Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Optimizing Cloud Native Applications With Autonomic Features Empowering Efficiency and Scalability 20230907170327jb2e
Uploaded by
Mohammad Yadin.N0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesCloud-native applications are built using microservices architecture and designed to run on cloud platforms. They are highly scalable, resilient, and can be easily deployed and managed. Autonomic computing refers to the ability of a system to self-manage, self-optimize, and self-heal. It enables cloud-native applications to automatically adjust resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance. Cloud-native applications leverage autonomic features such as auto-scaling, auto-recovery, and auto-optimization to dynamically allocate resources, recover from failures, and optimize performance.
Original Description:
Original Title
Optimizing Cloud Native Applications With Autonomic Features Empowering Efficiency and Scalability 20230907170327Jb2e
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCloud-native applications are built using microservices architecture and designed to run on cloud platforms. They are highly scalable, resilient, and can be easily deployed and managed. Autonomic computing refers to the ability of a system to self-manage, self-optimize, and self-heal. It enables cloud-native applications to automatically adjust resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance. Cloud-native applications leverage autonomic features such as auto-scaling, auto-recovery, and auto-optimization to dynamically allocate resources, recover from failures, and optimize performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesOptimizing Cloud Native Applications With Autonomic Features Empowering Efficiency and Scalability 20230907170327jb2e
Uploaded by
Mohammad Yadin.NCloud-native applications are built using microservices architecture and designed to run on cloud platforms. They are highly scalable, resilient, and can be easily deployed and managed. Autonomic computing refers to the ability of a system to self-manage, self-optimize, and self-heal. It enables cloud-native applications to automatically adjust resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance. Cloud-native applications leverage autonomic features such as auto-scaling, auto-recovery, and auto-optimization to dynamically allocate resources, recover from failures, and optimize performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Enhancement of Cloud-
Native Applications with
Autonomic Features
Today, we're talking about a new way to
INTRODUCTION make software, called "cloud-native
applications." But don't worry, it's not as
complicated as it sounds! Imagine you want
to build a super-fast, flexible, and reliable
app. That's where cloud-native comes in. It's
like building a car specifically designed for
the smoothest roads. So, why is this
important? Because in our fast-paced
world, we need software that can keep up.
Cloud-native apps help us do things
quicker, cheaper, and better. Whether
you're a tech wizard or just curious,
understanding cloud-native is like learning
the secret recipe for building software that
works amazingly well in the modern world.
Stick around, and we'll break it down step
by step. Cloud-native is the future, and it's
simpler than you might think!
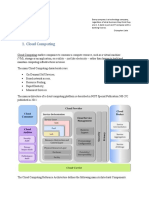
Cloud native applications are built using
What are Cloud Native Applications? microservices architecture and are
designed to run on cloud platforms. They
are highly scalable, resilient, and can be
easily deployed and managed.
Benefits of Cloud Native Applications
Cloud native applications offer
several benefits, including
flexibility, agility, and cost
efficiency. They enable
organizations to quickly adapt to
changing business needs and
scale resources as required.
Autonomic computing refers to the ability
of a system to self-manage, self-optimize,
Autonomic Computing and self-heal. It enables cloud native
applications to automatically adjust
resources based on demand, ensuring
optimal performance.
AUTONOMIC COMPUTING OVERVIEW
Autonomic computing is an approach to building self-managing
systems that can operate with minimal human intervention. It's like
giving your computer or application some self-awareness and decision-
making abilities.
In relevance to modern applications, autonomic computing is
essential because it helps software systems handle the complexity of
today's dynamic IT environments. It allows applications to:
Self-Heal: Autonomic systems can detect and fix issues on their own,
reducing downtime and improving reliability.
Self-Optimize: They can adjust their performance to meet changing
demands, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Self-Protect: Autonomic systems can detect and respond to security
threats automatically, enhancing overall security
Self-Configure: They can adapt to new environments or scale
up/down as needed without manual intervention, improving
scalability.
In a world where technology evolves rapidly, autonomic computing
enables applications to remain efficient, secure, and adaptable,
ultimately delivering a better experience for users and reducing
operational burdens for organizations.
Autonomic Features in Cloud Native Applications
Cloud native applications
leverage autonomic features
such as auto-scaling, auto-
recovery, and auto-optimization.
These features enable
applications to dynamically
allocate resources, recover from
failures, and optimize
performance.
Autonomic scaling allows cloud native
applications to automatically adjust Efficiency through Autonomic Scaling
resources based on workload. It ensures
efficient resource utilization and eliminates
the need for manual scaling, saving time
and costs.
Self-Recovery and Resilience
Autonomic features enable cloud
native applications to self-
recover from failures and
maintain resilience. They
automatically detect failures,
initiate recovery processes, and
ensure continuous availability of
the application.
Scalability and Elasticity
Cloud native applications can
easily scale horizontally by adding
more instances of microservices.
This scalability ensures that the
application can handle increased
user demand without
compromising performance.
Autonomic features in cloud native
Optimizing Performance with Autonomic applications help optimize performance by
Features
automatically tuning resources, balancing
workloads, and optimizing
configurations. This ensures that the
application operates at peak efficiency.
Case Study : IBM's Autonomic
CASE STUDIES Computing Initiative
1.IBM's Autonomic Computing Initiative, launched
in the early 2000s, aimed to create self-managing
computing systems.
2.They developed technologies like IBM
Tivoli, which used autonomic principles to
monitor, diagnose, and optimize IT
resources.
3.This initiative demonstrated the
feasibility of autonomic computing in
large-scale enterprise environments,
improving system reliability and reducing
operational costs.
Challenges and Considerations 1.Complexity: Developing autonomic systems can
be complex, requiring expertise in both
application domain and autonomic computing
principles.
2.Integration: Integrating autonomic features
with existing systems may be challenging and
may require significant modifications.
3.Security: Ensuring the security of autonomic
components is critical, as they may have access to
sensitive system functions.
4.Monitoring and Debugging: Debugging
autonomic systems can be difficult, as their
actions are automated. Effective monitoring and
debugging tools are essential.
5.Cost: Implementing autonomic features may
require an investment in new technologies and
training, impacting project budgets.
Conclusion
Optimizing cloud native
applications with autonomic
features empowers organizations
to achieve efficiency, scalability,
and resilience. By leveraging
these features, organizations can
unlock the full potential of cloud
native applications and drive
business success.
Thanks!
Do you have
any
questions?
You might also like
- Magic Bullets PreviewDocument50 pagesMagic Bullets PreviewLove Systems88% (16)
- IBM Turbonomic 101 Client PresentationDocument17 pagesIBM Turbonomic 101 Client Presentationwhitsters_onit2925No ratings yet
- Azure Fundamentals - Condensed Prep NotesDocument105 pagesAzure Fundamentals - Condensed Prep NotesUserNo ratings yet
- Cloud MobilityDocument18 pagesCloud MobilityYo Gain DrawNo ratings yet
- Client Management - AbsoluteDocument6 pagesClient Management - Absoluteinfosec10No ratings yet
- Required Data For Generator Decrement Curve PDFDocument2 pagesRequired Data For Generator Decrement Curve PDFgilbertomjcNo ratings yet
- Amazon VRF Site Monitor Software Instruction 130131 PDFDocument8 pagesAmazon VRF Site Monitor Software Instruction 130131 PDFReginaldo LealNo ratings yet
- All Model LCDDocument240 pagesAll Model LCDlaxmansonawane75% (12)
- Cloud Native DevelopmentDocument13 pagesCloud Native DevelopmentSiddhant BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation Cloud Infrastructure: EssentialsDocument15 pagesNext-Generation Cloud Infrastructure: EssentialsHussein ElgamalNo ratings yet
- Digital Craftsmen Automation Whitepaper V2Document9 pagesDigital Craftsmen Automation Whitepaper V2ksnarookaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Infrastructure and AutomationDocument100 pagesModule 7 - Infrastructure and AutomationDaniilNo ratings yet
- Created GCC Unit 4Document22 pagesCreated GCC Unit 4shiva751514No ratings yet
- DEVASC Module 7Document112 pagesDEVASC Module 7JUAN MAURICIO QUEZADA JAMASMIENo ratings yet
- Lead in A Hybrid Cloud World With Smarter Application ManagementDocument13 pagesLead in A Hybrid Cloud World With Smarter Application ManagementjamesNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 2 Imp QuestionsDocument10 pagesCC Unit 2 Imp QuestionsSahana UrsNo ratings yet
- With Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesWith Cloud ComputingGeby LengguNo ratings yet
- Cloud AssignmentDocument22 pagesCloud Assignmentsoftware projectNo ratings yet
- Management of Info System Term PaperDocument4 pagesManagement of Info System Term PaperAnand DeshmaneNo ratings yet
- AWS Modern Applications EbookDocument23 pagesAWS Modern Applications EbookAndreas GalazisNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Private Cloud SecurityDocument12 pagesA Guide To Private Cloud Securitysafiya marwaNo ratings yet
- Modern Apps Need Modern OpsDocument11 pagesModern Apps Need Modern OpsHadi Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument21 pagesOriginalKylie NelsonNo ratings yet
- Choose An Automation Tool Ebook Red Hat DeveloperDocument22 pagesChoose An Automation Tool Ebook Red Hat DevelopernetwizardssNo ratings yet
- AWS Cloud ArchitecturesDocument14 pagesAWS Cloud ArchitecturesdantsonNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesMush0911No ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesThien LuuNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicessarfraznawazbrohiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesMush0911No ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Jinesh Varia Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServiceskenbusyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AnswerDocument5 pagesCloud Computing Answer07.ravishNo ratings yet
- CC 1Document41 pagesCC 1Esha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Name: Tanisha Registration No: 16bce1357 Prof: Shyamala Mam: Data Centre AutomationDocument6 pagesName: Tanisha Registration No: 16bce1357 Prof: Shyamala Mam: Data Centre AutomationTanisha BittuNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesTOPLAPNo ratings yet
- Cloud Architectures: Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesDocument14 pagesCloud Architectures: Technology Evangelist Amazon Web ServicesSahar AbduljalilNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide To Modern ApmDocument10 pagesThe Essential Guide To Modern ApmKunto UtoroNo ratings yet
- Session SlidesDocument15 pagesSession SlidesAIR CATALOGNo ratings yet
- Simplify and Automate Application Resource Management: With Cisco Intersight Workload OptimizerDocument2 pagesSimplify and Automate Application Resource Management: With Cisco Intersight Workload OptimizerKeluarga ZulfanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Ready Applications - Cource Notes - 1-6Document28 pagesCloud Ready Applications - Cource Notes - 1-6Vadim CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web ServicesDocument16 pagesAmazon Web Servicesarmeena anjumNo ratings yet
- App Modernization Field GuideDocument36 pagesApp Modernization Field GuideJhonatan Ríchard RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AUDocument11 pagesCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Portal For SmesDocument10 pagesCloud Computing Portal For SmesdreamingtechNo ratings yet
- Application Modernization On IBM PowerDocument16 pagesApplication Modernization On IBM Powercheonsoo.leeNo ratings yet
- Us Deloitte and Ibm App Modernization Field GuideDocument34 pagesUs Deloitte and Ibm App Modernization Field GuideRakesh RajNo ratings yet
- Company DOCUMENTATIONDocument61 pagesCompany DOCUMENTATIONRANJITH KUMAR RAMINENINo ratings yet
- Adv DBMS Assgn CA 1Document10 pagesAdv DBMS Assgn CA 1sd.21u10564No ratings yet
- Testing The Cloud: White PaperDocument4 pagesTesting The Cloud: White PaperalifatehitqmNo ratings yet
- 1 Evolution of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pages1 Evolution of Cloud ComputingSantanuNo ratings yet
- Five Essentials of Modern IT Infrastructure ManagementDocument11 pagesFive Essentials of Modern IT Infrastructure Managementgppp100% (1)
- Unit 1 Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Cloud Computingjaysukhv234No ratings yet
- Enterprise CloudDocument12 pagesEnterprise CloudNitesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC OpenManage Enterprise Solution BriefDocument2 pagesDell EMC OpenManage Enterprise Solution BriefPaulo Victor SilvaNo ratings yet
- ISAD GROUP 1 Virtualization and Cloud Computing Environment and Business Application System 1Document47 pagesISAD GROUP 1 Virtualization and Cloud Computing Environment and Business Application System 1jordanishra100% (1)
- Cloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Document7 pagesCloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Srini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Microservices: Submitted For Partial Fulfilment of Credits For MCA-362Document16 pagesSeminar On Microservices: Submitted For Partial Fulfilment of Credits For MCA-362Jesica TandonNo ratings yet
- Microservices Parte 12Document23 pagesMicroservices Parte 12Caio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Assessment IVDocument12 pagesCloud Computing: Assessment IVArindam MondalNo ratings yet
- App Modernization Field GuideDocument36 pagesApp Modernization Field GuideSurajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Devansh Presentation 1-2Document10 pagesDevansh Presentation 1-2Agrawal DevanshNo ratings yet
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document5 pagesWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- Arista Cloudvision®: Cloud Automation For Everyone: White PaperDocument15 pagesArista Cloudvision®: Cloud Automation For Everyone: White PaperAnirudha BhamidipatiNo ratings yet
- Information System For ManagersDocument12 pagesInformation System For ManagersTangerine Ila TomarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToDocument2 pagesA Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToPaulo Taganas MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Torch TorrentDocument1 pageTorch TorrentAbhinav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- IP ChartDocument693 pagesIP ChartmattsdNo ratings yet
- M2: Manuscript Guidelines: Lady Stephenson Library Newcastle Upon Tyne Ne6 2pa UnitedDocument4 pagesM2: Manuscript Guidelines: Lady Stephenson Library Newcastle Upon Tyne Ne6 2pa UnitednaidademNo ratings yet
- Me2402 - CimDocument1 pageMe2402 - CimhariccetNo ratings yet
- VMW VCP DCV 8 Exam GuideDocument12 pagesVMW VCP DCV 8 Exam GuideinaccuratetranslatorNo ratings yet
- Stratus FtServer ZTC EverRun For L&TDocument49 pagesStratus FtServer ZTC EverRun For L&TAshok CANo ratings yet
- Suricata - Ubuntu Getting Started With SuricataDocument6 pagesSuricata - Ubuntu Getting Started With SuricataZosemu BotNo ratings yet
- Big Data: New Tricks For Econometrics: Hal R. VarianDocument55 pagesBig Data: New Tricks For Econometrics: Hal R. VarianIVETH GUADALUPE CORONA GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.3at Power Over Gigabit Ethernet Extender: POE-E201Document3 pagesIEEE 802.3at Power Over Gigabit Ethernet Extender: POE-E201alejandroNo ratings yet
- FishFillets WalkthroughDocument47 pagesFishFillets WalkthroughHamad_SpiderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)Document10 pagesAnatomy of Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)Ecuaman EcuamanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Medium Template Class FileDocument4 pagesCambridge Medium Template Class FileFresh Prince Of NigeriaNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument12 pagesBrochuregoangagoanga99No ratings yet
- Steca PR 10 30 Specification enDocument1 pageSteca PR 10 30 Specification ensolaris-novigradNo ratings yet
- Cyber BullyingDocument1 pageCyber Bullyingkororo mapaladNo ratings yet
- ProcobolDocument500 pagesProcobolRoberto de Gênova100% (1)
- PLC Connection GuideDocument1,142 pagesPLC Connection Guideraulc1983100% (1)
- XX25 Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesXX25 Data Sheet PDFbillxuNo ratings yet
- CMOS Ring Oscillator AnalysisDocument5 pagesCMOS Ring Oscillator AnalysisVinitKharkarNo ratings yet
- Tales of Destiny I - Stahns SkillsDocument9 pagesTales of Destiny I - Stahns SkillsEduardoBugsNo ratings yet
- Ch.3.requirements AnalysisDocument22 pagesCh.3.requirements AnalysisAnuj NikamNo ratings yet
- Dow Vinerobot (610953) 2013-09-10Document110 pagesDow Vinerobot (610953) 2013-09-10Jean-Marc DeHaeneNo ratings yet
- 300W Single Output Battery Charger: SeriesDocument2 pages300W Single Output Battery Charger: SeriesCsaba WielandNo ratings yet
- Hank Foreman Resume 9-2014Document1 pageHank Foreman Resume 9-2014api-237189772No ratings yet
- 01 Hikvision LCD Video Wall 2018.8.23Document34 pages01 Hikvision LCD Video Wall 2018.8.23crishtopher saenzNo ratings yet