Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meningitis TB
Uploaded by
Siq Febri Smnjtk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesOriginal Title
meningitis tb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesMeningitis TB
Uploaded by
Siq Febri SmnjtkCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS
Dr. Steven, M.Si.Med, Sp.S
§ Commonest manifestation of tuberculous
infection of the nervous system
§ In children : TB milier à bacteraemia à
meningitis
§ In adult :
- occur many years after the primary
infection
- Following bacteraemia, metastatic foci of
infection lodge in: meninges, cerebral or
spinal tissue, choroid plexus
- Rupture à into the subarachnoid space
(spontaneously or impaired immunity)
Clinical features
Stage 1 (early) Stage 2 (intermediate) Stage 3 (advanced)
Non-specific symtoms Confusion Coma
- Fever (in 80%) Cranial nerve pares is
Meningism
- Lethargy
Vasculitis à Hemiparesis
Ataxia
Dysarthria
Staging is useful for predicting outcome
§ Seizures may occur at the onset
§ Involuntary movement (chorea, Myoclonus)
occur in 10%
§ Arachnoidit is inflammatory exudate may result in
hydrocephalus
Investigations
§ General : anaemia, leucocytosis, hyponatraemia
(if inappropriate ADH)
§ Cerebrospinal f luid
§ Xanthocrome, pellicle (+)
§ Cell count is elevated, predominant ly
lymphocytes
§ Glucose is depressed (<50% blood sugar)
§ Protein elevated
§ Culture for M. tuberculosis (50
(50--80% +)
§ PCR
§ Tuberculin skin t est
Positive in 50% of cases
§ Chest x-x-ray
infiltrate / cavitation / effusion / scar
§ Ct scan and MRI (+ contrast)
Hydrocephalus,
basal meningeal thickening,
infarct, oedema, tuberculoma
Treatment
§ Recomemended treatment programme:
Normal regime:
INH (300 mg daily) INH
2 months
Rifampicin (600 mg daily) Rifampicin 6 months
PZA (15-30 mg/kg daily)
Drug resistance suspected due to previous antituberculous
therapy, eg: - developing countries
- history of previous inf ection
àAdd a fourth drug – streptomycin (1 g daily) or ethambutol
(25 mg/kg daily)
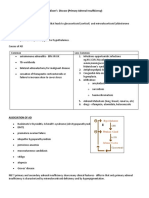
Antiturberculous Drug Penetrati on to CSF
Drug Inflamed Non Inflamed
• Streptomicin Good Poor
• INH Good Good
• Rifampicin Good Poor
• Pyrazinamid Good Good
• Ethionamid Good Good
• Cycloserin Good Good
• Ethambutol Good Poor
§ Side effects:
- INH – peripheral neuropathy à pyridoxine 50
mg daily
- Ethambutol – optic atrophy
- Streptomysin – 8th cranial nerve damage
- All antituberculous drugs à nausea, vomiting,
abnormal liver function and skin rashes
Steroid tend to be given when :
- conscious level declines
- neurological sign progress
- Spinal block develops
You might also like
- Epilepsy NotesDocument6 pagesEpilepsy NotesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (1)
- Handbook For Vaccine and Cold Chain HandlersDocument128 pagesHandbook For Vaccine and Cold Chain HandlersRyza Jazid Baharuddin NurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lab 3 Skill Performance Checklist Administering A Blood Transfusion S U NP CommentsDocument2 pagesNursing Lab 3 Skill Performance Checklist Administering A Blood Transfusion S U NP CommentsCandice Cheng88% (8)
- Autoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursDocument7 pagesAutoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursdNo ratings yet
- Anak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTDocument21 pagesAnak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTAnastasia PinkyNo ratings yet
- PAED MicrocephalyDocument18 pagesPAED Microcephalyaboje ochekwuNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Seizures: - Dr.C.S.N.VittalDocument23 pagesNeonatal Seizures: - Dr.C.S.N.VittalRidanna HartateanaNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy & Antiepileptic Drugs: Dr. Siva Priya Sonali Thanushanthan Tivashkar Srinaath SidhantasahooDocument40 pagesEpilepsy & Antiepileptic Drugs: Dr. Siva Priya Sonali Thanushanthan Tivashkar Srinaath Sidhantasahoothanush_15No ratings yet
- Hypoxic Ischemic EncephalopathyDocument10 pagesHypoxic Ischemic EncephalopathyPadmaNo ratings yet
- CURS Pneumonii 2014 ADocument176 pagesCURS Pneumonii 2014 AAda Dinu100% (1)
- Neurology LectureDocument48 pagesNeurology Lecturehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Disease Study: A. Myasthenia GravisDocument6 pagesDisease Study: A. Myasthenia GravisMark Lemuel AbadaNo ratings yet
- Meningitis in Children: Shakilu J MD University of DodomaDocument47 pagesMeningitis in Children: Shakilu J MD University of DodomaGimson kanimbaNo ratings yet
- CNS, NBL, HBL, Gonads, NephroDocument67 pagesCNS, NBL, HBL, Gonads, NephroMaulana Heru JatmikoNo ratings yet
- Tetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDocument32 pagesTetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDr. Amb. Monday ZaccheausNo ratings yet
- Status Epilepticus: MD Neurologist, Epilepsy and General Neurology, Comprehensive Epilepsy ProgramDocument28 pagesStatus Epilepticus: MD Neurologist, Epilepsy and General Neurology, Comprehensive Epilepsy ProgramHayley JuniorNo ratings yet
- 20 Bacterial MeningitisDocument35 pages20 Bacterial MeningitisBhakti WashilkarNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument44 pagesMyasthenia GravisAli KhaqaanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Management of The First Seizure in Adults: Adults?Source Search - Result&Search Epilepsy&Selectedtitle 1 150Document8 pagesEvaluation and Management of The First Seizure in Adults: Adults?Source Search - Result&Search Epilepsy&Selectedtitle 1 150ales_sandriNo ratings yet
- CNS Infections: Rashmi KumarDocument32 pagesCNS Infections: Rashmi Kumarfasil tadesseNo ratings yet
- Child Hood Seizuer ManagmantDocument78 pagesChild Hood Seizuer Managmantsentayehu siyumNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Neurology BAUDocument56 pagesPediatric Neurology BAUمجاهد أسعدNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 KGD AditDocument70 pagesPemicu 4 KGD AditAditya SuksmawanNo ratings yet
- Convulsions (Seizures and Epilepsy) : Mr. Dipti SorteDocument33 pagesConvulsions (Seizures and Epilepsy) : Mr. Dipti SorteijklmnopqurstNo ratings yet
- 12 ComainpediatricDocument24 pages12 Comainpediatricsunil singhNo ratings yet
- Adrenal DisordersDocument36 pagesAdrenal DisordersMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- ENDO - Adrenal CrisisDocument8 pagesENDO - Adrenal CrisisHajime NakaegawaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Presentation and Discussion On Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Sle)Document59 pagesWeekly Presentation and Discussion On Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Sle)Dr AnilNo ratings yet
- Pharm Care in Stroke-1Document45 pagesPharm Care in Stroke-1Achmad Triwidodo AmoeNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument20 pagesAcute Rheumatic Feverfaizal samadNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument24 pagesMultiple SclerosisKulgaurav RegmiNo ratings yet
- Hypoxic-Ischemic EncephalopathyDocument34 pagesHypoxic-Ischemic EncephalopathyJim Christian EllaserNo ratings yet
- Case ObjectivesDocument27 pagesCase ObjectivesJanetta RheaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument37 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosusFirman Ichlasul AmalNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)Document5 pagesAddison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)sunnnydayNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1medhanit anjuloNo ratings yet
- Headaches and Differentials: Resources: Overview#showal Murtagh J. General Practice, 5th Ed. 584-600Document17 pagesHeadaches and Differentials: Resources: Overview#showal Murtagh J. General Practice, 5th Ed. 584-600dr. Ukie HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Neurological EmergenciesDocument47 pagesNeurological EmergenciesStellate Repentance100% (1)
- m1 C. Mhango - Eclamptic Patient and ManagementDocument24 pagesm1 C. Mhango - Eclamptic Patient and ManagementAddisNo ratings yet
- Saraf DR - Steven - Meningitis TBDocument10 pagesSaraf DR - Steven - Meningitis TBxyrosNo ratings yet
- Prince Sultan Military College For Health SciencesDocument20 pagesPrince Sultan Military College For Health SciencesmahaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseDocument8 pagesNursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- 2011 CNS Bacterial InfectionDocument47 pages2011 CNS Bacterial InfectionZEMENAY TRUNEHNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument61 pagesThyroid DisordersdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument30 pagesMyasthenia GravisMridula Mary AugustineNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument37 pagesNeurologyDevangkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument26 pagesNephrotic Syndromeamalfayiz84No ratings yet
- Neuro 2 AnsDocument14 pagesNeuro 2 AnsSantiago AldayNo ratings yet
- Reumato and EndocrineDocument106 pagesReumato and Endocrinehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- ARF PresentationDocument39 pagesARF PresentationRichard SsenyondoNo ratings yet
- Meningitis in ChildrenDocument27 pagesMeningitis in Childrensai saiNo ratings yet
- General PresentationDocument306 pagesGeneral PresentationJamie IllmaticNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor.Document19 pagesBrain Tumor.Mission JupiterNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis in HIV PatientsDocument49 pagesToxoplasmosis in HIV PatientsLily SolNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Meningitis in NeonatesDocument3 pagesBacterial Meningitis in Neonatesyoke limuriaNo ratings yet
- Management of Neurologic ConditionsDocument193 pagesManagement of Neurologic ConditionsAnna ReyesNo ratings yet
- Morning Report: Cysticercosis: Palak Parikh December 12, 2008Document29 pagesMorning Report: Cysticercosis: Palak Parikh December 12, 2008Jayarani AshokNo ratings yet
- Aes PPT Pooja KumariDocument27 pagesAes PPT Pooja KumariAbhilasha Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- AAAA2Document142 pagesAAAA2Sruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- LEC 03 - Pituitary TumoursDocument54 pagesLEC 03 - Pituitary TumoursIoana CozmaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Pituitary GlandDocument60 pagesDiseases of The Pituitary GlandJonsu1517No ratings yet
- Pediatric NephroticDocument45 pagesPediatric NephroticMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- CNS Bacterial Infections: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaDocument47 pagesCNS Bacterial Infections: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaJanPaulaDelaPenaNo ratings yet
- Viêm Khớp Dạng Thấp Và Thấp TimDocument57 pagesViêm Khớp Dạng Thấp Và Thấp TimLai QlocNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever - New Diagnostic CriteriaDocument5 pagesRheumatic Fever - New Diagnostic CriteriaSiq Febri SmnjtkNo ratings yet
- Poststreptococcal Illness: Recognition and Management: Streptococcus PyogenesDocument6 pagesPoststreptococcal Illness: Recognition and Management: Streptococcus PyogenesSiq Febri SmnjtkNo ratings yet
- PREOPERATIF EVALUASI & PERSIAPAN ANESTESI (Autosaved)Document42 pagesPREOPERATIF EVALUASI & PERSIAPAN ANESTESI (Autosaved)Siq Febri SmnjtkNo ratings yet
- JURNAL READING Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Neonates and Children From China A ReviewDocument12 pagesJURNAL READING Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Neonates and Children From China A ReviewSiq Febri SmnjtkNo ratings yet
- Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) : Dr. Parluhutan Siagian, M.ked (Paru), SP.P (K), FISRDocument24 pagesMultidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) : Dr. Parluhutan Siagian, M.ked (Paru), SP.P (K), FISRMelly MirandaNo ratings yet
- Influenza Declination Form 2019 (2957)Document1 pageInfluenza Declination Form 2019 (2957)deNo ratings yet
- Blood 1997 Jennings 2863 92Document31 pagesBlood 1997 Jennings 2863 92Neo Mervyn MonahengNo ratings yet
- Cellular Mediated Immune Response: DR - Tetty Aman Nasution, Mmedsc Departemen Mikrobiologi FK UsuDocument60 pagesCellular Mediated Immune Response: DR - Tetty Aman Nasution, Mmedsc Departemen Mikrobiologi FK UsuMarisi PaulinaNo ratings yet
- Patophysiology Oral Q 1Document134 pagesPatophysiology Oral Q 1TijanaNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateSubhajit MandalNo ratings yet
- Revised National TB Control ProgramDocument12 pagesRevised National TB Control ProgramsaurabhNo ratings yet
- Cartão de Vacina CovidDocument2 pagesCartão de Vacina CovidEvanildo MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Respiratory: Tuberculosis PneumoniaDocument37 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Respiratory: Tuberculosis PneumoniaCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument2 pagesArgumentative Essayjoyce anne GarciaNo ratings yet
- 21-22 - Laboratory Examination and Work-Up For Hematologic Disorders - DR - Ariful HayatDocument111 pages21-22 - Laboratory Examination and Work-Up For Hematologic Disorders - DR - Ariful HayatGiselleNo ratings yet
- Biology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsDocument37 pagesBiology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsSaveen Kadian75% (4)
- What Is COVID-19?: Essay On Coronavirus Class 8ThDocument10 pagesWhat Is COVID-19?: Essay On Coronavirus Class 8ThSappurd Ali SaqibNo ratings yet
- Infection CommitteeDocument6 pagesInfection Committeejuveria nausheenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196655316001693 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S0196655316001693 MainSandu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 1526931449Document123 pages1526931449Lika KipshidzeNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Map Labelling IELTS ListeningDocument29 pagesBài Tập Map Labelling IELTS ListeningHào Vũ ThếNo ratings yet
- Managing Allergic Rhinitis in Children Through Ayurvedic Herbal MedicinesDocument11 pagesManaging Allergic Rhinitis in Children Through Ayurvedic Herbal MedicinesAyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Frequent and Potentially Severe DiseaseDocument5 pagesChronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Frequent and Potentially Severe Diseasemedicina146No ratings yet
- Handbook of Poultry DiseasesDocument22 pagesHandbook of Poultry DiseasesSoufian CherkiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency MedicineDocument398 pages2022 Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency MedicinekaldasNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Implementation of Expanded Program On Immunization in Barangay Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del Norte From 2014-2018Document15 pagesAssessment of The Implementation of Expanded Program On Immunization in Barangay Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del Norte From 2014-2018Diana Grace ViñaNo ratings yet
- Molluscum ContagiosumDocument2 pagesMolluscum ContagiosumMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- ThalaiTe Inleng NOVEMBERDocument4 pagesThalaiTe Inleng NOVEMBERLalmuansanga Chhakchhuak StcNo ratings yet
- 10 UtiDocument12 pages10 UtiLorenzo Farala Cruz IIINo ratings yet
- Anbio IFU English 1 JusteradDocument3 pagesAnbio IFU English 1 JusteradVasilij PupkinNo ratings yet