Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3 Quick Reference Guide
Uploaded by
Fatih SahinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3 Quick Reference Guide
Uploaded by
Fatih SahinCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Corporate Finance MOOC:
Module 3, Bonds
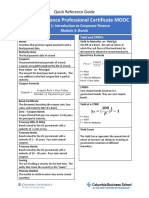
Bond Terminology Yield and STRIPs
Bonds Yield to Maturity -or- Yield (y)
Securities that promise regular payments until a The IRR of a Bond. The rate of return at
final payment date. which the cash flows of the bond must be
Maturity Date discounted to obtain the current bond price.
The final payment date of a bond Bond Price Formula
Coupons
The promised interest payments of a bond. 𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑜𝑛 𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑜𝑛 + 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑉
𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 = + ⋯+
Coupons are paid throughout the life of a bond. 1+𝑦 (1 + 𝑦)𝑇
Face Value - or - Principal
P = Price
The amount the bond pays back at maturity. This
y = Yield
is in addition to the final coupon that is paid at T = Time to Maturity
maturity. FaceV = Face Value
Coupon Formula
STRIPS
𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑜𝑛 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑥 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑒 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 Zero coupon bonds based on U.S.
𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑜𝑛 =
𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑃𝑎𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 government bonds. They are zero coupon
bonds.
Bond Certificate
The document describing the coupon rate, face Yield of a STRIP
value, and maturity date of a bond. 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝟏
Zero – Coupon Bonds 𝒚𝑻 = ( )𝑻 − 𝟏
A type of bond that pays no coupons. It only pays 𝑷
P = Price
the principal at maturity. y = Yield
Treasury Bills (T-bills) T = Time to Maturity
Bonds issued by the US government with a
maturity of 1 year or less Yield Curve
Treasury Notes
Bonds issued by the US government with a The Yield Curve represents the annual rate of
maturity of 2 – 10 years. Pays semi-annual return an investor can obtain by investing in
coupons. governments securities of different
Treasury Bonds maturities.
Bonds issued by the US government with a
maturity of 10 – 30 years. Pays semi-annual
coupons.
Issuing
The act of selling a security for the first time. The
entity that issues the security is the “issuer.”
Primary Market
The market in which investors buy newly-issued
securities.
You might also like
- IAS Chemistry Student Book 1 (2018) AnswersDocument53 pagesIAS Chemistry Student Book 1 (2018) AnswersGazar61% (119)
- Experiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideDocument12 pagesExperiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideMark Ryan Tripole92% (13)
- CH07 Assessment PreparationDocument13 pagesCH07 Assessment PreparationEthan RuppNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document4 pagesExperiment 7Edon EduinNo ratings yet
- Peptidomimetics FINAL PDFDocument21 pagesPeptidomimetics FINAL PDFVissarapu NagalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Professional Certificate MOOC: Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageCorporate Finance Professional Certificate MOOC: Quick Reference GuideShivani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Seminar of Bond ValuationDocument27 pagesSeminar of Bond ValuationRupesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Valuation and Cost of CapitalDocument92 pagesChapter 3 Valuation and Cost of Capitalyemisrach fikiruNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation: by Sarah M. Balisacan, CPADocument13 pagesBond Valuation: by Sarah M. Balisacan, CPAChristine CabonegroNo ratings yet
- RE8013 Financial Management NotesDocument2 pagesRE8013 Financial Management NotesRyan M. TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Cont..Document30 pagesChapter 4 Cont..Lan Nhi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Bonds and SharesDocument39 pagesValuation of Bonds and Shareskunalacharya5No ratings yet
- Valuation of Bonds: SA Sem 3Document48 pagesValuation of Bonds: SA Sem 3anindya_kunduNo ratings yet
- Bonds and Their ValuationDocument40 pagesBonds and Their ValuationImran AliNo ratings yet
- Bonds CH08Document16 pagesBonds CH08An HoàiNo ratings yet
- Bonds Valuation PowerpointDocument39 pagesBonds Valuation Powerpointttongoona3No ratings yet
- What Are Bonds?Document21 pagesWhat Are Bonds?ashish20gupta86No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Review of Bond Concepts and Term Structure of Interest RatesDocument20 pagesLecture 1 - Review of Bond Concepts and Term Structure of Interest RatesNiyati ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Financial Instrument Valuation and Investment DecisionDocument69 pagesChapter 3 - Financial Instrument Valuation and Investment Decision21124014No ratings yet
- DM Theory Part 2Document40 pagesDM Theory Part 2Atharva GoreNo ratings yet
- Fixed in ComeDocument29 pagesFixed in ComeayyazmNo ratings yet
- Bonds, Bond Valuation, and Interest RatesDocument59 pagesBonds, Bond Valuation, and Interest RatesHawraa AlabbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Valuation of Bonds FM1Document25 pagesChapter 6 Valuation of Bonds FM1Alona Jane ObilloNo ratings yet
- Bộ Đề Speaking Part 1 Winter 2016 - Version 01Document53 pagesBộ Đề Speaking Part 1 Winter 2016 - Version 01Eli LiNo ratings yet
- FM I Bond ValuationDocument16 pagesFM I Bond Valuationdanielnebeyat7No ratings yet
- Review Session# 2 #17 July 2021Document23 pagesReview Session# 2 #17 July 2021Diff EnderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 1 Determination of Interest RatesDocument63 pagesChapter 2 1 Determination of Interest RatesLâm Bulls100% (1)
- The Valuation of Long-Term SecuritiesDocument54 pagesThe Valuation of Long-Term SecuritiesSana ZahidNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income - FinalDocument145 pagesFixed Income - Finalvishgupta1987No ratings yet
- 5 - Bond and Stock Valuation (Compatibility Mode)Document58 pages5 - Bond and Stock Valuation (Compatibility Mode)Ái Mỹ DuyênNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 (Bond Valuation)Document13 pagesCh. 7 (Bond Valuation)Wael ElarnaoutyNo ratings yet
- Bond ValuationDocument38 pagesBond ValuationAbdii DhufeeraNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Bonds (Basics + Advanced)Document12 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Bonds (Basics + Advanced)devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 BOND VALUATIONDocument35 pagesChapter5 BOND VALUATIONKahbwe Kãytiencë ChamaNo ratings yet
- AFC 2140 Corporate Finance Teaching Week 3: Topic 3: Valuation of Bonds and EquitiesDocument18 pagesAFC 2140 Corporate Finance Teaching Week 3: Topic 3: Valuation of Bonds and EquitiesMoud KhalfaniNo ratings yet
- 9.bond Valuation (FI)Document4 pages9.bond Valuation (FI)Kumar KhatriNo ratings yet
- Valuation ConceptsDocument54 pagesValuation Conceptsmarine19.vedelNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets BondsDocument15 pagesSummary Sheets Bondsrohit bhosadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document33 pagesLecture 3hafsaNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document23 pagesCH 4Gizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Commerce 308: Introduction To Finance: Bond Valuation & Interest RatesDocument47 pagesCommerce 308: Introduction To Finance: Bond Valuation & Interest RatesPamela Santos100% (1)
- Valuation of Securities-Bonds StocksDocument50 pagesValuation of Securities-Bonds StocksMega capitalmarketNo ratings yet
- Bond MathematicsDocument35 pagesBond Mathematicsrohan.explorerNo ratings yet
- Issued by Bonds Bonds: OftenDocument11 pagesIssued by Bonds Bonds: OftenMd. Abdul HaiNo ratings yet
- 4,5,6,7Document121 pages4,5,6,7SI PNo ratings yet
- Bas250 FT 2 2023 2Document44 pagesBas250 FT 2 2023 2elifeet123No ratings yet
- Kuliah 4 Valuasi Bond N StockDocument43 pagesKuliah 4 Valuasi Bond N StockArry AnandaNo ratings yet
- Valuation of BondsDocument25 pagesValuation of BondsSUDIPTA SHIBNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation: Bond Analysis: Returns & Systematic RiskDocument50 pagesBond Valuation: Bond Analysis: Returns & Systematic RiskSamad KhanNo ratings yet
- SAPM Quiz 3Document137 pagesSAPM Quiz 3Netflix FlixNo ratings yet
- Bond Prices and Interest Rate RiskDocument100 pagesBond Prices and Interest Rate RiskMarwa HassanNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Interest Rate: Cecchetti, Chapter 7 Mishkin, Chapter 2Document50 pagesThe Meaning of Interest Rate: Cecchetti, Chapter 7 Mishkin, Chapter 2Trúc Ly Cáp thịNo ratings yet
- Debt ValuationDocument30 pagesDebt ValuationSiddharth BirjeNo ratings yet
- 3chapter Three FM ExtDocument19 pages3chapter Three FM ExtTIZITAW MASRESHANo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation: © 2007 Thomson South-WesternDocument12 pagesBond Valuation: © 2007 Thomson South-WesternMuhammad MansoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thee Valuation of Financial AssetsDocument143 pagesChapter Thee Valuation of Financial AssetsDejene GurmesaNo ratings yet
- Bond ValuationDocument58 pagesBond Valuationpassinet100% (1)
- Chapter 3 B Bond ValuationDocument38 pagesChapter 3 B Bond ValuationLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Fixed Income Securities - Bond Charecrtisitcs 1Document44 pagesCH 8 Fixed Income Securities - Bond Charecrtisitcs 1sanketNo ratings yet
- Cost of Capital and Bond and Stock ValuationDocument37 pagesCost of Capital and Bond and Stock Valuationzedingel100% (1)
- Bond Valuation: Characteristics of BondsDocument6 pagesBond Valuation: Characteristics of Bondssincere sincereNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 & 5 - Bond Yields and Prices (STU)Document67 pagesTopic 4 & 5 - Bond Yields and Prices (STU)Thanh XuânNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2From EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020Document34 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2020Anonymous hrjVVK100% (1)
- You Have Just Run A Regression of Monthly Returns OnDocument1 pageYou Have Just Run A Regression of Monthly Returns OnAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- ATRAM Total Return Peso Bond Fund Fact Sheet Apr 2020Document2 pagesATRAM Total Return Peso Bond Fund Fact Sheet Apr 2020anton clementeNo ratings yet
- Duration Problems: Problem 1Document6 pagesDuration Problems: Problem 1SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Solved The Mosquito Abatement Commission Is A Newly Organized Federal AgencyDocument1 pageSolved The Mosquito Abatement Commission Is A Newly Organized Federal AgencyAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- Restrictive Endorsements - CFR 2016 Title31 Vol2 Part328Document4 pagesRestrictive Endorsements - CFR 2016 Title31 Vol2 Part328Kaizen WillowNo ratings yet
- Chem 1411 Sample 4 CHPT 9-10Document13 pagesChem 1411 Sample 4 CHPT 9-10Reginald TeeNo ratings yet
- Colour Reaction of Amino AcidsDocument27 pagesColour Reaction of Amino AcidsJacqueline Ann71% (7)
- FIN500 Exercises - Stock and BondDocument2 pagesFIN500 Exercises - Stock and BondWADHA SALMAN GHAZI ALDHUFAIRINo ratings yet
- BootstrappingDocument34 pagesBootstrappingHarshit DwivediNo ratings yet
- Bonds PayableDocument8 pagesBonds Payablekrisha milloNo ratings yet
- Mini-Case: STIPS and Arbitraging OpportunityDocument3 pagesMini-Case: STIPS and Arbitraging OpportunityTrisha SethNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Of-Olefins-By-Palladiumii 6pDocument6 pagesOxidation-Of-Olefins-By-Palladiumii 6pLi HojunNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Identification of Functional GroupsDocument14 pagesLab 2 - Identification of Functional GroupsShamaya Murray60% (5)
- Bond Value.: B.Value YTM PTM Yeild Face ValueDocument4 pagesBond Value.: B.Value YTM PTM Yeild Face ValueshabywarriachNo ratings yet
- BMO ETF Profile BookDocument210 pagesBMO ETF Profile Booknsheth0126No ratings yet
- The Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument35 pagesThe Molecular Basis of Inheritanceprehealthhelp80% (5)
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 6Document56 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 6LaurenNo ratings yet
- Solution pdf-51Document68 pagesSolution pdf-51Tanmay GoyalNo ratings yet
- IAS - Chemistry - SB1 - Mark Scheme - T3 PDFDocument3 pagesIAS - Chemistry - SB1 - Mark Scheme - T3 PDFLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Why Inflation Matters ?: Rohit ChauhanDocument9 pagesWhy Inflation Matters ?: Rohit ChauhanhamsNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Securities Market Indicators: Securities Board of NepalDocument42 pagesQuarterly Securities Market Indicators: Securities Board of NepalManoj ShreshtaNo ratings yet
- Markovnikov's RuleDocument3 pagesMarkovnikov's Ruledescata100% (1)
- Research Paper On D and F Block PDFDocument9 pagesResearch Paper On D and F Block PDFVishwa RahulNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Portfolio Performance: Financial Analysts JournalDocument7 pagesDeterminants of Portfolio Performance: Financial Analysts JournalDasulea V.No ratings yet
- Bond Quotes: Coupon Interest RateDocument18 pagesBond Quotes: Coupon Interest RateChristine CaridoNo ratings yet