Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pages From STAL9781607500315-2439 4
Pages From STAL9781607500315-2439 4
Uploaded by
ardabiliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pages From STAL9781607500315-2439 4
Pages From STAL9781607500315-2439 4
Uploaded by
ardabiliCopyright:
Available Formats
W. Lemanza and A.
Lesmana / Deep Soil Improvement Technique Using DMJG Method 2441
Table 1. DMJG treatment parameters adopted in NCH Station. 3.4 DMJG Treatment Results
Blade Diameter
1,600 mm The corings and laboratory tests results from the treated soil
(Mechanical Part)
Column Diameter 2,800 mm specimens had met all requirements of the soil improvement
Water Cement Ratio 100% criteria. The results showed drastic improvement of the original
For E Layer 600 kg/m3
soil properties. Table 2 presents the soil parameters comparison
Mechanical Mixing Part
Cement Dosage
For Other Layers 400 kg/m3
of before and after DMJG treatments.
Number of Blade Cuts 400 times/m
Table 2. Soil properties comparison of before and after treatment.
For F2 Layer 300 L/min
Slurry Discharge Rate Original Soil Properties
For Other Layers 300 L/min
Jet Grouting Part
For F2 Layer 8 min/m SOIL Average Average N-SPT
Withdrawal Speed Depth (m) E50 (kPa)
For Other Layers 7 min/m TYPE cu (kPa) (blows/300mm)
E 10 15 +1.2 (z-10) 0~1 300Cu
M 10 15 +1.2 (z-10) 0~1 300Cu
F1 10 N/A 3 ~ 17 1500N
DMJG Treated Soil Properties
SOIL Average Average N- SPT Average E50
Depth (m)
TYPE qu (MPa) (blows/300mm) (MPa)
E 10 2.8 > 100 390
M 10 3.8 > 100 548
F1 10 3.3 > 100 523
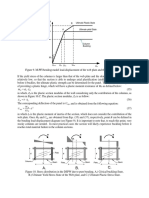
Figure 3. Typical DMJG column arrangement.
As shown in Figure 5 and 6, the laboratory tests of DMJG core
3.3 Quality Control samples show both mechanical part and jet grouting part share similar
statistical trends in terms of strength represented by the Unconfined
During the treatment process, the soil improvement quality was Compressive Strength (qu) and stiffness (E50). The mean of qu and E50
ensured through the utilization of computerized quality control for mechanical part are 3.89 MPa and 565 MPa, whereas for jet
system to monitor and record improvement depth, penetration grouting part are 3.56 MPa and 544 MPa respectively.
and withdrawal rate, and slurry discharge rate at every meter of
depth.
For the final product, i.e. treated soil uniformity and 60
properties, an extensive coring and laboratory test regime were Mechanical Part Jet Grout Part
carried out for the mechanical part as well as the jet grouting 50
Frequency (%)
49
part. Figure 4 illustrates the coring locations for both
mechanical and jet grouting parts. 40
32
30
20
12
10 9 9 9 810
6 7
6 7
5 6
4
3 4 4
2 2 2 2 1
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
qu (MPa)
Figure 5. Statistical distribution of qu of all DMJG core samples.
60
Mechanical Part Jet Grout Part
Figure 4. Coring locations of mechanical and jet grouting parts. 50
Frequency (%)
The quality of coring was examined in accordance to 40
Singapore Land Transport Authority (LTA) material and
workmanship (M&W) specification, which requires Total Core 30
`
Recovery (TCR) to be minimum 85%. In addition, core samples 19
21
were sent to laboratory for Unconfined Compression Test. The 20
13 20
16
acceptance criteria were based on the design requirements that 16 17 9
specified stiffness (E50) of 90 MPa and Unconfined 10
3
6
10 10 4 4
9 2
Compressive Strength (qu) of 900 kPa at 28 days. 5 6 5
1 1
0
In total, the corings were carried out at 107 locations with 36 0 200 400 600 800 1000
1 1
1200
1
1400 1600
cores for the mechanical part and 71 cores for the jet grouting E50 (MPa)
part. In addition, 87 boreholes of Standard Penetration Test
(SPT) were also carried to provide in-situ strength check of the Figure 6. Statistical distribution of E50 (stiffness) of all DMJG core
treated soil mass complying to LTA M&W Specification. samples.
You might also like
- 9851 3139 01 - Cop 1238KDocument2 pages9851 3139 01 - Cop 1238Kbundajoseph148No ratings yet
- Mac DrainDocument24 pagesMac Drainsundra0No ratings yet
- Design of Transformer Foundation Transformer Detail: Ref DRG NoDocument16 pagesDesign of Transformer Foundation Transformer Detail: Ref DRG Nottbharat67% (3)
- Geomembrane HDPE Smooth Black PDFDocument1 pageGeomembrane HDPE Smooth Black PDFandriarisetiawan0% (1)
- Gas Pipeline Blowdown TimeDocument3 pagesGas Pipeline Blowdown Timeankur2061No ratings yet
- CompreDocument53 pagesCompreGEr JrvillaruEl0% (3)
- Duct Work-Safid - 37261Document14 pagesDuct Work-Safid - 37261Hasan RiazNo ratings yet
- Static Calculation of Jacking Pipes - TableofcontentsDocument13 pagesStatic Calculation of Jacking Pipes - Tableofcontentsbimbim1611No ratings yet
- Docol 1300M: General Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesDocol 1300M: General Product DescriptionAnonymous wR1jrmpYANo ratings yet
- Bhavannarao@yahoo - Co.in: D.V .Bhavanna Rao Retired R&B Chief Engineer E-Mail: Phone: +919494440202Document192 pagesBhavannarao@yahoo - Co.in: D.V .Bhavanna Rao Retired R&B Chief Engineer E-Mail: Phone: +919494440202saibal deyNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Uk MacdrainDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet Uk MacdrainMe Kang He Kodos We Kang And KodosNo ratings yet
- Somos PerFORM SS-PDS Letter PDFDocument2 pagesSomos PerFORM SS-PDS Letter PDFAdriano AraujoNo ratings yet
- 6070 EN HDPE SmoothDocument1 page6070 EN HDPE SmoothMarikajNo ratings yet
- 1le5584 3aa03 4ab4Document2 pages1le5584 3aa03 4ab4Dharmesh ChanawalaNo ratings yet
- TDS Contec AMHS0101Document1 pageTDS Contec AMHS0101maulanimeli89No ratings yet
- Husky G-PET - Product GuideDocument19 pagesHusky G-PET - Product GuideDawn UnderNo ratings yet
- 1LE1023-1AA43-4AB4-Z L22+L23 Datasheet enDocument2 pages1LE1023-1AA43-4AB4-Z L22+L23 Datasheet enTien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pda V1974Document3 pagesPda V1974Afiq AdnanNo ratings yet
- Influence of Sand Ratio On The Fluidity Properties of SCC in CRTS III Type Track SystemDocument6 pagesInfluence of Sand Ratio On The Fluidity Properties of SCC in CRTS III Type Track SystemDastardly HeelNo ratings yet
- Rigid PavementDocument3 pagesRigid PavementPrabhakar LadNo ratings yet
- Pages From STAL9781607500315-2439 5Document1 pagePages From STAL9781607500315-2439 5ardabiliNo ratings yet
- Paling BillDocument5 pagesPaling Billanon_b186No ratings yet
- NSW Pump Calculation 26-05-2017-r4Document28 pagesNSW Pump Calculation 26-05-2017-r4Ardian200% (1)
- Corection Chapter 12Document2 pagesCorection Chapter 12Shweta BagdiNo ratings yet
- #02. ST1051E - D30G Training Manual - CompDocument78 pages#02. ST1051E - D30G Training Manual - CompAugusto NuñezNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 1CV2310A Simotics XP - 315 S - Im V1 - 2PDocument2 pagesData Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 1CV2310A Simotics XP - 315 S - Im V1 - 2PMARIAM100% (1)
- The Impact of Surface Roughness On Axial Compressor Performance DeteriorationDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Surface Roughness On Axial Compressor Performance DeteriorationAlozie OgechukwuNo ratings yet
- Infinair Fan Data SheetDocument2 pagesInfinair Fan Data SheetInsertec LtdaNo ratings yet
- Rheology Applications Note: Automatic Gap ClosureDocument3 pagesRheology Applications Note: Automatic Gap ClosuretadirambabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3harshitNo ratings yet
- AVL Microsoot SensorDocument17 pagesAVL Microsoot SensorWidodo Budi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Media Charge - Dynamics - SAG MillsDocument31 pagesMedia Charge - Dynamics - SAG Millsedwin javier valdivia guillenNo ratings yet
- Somos PerFORM Datasheet Complete PDFDocument4 pagesSomos PerFORM Datasheet Complete PDFAdriano AraujoNo ratings yet
- 5680GN Pag8Document11 pages5680GN Pag8payoseNo ratings yet
- Media Charge Dynamics Ball MillsDocument31 pagesMedia Charge Dynamics Ball Millsedwin javier valdivia guillenNo ratings yet
- Ir ADV C70xx - C90xx PRO Bulletin - Mottled Blank On Image 1Document41 pagesIr ADV C70xx - C90xx PRO Bulletin - Mottled Blank On Image 1troy2k0No ratings yet
- Ds - TECHDRAIN GTG 720 - enDocument1 pageDs - TECHDRAIN GTG 720 - enThameem SharaafNo ratings yet
- MacMat Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageMacMat Technical Data SheetinfoNo ratings yet
- TC PC WireDocument3 pagesTC PC WireSM AreaNo ratings yet
- Estimates of Electromagnetic Damping Across An Induction Motor Air Gap (GMC 2015)Document12 pagesEstimates of Electromagnetic Damping Across An Induction Motor Air Gap (GMC 2015)Camilo Andres QuinteroNo ratings yet
- 1989 Reff2019Document6 pages1989 Reff2019Raju Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- DGN 400 4 100H A1FT5 3Ph 4pole DatasheetDocument3 pagesDGN 400 4 100H A1FT5 3Ph 4pole Datasheetaldenijsk1994No ratings yet
- 1MB1553-1AA42-3AA4-Z B02+H19 Datasheet enDocument2 pages1MB1553-1AA42-3AA4-Z B02+H19 Datasheet enranjithNo ratings yet
- 1LE1501-3AB53-4AB4 Datasheet enDocument1 page1LE1501-3AB53-4AB4 Datasheet enfarid.chira2No ratings yet
- A Bolted Moment Connection Model For Precast Column-Beam JointDocument8 pagesA Bolted Moment Connection Model For Precast Column-Beam JointSZC PrecastNo ratings yet
- Compound Wall SinghaniaDocument1 pageCompound Wall SinghaniaAHSANNo ratings yet
- 23882Document1 page23882skiu paket 31No ratings yet
- 1LE1003-1AA43-4AB4 Datasheet enDocument1 page1LE1003-1AA43-4AB4 Datasheet enAhmed Mahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Research Flow ChartDocument23 pages3.1 Research Flow ChartHendri HermawanNo ratings yet
- Design Parameter PositionDocument38 pagesDesign Parameter PositionLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- 1MB1533-1EB49-0FB4-Z B43+M4B Datasheet enDocument2 pages1MB1533-1EB49-0FB4-Z B43+M4B Datasheet enrianandiyahooNo ratings yet
- Euro-Composites Panel Datasheet EC-PA Aviation PanelsDocument1 pageEuro-Composites Panel Datasheet EC-PA Aviation PanelsWurstNo ratings yet
- EXA M DatasheetsDocument2 pagesEXA M DatasheetsTun JebatNo ratings yet
- Sandy Drifterz, Vcet: Madurai, Tamil NaduDocument15 pagesSandy Drifterz, Vcet: Madurai, Tamil NaduNaveenNo ratings yet
- Fastners MTCDocument18 pagesFastners MTCmaheshmalaichamy007No ratings yet
- Analytical Design of Axial Flux PMG For Low Speed Direct DriveDocument11 pagesAnalytical Design of Axial Flux PMG For Low Speed Direct DriveSeksan KhamkaewNo ratings yet
- Daily Mud Report No. 62: Bit Information Bit Hydraulics VOLUMES (BBL)Document5 pagesDaily Mud Report No. 62: Bit Information Bit Hydraulics VOLUMES (BBL)Tahir Iqbal. Kharpa RehanNo ratings yet
- Switchyard Earthing Report - AkkareipattuDocument12 pagesSwitchyard Earthing Report - AkkareipattuManjithaGeethadharaGunarathneNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Yanmar 4TNV98 GGEDocument3 pagesCatalogue Yanmar 4TNV98 GGEAdmin Bisnis0% (1)
- BG 33 H Fisa TehnicaDocument2 pagesBG 33 H Fisa Tehnicalorenz sarimNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Modes: Theory and Applications in Antenna EngineeringFrom EverandCharacteristic Modes: Theory and Applications in Antenna EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Interface / Interphase in Polymer NanocompositesFrom EverandInterface / Interphase in Polymer NanocompositesAnil N. NetravaliNo ratings yet
- The Design of Geotechnical Structures Using Numerical MethodsDocument10 pagesThe Design of Geotechnical Structures Using Numerical MethodsardabiliNo ratings yet
- JPG Volume 6 Issue 3 Pages 9-20Document12 pagesJPG Volume 6 Issue 3 Pages 9-20ardabiliNo ratings yet
- Weak StoryDocument1 pageWeak StoryardabiliNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Finite Element Analysis of Safety FactorDocument8 pagesNon Linear Finite Element Analysis of Safety FactorardabiliNo ratings yet
- Rep 9 (2002) Different Binding AgentsDocument50 pagesRep 9 (2002) Different Binding AgentsardabiliNo ratings yet
- Simpson-2008 4Document1 pageSimpson-2008 4ardabiliNo ratings yet
- D M F Z M A B Z A N B N M M F F F:, T Are Height, Web Thickness and Flange Width of The Column Respectively, andDocument1 pageD M F Z M A B Z A N B N M M F F F:, T Are Height, Web Thickness and Flange Width of The Column Respectively, andardabiliNo ratings yet
- JPG - Volume 6 - Issue 3 - Pages 9-20 6Document1 pageJPG - Volume 6 - Issue 3 - Pages 9-20 6ardabiliNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of The M-Pfi Method: Intability in The Frame and Buckling of The ColumnDocument1 pageEffectiveness of The M-Pfi Method: Intability in The Frame and Buckling of The ColumnardabiliNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Yielding State of Web Plate in Pure Bending: CR CR CR T CR CR T T T TDocument1 pageUltimate Yielding State of Web Plate in Pure Bending: CR CR CR T CR CR T T T TardabiliNo ratings yet
- Densification of Saturated Silty Soils Using Composite Stone Columns For Liquefaction MitigationDocument13 pagesDensification of Saturated Silty Soils Using Composite Stone Columns For Liquefaction MitigationardabiliNo ratings yet
- Simpson-2008 5Document1 pageSimpson-2008 5ardabiliNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferencesardabiliNo ratings yet
- Basic Assumptions: Critical Buckling State of DSPW in Pure BendingDocument1 pageBasic Assumptions: Critical Buckling State of DSPW in Pure BendingardabiliNo ratings yet
- CR Ty: Bending - Shear Interaction For Ultimate StateDocument1 pageCR Ty: Bending - Shear Interaction For Ultimate StateardabiliNo ratings yet
- Bending - Shear Interaction For Ductile Steel Plate Walls: BD E D G D EI M D G U S M/ C CDocument1 pageBending - Shear Interaction For Ductile Steel Plate Walls: BD E D G D EI M D G U S M/ C CardabiliNo ratings yet
- Effect of Rigidity of Beams and Columns On Steel Plate: We FeDocument1 pageEffect of Rigidity of Beams and Columns On Steel Plate: We FeardabiliNo ratings yet
- Bending and Shear Analysis and Design of Ductile Steel Plate WallsDocument1 pageBending and Shear Analysis and Design of Ductile Steel Plate WallsardabiliNo ratings yet
- Shear Analysis of Ductile Steel Plate WallsDocument1 pageShear Analysis of Ductile Steel Plate WallsardabiliNo ratings yet
- M B Ultimate Plastic State M Ultimate Yield State: Is As FollowDocument1 pageM B Ultimate Plastic State M Ultimate Yield State: Is As FollowardabiliNo ratings yet
- ⋅ ⋅ Θ ⋅ ⋅ + Θ ⋅ + =) 2 sin 2 2 sin 2 1 (σ τ σ τ: d t b KDocument1 page⋅ ⋅ Θ ⋅ ⋅ + Θ ⋅ + =) 2 sin 2 2 sin 2 1 (σ τ σ τ: d t b KardabiliNo ratings yet
- WCR CR WCR WCR CR WCRDocument1 pageWCR CR WCR WCR CR WCRardabiliNo ratings yet
- CBD Integral Curb CBD Separate Curb & Gutter CBD Integral Curb & GutterDocument10 pagesCBD Integral Curb CBD Separate Curb & Gutter CBD Integral Curb & GutterardabiliNo ratings yet
- Two Grate Inlet Four Grate Inlet Six Grate Inlet Eight Grate InletDocument10 pagesTwo Grate Inlet Four Grate Inlet Six Grate Inlet Eight Grate InletardabiliNo ratings yet
- B T E K: PlateDocument1 pageB T E K: PlateardabiliNo ratings yet
- Description: City of Dallas, TexasDocument10 pagesDescription: City of Dallas, TexasardabiliNo ratings yet
- City of Dallas, Texas: Front Elevation at Curb FaceDocument9 pagesCity of Dallas, Texas: Front Elevation at Curb FaceardabiliNo ratings yet
- Department of Public Works: Standard Construction DetailsDocument10 pagesDepartment of Public Works: Standard Construction DetailsardabiliNo ratings yet
- Field Check For Water Tightness Property of Curtain Wall Facades & WindowsDocument2 pagesField Check For Water Tightness Property of Curtain Wall Facades & WindowsardabiliNo ratings yet
- Steel-Supported Glazed Facades and RoofsDocument17 pagesSteel-Supported Glazed Facades and RoofsardabiliNo ratings yet
- 2 Piles Cap Design ExampleDocument3 pages2 Piles Cap Design ExampleSilvanus ChepkocheiNo ratings yet
- Store Resp: Store Level Vending ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesStore Resp: Store Level Vending ResponsibilitiesDrahosDostalNo ratings yet
- System No. W-L-2276: F Rating - 2 HR T Rating - 2 HRDocument2 pagesSystem No. W-L-2276: F Rating - 2 HR T Rating - 2 HRDatNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MCQ'sDocument1 pageCivil Engineering MCQ'sNISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Thermal Management CourseDocument17 pagesVehicle Thermal Management CourseShivakumar SatyanarayanNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Guo Li, Lei Dong, Zhu'an Bai, Ming Lei, Jianmin DuDocument7 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Guo Li, Lei Dong, Zhu'an Bai, Ming Lei, Jianmin DuHaniel FcNo ratings yet
- Response of Mild Steel Chimney Under Wind LoadsDocument10 pagesResponse of Mild Steel Chimney Under Wind LoadsSayan MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Discipline: Rev. No.: Size: Document No.: Unit / Area NameDocument5 pagesDiscipline: Rev. No.: Size: Document No.: Unit / Area NameRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, Vol. 15Document6 pagesReview of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, Vol. 15amin110110No ratings yet
- Installation Instructions Montageanleitung Notice de Montage Istruzioni Di Montaggio Instrucciones de Montaje Montageaanwijzing Mettler Toledo Quick Pit PFADocument16 pagesInstallation Instructions Montageanleitung Notice de Montage Istruzioni Di Montaggio Instrucciones de Montaje Montageaanwijzing Mettler Toledo Quick Pit PFAjean pablo huancas reañoNo ratings yet
- 02-GB 50003-2011砌体结构设计规范 - en - newDocument114 pages02-GB 50003-2011砌体结构设计规范 - en - newyyyy071220No ratings yet
- DT-P4300NSR NDR 4G Sept2017 - ANGLAISDocument11 pagesDT-P4300NSR NDR 4G Sept2017 - ANGLAISClaudio Valencia MarínNo ratings yet
- B37Document2 pagesB37wpwmhatNo ratings yet
- Gaggenau BX 280Document1 pageGaggenau BX 280PurcellMurrayNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL (High) PRICED BOQDocument74 pagesELECTRICAL (High) PRICED BOQhazihappy100% (1)
- Characterisation of Bakelite-Modified Bitumen PDFDocument15 pagesCharacterisation of Bakelite-Modified Bitumen PDFEr. Piyush Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Enginagar Construction Pvt. LTD Dhumbarahi 04, KMC, Kathmandu Opening Schedule DetailsDocument2 pagesEnginagar Construction Pvt. LTD Dhumbarahi 04, KMC, Kathmandu Opening Schedule DetailsRoman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Rab ElektrikalDocument3 pagesRab ElektrikalTataNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Engineered Geopolymer Composite 2022 ConstructionDocument25 pagesA Critical Review of Engineered Geopolymer Composite 2022 ConstructionYoukhanna ZayiaNo ratings yet
- L17 - Transient AnalysisDocument10 pagesL17 - Transient AnalysisSamiullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Submittal PVC Pipe - Perforated PDFDocument60 pagesSubmittal PVC Pipe - Perforated PDFDusngi MoNo ratings yet
- ACI Deflection MOD MotiurDocument5 pagesACI Deflection MOD Motiurbasum matNo ratings yet
- Freyssibar BrochureDocument12 pagesFreyssibar BrochureNick BesterNo ratings yet
- Ce151 hw1Document16 pagesCe151 hw1Kristopper AcostaNo ratings yet
- Gate Question Papers Download Architecture and Planning 2009Document0 pagesGate Question Papers Download Architecture and Planning 2009Rohit AnandNo ratings yet
- Polyflor Global Approved AdhesivesDocument24 pagesPolyflor Global Approved AdhesivesRatna Ayu K 201102No ratings yet