0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views8 pagesChemistry Class 10
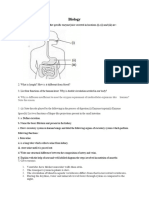
This document contains 21 chemistry questions covering topics like electrolysis, chemical reactions, acids and bases, organic compounds, and more. Key questions ask about the volume of gas produced during water electrolysis, identifying reactants and products in sample reactions, and describing processes like esterification, hydrogenation, and decomposition reactions. The document tests understanding of fundamental chemistry concepts.
Uploaded by
Sangithaa RaghuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views8 pagesChemistry Class 10
This document contains 21 chemistry questions covering topics like electrolysis, chemical reactions, acids and bases, organic compounds, and more. Key questions ask about the volume of gas produced during water electrolysis, identifying reactants and products in sample reactions, and describing processes like esterification, hydrogenation, and decomposition reactions. The document tests understanding of fundamental chemistry concepts.
Uploaded by
Sangithaa RaghuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd