Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of Computing Paradigm
Uploaded by
chirayush chakrabortyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of Computing Paradigm
Uploaded by
chirayush chakrabortyCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of Computing Paradigm
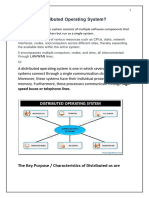
● Distributed Computing: A distributed computing system consists of multiple software
components that are on multiple computers but run as a single system. Computers in distributed
systems can be physically close together by a local network or they can be geographically distant
connected by a wide area network.
● Cluster Computing: A cluster is a type of parallel computing system where a collection of
interconnected stand alone computers works together as a single integrated computing
resource. It improves speed, reliability and cost effectiveness over a single computer.
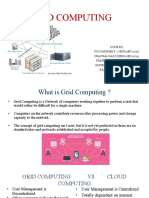
● Grid Computing: It enables the virtualization of Distributed computing and data resources such
as processing speed, network bandwidth and storage capacity to create a single system image,
granting users and applications seamless access to vast IT capabilities.
Types of Grid Computing:
1) Computational Grid: These grids provide secure access to a huge pool of shared processing power
suitable for high throughput applications and intensive computing.
2) Data Grid: It provides an infrastructure to support large data storage, data discovery, data handling
and data manipulation of large volumes of data stored in various heterogeneous databases and file
systems.
3) Collaboration Grid: With the advent of the internet, there is increased demand for collaboration. This
is done using a collaboration grid. Users can work on different components of a project without
disclosing their proprietary technologies.
4) Network Grid: It provides fault tolerant and high performance communication services. Each grid
node works as a data router between two communication points, providing data caching to speed up
communication between such points.
5) Utility Grid: In Utility grid, apart from data, software or other resources are shared. The major services
provided through utility grids are software and special equipment.
● Utility Computing: It is a model in which the service provider makes computing resource and
infrastructure management available to customers as needed and charges them for specific
usage rather than flat rate. It also facilitates computational resources to be rented, as a result
very low cost is incurred.
You might also like
- NPTEL Cloud Computing NotesDocument26 pagesNPTEL Cloud Computing Notesrupa reddy0% (1)
- Grid ComputingDocument24 pagesGrid ComputingkomalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelDocument9 pagesUnit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelRitu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CC Cheat MidsemDocument12 pagesCC Cheat Midsemamsrivastava2002No ratings yet
- Work 2Document40 pagesWork 2ddamuliracharles88No ratings yet
- Grid ArchitectureDocument19 pagesGrid ArchitectureBittu VermaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presented By: Sehar Sultan M.SC (CS) 4 Semester UAFDocument33 pagesSeminar Presented By: Sehar Sultan M.SC (CS) 4 Semester UAFSahar SultanNo ratings yet
- Grid ComputingDocument28 pagesGrid Computinggoutham_nrNo ratings yet
- The VPC Offers The Function of The PrivateDocument3 pagesThe VPC Offers The Function of The PrivatedaliasobhiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 90%Document9 pagesUnit-1 90%vishal roshanNo ratings yet
- Module1 1642682811816Document46 pagesModule1 1642682811816bhat.prateek97No ratings yet
- Grid Architecture and Its Relation Through Various DistributedDocument27 pagesGrid Architecture and Its Relation Through Various DistributedrohitNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Question BankDocument54 pagesCloud Computing - Question BankNishtha SinghNo ratings yet
- Distributed Operating SystemDocument18 pagesDistributed Operating SystemRajni ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Commuinity MGrid ComputingDocument4 pagesCommuinity MGrid Computingsowarav742No ratings yet
- Overview of The Computing Paradigm: 1.1 Recent Trends in Distributed ComputingDocument5 pagesOverview of The Computing Paradigm: 1.1 Recent Trends in Distributed ComputingjojotitiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AssignmentDocument11 pagesCloud Computing AssignmentYosief DagnachewNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Grid Computing and Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesDifference Between Grid Computing and Cloud Computingusama ijazNo ratings yet
- Lec-1-Distributed Operating System Why When HowDocument6 pagesLec-1-Distributed Operating System Why When HowDA AlSSSNo ratings yet
- Computing PradigmDocument10 pagesComputing PradigmHtun Aung LynnNo ratings yet
- Grid - and - Cloud Computing - Important - Questions - Unit - 1 - Part - ADocument5 pagesGrid - and - Cloud Computing - Important - Questions - Unit - 1 - Part - ASridevi SivakumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Overview of Grid ComputingDocument16 pagesUNIT-1: Overview of Grid ComputingFake SinghNo ratings yet
- Grid ComputingDocument12 pagesGrid ComputingMohammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- AC VivaDocument7 pagesAC VivadavidNo ratings yet
- Group No 13Document15 pagesGroup No 13Waleed Abdullah2k19 EE603No ratings yet
- CSE 423 Virtualization and Cloud Computinglecture0Document16 pagesCSE 423 Virtualization and Cloud Computinglecture0Shahad ShahulNo ratings yet
- Cloud Technologies: Grid ComputingDocument13 pagesCloud Technologies: Grid ComputingNarmatha ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing FinalDocument18 pagesGrid Computing FinalRamya KashyapNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 & Ii GCCDocument37 pagesUnit-1 & Ii GCCpabithasNo ratings yet
- Study and Applications of Cluster Grid and Cloud Computing: Umesh Chandra JaiswalDocument6 pagesStudy and Applications of Cluster Grid and Cloud Computing: Umesh Chandra JaiswalIJERDNo ratings yet
- FINALGrid Computing Seminar ReportDocument34 pagesFINALGrid Computing Seminar ReportMiraj Kumar100% (3)
- Cloud Computing Is The On-Demand Availability ofDocument8 pagesCloud Computing Is The On-Demand Availability ofVovNo ratings yet
- CCDocument4 pagesCCSandeepan KalitaNo ratings yet
- Power System Control Centers Using Cloud Computing: Shweta Saha Prof. S. Margret AnounciaDocument6 pagesPower System Control Centers Using Cloud Computing: Shweta Saha Prof. S. Margret AnounciaRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing 1Document41 pagesCloud Computing 1walid.bajawriNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing & Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesGrid Computing & Cloud ComputingZohaib ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing 1Document11 pagesGrid Computing 1DannyNo ratings yet
- Distributed SystemsDocument67 pagesDistributed SystemsNitesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- GCC QBDocument16 pagesGCC QBSherril Vincent100% (1)
- CCunit 1Document69 pagesCCunit 1aman kumarNo ratings yet
- Distributed ProgrammingSolutionsDocument20 pagesDistributed ProgrammingSolutionsmassablaisetamfuNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing Seminar ReportDocument36 pagesGrid Computing Seminar ReportChennam Ranjit Reddy100% (1)
- MCA 502 - Cloud: Computing Theory 80 + 20 Marks Lab: 80 + 20 MarksDocument33 pagesMCA 502 - Cloud: Computing Theory 80 + 20 Marks Lab: 80 + 20 MarkskvrNo ratings yet
- Grid and Cloud Full NotesDocument80 pagesGrid and Cloud Full NotesVive Kowsal YanissNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud Computinglederod707No ratings yet
- CC Question Bank All UnitsDocument28 pagesCC Question Bank All Unitsasmitha0567No ratings yet
- Boundary and Communication ControlsDocument6 pagesBoundary and Communication Controlsmercymatsvayi2001No ratings yet
- Ref 6 ShivDocument7 pagesRef 6 ShivAkhilesh KhareNo ratings yet
- Grid Computing: Qis College Ofenginering&TechnologyDocument12 pagesGrid Computing: Qis College Ofenginering&Technologyapi-19799369No ratings yet
- CSC - 406 - 1 - Intro To Distributed SystemDocument22 pagesCSC - 406 - 1 - Intro To Distributed SystemSamadNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument53 pagesUnit INameis GirishNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes (UNIT - 01)Document10 pagesCloud Computing Notes (UNIT - 01)BAD BOYSNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Distributed SystemsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Distributed SystemszanchoozanchooNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Grid ComputingDocument55 pagesUNIT 1 Grid ComputingAbhishek Tomar67% (3)
- Cloud Infrastructure and Security NotesDocument13 pagesCloud Infrastructure and Security Notesisha gaonkarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Cloud Computing (Nep) PDFDocument36 pagesUnit-1 Cloud Computing (Nep) PDFbehiro7856100% (1)
- Differences Unit 1Document7 pagesDifferences Unit 1manpreet singhNo ratings yet
- CC Notes UNIT 1Document21 pagesCC Notes UNIT 1amanbabu839383607No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Cloud, Cluster and Grid ComputingDocument2 pagesDifference Between Cloud, Cluster and Grid Computingchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Diagrams Module-1Document4 pagesDiagrams Module-1chirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- DC Machine - AssignmentDocument1 pageDC Machine - Assignmentchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics & Design (MECH1052) : 1. Basic IntroductionDocument28 pagesEngineering Graphics & Design (MECH1052) : 1. Basic Introductionchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet