Professional Documents
Culture Documents
APJCP Volume 13 Issue 4 Pages 1709-1710
Uploaded by
Tata Usaha Dirjen Pelayanan KesehatanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
APJCP Volume 13 Issue 4 Pages 1709-1710
Uploaded by
Tata Usaha Dirjen Pelayanan KesehatanCopyright:
Available Formats
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.4.
1709
Population-Based Cancer Registration in Indonesia
COMMENTARY
Population-Based Cancer Registration in Indonesia
Mugi Wahidin1, Rini Noviani1, Sofia Hermawan2, Vita Andriani2, Ardi Ardian3,
Hernani Djarir4
Abstract
Cancer is a major public health problem in Indonesia, becoming the 7th largest cause of death based on a
national survey in 2007, accounting for 5.7 of all mortality. A cancer registry was started in 1970, but it was
partial and was stopped mainly because no government body was responsible. Realizing the above situation,
the Indonesian government established the Sub Directorate of Cancer Control within the Ministry of Health,
with responsibility for developing a national cancer control program, including a cancer registry. A sustainable
cancer registry was then started in 2007 within Jakarta Province, first hospital-based but then expanded to be
population-based. Steps of cancer registration in Jakarta are data collection, data verification, data validation,
data management and analysis, and data publication. Data collection is conducted by health facilities (hospitals,
laboratories, primary health centers) at the district/municipal level, with reports to the provincial level. Data
are collected passively by holding meetings every three months in the district/municipality. Verification of data
is the responsibility of the medical doctor or pathologist in each data source. Data validation is conducted by a
team in the cancer registry, consisting of district/municipal/province health officers, pathologists, and registrars.
Data management and analyses are conducted by a cancer registry team at the provincial level, assisted by
the national team. We use software named Indonesian Cancer Registry System (SRIKANDI) which is adopted
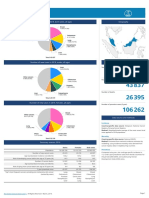
from CanReg4 IARC. Data from the population-based cancer registry in Jakarta Province showed the leading
cancers among females in 2005-2007 to be breast cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer and
among males are bronchus and lung cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, pharyngeal cancer, and prostate
cancer. The leading childhood cancers are leukaemia and retinoblastoma.
Keywords: Cancer registration - population-based - Jakarta, Indonesia
Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev, 13, 1709-1710
Introduction conducted for cancer diagnosed by all parts of hospital.
This registry is aimed to help hospital management to
One main public health problem in Indonesia is cancer. make good plan, organize resources and optimalize cancer
Based on Basic Health Research 2007, cancer is the 7th treatment in hospital. Population-based cancer registry
cause of death among all causes of deaths (5,7%). National is registry which is conducted based on cancer data in a
prevalence of cancer is 4.3 per 1000 population. certain population from all health facilities diagnosing
The above data is baseline data of cancer burden in and treating cancer, such as hospital, laboratory, health
Indonesian population. But, the data is not represent valid center, and clinic. This registry is aimed to get cancer
information in such population, because it is survey based. burden in a certain population, both morbidity (prevalence,
Valid cancer data will be resulted from cancer registry that incidence) and mortality, that will be sources of planning
avoid data duplication. and evaluation of cancer control program.
Cancer registry is ongoing and systematic data Attempts to develop cancer regsitry in Indonesia was
collection of cancer on accurance, characteristic, and started in Semarang, Central Java in 1970. Then, many
outcome, and data processing, storage, and data analyze cancer registries, such as hospital based, pathological-
to produce information on cancer. Information resulted based, and population based were developed till 2004.
from cancer registry will be source of policy development, Unfortunately, these attempts are stopped because of
planning, and evaluation of cancer control program. There some reasons, such as lack of human resources and no
are several cancer registry types based on data collection national body/unit which is responsible to develop policy
method, such as hospital-based cancer regsitry and and implementation of cancer registry.
population-based cancer registry. Then, since establishment of Sub Directorate of Cancer
Hospital-based cancer registry is a registry which is Control within Directorate of Noncommunicable Disease
Sub Directorate of Cancer Control, 2Sub Directorate of Specialistic Medical Services, Ministry of Health, 3Jakarta Province Health
1
Office, 4WHO Representative to Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia *For correspondence: wahids_wgn@yahoo.co.id
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13, 2012 1709
Mugi Wahidin et al
Control, Ministry of Health in 2006, sustainable cancer Findings
registry was restarted again. Population based cancer
registry was started in 2007 with modeling in Jakarta Data resulted from Jakarta Cancer registry shows
Province. The registry was started by hospital based, then that top 10 leading cancers among felame 2005-2007 are
expanded to be population-based. This model is developed breast cancer (incindce 18.6 per 100,000), cervical cancer
by sub directorate of cancer control in collaboration (9.25 per 100,000), ovarium cancer (4.27 per 100,000),
with many parties such as directorate of referral medical colorectal cancer (3.15 per 100,000), and bronchus and
services, Dharmais National Cancer Hospital, Provincial lung cancer (2.40 per 100,000), thyroid cancer (2.21
Health Office of Jakarta. This model becomes reference per 100,000), corpus utery cancer (1.76 per 100,000),
on developing cancer regsitry in other areas in Indonesia. pharingeal cancer (1.72 per 100,000), leukaemia (1.61
per 100,000), and liver cancer (1.41 per 100,000).
Procedures The top 10 leading cancers among male are bronchus
and lung cancer (incidence 5.81 per 100,000), colorectal
Steps of development of cancer registry in Jakarta cancer (4.13 per 100,000), liver cancer (4.01 per 100,000),
province are advocacy and socialization to related pharyngeal cancer (3.65 per 100,000), and prostate cancer
stakeholders, establishment of cancer registry team in (2.82 per 100,000).
national, provincial, and municipal level (5 municipalities, These results were submitted to Cancer in 5 Continents
Central Jakarta, East Jakarta, West Jakarta, North Jakarta, Volume X of International Agency for Research on Cancer
South Jakarta), development of forms (abstract) and (IARC) in 2011.
software, trainings, implementation, monitoring, and
evaluation. Conclusions and Recommendations
Technical steps of cancer registry in Jakarta province
are data collection, data verfication, data processing, In conclusion, the leading cancers in Jakarta province
analyze, and publication. Data collection is done in are breast cancer and cervical cancer (among females),
each health facility by trained registrars. Sources of data bronchus & lung cancer and colorectal cancer (among
are 79 hospitals, 44 sub district primary health centers males), as well as leukemia and retinoblastoma in
that cover 301 village health centers, 2 clinics, and 90 childhood. Modeling of population based cancer registry
pathology laboratories. Data is collected using abstract in Jakarta province has been successfully established,
forms that is inputed to software named SRIKANDI but needs improvement. Mechanism of cancer registry
(Indonesian Cancer Registry System). Raw data from each has been approved by related stakeholders and has been
facility is reported to Municipal Cancer Registry Team, implemented well so we are ready to expand cancer
then reported to Provincial Cancer Registry Team. Data registration to other areas of Indonesia.
collection is done passively by holding meeting every 3 Recommendations include: cancer registry in Jakarta
months. province need to be strengthened continuously through
Data verification is conducted to ensure that data collaboration of all related stakeholders; strengthening
inputed are cancer cases, not other cases. This activity is team of cancer registry in each level, municipality,
done in each data sources (health facility) by verificator, provincial and national; improve SRIKANDI software
pathologist or trained medical doctor. Data validation is (online, analyze process) to be implemented national wide;
done in municipal, provincial, and national level by cancer based on result of cancer registry, introduce adequate
registry team in each level. This steps is conducted to clean interventions for cancer control especially for the leading
data and avoid duplication. Besides data validation, cancer cancers; expand cancer registry to other areas in Indonesia
registry team in each level process re-verification. based on lesson learned of modeling of cancer registry in
Data processing/managing and analysing are conducted Jakarta province.
in municipal, provincial and national national level.
Provincial Cancer Registry Team assists these activities
in municipal level, and National Team assists provincial References
team. Because of limitation of SRIKANDI software that Basic Health Research, National Institute of Health Research and
only process data input, data processing and analyse is Development, Ministry of Health, Republic of Indonesia,
conducted using Microsoft Excel or SPSS. Information 2008
resulted from data anayse are incidence (cumulative Cancer Registry in Semarang City 1985-1989
incidence) and prevalence. Then, final information from Parkin DM, Chen VW, Ferlay J, et al (1994) Comparability and
is published through releasing documents/report book, Quality Control in Cancer Registration. IARC Technical
seminars, and papers and electronic medias. Report No. 19. Lyon, 1994
SRIKANDI software is adopted from CanReg 4 Parkin DM, Jensen OM (1991). Cancer Registration Principles
and Methods, IARC Scientific Publication No. 95. Lyon,
software, a software developed by International Agency
for Research on Cancer (IARC). The software consists
of 3 main parts, social information of patiens, tumor
information, and follow-up. The software is Microsoft
Access based, and works independently. Total variable in
the software are 32 for hospital and 18 for other facilities
(primary health center, clinic, laboratory).
1710 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13, 2012
You might also like
- Multiparametric Ultrasound Diagnosis of Breast DiseasesFrom EverandMultiparametric Ultrasound Diagnosis of Breast DiseasesGennady T. SukhikhNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Multiparametric Prostate MRI: With PI-RADS Approach and Anatomic-MRI-Pathological CorrelationFrom EverandAtlas of Multiparametric Prostate MRI: With PI-RADS Approach and Anatomic-MRI-Pathological CorrelationNo ratings yet
- Pre0510 - MR WAHIDINDocument4 pagesPre0510 - MR WAHIDINmochkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registries Research Paper SummaryDocument4 pagesCancer Registries Research Paper SummaryMustafa MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ChennaiCancerEpidemiologystudyIJCMPH PDFDocument8 pagesChennaiCancerEpidemiologystudyIJCMPH PDFpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registries Research PaperDocument9 pagesCancer Registries Research PaperMustafa MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registries in Four Provinces in Turkey: A Case Study: Research Open AccessDocument8 pagesCancer Registries in Four Provinces in Turkey: A Case Study: Research Open Accessjs14camaraNo ratings yet
- Cancer Diagnosis in MalaysiaDocument16 pagesCancer Diagnosis in MalaysiaLily SyafinazNo ratings yet
- Institution-Based Cancer Incidence in A Local Population in Pakistan: Nine Year Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesInstitution-Based Cancer Incidence in A Local Population in Pakistan: Nine Year Data AnalysisMurk NiazNo ratings yet
- Ket ProposalDocument37 pagesKet ProposalEneyew BirhanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Knowledge On Uptake of Breast Cancer Prevention Modalities Among Women in Kyadondo County, UgandaDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Knowledge On Uptake of Breast Cancer Prevention Modalities Among Women in Kyadondo County, Ugandalailatus sakinahNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Cancers in Iranian WomenDocument4 pagesThe Most Common Cancers in Iranian WomenfaradidNo ratings yet
- Ndizeye 2018Document8 pagesNdizeye 2018Ajup SafarudinNo ratings yet
- Factors Delaying Cancer Care and Outcomes in Tamil NaduDocument22 pagesFactors Delaying Cancer Care and Outcomes in Tamil NaduPrasanna ShanNo ratings yet
- 0 - Cancer Situation in KenyaDocument4 pages0 - Cancer Situation in KenyaMayaka AmosNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Sistem Registrasi Kanker Indonesia: April 2012Document7 pagesPengembangan Sistem Registrasi Kanker Indonesia: April 2012FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Bab I Pendahuluan: 1.1. Latar BelakangDocument6 pagesBab I Pendahuluan: 1.1. Latar BelakangDui Buana MustakimNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument15 pages5 PDFnorazizah rizkaNo ratings yet
- Stigmatised DDocument11 pagesStigmatised Darfa ahmadNo ratings yet
- 2093484625101077_manuscriptDocument18 pages2093484625101077_manuscriptfxbukenyaNo ratings yet
- CTPRDocument438 pagesCTPRAvin NasNo ratings yet
- Data Kanker 2019Document7 pagesData Kanker 2019Dhelila Yomia PutriNo ratings yet
- Incidence Mortality Survival and Prognostic AnalysDocument15 pagesIncidence Mortality Survival and Prognostic AnalyslhykaNo ratings yet
- National Cancer Control Program: IndiaDocument29 pagesNational Cancer Control Program: IndiaNitti PathakNo ratings yet
- The DOH Philippine Cancer Control Program CCCN1Document9 pagesThe DOH Philippine Cancer Control Program CCCN1Johnryl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Research 09Document16 pagesResearch 09Nandini SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Current Radiotherapy Facilities in Indonesia 5af9b3797f8b9a159c8b4675Document6 pagesCurrent Radiotherapy Facilities in Indonesia 5af9b3797f8b9a159c8b4675fadli puteraNo ratings yet
- Cancer Ap PDFDocument52 pagesCancer Ap PDFtiligopabNo ratings yet
- Go-5-Go 20 00155Document14 pagesGo-5-Go 20 0015515Mega RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Cancer Screening Among Doctors in The University of Port Harcourt Teaching HospitalDocument14 pagesKnowledge, Attitude and Practice of Cancer Screening Among Doctors in The University of Port Harcourt Teaching HospitalIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- National Cancer Control ProgrammeDocument16 pagesNational Cancer Control ProgrammemintuNo ratings yet
- Umbas Urology Cancer in Indonesia 2015Document5 pagesUmbas Urology Cancer in Indonesia 2015dony hendrawanNo ratings yet
- VN CanDocument5 pagesVN CanvuaphuNo ratings yet
- Article Review: Disease and Economic Burden of Prostate Cancer in Malaysia: A ReviewDocument8 pagesArticle Review: Disease and Economic Burden of Prostate Cancer in Malaysia: A ReviewMeiselAdeliaNo ratings yet
- Paper KIBOUDocument9 pagesPaper KIBOUQunalNo ratings yet
- Five-Year Cancer Epidemiology at The National Referral Hospital: Hospital-Based Cancer Registry Data in IndonesiaDocument14 pagesFive-Year Cancer Epidemiology at The National Referral Hospital: Hospital-Based Cancer Registry Data in IndonesiaaudibleNo ratings yet
- National Cancer Control Program - 2Document7 pagesNational Cancer Control Program - 2RishabhNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated with Cervical Cancer Screening in Padang CityDocument14 pagesFactors Associated with Cervical Cancer Screening in Padang CityvonyadrezaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Cancer Screening Awareness and Participation Among Indonesian WomenDocument11 pagesDeterminants of Cancer Screening Awareness and Participation Among Indonesian WomenVilla Sekar citaNo ratings yet
- Buccal Mucosa Cancer Final PDF 9.6.14 PDFDocument36 pagesBuccal Mucosa Cancer Final PDF 9.6.14 PDFTaufiqurrahman Abdul DjabbarNo ratings yet
- Retros 1Document5 pagesRetros 1denisdeniNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405844020304485 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2405844020304485 MainSome LaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kanser Prostat MalaysiaDocument13 pagesAnalisis Kanser Prostat MalaysiaMuhammad AimanNo ratings yet
- 920 2859 2 PBDocument2 pages920 2859 2 PBMarcelina FAINo ratings yet
- Monitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesDocument11 pagesMonitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesMihaela BarbuNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Breast Cancer Awareness Campaigns On Women's Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices in Uganda's Kampala DistrictDocument16 pagesThe Impact of Breast Cancer Awareness Campaigns On Women's Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices in Uganda's Kampala DistrictKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Pamj 22 26Document8 pagesPamj 22 26Yosie Yulanda PutraNo ratings yet
- Kaidt 2Document17 pagesKaidt 2الرشيد النووورNo ratings yet
- Important 1Document3 pagesImportant 1Edwin SinghNo ratings yet
- Bli10363 FMDocument4 pagesBli10363 FMMrBuu2012No ratings yet
- Early Detection of Breast and Cervical Cancer in South LampungDocument10 pagesEarly Detection of Breast and Cervical Cancer in South LampungThiramizzu RhaNo ratings yet
- Low Dose Computed Tomography For The Screening of Lung Cancer in AdultsDocument133 pagesLow Dose Computed Tomography For The Screening of Lung Cancer in AdultsAnush VedhNo ratings yet
- Cancer Incidence in Jordan - 2016 Statistical ReportDocument36 pagesCancer Incidence in Jordan - 2016 Statistical ReportJa'far HishamNo ratings yet
- The Correlation of Socio Demographic and Knowledge Factors Toward Therapy Options Among Breast Cancer PatientsDocument12 pagesThe Correlation of Socio Demographic and Knowledge Factors Toward Therapy Options Among Breast Cancer PatientsDikri NurfazrinNo ratings yet
- Challenges in The Recognition Management AKIDocument9 pagesChallenges in The Recognition Management AKISoniamartilovaNo ratings yet
- Ijbc2020 1963814Document6 pagesIjbc2020 1963814Kurnia AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Cancer ArticlesDocument2 pagesCancer ArticlesPle NgNo ratings yet
- Philippine Cancer Control Program.1.1Document8 pagesPhilippine Cancer Control Program.1.1Ruby Joy EspirituNo ratings yet
- Efektifitas Periksa Payudara Sendiri (SADARI) dalam Upaya Penanganan Dini Kanker PayudaraDocument10 pagesEfektifitas Periksa Payudara Sendiri (SADARI) dalam Upaya Penanganan Dini Kanker Payudaracinnn bwsNo ratings yet
- Jgo 23 147Document6 pagesJgo 23 147Yosua_123No ratings yet
- Understanding Cancer Cell Growth and SpreadDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Cancer Cell Growth and SpreadJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- The International System For Reporting Serous Fluid Cytopathology Diagnostic Categories and Clinical ManagementDocument30 pagesThe International System For Reporting Serous Fluid Cytopathology Diagnostic Categories and Clinical ManagementPaulo E M SouzaNo ratings yet
- Tumor Staging of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma .8Document10 pagesTumor Staging of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma .8elisasitohangNo ratings yet
- G. EDWARD GRIFFIN - World Without Cancer (The Story of Vitamin B17) PDFDocument359 pagesG. EDWARD GRIFFIN - World Without Cancer (The Story of Vitamin B17) PDFBegginner89% (28)
- New Gen Dr. Vita OPC Double Layer Tablet 20220727Document26 pagesNew Gen Dr. Vita OPC Double Layer Tablet 20220727Vicky AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Document1 pageLugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Mary's CatzNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Skeletal System1Document11 pagesIntroduction in Skeletal System1joana cortezNo ratings yet
- 2018 Article CIRSE2018 PDFDocument463 pages2018 Article CIRSE2018 PDFIulia LupascuNo ratings yet
- Mammographic Features of Benign Breast Lesions and Risk of Subsequent Breast Cancer in Women Attending Breast Cancer ScreeningDocument12 pagesMammographic Features of Benign Breast Lesions and Risk of Subsequent Breast Cancer in Women Attending Breast Cancer ScreeningOmair Hawk100% (1)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Submandibular SalivaryDocument4 pagesSquamous Cell Carcinoma of Submandibular SalivaryGuntur Bayu Bima PratamaNo ratings yet
- BED Formula PDFDocument15 pagesBED Formula PDFMichelle Mora MariñoNo ratings yet
- Artigo ApoioDocument11 pagesArtigo ApoioNayanne CunhaNo ratings yet
- Terapi Sistemik Pada Kanker Dengan Obat Anti Kanker (OAK) Pada Saat Pandemi COVID-19Document31 pagesTerapi Sistemik Pada Kanker Dengan Obat Anti Kanker (OAK) Pada Saat Pandemi COVID-19dayarni buuloloNo ratings yet
- Study of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseDocument7 pagesStudy of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Invasive Cytopathology UltreasoundDocument476 pagesInvasive Cytopathology UltreasoundAlexander KovalenkoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective FactorsDocument64 pagesEpidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective Factorsbo gum parkNo ratings yet
- Female Staff Nurse Recruitment Exam Question AnswersDocument7 pagesFemale Staff Nurse Recruitment Exam Question Answersjaved100% (1)
- Cancer Prevention Health Education ProgramDocument9 pagesCancer Prevention Health Education ProgramKheneille Vaughn Javier GuevarraNo ratings yet
- L1cam Defines The Regenerative Origen of MetastasisDocument31 pagesL1cam Defines The Regenerative Origen of Metastasisjuan carlos monasterio saezNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument52 pagesBreast CancerLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma TalkDocument23 pagesOesophageal Adenocarcinoma TalkS XUXNo ratings yet
- Anticancer (ANTI NEOPLASTIC)Document43 pagesAnticancer (ANTI NEOPLASTIC)Yani MulyaniNo ratings yet
- MammographyDocument38 pagesMammographyNoureddine BenarifaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Lymphoepithelial CystDocument6 pagesCervical Lymphoepithelial CystAhmed Al-jumailiNo ratings yet
- The Significance of Septations in A Renal CystDocument3 pagesThe Significance of Septations in A Renal CystJenina Clarisse B. PascuaNo ratings yet
- Communication From Theory To PracticeDocument5 pagesCommunication From Theory To PracticeGeorgya RasaduNo ratings yet
- Review 1. Efficacy and Safety of Cetuximab For CRCDocument13 pagesReview 1. Efficacy and Safety of Cetuximab For CRCcollianairaNo ratings yet
- Ethnobotany - Application of Medicinal Plants (PDFDrive)Document295 pagesEthnobotany - Application of Medicinal Plants (PDFDrive)Nadeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Malaysia cancer statistics and dataDocument2 pagesMalaysia cancer statistics and dataCatherineYeohNo ratings yet
- Competency Performance Checklist: Skill 30-14: Assessing The Breasts and Axillae Student: DateDocument2 pagesCompetency Performance Checklist: Skill 30-14: Assessing The Breasts and Axillae Student: DateKyle VargasNo ratings yet