Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DBT Overviewt
Uploaded by
Krysta DonnellyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DBT Overviewt
Uploaded by
Krysta DonnellyCopyright:
Available Formats
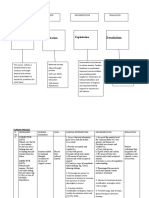
DBT – Overview of Approach and Treatment
Ways to approach any problem Components of treatment
1. Solve the problem 1. Individual therapy
2. Change your perception of the problem (session structure below)
3. Radically accept the problem
2. Skills group (CM, IPE, ER, DT)
4. Stay miserable
3. Phone skills coaching
4. Consult team
Primary Targets (hierarchy -levels)
1. Life-threatening behaviors (SI, NSSI)
Session structure:
2. Therapy-interfering behaviors (TIB)
1. Review Diary Card
3. Quality of life behaviors (QL)
2. Attention to target hierarchy
4. Skills acquisition
3. Chain Analysis on highest target
4. Weave in Solution Analysis
Stages of therapy: 5. Move down hierarchy to discuss
IV. Incompleteness Capacity for sustained joy skills related to current life
III. Problems in living Ordinary happiness & unhappiness situations
II. Quiet desperation Emotional experiencing
I. Severe Behavioral Dysregulation Control
Secondary targets (dialectical dilemmas):
Therapist characteristics
Emotional
Oriented to
vulnerability
Unwavering change
Unrelenting Active centeredness Benevolent
crisis passivity demanding
Apparent Compassionate
Inhibited
competence Nurturing flexibility
grief
Self- Oriented to
invalidation acceptance
Dialectical approach:
- Acceptance (validation) & Change (problem solving)
- Synthesis (and/both)
- Transactional (person & environment)
Adapted from M. Linehan (1993) by D. Barrett (2017) 1
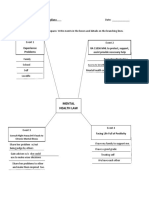
DBT – Overview of Approach and Treatment
Assumptions about patients Assumptions about therapists
1. People are doing the best that they can. 1. The most caring thing a therapist or
2. People want to improve treatment provider can do is help people
3. People must learn new behaviors both in change in ways that bring them closer to
therapy and in the context of their day-to- their own ultimate goals.
day life. 2. Clarity, precision and compassion are of
4. People cannot fail in DBT the utmost importance.
5. People may not have caused all of their 3. The treatment relationship is a real
problems, but they have to solve them relationship between equals.
anyway. 4. Principles of behavior are universal,
6. People need to do better, try harder and be affecting clinicians no less than clients.
more motivated to change. 5. Treatment providers need support
7. The lives of people who are suicidal are 6. Treatment providers can fail.
unbearable as they are currently being
lived.
Core Strategies = Validation + Problem Solving
Behaviors to Decrease
Interpersonal chaos Dialectical Strategies:
Labile emotions and moods
Impulsiveness Entering the paradox
Confusion about self and cognitive Metaphor
dysregulation Devil’s advocate
Quality-of-life interfering behaviors Extending
Activating Wise Mind
Making lemonade
Skills / behaviors to increase: Allowing natural change
Dialectical assessment
Core mindfulness
Interpersonal effectiveness
Emotion regulation Change Strategies:
Distress tolerance
Self-management and life skills Contingency management
Skills
Exposure
Cognitive Modification
Levels of Validation:
Validation Strategies
1. Being Present
2. Accurate Reflection Emotional validation
3. Reading Cues Behavioral validation
4. History
Cognitive validation
5. Normalizing
Cheerleading
6. Radical genuineness
Adapted from M. Linehan (1993) by D. Barrett (2017) 2
You might also like
- DIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)From EverandDIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)No ratings yet
- DBT Workbook For Clinicians-The DBT Clinician's Guide to Holistic Healing, Integrating Mind, Body, and Emotion: The Dialectical Behaviour Therapy Skills Workbook for Holistic Therapists.From EverandDBT Workbook For Clinicians-The DBT Clinician's Guide to Holistic Healing, Integrating Mind, Body, and Emotion: The Dialectical Behaviour Therapy Skills Workbook for Holistic Therapists.No ratings yet
- PsychodynamicDocument49 pagesPsychodynamicManvi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavioural TherapyDocument47 pagesDialectical Behavioural TherapyAthul Raj100% (1)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy Presentation Materials: The Behavioral Technology Transfer GroupDocument22 pagesDialectical Behavior Therapy Presentation Materials: The Behavioral Technology Transfer GroupAnand KirtiNo ratings yet
- ACT For Psychosis Workshop BABCP 2008 Eric Morris Gordon Mitchell Amy McArthurDocument11 pagesACT For Psychosis Workshop BABCP 2008 Eric Morris Gordon Mitchell Amy McArthurjlbermudezc100% (1)
- DBTDocument46 pagesDBTDiana Davis100% (1)
- Dialectical Behaviour TherapyDocument59 pagesDialectical Behaviour TherapyRiya GangwalNo ratings yet
- Module 5 AssignmentDocument3 pagesModule 5 AssignmentjessiejuliacNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism Care PlanDocument11 pagesAlcoholism Care Planilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- TCIS Study GuideDocument2 pagesTCIS Study GuideAndrew100% (2)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar SlidesDocument49 pagesDialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar SlidesJanelle100% (1)
- Dialectical Behaviour Therapy - Theoretical Principles and StrategiesDocument17 pagesDialectical Behaviour Therapy - Theoretical Principles and StrategiesYudhajit RoychowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Counsel - Lesson 2Document2 pagesCounsel - Lesson 2prans.sushiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavior TherapyDocument12 pagesCognitive Behavior TherapyMs. Rachel SamsonNo ratings yet
- DBTDocument28 pagesDBTShervin T-RadNo ratings yet
- Mindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesDocument1 pageMindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesKshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- Anam Sardar (DBT Presentation)Document37 pagesAnam Sardar (DBT Presentation)Anam SardarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 - Therapeutic ApproachesDocument12 pagesChapter-5 - Therapeutic ApproachestanavtaruNo ratings yet
- O A R S: Identify Behavior ChangesDocument10 pagesO A R S: Identify Behavior Changesjohn cutterNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NSG LecDocument63 pagesPsychiatric NSG LecChris ⏠⏝⏠ MarianoNo ratings yet
- CBT Basics and CTRS-2-13Document37 pagesCBT Basics and CTRS-2-13keerthadinnuNo ratings yet
- DBT Visual Review Flash CardDocument14 pagesDBT Visual Review Flash CardBeyza Gül89% (9)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar SlidesDocument49 pagesDialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar Slidesjean100% (1)
- DBT - Comparative Analysis ProjectDocument21 pagesDBT - Comparative Analysis Projectapi-608298797100% (1)
- Dialectical Behaviour TherapyDocument57 pagesDialectical Behaviour Therapydrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- DBT General HandoutDocument8 pagesDBT General HandoutMub ZtyleNo ratings yet
- Group 5 PresentationDocument22 pagesGroup 5 PresentationSana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavior TherapyDocument44 pagesDialectical Behavior TherapyRavitejaNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument1 pageNCP Disturbed Thought Processfretzie azoteNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument43 pagesPsychiatric NursingHaru100% (1)
- 5-3.2. Cognitive-Behavior Therapies, Therapeutic Milieu and Other Psychological Interventions - CICdocxDocument2 pages5-3.2. Cognitive-Behavior Therapies, Therapeutic Milieu and Other Psychological Interventions - CICdocxDane Mikhael CalicaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Benedict ZuluetaDocument47 pagesCognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Benedict ZuluetaMavi YalongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Psychological Treatments: Powerpoint SlidesDocument62 pagesChapter 15: Psychological Treatments: Powerpoint Slidesalice jacksonNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavioral TherapyDocument20 pagesDialectical Behavioral Therapynive1010100% (1)
- Treatments of Mental DisordersDocument11 pagesTreatments of Mental DisordersTim AroscoNo ratings yet
- Kinds of PsychotherapyDocument9 pagesKinds of PsychotherapyMarielle Anne TuazonNo ratings yet
- AB1601 Seminar 5 EmotionsDocument27 pagesAB1601 Seminar 5 EmotionsEthan ChiaNo ratings yet
- DBT Foundations Pt1Document20 pagesDBT Foundations Pt1Marianela CesanNo ratings yet
- Strss Mannagement & COPING SKILLSDocument36 pagesStrss Mannagement & COPING SKILLSImon PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument28 pagesChapter 5 NotesMehak AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ch. 14 SlidesDocument64 pagesCh. 14 Slidesamericangurl1284681No ratings yet
- The Experience of Loss, Death and GriefDocument14 pagesThe Experience of Loss, Death and GriefAries Gulle MacalamNo ratings yet
- NCM 217 SKILLS LAB Maladpative Nursing 3Document60 pagesNCM 217 SKILLS LAB Maladpative Nursing 3Sophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- MALadaptive PRELIMnotesDocument8 pagesMALadaptive PRELIMnotesNoel Calvo MacarineNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy Prelims ReviewerDocument14 pagesPsychotherapy Prelims ReviewerAnonymous v930HVNo ratings yet
- 02 - Organizational BehaviourDocument2 pages02 - Organizational BehaviourCelsozeca2011No ratings yet
- AP Psychology - THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES TableDocument3 pagesAP Psychology - THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES TableneelNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument1 pageDisturbed Thought Processfretzie azoteNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Dialectical Behaviour TherapyDocument70 pagesA Brief Introduction To Dialectical Behaviour TherapyAdrianaNorte100% (1)
- SIEGEL - Tailoring MindfulneDocument16 pagesSIEGEL - Tailoring Mindfulnejohannquesada100% (1)
- PCEP-PC Module 2 Slides and Key PointsDocument10 pagesPCEP-PC Module 2 Slides and Key PointsMan MedNo ratings yet
- Intro PsychopathDocument9 pagesIntro PsychopathRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Schema TherapyDocument1 pageSchema TherapyFederica ChaconNo ratings yet
- 5Document17 pages5Siyonaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Experience Problems: Time - Order ChartDocument5 pagesExperience Problems: Time - Order ChartLorbie Castañeda FrigillanoNo ratings yet
- DBT AssignmentDocument5 pagesDBT AssignmentTanya BhallaNo ratings yet
- Teknik Menanam Cabe HitamDocument36 pagesTeknik Menanam Cabe HitammuslimNo ratings yet
- Psych Reg Disruptive Behavioural Disorders 2009Document79 pagesPsych Reg Disruptive Behavioural Disorders 2009hopeIshanzaNo ratings yet
- Stepping Into Spiritual Oneness PDFDocument460 pagesStepping Into Spiritual Oneness PDFTaulant HoxhaNo ratings yet
- Supporting Grieving Students PresentationDocument29 pagesSupporting Grieving Students Presentationapi-553169681No ratings yet
- Final Com Research PaperDocument9 pagesFinal Com Research PaperLawrence CezarNo ratings yet
- Origin of LangaugeDocument5 pagesOrigin of LangaugeIbrahim Aftab KhanNo ratings yet
- Feelings PDFDocument4 pagesFeelings PDFachara_pNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Q and ADocument3 pagesReviewer Q and AgibraltarcyrmondNo ratings yet
- 1 The Reggio Emilia Concept or DifferentDocument14 pages1 The Reggio Emilia Concept or DifferentArian DinersNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Assignment 102Document9 pagesLifestyle Assignment 102api-561103587No ratings yet
- Legacies (MtAw) - WodDocument35 pagesLegacies (MtAw) - WodGnomeMadeIonNo ratings yet
- Motivating Office EmployeesDocument24 pagesMotivating Office EmployeesJG EusebioNo ratings yet
- Peter Pan SyndromeDocument4 pagesPeter Pan SyndromeDaltry Gárate100% (2)
- Psychology: Test Booklet No. Time: 2 Hours) (Maximum Marks: 200 Instructions For The CandidatesDocument40 pagesPsychology: Test Booklet No. Time: 2 Hours) (Maximum Marks: 200 Instructions For The CandidateskodalidhanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: The Self From The Perspective of AnthropologyDocument9 pagesLesson 3: The Self From The Perspective of AnthropologyJamela OrielNo ratings yet
- Prelim Module Prof Ed. 7 Assessment of Learning 2Document28 pagesPrelim Module Prof Ed. 7 Assessment of Learning 2Sarah Imarah MislangNo ratings yet
- Creative Facilitation ManualDocument55 pagesCreative Facilitation ManualHumberto VirgüezNo ratings yet
- DATE: February 11, 2020Document2 pagesDATE: February 11, 2020Ednell VelascoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Naicker SDocument165 pagesDissertation Naicker SPerseverance Wendy MathebulaNo ratings yet
- G12 PerDev Week 5Document11 pagesG12 PerDev Week 5Hersley PhynomeNo ratings yet
- Theory of Love (The Psychotherapist)Document68 pagesTheory of Love (The Psychotherapist)AndresCordero100% (1)
- Patricia Carrington Clearing Blocks TranscriptDocument14 pagesPatricia Carrington Clearing Blocks Transcriptmichingon100% (1)
- Pnas 2010 Kahneman 16489 93 2Document5 pagesPnas 2010 Kahneman 16489 93 2api-321994687No ratings yet
- Chapter Six - The Solar Plexus ChakraDocument12 pagesChapter Six - The Solar Plexus ChakraTengku SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Coaching Your Employees Ed Batista HBR Webinar Summary PDFDocument7 pagesCoaching Your Employees Ed Batista HBR Webinar Summary PDFDam To Minh100% (1)
- 21st Century Lit Lesson 2Document15 pages21st Century Lit Lesson 2mark padernalNo ratings yet
- The Aesthetics of Excess (Maria Heim)Document25 pagesThe Aesthetics of Excess (Maria Heim)茱萸褚No ratings yet
- Rape SlideDocument24 pagesRape SlideugomiesterNo ratings yet
- StressDocument16 pagesStressSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Superiority Inferiority ComplexDocument9 pagesSuperiority Inferiority ComplexAyesha AkbarNo ratings yet
- Encopresis Happens - Geoff GoodmanDocument18 pagesEncopresis Happens - Geoff GoodmanMariana JaninNo ratings yet
- Pascas Care Emotion Code - Energetic Imbalances PDFDocument58 pagesPascas Care Emotion Code - Energetic Imbalances PDFAnonymous h2EA8RnZ100% (2)