Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safari - 30 Août 2023 À 12:59
Safari - 30 Août 2023 À 12:59
Uploaded by
Alpha ;Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safari - 30 Août 2023 À 12:59
Safari - 30 Août 2023 À 12:59
Uploaded by
Alpha ;Copyright:
Available Formats
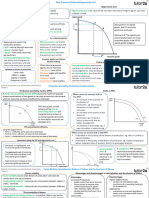
Understanding
business activity
Nature of Business
Activity
Needs: goods or services that we
need in order to live
Wants: goods or services which
people would like to have. But are
not essential for living.
People’s wants are unlimited (you
will always want something) but the
resources available to produce them
are limited which leads to scarcity
(the basic economic problem)
Scarcity: there are not enough
products to ful!l the wants of the
population
Resources (also known as factors of
production) include: Land, Labour,
Capital & Enterprise
Land – any natural resource
used in production
Labour – mental and physical
e"orts of a human
Capital – man-made goods used
in production
Enterprise – the risk-taking
ability of an entrepreneur
As there are limited resources,
people are always forced to make a
choice. This means that we will be
giving something up, this is known as
opportunity cost
Opportunity cost: it is the next best
alternative that is given up by
choosing another item.
Specialisation
Specialisation: when people and
businesses focus on what they are
best at.
Division of labour is when
production is split in di"erent tasks
and each worker performs one of
these tasks
Advantages Disadvantages
Workers Workers become
specialized in bored of doing
certain task, the same job.
increases E#ciency might
e#ciency fall
If a worker is
Less time is
absent, no other
wasted from
worker can do
one workbench
the job.
to another,
E#ciency might
more e#ciency
fall
As the business Employees have
is more e#cient, to rely on each
output increase other to produce
which may lead products, leading
to economies of to a fall in
scale productivity
Workers
become more
skilled and
experienced,
reducing the
mistakes made
Purpose of Business
Activity:
Businesses combine scarce factors of
production to produce goods or
services to satisfy people’s wants
A business also employs people as
worker and pays them wages to
allow them to consume products as
well
Added Value
Added value is the di"erence
between the selling price and the
cost of bought-in raw materials and
components.
Added Value = selling price – total cost
It is NOT the pro!t because added
value does not include the price to
pay for labour, transport etc.
To increase added value, a business
can either:
Increase the selling price of
product, while keeping the total
cost of material the same
Create a brand image
Improve packaging
Make products more appealing
by adding features
Provide higher quality goods and
services
Decrease the total cost of materials,
while keeping the selling price of the
product the same.
Classi:cation of
Businesses
Businesses can be put into three
sectors:
Primary sector – extraction of
natural resources. Ex. farming,
!shing
Secondary sector –
manufacturing and production
of goods. Ex. car manufacturer
Tertiary sector – provides
services. Ex. hairdressing,
banking
The relative importance of these
sectors in an economy depends on:
Number of workers employed
Value of output produced
Deindustrialisation occurs when
there is a decline in the importance
of the secondary sector.
This can happen due to:
Depletion of primary resources
in home country
Cheaper goods by developing
countries
Ability to spend more income on
services
Mixed Economy
Has both a private sector and a
public sector.
Private Sector: Businesses NOT
owned by government, will make
own decisions on what and how
to produce. The main aim is to
make pro!ts.
Public Sector: Owned by the
government. Government will
make decisions on what and
how to produce (i.e. healthcare,
education, defence, public
transport). The main aim is to
provide a service to customers.
Privatization refers to the selling of a
public sector business to the private
sector.
Privatisation may occur as private
sector is more e#cient, competitive
and will be able to make good quality
goods leading to higher pro!ts.
But private sector does not have
social objectives, making their
products una"ordable.
Enterprise, Business
Growth & Size
An entrepreneur is a person who
organises, operates and takes risk to
make the business better
Characteristics of entrepreneurs:
Hard working
Risk Takers
Creative
E"ective Communicators
Optimistic
Self-con!dent
Innovative
Independent.
Advantages and disadvantages of
being an entrepreneur:
Advantages Disadvantages
Independent,
entrepreneurs will
able to
have to put their
choose how
own money into the
to use time
business.
and money
many
Able to put
entrepreneur’s
own ideas
businesses fail
into practice
(risky)
May become
successful Lack of knowledge
and very and experience in
pro!table if starting and
business operating a business
grows
Able to make
Lost income from
use of
not being employee
personal
for another business
interests and
(Opportunity cost)
skills
Will have to invest
Pro!ts to
their own savings as
themselves,
well as !nd other
no need to
sources of !nance ,
share them
which is time taking
with anyone
and expensive
Who needs to know the size of a
business?
Investors
Government
Competitors
Workers
Bank
Business Plans
A business plan contains business
objectives, important details about
the operations, !nance, and the
owners
Business plans assist entrepreneurs
because:
It helps gain !nance. banks will
ask for a business plan before
agreeing to a loan or overdraft
for the business
It forces the entrepreneur to
plan ahead carefully, which
reduces risk of the business
failing.
The main parts of a business plan
include: name, type of organization,
business aim and forecast pro!t
Government Support for
Start-Ups
Governments encourage
entrepreneurs to set up a business
because start-ups:
Reduce unemployment, new
businesses create jobs
Increase competition, gives
consumers more choice
Increase output, economy
bene!ts from increased output
of goods and services
Can grow further and become
large and important businesses
which pay government more
taxes
Governments may give support to
entrepreneurs by:
Business ideas & help, they set
up support sessions held by
experienced business people
Finance, they may lend loans at
low interest rates or grants
Governments provide grants for
training employees to make
them more e#cient and
productive
Governments allow
entrepreneurs to use research
facilities in universities
Business Size
There are several di"erent
measurements of business size and
they all have limitations:
Measurements Limitations
Some businesses
The number of
employ few
people
people but
employed in the
produce high
business
output values
high level of
The value of
output does not
output of the
mean business is
business
big
di"erent
businesses sell
The value of di"erent
sales products
(expensive and
cheap)
The total value
of capital some companies
(money) may use cheap
invested into labor giving high
the business output with low-
(capital cost equipment
employed)
No way of measuring the size is
considered correct as each method
gives di"erent answers. Businesses
choose the method they think is the
best. Therefore, businesses may use
more than one method.
Reasons for business
Growth
Some businesses want to grow
because:
CHAPTERS
Higher pro!ts
CHAPTERS
More status for owners and
managers
can bene!t from Economies of
Scale (lower costs)
Larger share of its market, ‘big
names'
Ways of business
growth
Businesses can either grow by:
Internal Growth
External Growth
Internal Growth is when the business
expands its existing operations
External Growth is when the
business takes over or merges with
another business.
There are three types of External
Growth:
Horizontal Integration – !rm
taking over/merging with
another !rm in the same
industry
Ex. a paper company taking
over another paper
company
Bene!ts include economies
of scale and higher market
share
Problems include
diseconomies of scale and
di#cult to control and
manage the business
Vertical Integration – !rm taking
over/merging with another !rm
in same industry but di"erent
stage of production (there is
forwards and backwards)
Ex. paper manufacturing
company taking over paper
selling company
Bene!ts include pro!ts by
supplier/retailer are
absorbed and personal
attention is given
Conglomerate Merger - !rm
merging/taking over another
!rm in a di"erent industry. (also
known as ‘diversi!cation’)
Ex. paper company taking
over a food company
Bene!ts include spread of
risks and transfer of ideas.
Why small businesses
are at greater risk
Established by youngsters who lack
managed experience
Borrow money to begin so will have
to repay whether or not business is
successful
Start-ups have lesser experience and
information about the market in
order to make informed decisions
New entrepreneurs may not have a
realistic picture of the market
Why Businesses Fail
Poor management – from lack of
experience, poor choice of managers
(family business), bad decisions
Failure to plan for change –
businesses need to adapt
everchanging business environment.
Must take risks.
Poor money management – lack of
money to pay workers, suppliers,
landlords, etc.
Over-expansion – (diseconomies of
scale), management problems and
!nance
Competition with other
businesses – new businesses are at
more risk of failing than existing
businesses.
This is because start-ups have lack of
money, resources, poor planning &
don’t have much research
Sole Trader
A business owned by just one
person. It’s the smallest type of
business. Can employ other people
however.
Useful for people who are
setting up new business
Do not need much capital to get
business running
Will be dealing mainly with the
public
Advantages Disadvantages
Capital is usually
Easy to set up,
provided by
do not require a
owner, hard to
lot of money to
get capital to
set up
expand !rm
They are their They have
own boss, has unlimited liability
the freedom to (responsible for
choose their any debts of the
own holidays, business, bank
work hours, can take away
prices, who to possessions to
employ pay back)
Close
Business is likely
:
You might also like
- New - Delhi SouvenirDocument52 pagesNew - Delhi SouvenirDavid ThomasNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse: Business STUDIES (0450)Document36 pagesCaie Igcse: Business STUDIES (0450)Victoria Sáenz-Azcúnaga100% (1)
- Business Notes For Revison IgsceDocument85 pagesBusiness Notes For Revison IgsceZelda BourgoinNo ratings yet
- Business Studies NotesDocument126 pagesBusiness Studies NotesRishita SinghNo ratings yet
- Workbook (Edition 2)Document171 pagesWorkbook (Edition 2)Vineela Srinidhi DantuNo ratings yet
- Pdfcaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1 PDFDocument36 pagesPdfcaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1 PDFneil jhamnaniNo ratings yet
- Consultants List 2020Document262 pagesConsultants List 2020Ashraf NouriNo ratings yet
- GM 1927-16b Injection Molding Process AuditDocument6 pagesGM 1927-16b Injection Molding Process AuditfernandoNo ratings yet
- Business Note 0450Document32 pagesBusiness Note 0450larry wangNo ratings yet
- Idea Vodafone Project FileDocument36 pagesIdea Vodafone Project FilePranjal jain100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Standard CostingDocument33 pagesChapter 11 Standard CostingMaricar ManansalaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business NotesDocument45 pagesIGCSE Business NotesLin Nandar AungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE and O Level Business Studies (2nd Edition) Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCambridge IGCSE and O Level Business Studies (2nd Edition) Revision GuideRosetta Rose100% (1)
- Caie Igcse: Business STUDIES (0450)Document26 pagesCaie Igcse: Business STUDIES (0450)Amani macNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory 635c0944ab55c839d754bcba 633Document47 pagesCaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory 635c0944ab55c839d754bcba 633Abdelaziz walaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1Document47 pagesCaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1smNo ratings yet
- CIE Section 1 Revision SummaryDocument16 pagesCIE Section 1 Revision SummarySagar KumarNo ratings yet
- Business NotesDocument13 pagesBusiness NotesHelping MindNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Business Studies IGCSE 0450 2024Document57 pagesRevision Guide Business Studies IGCSE 0450 2024Profile 1No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Understanding Business ActivityDocument26 pagesChap 1 Understanding Business ActivityDennisNo ratings yet
- Business Key Notes Chapter 1Document1 pageBusiness Key Notes Chapter 1alilbitteralilsweetNo ratings yet
- Business Activity: What Are Needs and Wants?Document105 pagesBusiness Activity: What Are Needs and Wants?zahra gdehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Business Activity - IGCSE AIDDocument1 page1.1 - Business Activity - IGCSE AIDlydia.cNo ratings yet
- C1-5 BasicsDocument27 pagesC1-5 BasicsNot AndrewNo ratings yet
- Topic Reads - BusinessDocument6 pagesTopic Reads - BusinessNguyễn Phước Hà ThiênNo ratings yet
- 1 Business ActivityDocument3 pages1 Business Activitychristineshweyeshoonlae19No ratings yet
- Business Studies Notes 2Document120 pagesBusiness Studies Notes 2Josephat MugumbaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentKrishita ThakralNo ratings yet
- KoolfishDocument9 pagesKoolfishzaki544203No ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics: Factors of ProductionDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Economics: Factors of ProductionCherry BanadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Business ManagementDocument132 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To Business Managementlyuanlin12No ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory v4Document19 pagesCaie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory v4Shashwat Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory v3Document19 pagesCaie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory v3haroonadnan196No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Types of BusinessDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Types of BusinessAndrea CaparosoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 To 7 - BUSINESS ACTIVITYDocument8 pagesWEEK 1 To 7 - BUSINESS ACTIVITYJosephine MungaNo ratings yet
- Business Activity Specialisation: The Best Use If Limited ResourcesDocument2 pagesBusiness Activity Specialisation: The Best Use If Limited ResourcesKazi Rafsan NoorNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 Micro Pack 1Document12 pagesTheme 1 Micro Pack 118ali.aliNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument29 pagesMicroeconomicshottiemariam10No ratings yet
- Scarcity: Can Produce More Products.Document3 pagesScarcity: Can Produce More Products.ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document21 pagesWeek 2IDKNo ratings yet
- Business Mega Grid Definitions VERY USEFULDocument80 pagesBusiness Mega Grid Definitions VERY USEFULRaghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Unit 1 Business ActivityDocument5 pagesSection 1 Unit 1 Business Activityswati DesaiNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory 664dcb727fde7a0cc7792c97 201Document19 pagesCaie Igcse Economics 0455 Theory 664dcb727fde7a0cc7792c97 201Vera EzeokekeNo ratings yet
- Business NotesDocument95 pagesBusiness NotesMakkhayarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Environment IGSCE NotesDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Business Environment IGSCE NotesbienfaitchibariNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS - Documentos de GoogleDocument1 pageBUSINESS - Documentos de GoogleGonzalo LarrosaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies NotesDocument141 pagesBusiness Studies NotesPeter QuarteyNo ratings yet
- Part Iii. Structured Learning Exercises: Job Costing Involves The FollowingDocument1 pagePart Iii. Structured Learning Exercises: Job Costing Involves The FollowingLenaryle Dela Cerna RamosNo ratings yet
- Ch4 RN EngDocument2 pagesCh4 RN EngbloosmxeditNo ratings yet
- All Business Notes-Rehab Abdelgawad-1Document150 pagesAll Business Notes-Rehab Abdelgawad-1Casey WangNo ratings yet
- APPLIED ECON - Lesson 2Document4 pagesAPPLIED ECON - Lesson 2Deane TriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Business OrganazationsDocument15 pagesUnit 1: Business OrganazationsIvanCoHe (IvanCoHe)No ratings yet
- O.L Business PDFDocument159 pagesO.L Business PDFSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- SSM107 Lec#1 MidtermDocument5 pagesSSM107 Lec#1 MidtermMa. Krecia NicolNo ratings yet
- Business Mrs - Rehab Ch1Document2 pagesBusiness Mrs - Rehab Ch1mohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- Prelims Economics LectureDocument5 pagesPrelims Economics Lecturecalliebea13No ratings yet
- E1. The Basic Economic Problem Quiz Cards: Made by CattaystudiesDocument74 pagesE1. The Basic Economic Problem Quiz Cards: Made by CattaystudiesYashwinni VijayasekarNo ratings yet
- Section 4&5 Business Studies ZnotesDocument14 pagesSection 4&5 Business Studies ZnotesKim BoraNo ratings yet
- Glossary Topic 1 - Introduction Bus MGTDocument2 pagesGlossary Topic 1 - Introduction Bus MGTanne vega basozabalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Notesswati DesaiNo ratings yet
- Business Resumen Primer AñoDocument36 pagesBusiness Resumen Primer AñoSantiago BatistaNo ratings yet
- Operation MarketDocument2 pagesOperation Marketgv2vbrhqhgNo ratings yet
- AS Business 1 PDFDocument50 pagesAS Business 1 PDFSithembile MoyoNo ratings yet
- As Business Revision NotesDocument50 pagesAs Business Revision NotessleepNo ratings yet
- The EconomyDocument42 pagesThe EconomyAlicia HernándezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-B Definition Types of CooperativesDocument15 pagesLecture 1-B Definition Types of CooperativesAlzcareen Erie LiwayanNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis OCS May - Aug 2023Document16 pagesIndustry Analysis OCS May - Aug 2023Md FerozNo ratings yet
- Transformation Plan For Energy Transition: Didier HOLLEAUX, Executive Vice PresidentDocument24 pagesTransformation Plan For Energy Transition: Didier HOLLEAUX, Executive Vice Presidentvishal.nithamNo ratings yet
- In This Issue: Ag VisionDocument8 pagesIn This Issue: Ag VisionCalifornia Food and Justice CoalitionNo ratings yet
- Haircut SecuritiesDocument15 pagesHaircut Securitiesamiit.agarwalNo ratings yet
- KKDocument86 pagesKKKarthikeyan MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Origin: IndonesiaDocument3 pagesCertificate of Origin: IndonesiaRoni ArdianNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix VirginDocument3 pagesBCG Matrix VirginSubhkanish Ravindra RajanNo ratings yet
- Chintan Shivir: Production Planning of With Enabling ConditionsDocument25 pagesChintan Shivir: Production Planning of With Enabling ConditionsKudlappa DesaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing CompendiumDocument77 pagesMarketing CompendiumArnab ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Relevant Costing and DMDocument10 pagesRelevant Costing and DMabdulqadeersoomro50No ratings yet
- PM Heavy Equipment, AC, PC RecoveryDocument11 pagesPM Heavy Equipment, AC, PC Recoveryfadli arsyadaNo ratings yet
- Compression Spring Suppliers, Torsion SpringDocument5 pagesCompression Spring Suppliers, Torsion SpringBhagwati Spring IndustriesNo ratings yet
- Global Procurement CLO3: Describe Solutions To Be Sustainable ProcessesDocument5 pagesGlobal Procurement CLO3: Describe Solutions To Be Sustainable ProcessesA - SIB1728 - Aliff HaiqalNo ratings yet
- IATF - International Automotive Task Force: Rules For Achieving and Maintaining IATF Recognition IATF Rules 5 EditionDocument22 pagesIATF - International Automotive Task Force: Rules For Achieving and Maintaining IATF Recognition IATF Rules 5 Editionviveknarula295382No ratings yet
- Karawang Youth Farmer - Organization Profile 2022Document25 pagesKarawang Youth Farmer - Organization Profile 2022YudiNo ratings yet
- The Indian Forest Under British RajDocument26 pagesThe Indian Forest Under British RajKovid VermaNo ratings yet
- DAGS Travel Order September 2023-Pick-Up I-BEAMSDocument8 pagesDAGS Travel Order September 2023-Pick-Up I-BEAMSFrancis Danver EmerzNo ratings yet
- Warrants For RoundaboutsDocument9 pagesWarrants For RoundaboutsSantiago PuertaNo ratings yet
- Delegate List For AttendeesDocument4 pagesDelegate List For Attendeesनरेश देसाईNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument11 pagesNarrative ReportBrenna Bustamante0% (1)
- CH9 - Inventory Costing and Capacity AnalysisDocument51 pagesCH9 - Inventory Costing and Capacity AnalysisKatsuhira KizunaNo ratings yet
- Project Work of Accounts: Topic-BUSINESS TransactionDocument34 pagesProject Work of Accounts: Topic-BUSINESS TransactionRIMIKA GAYATRINo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 TQM POLIDARIO PDFDocument9 pagesAssignment 9 TQM POLIDARIO PDFALIAHDAYNE POLIDARIONo ratings yet