Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statics LN-02
Statics LN-02
Uploaded by
HydraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statics LN-02
Statics LN-02
Uploaded by
HydraCopyright:
Available Formats
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
Statistical methods
Ungrouped vs. Grouped Data
• Data can be classified as grouped or ungrouped.
• Ungrouped data are data that are not organized, or if arranged, could only be from highest to lowest or
lowest to highest.
• Grouped data are data that are organized and arranged into different classes or categories.
Presentation of Data
Stem and Leaf plot
Page 1 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
BAR DIAGRAM
BIRTH RATES OF COUNTRIES IN PARTICULAR PERIOD OF TIME
COMPOUND BAR DIAGRAM
PIE DIAGRAM
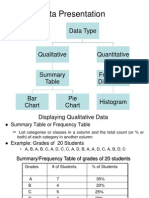
Sample of a Frequency Distribution Table for Ungrouped Data
Page 2 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
Sample of a Frequency Distribution Table for Grouped Data
Lower Class Limits and upper class limits
Class Boundaries
Page 3 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
Class Midpoints
Class Width
Relative Frequency Table
Cumulative Frequency Table
Page 4 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
Complete Frequency Table
Exercise:
For each of the following class intervals, give the class width(i), class mark (x), and class boundary (cb)
Exercise:
The following are the IQ scores of 60 student applicants in a certain high school
Construct a complete FDT with 7 classes
Page 5 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
HISTOGRAM
FREQUENCY POLYGONS
FREQUENCY CURVE
Page 6 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY CURVE/ OGIVE
Measures of Central Tendency
• Measure of central tendency provides a very convenient way of describing a set of scores with a single
number that describes the PERFORMANCE of the group.
• There are three commonly used measures of central tendency.
MEAN
MEDIAN
MODE
MEAN
• It is the most commonly used measure of the center of data
• It is also referred as the “arithmetic average”
• Computation of Sample Mean
Page 7 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
• Computation of the Mean for Ungrouped Data
Example:
• Scores of 15 students in Mathematics I quiz consist of 25 items. The highest score is 25 and the lowest score
is 10. Here are the scores: 25, 20, 18, 18, 17, 15, 15, 15, 14, 14, 13, 12, 12, 10, 10. Find the mean in the
following scores.
Example:
• Find the Grade Point Average (GPA) of Paolo Adade for the first semester of the school year 2013-2014. Use
the table below:
Mean for Grouped Data
• Grouped data are the data or scores that are arranged in a frequency distribution.
• Frequency distribution is the arrangement of scores according to category of classes including the frequency.
• Frequency is the number of observations falling in a category.
Mean for Grouped Data
Example:
• Scores of 40 students in a science class consist of 60 items and they are tabulated below.
Page 8 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
MEDIAN
• Median is what divides the scores in the distribution into two equal parts.
• Fifty percent (50%) lies below the median value and 50% lies above the median value.
• It is also known as the middle score or the 50th percentile.
Median of Ungrouped Data
1. Arrange the scores (from lowest to highest or highest to lowest).
2. Determine the middle most score in a distribution if n is an odd number and get the average of the two middle
most scores if n is an even number.
Median of Ungrouped Data
Example:
• Find the median score of 8 students in an English class.
Median of Grouped Data
Formula:
MODE
• The mode or the modal score is a score or scores that occurred most in the distribution.
Page 9 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
2- Statistical techniques CIVIL
Mathematics for construction Tutorial -2
• The score that appeared most in Section A is 20, hence, the mode of Section A is 20. There is only one mode,
therefore, score distribution is called unimodal.
• The modes of Section B are 18 and 24, since both 18 and 24 appeared twice. There are two modes in Section
B, hence, the distribution is a bimodal distribution.
• The modes for Section C are 18, 21, and 25. There are three modes for Section C, therefore, it is called a
trimodal or multimodal distribution.
Mode for Grouped Data
• In solving the mode value in grouped data, use the formula:
Page 10 of 16 Eng. C. M. Shafraz
You might also like
- Statistics-April 2021Document37 pagesStatistics-April 2021Dona Kris GumbanNo ratings yet
- Data Management: Module OverviewDocument42 pagesData Management: Module OverviewMyoui Mina100% (2)
- E-Tivity 2.2 Tharcisse 217010849Document7 pagesE-Tivity 2.2 Tharcisse 217010849Tharcisse Tossen TharryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Eqt 271 (Part 1) : Basic StatisticsDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Eqt 271 (Part 1) : Basic StatisticsJames TheeNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Data ManagementDocument38 pagesModule 4 - Data ManagementKobeNo ratings yet
- Measures of CeMEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY - Pptntral TendencyDocument47 pagesMeasures of CeMEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY - Pptntral TendencyEnamul Huque SarkerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - CH3 (Numerical Measures)Document6 pagesWorksheet 3 - CH3 (Numerical Measures)abbasalawieh808No ratings yet
- ACTED061L Lesson 2 - Measures For Grouped DataDocument11 pagesACTED061L Lesson 2 - Measures For Grouped DataClaira LebrillaNo ratings yet
- Part A Assignment - No - 3Document16 pagesPart A Assignment - No - 3Akshay GadadeNo ratings yet
- MAT 152 - P2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesMAT 152 - P2 Reviewerfernandezmaekyla1330No ratings yet
- Ug Stat Pract ManualDocument108 pagesUg Stat Pract ManualKeerthi Subramani100% (1)
- Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument42 pagesEngineering Probability and StatisticsKevin RamosNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics - Module 16 - Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument11 pagesBusiness Mathematics - Module 16 - Measures of Central Tendency and Variabilityluxtineury2310No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document64 pagesChapter 2katchibiNo ratings yet
- Describing Data:: Numerical MeasuresDocument37 pagesDescribing Data:: Numerical Measuresmd_shagorNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Statistics: Instructor: Dr. Deshi YeDocument42 pagesMathematical Statistics: Instructor: Dr. Deshi YeAhmed Kadem ArabNo ratings yet
- Describing Data:: Numerical MeasuresDocument43 pagesDescribing Data:: Numerical MeasuresChowdhury KibriaNo ratings yet
- Selvanathan 5e Chapter 02Document77 pagesSelvanathan 5e Chapter 02syw0210No ratings yet
- Topic 3Document22 pagesTopic 3eddyyowNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6: Introduction To Data ScienceDocument25 pagesLecture-6: Introduction To Data ScienceSaif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- STAT 1770 Lab 2-2Document3 pagesSTAT 1770 Lab 2-2ishaankakade21No ratings yet
- LA1 Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageLA1 Descriptive StatisticsEhron RiveraNo ratings yet
- Measure of SkewnessDocument121 pagesMeasure of SkewnessDevashishGuptaNo ratings yet
- Review Lecture 3 Descriptive Statistics, Part 2Document4 pagesReview Lecture 3 Descriptive Statistics, Part 2Amierson TilendoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World Chapter 4-Data-ManagementDocument41 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Chapter 4-Data-ManagementMarc Loui Rivero0% (1)
- Cae 2 Set 1 Original - KEYDocument5 pagesCae 2 Set 1 Original - KEYJANILA J.No ratings yet
- Hand Out2 Data Presentation 1Document10 pagesHand Out2 Data Presentation 1Caryl GalocgocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Handout Jan 30Document12 pagesChapter 2 Handout Jan 30Information MeNo ratings yet
- Eda Module 2 Frequency Distribution GraphsDocument24 pagesEda Module 2 Frequency Distribution GraphsLenie BaradasNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Unit-1)Document101 pagesStatistics (Unit-1)mannu02.manishNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Additional NotesDocument7 pagesModule 1 Additional NotesWaqas KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5: Introduction To Data ScienceDocument28 pagesLecture-5: Introduction To Data ScienceSaif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter-IIDocument66 pagesStatistics Chapter-IIMiley GirmayNo ratings yet
- It B.tech II Year II Sem DV (R18a0555)Document73 pagesIt B.tech II Year II Sem DV (R18a0555)kandocrush2004No ratings yet
- B.Sc. Statistics - RemovedDocument2 pagesB.Sc. Statistics - RemovedRithuNo ratings yet
- Data Science 3ADocument50 pagesData Science 3AkagomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document30 pagesChapter 03mostafaelshahataliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statistics: Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research University of Kirkuk College of EngineeringDocument15 pagesEngineering Statistics: Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research University of Kirkuk College of Engineeringfaroze libraryNo ratings yet
- LU 3 Descriptive Statistics in SPSSDocument60 pagesLU 3 Descriptive Statistics in SPSSKristhel Jane Roxas NicdaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Part 1 - Student PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 4 - Part 1 - Student PDFparklong16No ratings yet
- FROM DR Neerja NigamDocument75 pagesFROM DR Neerja Nigamamankhore86No ratings yet
- MCT UngroupedDocument25 pagesMCT UngroupedMikee Amanda Eunice GraydaNo ratings yet
- GE 7 Module 4Document33 pagesGE 7 Module 4Emmanuel DalioanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ModuleDocument11 pagesLesson 3 - ModuleSalonga Christalyn Mae F.No ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics C1-4Document130 pagesInferential Statistics C1-4Louis De Thanh NgaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FodDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Fodit hodNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, ModeDocument28 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, ModeFerlyn Claire Basbano LptNo ratings yet
- DM 02 01 Data UndrestandingDocument35 pagesDM 02 01 Data UndrestandingPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FodDocument32 pagesUnit 2 FodkarthickamsecNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Measures of Central TendencyDocument38 pagesLesson 5 Measures of Central Tendencyregine seldaNo ratings yet
- Methods For Describing Sets of Data: (Sections 2.1 and 2.2)Document19 pagesMethods For Describing Sets of Data: (Sections 2.1 and 2.2)A KNo ratings yet
- DSBDL Asg 3 Write UpDocument6 pagesDSBDL Asg 3 Write UpsdaradeytNo ratings yet
- DescriptiveStatsFormulas JMP SASDocument21 pagesDescriptiveStatsFormulas JMP SASPham TinNo ratings yet
- Describing Data:: Numerical MeasuresDocument52 pagesDescribing Data:: Numerical MeasuresMD.Rakibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Tech in BusinessDocument20 pagesQuantitative Tech in BusinessHashir KhanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Xi IpaDocument21 pagesStatistics Xi Ipaprofesor27No ratings yet
- 2.1 Measures of Central TendencyDocument32 pages2.1 Measures of Central Tendencypooja_patnaik237No ratings yet
- Sit 212 Lecture NoteDocument99 pagesSit 212 Lecture NoteTracy JaneNo ratings yet