Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Pump
Uploaded by
mikhail0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageResearch on heat pumps for physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentResearch on heat pumps for physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageHeat Pump
Uploaded by
mikhailResearch on heat pumps for physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Heat Pump
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a device that is used to transfer heat from one location to another. It's
capable of both heating and cooling spaces, making it an energy-efficient alternative to
traditional heating and cooling systems. Heat pumps work based on the principles of
thermodynamics and use a refrigeration cycle to achieve their operation.
Components of a heat pump:
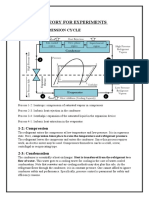
Compressor:
The compressor is the heart of a heat pump system. First, it pumps refrigerant through the
evaporator and condenser coils to transfer heat. The refrigerant gas is then compressed to
increase the pressure and the temperature before releasing it into the condenser coil.
Expansion Valve:
The expansion valve regulates the refrigerant flow in a heat pump system by controlling how
much liquid or gas enters each component at any given time. It does this by using a metering
device that opens or closes depending on the pressure in each element. This ensures that all
components receive enough refrigerant for optimal performance and efficiency.
Evaporator Coil:
The evaporator indoor coil of air source heat pump system absorbs thermal energy from the
outside air and converts it into cool air inside your home or building. It uses a fan-forced
airflow system called “evaporation” cooling technology.
Condenser Coil:
The condenser coil takes hot compressed gas from the compressor and releases it outdoors,
where it can dissipate safely away from people’s living spaces.
Reversing Valve:
Another essential part of a heat pump. A reversing valve allows you to switch between
heating mode (for colder climates) & cooling mode (for warmer temperatures).
High and Low – Pressure switches:
These switches are installed within the refrigerant lines to prevent excessive pressure from
reaching any components.
You might also like
- Thermodynamics: Heat PumpsDocument13 pagesThermodynamics: Heat PumpsRoanne Maye Oligario ArqueroNo ratings yet
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- 1,2 - Unit 1Document137 pages1,2 - Unit 1Saran T SNo ratings yet
- HVAC Unit 1&2Document22 pagesHVAC Unit 1&2LOYOLA RS 200No ratings yet
- Experiment 5 6Document14 pagesExperiment 5 6Rizwan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Systemabenezer1425No ratings yet
- Types of ChillerDocument13 pagesTypes of Chillerzakaria masud sonyNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerairanicolebrugada08No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning - Building ServiceDocument12 pagesAir Conditioning - Building ServiceHarini Andal AgnihotramNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objectiveمیاں اسامہ صفدرNo ratings yet
- HVAC TerminologyDocument4 pagesHVAC Terminologyhuy luongNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocument25 pagesGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Rac Lab MannualDocument24 pagesRac Lab MannualRAZA ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditiong Lab MannualDocument24 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditiong Lab MannualCreative 360No ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump TrainerDocument6 pagesHeat Pump TrainerAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump AssignmentDocument10 pagesHeat Pump AssignmentOmer NadeemNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Basic Mechanism and PrincipleDocument2 pagesBasic Mechanism and PrinciplesahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Parts of Air ConditionerDocument6 pagesParts of Air ConditionerAntonio Lara MuñozNo ratings yet
- Portable Air ConditonerDocument4 pagesPortable Air ConditonerAmit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning CycleDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning CycleJared ParaynoNo ratings yet
- Bu ResearchDocument10 pagesBu ResearchToteng TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Air Condition IndustrialDocument10 pagesAir Condition IndustrialroylojunjunNo ratings yet
- How Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkSaad jamilNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Test RigDocument28 pagesRefrigeration Test RigOxmere SalesNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesLab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet
- Main and Auxiliary Parts of ACDocument9 pagesMain and Auxiliary Parts of ACRicaMyrivilleArellagaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning BasicsDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning BasicsLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4RACDocument32 pagesChapter 4RACSameer AhmadNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Hvac SystemDocument3 pagesHvac SystemNimra EhsanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Wafa RiazDocument93 pagesPrepared By: Wafa RiazrohanasifNo ratings yet
- Hvac LabDocument20 pagesHvac LabMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2 Gill APST201 AC ComponentsDocument35 pages2 Gill APST201 AC Componentscibaya4619No ratings yet
- Air Condition How Does It Works?Document10 pagesAir Condition How Does It Works?Gwapong CrisNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- Centralised20ac20system 190120171416Document23 pagesCentralised20ac20system 190120171416Saba ArifNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning, Nonductable, Ductable-PackagedDocument6 pagesAir Conditioning, Nonductable, Ductable-PackagedRAVIRAJ KARKENo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument37 pagesRefrigeration SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- Liquid Cooled SystemsDocument9 pagesLiquid Cooled Systemsananth k rNo ratings yet
- AC Plant Includes The CompressorDocument3 pagesAC Plant Includes The CompressorsidhumoosewalaNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Hvac Vapor-Compression RefrigerationDocument2 pagesHeat Energy Hvac Vapor-Compression RefrigerationanandanNo ratings yet
- How HVAC Heat Pumps WorkDocument9 pagesHow HVAC Heat Pumps Workjohnking5555No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument10 pagesAbstractabushasolomon75% (4)
- Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning by Krishnanand MDocument15 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning by Krishnanand MMystic Prince XNo ratings yet
- Building Services III-hvac NotesDocument28 pagesBuilding Services III-hvac NotesSri SandhiyaNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- Heat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document3 pagesHeat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Den Mas DeepNo ratings yet
- HVAC System in VehiclesDocument14 pagesHVAC System in Vehiclespmu2273100% (1)
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Thermo LabDocument2 pagesThermo Labmuhyideen6abdulganiyNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet