Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elastisitas Permintaan
Uploaded by
New AccOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastisitas Permintaan
Uploaded by
New AccCopyright:
Available Formats
Price Elasticity of Demand (pp.
124–130)
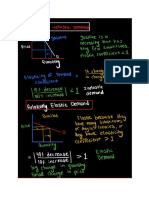
◆■ Elasticity is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a
change in its price, other things remaining the same.
◆■ Price elasticity of demand equals the percentage change in the quantity demanded
divided by the percentage change in the price.
◆■ The larger the magnitude of the price elasticity of demand, the greater is the
responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a given price change.
◆■ If demand is elastic, a cut in price leads to an increase in total revenue. If demand is
unit elastic, a cut in price leaves total revenue unchanged. And if demand is inelastic, a cut in
price leads to a decrease in total revenue.
◆■ Price elasticity of demand depends on how easily one good serves as a substitute for
another, the proportion of income spent on the good, and the length of time elapsed since
the price change. Working Problems 1 to 5 will give you a better under standing of the price
elasticity of demand. More Elasticities of Demand (pp. 131–134)
◆■ Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in
income, other things remaining the same. For a normal good, the income elasticity of
demand is positive. For an inferior good, the income elasticity of demand is negative.
◆■ When the income elasticity of demand is greater than 1 (income elastic), the
percentage of income spent on the good increases as income increases.
◆■ When the income elasticity of demand is less than 1 (income inelastic or inferior), the
percentage of income spent on the good decreases as income increases.
◆■ Cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the demand for one good to
a change in the price of a substitute or a complement, other things remaining the same.
◆■ The cross elasticity of demand with respect to the price of a substitute is positive. The
cross elasticity of demand with respect to the price of a complement is negative. Working
Problems 6 to 8 will give you a better under standing of cross and income elasticities of
demand. Elasticity of Supply (pp. 134–136)
◆■ Elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a good to a
change in its price, other things remaining the same.
◆■ The elasticity of supply is usually positive and ranges between zero (vertical supply
curve) and infinity (horizontal supply curve).
◆■ Supply decisions have three time frames: momentary, short run, and long run.
◆■ Momentary supply refers to the response of the quantity supplied to a price change at
the instant that the price changes.
◆■ Shortrun supply refers to the response of the quantity supplied to a price change after
some of the technologically feasible adjustments in production have been made.
◆■ Longrun supply refers to the response of the quantity supplied to a price change when
all the technologically feasible adjustments in production have been made
You might also like
- Elasticities of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticities of Demand and SupplyGrace AvilaNo ratings yet
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Athanassakos, G. 2011. Do Value Investors Add Value. Journal of Investing, 20 (2), 86-100.Document16 pagesAthanassakos, G. 2011. Do Value Investors Add Value. Journal of Investing, 20 (2), 86-100.firebirdshockwaveNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Sun PharmaDocument7 pagesFinancial Analysis of Sun PharmahemanshaNo ratings yet
- Domestic Auto Parts (Eriko Timothy Ginting)Document2 pagesDomestic Auto Parts (Eriko Timothy Ginting)Eriko Timothy GintingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Eunoia Junior College - Suggested Answers For 2017 H2 Economics A Level PaperDocument48 pagesEunoia Junior College - Suggested Answers For 2017 H2 Economics A Level PaperLee Jia QingNo ratings yet
- BUS420 - Strategy in Action (Coca Cola)Document59 pagesBUS420 - Strategy in Action (Coca Cola)Mitali BiswasNo ratings yet
- CM102 - D&B - Equity Markets.20070118Document110 pagesCM102 - D&B - Equity Markets.20070118Nikita Poddar100% (1)
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Micro Economics Assignment: Submitted To Mr. Raj KumarDocument12 pagesMicro Economics Assignment: Submitted To Mr. Raj Kumarpriyaleo_19894819No ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument28 pagesElasticity of DemandAkankshya MishraNo ratings yet
- Kotler Mm15e Inppt 02Document43 pagesKotler Mm15e Inppt 02Prathamesh411No ratings yet
- Various Methods of Price Elasticity of DemandDocument9 pagesVarious Methods of Price Elasticity of Demandsalim132150% (2)
- ElasticityDocument25 pagesElasticityaljohn anticristoNo ratings yet
- BCG PDFDocument68 pagesBCG PDFRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Management Review of Pakistan RailwaysDocument28 pagesA Strategic Management Review of Pakistan RailwaysBilal100% (3)
- Applied Economics Pre-AssessmentDocument4 pagesApplied Economics Pre-AssessmentJEANNE PAULINE OABELNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 ElasticityDocument14 pagesChap 4 ElasticityLâmViênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4clararamy2No ratings yet
- Ch. 18: Elasticity: Del Mar College John DalyDocument24 pagesCh. 18: Elasticity: Del Mar College John DalyManthan PatelNo ratings yet
- ME Session 6 7Document31 pagesME Session 6 7vaibhav khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Chap Elasticity and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesChap Elasticity and ApplicationsIce burgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Econ 101 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Econ 101 NotesSamuel NettoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - ElasticityofdmdDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - ElasticityofdmdSWETA KUMARINo ratings yet
- CH 20 ElasticityDocument24 pagesCH 20 ElasticityLutfun Nesa Aysha 1831892630No ratings yet
- Elasticities of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticities of Demand and SupplyAndre SoaresNo ratings yet
- Andreas Audi Kemal Setiawan-Business Economics GM11-Summary of Price and Income ElasticityDocument4 pagesAndreas Audi Kemal Setiawan-Business Economics GM11-Summary of Price and Income ElasticityAndreas Audi KemalNo ratings yet
- Changes in Market EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChanges in Market Equilibriumfoyzul 2001No ratings yet
- Agricultural EconomicsDocument33 pagesAgricultural EconomicsFarai Faustos100% (1)
- Elasticity ExtendedDocument16 pagesElasticity ExtendedEmon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- BASMIC Group 3Document49 pagesBASMIC Group 3Jasmine Renee Buga-ayNo ratings yet
- Elasticity EconomicsDocument14 pagesElasticity EconomicsYiwen LiuNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 3rd Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadDocument25 pagesMicroeconomics 3rd Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadSharon Clay100% (22)
- Topic 3-Demand Theory PDFDocument38 pagesTopic 3-Demand Theory PDFPatricia Ann TamposNo ratings yet
- Ch. 20: Elasticity: S M Zahid IqbalDocument23 pagesCh. 20: Elasticity: S M Zahid IqbalEmon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ch. 20: Elasticity: S M Zahid IqbalDocument23 pagesCh. 20: Elasticity: S M Zahid IqbalEmon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 LectureDocument5 pagesChapter 8 LectureJULIANADAM PAGALNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument27 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationravi_nyseNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument62 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplySANSKRITI YADAV 22DM236No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Econ SummaryDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Econ SummaryAiza Bernadette NahialNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadDocument22 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadDaniel Salazar100% (27)
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument19 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supplydev.m.dodiyaNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument21 pagesElasticityHarshit Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesElasticity Price Elasticity of DemandArrini TsaltsaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesCh. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandVarun SanjayNo ratings yet
- Elasticity-Of-Demand 8552087 PowerpointDocument21 pagesElasticity-Of-Demand 8552087 PowerpointChandan NNo ratings yet
- Market PriceDocument2 pagesMarket PriceNew AccNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument26 pagesElasticitysajannt1538No ratings yet
- Microeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadDocument25 pagesMicroeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual DownloadJessica Carr100% (23)
- Basic Microeconomics Day 3 LectureDocument16 pagesBasic Microeconomics Day 3 LectureRoentgen Djon Kaiser IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Chapter 3-Empirical Methods For Demand Analysis Session 2Document44 pagesManagerial Economics - Chapter 3-Empirical Methods For Demand Analysis Session 2Aabraham Samraj PonmaniNo ratings yet
- Econ 1 Key TermsDocument3 pagesEcon 1 Key TermsCorazon ReymarNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument15 pagesElasticityNikitha CmNo ratings yet
- Hapter Upply AND Emand: Chapter SummaryDocument24 pagesHapter Upply AND Emand: Chapter SummaryLJ DursNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument18 pagesElasticityHaris Mahmood MughalNo ratings yet
- Textile and Apparel Management-Lecture 4Document13 pagesTextile and Apparel Management-Lecture 4shahadat hossainNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument51 pagesElasticity of DemandAmbuj AroraNo ratings yet
- Elastic Review SheetDocument4 pagesElastic Review SheetjoisbastaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 1St Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 1St Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFadrianavillanuevajzsifoacen100% (10)
- Managerial Econo Final Exam Suggestions Q&aDocument9 pagesManagerial Econo Final Exam Suggestions Q&aShakila Sultana MitiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manualclubhandbranwq8100% (29)
- Microeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manualjaydenur3jones100% (13)
- Elasticity of DemandDocument6 pagesElasticity of DemandVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Chapter 5, Elasticity of Demand and Supply - Part 1Document18 pagesBusiness Economics Chapter 5, Elasticity of Demand and Supply - Part 1sharukh kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument29 pagesElasticity of Demandcyril george100% (1)
- Notions of Elasticity: Prepared byDocument26 pagesNotions of Elasticity: Prepared byAndrea SiladanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Demand: Dr. Syed AzharDocument24 pagesAnalysis of Demand: Dr. Syed AzharDr S NeelimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Elasticity of Demand and SupplykhaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Supply and Demand in Individual MarketDocument56 pagesChapter5-Supply and Demand in Individual MarketTony MontaanaNo ratings yet
- VSR CalculatorDocument7 pagesVSR Calculatorgharavii2063No ratings yet
- Microsoft Stock Analysis ReportDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Stock Analysis ReportInvestingSidekickNo ratings yet
- LN10Moffett38115 04 FMF LN10Document77 pagesLN10Moffett38115 04 FMF LN10Kwichobela BonaventureNo ratings yet
- MaDocument7 pagesMaamitdharamsiNo ratings yet
- Initiating Price Cuts Several Situations May Lead A Firm To Consider Cutting Its PriceDocument1 pageInitiating Price Cuts Several Situations May Lead A Firm To Consider Cutting Its PriceAdil ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Review of Supply and Demand FunctionsDocument19 pagesTopic 1 Review of Supply and Demand FunctionsCHOPLAZNo ratings yet
- Forum Interview - Trent Westside Zudio Business Analysis-15 Jul 2019 - EngDocument12 pagesForum Interview - Trent Westside Zudio Business Analysis-15 Jul 2019 - EngDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- William Thorndike,: The OutsidersDocument17 pagesWilliam Thorndike,: The OutsidersAnkurNo ratings yet
- MObile GarageDocument21 pagesMObile Garageanjum malek100% (1)
- Cost Benefit Analysis With Inclusion of BridgesDocument4 pagesCost Benefit Analysis With Inclusion of BridgesMuani HmarNo ratings yet
- CPW Case StudyDocument2 pagesCPW Case StudySherNo ratings yet
- Pcab LlimDocument634 pagesPcab LlimPankaj RaneNo ratings yet
- Marketing Planning - A Global Perspective-Svend HollensenDocument477 pagesMarketing Planning - A Global Perspective-Svend HollensenAzhaan HabeebNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Written ReportDocument11 pagesComprehensive Written ReportKen GomezNo ratings yet
- Chap 006Document54 pagesChap 006Imad RahimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 - 2017010000078Document3 pagesAssignment 01 - 2017010000078Istiak HasanNo ratings yet
- How Do We Get There? What Direction Should We Take?: Strategic ChoiceDocument39 pagesHow Do We Get There? What Direction Should We Take?: Strategic ChoiceRichille SordillaNo ratings yet
- PIDE Reform Agenda ReportDocument100 pagesPIDE Reform Agenda Reportgood qureshiNo ratings yet
- Assiment Product and BrandDocument53 pagesAssiment Product and BrandAnuj Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Ac - Adeoti Sikiru Hammed - June, 2023 - 272234316 - FullstmtDocument2 pagesAc - Adeoti Sikiru Hammed - June, 2023 - 272234316 - FullstmtADEOTI HAMMED (Colt graphic)No ratings yet