagpur - Times of Indiaamit_264No ratings yet
- Unclaimed InterimDocument126 pagesUnclaimed InterimSayyed Mohsin Aamer0% (1)
- Dance in IndiaDocument4 pagesDance in Indiaprofessor_manojNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Forecast MumbaiDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment and Forecast MumbaihariluvsuNo ratings yet
- New Gratuity 7,00,000 PRC 2010 G.ODocument3 pagesNew Gratuity 7,00,000 PRC 2010 G.OSEKHARNo ratings yet
- NVS Ro Shilong JNVST Result PDFDocument446 pagesNVS Ro Shilong JNVST Result PDFHabibul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Mpse 001Document4 pagesMpse 001maramara2No ratings yet
- Medal Detail DGP 05012017Document82 pagesMedal Detail DGP 05012017Kishor JaniNo ratings yet
- 10 BJP Leaders Accused of Rape and Sexual OffensesDocument7 pages10 BJP Leaders Accused of Rape and Sexual OffensesTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Simone TataDocument5 pagesSimone TataHarry Khanna100% (1)
- Vestige Uttarakhand Branch PDF - DLCPDocument4 pagesVestige Uttarakhand Branch PDF - DLCPMd FirdoshNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mughal Administrative Institutions: Mansab, Jagir Land Revenue SystemDocument6 pagesEvolution of Mughal Administrative Institutions: Mansab, Jagir Land Revenue SystemNiranjan BhuyanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Mega Merger of SBI With Its Five SubsidariesDocument4 pagesA Case Study On Mega Merger of SBI With Its Five SubsidariesPooja MauryaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Trade Union Act 1926Document10 pagesObjectives of Trade Union Act 1926UTKARSH MISHRANo ratings yet
- Article 32060Document10 pagesArticle 32060ramchandragiri828109No ratings yet
- Home Page TatamotorDocument3 pagesHome Page Tatamotorsaur1No ratings yet
- List of NBFC-Peer to Peer lending companiesDocument3 pagesList of NBFC-Peer to Peer lending companiesDhananjayan GopinathanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Americanization (Americanisation)Document24 pagesPresentation On Americanization (Americanisation)Akshat BoudhNo ratings yet
- Assignments Submission Guidelines For June 2023 - RC Delhi-1Document4 pagesAssignments Submission Guidelines For June 2023 - RC Delhi-1ruby rubyNo ratings yet
- Office Locations: Delhi, Gurgaon, Noida & FaridabadDocument22 pagesOffice Locations: Delhi, Gurgaon, Noida & FaridabadhemkumargargNo ratings yet
- LTCDocument1 pageLTCNitin PatneNo ratings yet
- Telangana HistoryDocument6 pagesTelangana HistoryKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- List of National Highways in India by Old Highway Number - Wikipedia PDFDocument28 pagesList of National Highways in India by Old Highway Number - Wikipedia PDFROBIN SHARMANo ratings yet
- Social Science Sec 2024-25Document65 pagesSocial Science Sec 2024-25Aksh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chinese String of Pearls TheoryDocument1 pageChinese String of Pearls TheoryTigran YepremyanNo ratings yet
- Ambedkar ScansDocument9 pagesAmbedkar ScansVikram Raj Singh0% (1)
- Indian English Lit - Its Unique QualitiesDocument6 pagesIndian English Lit - Its Unique QualitiesKrystian Kosowski100% (2)
- Respondent Case Table Highlights Constitutional and Statutory CasesDocument5 pagesRespondent Case Table Highlights Constitutional and Statutory CasesUditanshu MisraNo ratings yet
- Pakistan History Events MCQs 1857-1947Document5 pagesPakistan History Events MCQs 1857-1947Haider Abbas0% (1)
- Electronic Banking in IndiaDocument1 pageElectronic Banking in IndiaJatinder KaurNo ratings yet