Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Employment Reading
Uploaded by
Nicole WagdyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Employment Reading
Uploaded by
Nicole WagdyCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2 – How do jobs differ around the world?
Different types of jobs can be classified into different sectors – Primary, secondary, tertiary
and quaternary. The employment structure of a country shows how the work force is divided
into the different sectors.
The four main sectors:
Primary Industry: the extraction of raw materials from the land or sea.
Secondary Industry: manufacturing (making something) where raw materials are converted
into a finished product.
Tertiary Industries: The tertiary sector is also called the service sector and involves the selling
of services and skills. They can also involve selling goods and products from primary and
secondary industries.
Quarternary Industries: Provide information and expert help. They are often associated with
creative or knowledge based industries.
Together, the balance of these is known as a countries employment structure. All countries
have an element of each sector but which type of often linked to the level of development
within a country.
How job sectors vary between different types of country:
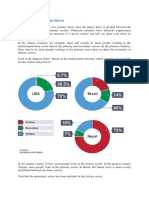
The employment structure of a country can tell you quite a lot about its economy. In the
richest countries, for example, there will usually be more people working in the
tertiary/quaternary sector than in the primary and secondary sectors. This is usually because
more people are likely to be highly skilled and have benefitted from an education. In the
poorest countries, there tend to be more people working in the primary sector than in either
the secondary or tertiary sectors. Look at the diagram above. In the most developed country
(USA), most people work in the tertiary sector. In developing countries (Nepal), most people
work in the primary sector. In Brazil, an emerging country the labour force is more evenly
distributed between the three sectors.
(Note that the quaternary sector has been included in the tertiary sector)
You might also like
- Geography Form 3 Week 2 Lesson 1 Study PackDocument8 pagesGeography Form 3 Week 2 Lesson 1 Study PackIss MeNo ratings yet
- Industry Pt3 - Employment StructuresDocument5 pagesIndustry Pt3 - Employment StructuresMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Non-Economic Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesNon-Economic Characteristics: Objectivedakch49No ratings yet
- LateeeDocument4 pagesLateeeCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Ayaan de 3Document6 pagesAyaan de 3ayaan azizNo ratings yet
- Eco-Sectors of Indian Economy-NotesDocument8 pagesEco-Sectors of Indian Economy-NotesLatika MarwahaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument19 pagesNotesd9353355259No ratings yet
- Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 - People As ResourceDocument5 pagesClass 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 - People As ResourceMd AlamNo ratings yet
- JSS3 Geography Note.Document16 pagesJSS3 Geography Note.muhammadyus076No ratings yet
- Economic Development AssignmentDocument5 pagesEconomic Development AssignmentJasmin DorueloNo ratings yet
- ClassIXEco. TBQ & Assign. (Ch-2) SolDocument11 pagesClassIXEco. TBQ & Assign. (Ch-2) SolSujitnkbpsNo ratings yet
- Economics ch2 People As A ResourceDocument4 pagesEconomics ch2 People As A ResourceDIVYA HARSHINI KURMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2events.tsintNo ratings yet
- ECON Week2Document8 pagesECON Week2ocsapwaketsNo ratings yet
- Eco Sectors of EconomyDocument5 pagesEco Sectors of EconomynirikdhaNo ratings yet
- Notes For The Teacher: Chapter 2: Sectors of The Indian EconomyDocument20 pagesNotes For The Teacher: Chapter 2: Sectors of The Indian EconomyBabul Kumar BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Suggested Activity/Activities: WWW - Pinterest.ph/pin/345932815098537474Document4 pagesLesson 1: Suggested Activity/Activities: WWW - Pinterest.ph/pin/345932815098537474Christlly LamyananNo ratings yet
- Booklet: Curse: 4º 1 (Economics)Document47 pagesBooklet: Curse: 4º 1 (Economics)ciber interkNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Final ProjectDocument13 pagesMacroeconomics Final Projectismail malikNo ratings yet
- Human ResourcesDocument20 pagesHuman ResourcesPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Development Studies New VersionDocument175 pagesDevelopment Studies New Versionj33966141No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Diverse Structure and Common Characteristics of Developing NationsDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Diverse Structure and Common Characteristics of Developing NationsHussain Shahbaz Shahbaz PevaizNo ratings yet
- The Knowledge Economy (T1-T13)Document11 pagesThe Knowledge Economy (T1-T13)Pang Kok ShengNo ratings yet
- NOTES FOR CH 2 People As Resource EconomicsDocument2 pagesNOTES FOR CH 2 People As Resource EconomicsSGIP SchoolNo ratings yet
- People As Resource NOTESDocument9 pagesPeople As Resource NOTESAuraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Part 1) : Determinants of Economic Development, Problems and Development StrategiesDocument5 pagesModule 3 (Part 1) : Determinants of Economic Development, Problems and Development StrategiesMark James GarzonNo ratings yet
- LP - AE 1 - Applied Economics (1.3 Basic Economic Problems and The Philippine Socioeconomic Development in The 21st Century)Document5 pagesLP - AE 1 - Applied Economics (1.3 Basic Economic Problems and The Philippine Socioeconomic Development in The 21st Century)Chenee Rose Rodriguez CanariaNo ratings yet
- Development: Learning ObjectivesDocument43 pagesDevelopment: Learning ObjectivesMohammed ShabzNo ratings yet
- Conworld Finals ExplanationDocument11 pagesConworld Finals ExplanationG11. Cunanan, Dominique Gail S.No ratings yet
- ENTRE 3 MicroeconomicsDocument1 pageENTRE 3 MicroeconomicsQuinn De CastroNo ratings yet
- Notes - Sectors of Indian Economy - Class X - EconomicsDocument16 pagesNotes - Sectors of Indian Economy - Class X - EconomicsabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- People As ResourcesDocument25 pagesPeople As ResourcesthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Written Narrative Report Guidelines VIDAL CORPUZ ALCAIDEDocument7 pagesWritten Narrative Report Guidelines VIDAL CORPUZ ALCAIDEVidal Angel Glory Borj A.No ratings yet
- Week 4 Las Dela Cruz, Marc Noel S.-Geco3 - The Global Economy (Groupings)Document9 pagesWeek 4 Las Dela Cruz, Marc Noel S.-Geco3 - The Global Economy (Groupings)Marc Noel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- X Economics Chapter 2 - Sectors of The Indian Economy Notes (2022-23)Document9 pagesX Economics Chapter 2 - Sectors of The Indian Economy Notes (2022-23)ThunderNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Applied Economics: Quarter 3: Module 1Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet No. 1 Applied Economics: Quarter 3: Module 1Ben A MalanyaonNo ratings yet
- Sectors in Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesSectors in Indian EconomytnssbhaskarNo ratings yet
- People As Resource Class 9 Extra NotesDocument5 pagesPeople As Resource Class 9 Extra Notessidd23056% (9)
- Chapter 2 SECTORS OF INDIAN ECONOMY (AutoRecovered)Document17 pagesChapter 2 SECTORS OF INDIAN ECONOMY (AutoRecovered)pujaNo ratings yet
- Common Characteristics of Developing CountriesDocument5 pagesCommon Characteristics of Developing CountriesFaisal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Common Characteristics PDFDocument5 pagesCommon Characteristics PDFFaisal AhmedNo ratings yet
- People As Resource Class 9 Extra Notes PDFDocument5 pagesPeople As Resource Class 9 Extra Notes PDFKahkashan BanooNo ratings yet
- Geo Short Notes: Conomic Activity and EnergyDocument24 pagesGeo Short Notes: Conomic Activity and EnergyAkashNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Module 2Document9 pagesApplied Economics Module 2Arap MamboNo ratings yet
- Sectors of The EconomyDocument8 pagesSectors of The Economyranjansameer928No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Câu Hỏi Tuần 1)Document3 pagesChapter 1 (Câu Hỏi Tuần 1)chanhleonNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET Title of The Activity: Basic Economic Problems of SocietyDocument6 pagesACTIVITY SHEET Title of The Activity: Basic Economic Problems of SocietyMariella Olympia PanuncialesNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS CH 2.docx1690478179-SmsDocument2 pagesECONOMICS CH 2.docx1690478179-Smsskmajidali02No ratings yet
- "Understanding The Indian Economy": Class 9Document3 pages"Understanding The Indian Economy": Class 9MuzaFarNo ratings yet
- Geo AssDocument6 pagesGeo AssAli DiabNo ratings yet
- Development IGCSEDocument44 pagesDevelopment IGCSEHadad LwazeNo ratings yet
- Northern Iloilo Polytechnic State College School of ManagementDocument25 pagesNorthern Iloilo Polytechnic State College School of ManagementErolle SolivioNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 6: Productivity and Human Capital I. Standard of Living Around The WorldDocument6 pagesLecture Chapter 6: Productivity and Human Capital I. Standard of Living Around The WorldKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Ud1 - Economic Activities and Geographical Spaces PDFDocument6 pagesUd1 - Economic Activities and Geographical Spaces PDFKhronos HistoriaNo ratings yet
- 3º Eso - Ud1 - Economic Activities and Geographical Spaces PDFDocument6 pages3º Eso - Ud1 - Economic Activities and Geographical Spaces PDFKhronos HistoriaNo ratings yet
- College of Business Management and AccountingDocument12 pagesCollege of Business Management and AccountingShaker ShahrerNo ratings yet
- Global Economy Can Be Defined As The Sum of Activities That Take Place Both Within A Country and Between Different CountriesDocument3 pagesGlobal Economy Can Be Defined As The Sum of Activities That Take Place Both Within A Country and Between Different CountriesKim ReyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics WeekDocument182 pagesIntroduction To Economics WeekChristianahNo ratings yet
- Disruption: Lifelong Learning in the Knowledge EconomyFrom EverandDisruption: Lifelong Learning in the Knowledge EconomyNo ratings yet