Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PTH Regulation
Uploaded by
JetGoliath 260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesThis document discusses the regulation of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH is secreted by the parathyroid glands and acts to regulate blood calcium levels. When calcium levels decrease, PTH secretion increases to stimulate calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, activate vitamin D to increase calcium absorption in the intestines, and release calcium from bones. PTH secretion is regulated by calcium, vitamin D, phosphate, and magnesium levels in the blood. Disorders of PTH include hypoparathyroidism causing low calcium and hyperparathyroidism which can be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the cause.
Original Description:
Original Title
PTH regulation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the regulation of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH is secreted by the parathyroid glands and acts to regulate blood calcium levels. When calcium levels decrease, PTH secretion increases to stimulate calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, activate vitamin D to increase calcium absorption in the intestines, and release calcium from bones. PTH secretion is regulated by calcium, vitamin D, phosphate, and magnesium levels in the blood. Disorders of PTH include hypoparathyroidism causing low calcium and hyperparathyroidism which can be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the cause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesPTH Regulation
Uploaded by
JetGoliath 26This document discusses the regulation of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH is secreted by the parathyroid glands and acts to regulate blood calcium levels. When calcium levels decrease, PTH secretion increases to stimulate calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, activate vitamin D to increase calcium absorption in the intestines, and release calcium from bones. PTH secretion is regulated by calcium, vitamin D, phosphate, and magnesium levels in the blood. Disorders of PTH include hypoparathyroidism causing low calcium and hyperparathyroidism which can be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the cause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Module :LOCOMOTOR
Topic: REGULATION OF PTH
FIRST Year MBBS 2022
Dr. Arisha Sohail
Dep. Of Biochemistry
DIMC,DUHS
Objectives
• determination of the physiological function of the parathyroids,
• determination of the regulation of the parathyroid hormone
• the pathophysiology due to hormone excess or deficiency,
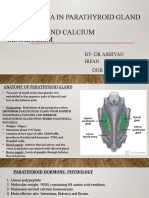
Function
• Effects of the parathyroid glands are exerted through chief cells,
which produce and secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH):
• Regulate calcium levels in the blood
• Calcium-sensing receptors (CaSRs) within chief cells monitor calcium
blood levels and moderate PTH secretion.
• ↓ Blood calcium levels → ↑ secretion of PTH → ↑ serum calcium
PTH effects:
• Stimulation of calcium reabsorption and phosphate excretion in the
distal tubule of the kidney
• Increases renal activation of vitamin D:
• Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) is the active form.
• Increases intestinal reabsorption of calcium
• Stimulation of calcium and phosphate release from the bones
through osteoclast activation
PTH secretion regulation:
• Stimulated by:
• Decreases in serum calcium
• Low levels of calcitriol
• Hyperphosphatemia
• Mild hypomagnesemia
• Inhibited by high levels of serum calcium
Hypoparathyroidism
• Hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia and tetany
• most commonly post-surgical
• idiopathic disease
• Pseudohypoparathyroidism (resistance to hormone action rather than
defective hormone production)
Hyperparathyroidism
• Depending on the pathogenesis, the presentation may be primary,
secondary, or tertiary hyperparathyroidism
• The most frequent cause is adenomas of the parathyroid gland which
can be localized
• Hyperfunctioning adenomas are typically removed with surgery.
Paradox of PTH biological action: therapeutic
use vs physiological function
Homeostatic role Sustained elevation of PTH can
maintain blood calcium against
challenge of prolonged calcium
deficiency by withdrawal from
bone ‘bank’, reduces bone mass
Therapeutic role Deliberate, short pulses of PTH
dramatically build bone mass. a.
Continuous elevation in PTH blood
levels (>2 hrs): bone mass b.
Intermittent elevation in PTH
blood levels (
You might also like
- Hormonal Control of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument50 pagesHormonal Control of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismhamidNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism & Calcium Metabolism DisordersDocument45 pagesCalcium Metabolism & Calcium Metabolism Disorderstrisya arthaputriNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid DisordersDocument37 pagesParathyroid DisordersMannat ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland: Dr. Mustafa Abdalgadir Khandgawi Ibrahim 2016Document24 pagesParathyroid Gland: Dr. Mustafa Abdalgadir Khandgawi Ibrahim 2016Mustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandDocument25 pagesParathyroid GlandJasmine Rey QuintoNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument80 pagesHypothyroidismDemewoz FikirNo ratings yet
- Homeostatic Function of Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland & Calcium HomeostasisDocument15 pagesHomeostatic Function of Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland & Calcium HomeostasisGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument4 pagesParathyroid GlandsMary Grace Buscargas PolancosNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid: Calcium and Vitamin DDocument135 pagesParathyroid: Calcium and Vitamin DPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Calcium & Phosphorus AnishDocument52 pagesCalcium & Phosphorus AnishAnish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology PsriDocument40 pagesHypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology Psriind78No ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland: Clinical Chemistry - 3Document16 pagesParathyroid Gland: Clinical Chemistry - 3Mary Rose BarrigaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Parathyroid Gland Anatomy and FunctionDocument3 pagesLecture 15 Parathyroid Gland Anatomy and FunctionbomabenediNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone: Shahab Ullah Khan Ayub Medical CollegeDocument28 pagesParathyroid Hormone: Shahab Ullah Khan Ayub Medical CollegeDr KhanNo ratings yet
- Control Blood of Calcium LevelsDocument2 pagesControl Blood of Calcium Levelswoman in stemNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone and Calcium Regulation: By: Abebe TDocument29 pagesParathyroid Hormone and Calcium Regulation: By: Abebe TLidiya TeshomeNo ratings yet
- 3ES-4 CA Metabloism Final 1436Document47 pages3ES-4 CA Metabloism Final 1436Muath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Calcium HomeostasisDocument37 pagesCalcium Homeostasispolog.jm610No ratings yet
- Diseases of The Parathyroid GlandDocument60 pagesDiseases of The Parathyroid GlandRuDy RaviNo ratings yet
- Lect 9 Parathyroid Gland-1Document30 pagesLect 9 Parathyroid Gland-1warda farooqNo ratings yet
- Paratiroid Dan KalsiumDocument80 pagesParatiroid Dan KalsiumFebrina EvaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Homeostasis INFOODocument2 pagesCalcium Homeostasis INFOOMika Sophia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Parathyroid GlandsDocument30 pagesDisorders of The Parathyroid Glandsikram ullah khan100% (1)
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument17 pagesParathyroid GlandsMalik TamimiNo ratings yet
- Endo Lect - ParathyroidDocument25 pagesEndo Lect - ParathyroiddoctorrfarrukhNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument74 pagesStudy Guide For Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismMohammad MamunuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Hyper para Thyroid Is MDocument27 pagesHyper para Thyroid Is MIbrahimWagesNo ratings yet
- 5 Parathyroid GlandDocument24 pages5 Parathyroid GlandReem 10No ratings yet
- 6.1 Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisDocument17 pages6.1 Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisAsem AlhazmiNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroids and Calcium MetabolismDocument28 pagesThe Parathyroids and Calcium MetabolismPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism / Hypocalcemia: Abrar Alharbi, F1Document32 pagesHypoparathyroidism / Hypocalcemia: Abrar Alharbi, F1abrarNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of Calcium Homeostasis Chapter 9Document8 pagesHormonal Control of Calcium Homeostasis Chapter 9Roua SafwatNo ratings yet
- Share Market Report 6Document13 pagesShare Market Report 6Nithish DevadigaNo ratings yet
- Physiology, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) : Statpearls (Internet)Document10 pagesPhysiology, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) : Statpearls (Internet)chafeb febiNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone: DR Pramod Kumar Asstt. Professor Department of Veterinary Physiology Bihar Veterinary College, PatnaDocument19 pagesParathyroid Hormone: DR Pramod Kumar Asstt. Professor Department of Veterinary Physiology Bihar Veterinary College, PatnasanathNo ratings yet
- Calcium HomeostasisDocument10 pagesCalcium Homeostasiszsf8m52ky4No ratings yet
- CKD MBDDocument17 pagesCKD MBDizzati samsudinNo ratings yet
- Calcium HomeostasisDocument38 pagesCalcium Homeostasiskelvinmaina9993No ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism and RegulationDocument39 pagesCalcium Metabolism and RegulationSanchita SahaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland: Clinical Chemistry - 3Document12 pagesParathyroid Gland: Clinical Chemistry - 3Vincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- PHD 7Document7 pagesPHD 7Elham AlwagaaNo ratings yet
- Calcemic Hormones: Leonard Waite, PHD Dept. of Pharmacology and ToxicologyDocument51 pagesCalcemic Hormones: Leonard Waite, PHD Dept. of Pharmacology and ToxicologyPritesh KuNo ratings yet
- General Instructions: - The Search Should Contain The FollowingsDocument15 pagesGeneral Instructions: - The Search Should Contain The FollowingsDr-AHmad Fasfous AL-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid HormoneDocument12 pagesParathyroid HormoneJamesNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid HormonesDocument104 pagesParathyroid Hormonesc96gtf8hkkNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroid GlandDocument66 pagesThe Parathyroid GlandMohammed GamalNo ratings yet
- MK Biokimia - Metabolisme MineralDocument84 pagesMK Biokimia - Metabolisme MineralmusimsemiNo ratings yet
- Schenck 2007Document16 pagesSchenck 2007Luisa Fernanda Rojas DiazNo ratings yet
- Functions of Parathyroid HormoneDocument16 pagesFunctions of Parathyroid HormoneAnupam MittalNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia (F&e)Document3 pagesHypercalcemia (F&e)Sarah Grace CajucomNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach of HypoCa in ChildrenDocument5 pagesPractical Approach of HypoCa in ChildrenPhilip LingNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia: Endocrine University 2018-Bone Module Rochester, Minnesota March 7, 2018Document26 pagesHypocalcemia: Endocrine University 2018-Bone Module Rochester, Minnesota March 7, 2018Abdullah SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DR Yogesh Swami 3Document11 pagesEndocrine System DR Yogesh Swami 3chiragm1408No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Calcium Balance: Harsh Vinayak Roll No. 39 Mbbs 2 Yr Student BATCH 2019 Rdasmc, AyodhyaDocument24 pagesDrugs Affecting Calcium Balance: Harsh Vinayak Roll No. 39 Mbbs 2 Yr Student BATCH 2019 Rdasmc, AyodhyaA2Z GyanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone ConditionsDocument66 pagesMetabolic Bone ConditionsNaeem AminNo ratings yet
- Calcitropic Hormones Presented By: Dr. Pallavi Anand Asst. ProfessorDocument16 pagesCalcitropic Hormones Presented By: Dr. Pallavi Anand Asst. ProfessorShiraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium MetabolismDocument53 pagesDisorders of Calcium Metabolismadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Medical Technology - Lecture #6 - The PARATHYROID GLANDDocument15 pagesLecture Notes in Medical Technology - Lecture #6 - The PARATHYROID GLANDKat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersDocument25 pagesAnaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersAshiyan IrfanNo ratings yet