Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mba II Sem. - Syllabus
Uploaded by
Darshan M BevoorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mba II Sem. - Syllabus
Uploaded by
Darshan M BevoorCopyright:
Available Formats
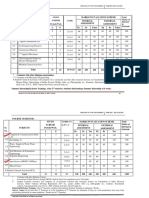
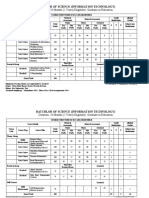
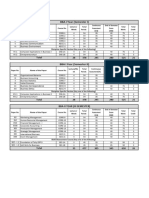
MBA -II SEMESTER
Teaching Examination
Course Code
Course Title
Category
Practi
Durations/
Theor
(in Hours)
(in Hours)
Durations
Course
Sl. No.
Practical
Theory/
cal
Internal
Credits
y
Marks
Marks
Marks
Week
Total
T P
1 RM Financial 2 2+4=
DC 2 56 40 60 100 4
2.1 Management (4) 6
2 RM Marketing 1 3+2=
DC 3 56 40 60 100 4
2.2 Management (2) 5
3 Human
RM
DC Resource 4 - 4 56 40 60 100 4
2.3
Management
4 Research
RM 1 3+2=
DC Methods and 3 56 40 60 100 4
2.4 (2) 5
Statistical Tools
5 Life and
SE 1 1+2
SEC Professional 1 28 20 30 50 2
2.1 (2) =3
Skills
6 Advanced Skills
FA
in Agriculture 2 0+
SEC A 0 30 20 30 50 2
and Allied (4) 4=4
2.1
Activities
7 Rural
SE
SEC Immersion / - - - - 25 25 50 2
2.2
Rural Camps
13 +
22 7
Total 13 14 = 282 325 550 22
5 (14)
27
Study Visit (1/2 Days) - Agribusiness and Rural Development Organisation,
Universities, NGO, Corporates in India
Internship / Minor Research Project for 4 weeks after II Semester
*DC – Discipline Course
*SEC – Skill Enhancement Course
* 1 Practical Class = 2 Lab Hours
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 1
Financial Management
Sub. Code: RM 2.1 Total Marks (I+E) = 40+60 =100
Internal Assessment Marks = 40 External Examination Marks
= 60
Credits: 4 Total Hours = 56
Hours Per Week (T + P) = 2 + 2(4) =
6
Course Objectives:
1. Provide knowledge on financial management of the firm
2. Develop knowledge on the allocation, management and funding of
financial resources and Capital management
3. Improving students’ understanding of the time value of money concept
and the role of a financial manager in the current competitive business
scenario.
Course Outcome:
At the end of the course students are able to:
1. Apply the concepts, tools and techniques of financial management in
financial decision making.
2. Elaborate the key decision areas in financial management - investment,
financing, dividend and working capital management
3. Discuss the various factors to be considered in designing the target
capital structure.
4. Determine the working capital requirements for a firm
Module I Financial Management 11 hours
Meaning, objectives, scope, importance and organization of the financial
management function; Emerging role of finance managers; Interface of Financial
Management with other functional areas; Indian Financial System - primary
market, secondary market, stocks and commodities market; Sources of
Financing: shares, debentures, term loans, lease financing and hybrid
financing; Money market and instruments; Forex markets.
Module II Capital Structure 12
Hours
Meaning, optimum capital structure, factors determining capital structure,
Capital structure theories, capital structure planning and steps, relevance of
capital structure; New financial Instruments; Capital recovery and loan
amortization; Leverage - concept of leverage, financial leverage and risk, types
and measurement.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 2
Module III Management of Earnings 10
Hours
Nature and scope of management of earnings; Dividend Policy and Dividend
Models, Walter's Model, Gordon's Model, MM Hypothesis; Pattern of dividend
policies; Determinants of Dividend Policy; Company stock splits and issue of
bonus shares in India.
Module IV Capital Budgeting 12
Hours
Nature and features of capital budgeting decisions; process of capital budgeting;
Net present value; Internal rate of return; Modified internal rate of return;
Profitability index; Payback period; discounted payback period; accounting rate
of return; Estimation of cash flow for new project; Replacement projects.
Module V Working Capital Management 11
Hours
Meaning and concepts of working capital, determinants of working capital;
Major issues in working capital management and financing of working capital;
Estimation of working capital requirements, determining the financing mix;
Cash, receivables and inventory management; Financing of working capital in
India.
Practicum (Assignment / Activities):
1. Solve the Hola-Kola - The Capital Budgeting Decision, case study
(downloadable from the net)
2. Estimate the working capital requirement for a small firm
3. Visit any local firm and find how they estimate working capital
requirements. Submit a 1000 word write-up on this.
4. Visit financial websites like moneycontrol.com , goodreturns.in,
economictimes.com, indiatimes.com and find the Capital Structure of any
5 companies.
Text Book
1. Financial AccountingBook by Jain S P and Narang K L
2. Financial Management by Khan & Jain, McGraw-Hill Education
Reference:
1. Pandey I M, (2004), Financial Management, Vikas Publishing House.
2. Khan and Jain, Financial Management, Tata McGraw Hill,
3. PrasannaChandra(2004), Fundamentals of Financial Management
4. Chandra Prasanna ,Financial Management: Theory and Practice, McGraw-
Hill
5. Brigham, Financial Management Theory and Practice.
6. S.N. Maheshwari, Financial Management.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 3
7. Lawrence J. Gitman, (2004), Principles of Managerial Finance, Pearson
Education.
8. R P Rustagi, (2000), Financial Management, Galgotia Publications
Marketing Management
Sub. Code: RM 2.2 Total Marks (I+E) = 40+60 =100
Internal Assessment Marks = 40 External Examination Marks = 60
Credits: 4 Total Hours = 56
Hours Per Week (T + P) = 3+1(2) = 5
Course Objectives:
1. *To understand the concepts of marketing management
2. To learn about marketing process for different types of products and
services
3. To understand the tools used by marketing managers in decision making
4. To understand the marketing environment
Course Outcome
At the end of the course students are able to:
1. Analyse how the knowledge of marketing concepts and applications aid
in effective decision making in an organisational set up
2. Acquire insight to basic concepts of marketing management.
3. Apply the various marketing concepts to effectively market the products
4. Develop analytical skills in identification and resolution of problems
pertaining to marketing management.
Module I Introduction 10 hours
Definition, nature, scope and importance of Marketing; Evolution of Marketing,
Marketing mix; Strategic marketing, Market segmentation, Market analysis and
selection: Marketing environment - micro and macro components and their
impact on marketing decisions;Techniques used in environment analysis;
Contemporary Indian marketing environment; Marketing to the 21st century
customer
Module II Product Decisions 14
Hours
Concept of a product; Classification of products; Product hierarchy, line and
product mix; New product development; Product life cycle and strategies;
Branding - Concept of branding, types, brand equity and branding strategies;
Packing as a marketing tool and role of labeling in packing. Pricing Decisions:
Objectives and importance; Factors affecting price determination; Pricing
policies and strategies.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 4
Module III Place Decision 12
Hours
Distribution channels, nature, functions and types; Physical distribution
decisions; Channel management decisions; Retailing and wholesaling.
Promotion Decision: Communication Process; Promotion mix, Media selection;
Personnel selling; Advertising; advertising strategies, advertising effectiveness -
advertising effectiveness evaluation, Social media for advertising; Publicity;
Public Relations; Sales promotion - tools and techniques. Integrated marketing
communication
Module IV Consumer Behaviour 10
Hours
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior; AIDA Model; Five stage model of
consumer buying decision process; Buying roles and motives; Managing
customer relationships; Market Potential & Market Share; Market Segmentation
- levels, segmenting consumer markets; bases for segmenting consumer
markets; Market Targeting; Positioning - meaning, product differentiation
strategies and tasks involved in positioning.
Module V Marketing Plan 10
Hours
Marketing Planning & Steps; Marketing Information Systems (MKIS);Marketing
forecast, Marketing Audit; Services Marketing; Rural Marketing; Digital
Marketing; Green Marketing; Social, Ethical and Legal aspects of marketing;
Marketing Strategies and Plans, Marketing control- nature and importance of
marketing control, annual plan control, profitability control, efficiency control
and strategic control.
Practicum (Assignment / Activities):
1. Presentation on various marketing strategies
2. Case study on marketing management practices adopted by various
companies
3. Group discussion on latest trends in marketing.
Text Book
1. Philip Kotler, Kevinlane Keller, Abraham Koshy, And M. Jha, 2009,
Marketing Management – A south Asian Perspective. New Edition.
2. RAJAN SAXENA, 1997, Marketing Management, Tata McGraw – Hill
Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi.
Reference:
1. Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, Prentice Hall, New Delhi.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 5
2. Stanton, Etzel, Walker, Fundamentals of Marketing, Tata-McGraw Hill, New
Delhi.
3. Saxena, Rajan, Marketing Management, Tata-McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
4. McCarthy, E.J., Basic Marketing: A managerial approach, Irwin, New York.
5. Marketing Management: Indian Context. Global Perspective (Chapter 3,
Page No. 67)
6. by Ramaswamy and Namakumari- Sage Publication; 6 Edition.
7. Kazmi&Batra, Advertising & Sales Promotion, ,Excel Books, 2008
8. RajendraNargundkar, Services Marketing: Text & Cases, Tata McGraw-Hill
9. Pubishing Company, New Delhi, 2008.
10. S.C. Gupta, Marketing Research, Excel Books India, 2007.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 6
Human Resource Management
Sub. Code:RM 2.3 Total Marks (I+E) = 40+60 =100
Internal Assessment Marks = 40 External Examination Marks = 60
Credits:4 Total Hours = 56
Hours Per Week (T + P) = 4 + 0 = 4
Course Objectives:
1. To make students understand the changing needs and requirements of
today’s HR in companies.
2. To make students change their perspective towards traditional to
modern HRM
3. To make students learn to develop themselves to meet today’s HR
challenges.
Course Outcome:
At the end of the course students are able to:
1. Learn different strategy and modified skills of manager under changing
environment.
2. Learn different requirements of recruitment & selection
3. Gain the knowledge of on & off methods of training & development
4. Learn how the performance is controlled and evaluated in the companies
using tools nationally and internationally.
Module I Introduction to HRM 8 hours
Meaning and definitions of Human Resource Management; Functions of Human
Resource Management; HRM in a changing environment; The new human
resource manager ; IHRM- multinational management and global staffing, MNC
and IR/HR policy transfer- standardization V/S localization.
Module II Recruitment and Selection 15
Hours
Introduction to recruitment & selection; Three paradigms for recruitment &
selection- psychometric paradigm, social paradigms, personal paradigms; job
analysis- job description, job specification; selection process; selection using
analytic , machine learning and artificial intelligence; selection from global
perspective.
Module III Training and Development 12
Hours
Introduction to Training and Development: Training need assessment; Overview
of training process; Training methods- on the job training, off the job training;
evaluating training and development effectiveness; International training and
development issues.
Module IV Performance Management 15
Hours
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 7
Introduction to performance management; definition and evolution of
performance management; performance management process; performance
management as a system of control; tools for appraising performance;
difficulties in performance management system; performance management: a
system that confers organization value; effectiveness of performance appraisal.
Module V Inclination in HRM 06
Hours
HRM strategy and analysis- strategic management process, types of strategy;
HRM in emerging markets; HR Practices to diversity management; HR Metrics-
CII HR excellence model, Benchmarking and Data Analytic.
Practicum (Assignment / Activities):
1. Apply HR practices to the start up’s
2. State the recruitment and selection paradigm of any company
3. Demonstrate the process of online training and development
4. Identify competent performance parameter as per today’s corporate
5. Highlight the present trends in HRM
Text Book
1. David G, Geoffrey T.WOOD and Leslie T.Szamosi,Human Resource
Management- A Critical approach (2nd Edition), Routledge.
2. David A. DeCenzo, Stephen P.Robbins, Susan L.Verhulst, Human Resouce
Management (11th edition), John Wiley & sons Singapore pvt ltd.
3. Gary Dessler, BijuVarkkey, Human Resource Management (16th
edition),Pearson.
Reference:
1. Cameron K.S(1994), Stratergies for successful organizational downsizing.
Human resource management, 33(2):189-211.
2. Cook,H., Mackenzie,R and Forde,C. (2016), HRM and performance: the
vulnerability of soft HRM practices during recession and retrenchment,
Human Resource Management journal, 26(4):557-571.
3. H.M Findley, K.W.Mossholder, and W,F.Giles, “Performance appraisal
process ans system facets: relationship with contextual perfromance,
“Journal of Applied Psychology, (August 2000), pp 634-640.
4. Dessler, Gary, Human Resource Management (15th Edition), Pearson
5. Durai, Pravin, Human Resource Management (2nd Edition), Pearson
Education
6. K, Aswathappa, Human Resource Management: Text and Cases (7th
edition),Tata McGraw- Hill Education, 2013
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 8
7. Armstrong,Michael, A Handbook of Human Resource Management
Practice (14th edition)
8. Dwivedi, R,S, A Textbook of Human Resource Management, Vikas
Publishing
9. Subba Rao, P. 2004. Essentials of Human Resource Management and
Industrial Relations. Himalaya Publ. House.
10. V.S.P.Rao and C.B. Mamoria (2012), “Personal Management (Text and
Cases)”, Himalaya Publications, Thirtieth Edition.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 9
Research Methods and Statistical Tools
Sub. Code: RM 2.4 Total Marks (I+E) =40+60 =100
Internal Assessment Marks = 40 External Examination Marks = 60
Credits:4 Total Hours = 60
Hours Per Week (T + P) = 3+1(2) = 5
Course Objectives:
Research is the powerful tool in the modern world. Managers need to have
essence of systematic answers for their hypothesis.
1. To experience the skills of Business Research in all functional area this
gives creativity, thinking and knowledge with working knowledge of
software.
2. To understand the nature of problem to be studied and identifying the
related area of knowledge and Reviewing literature to understand how
others have approached or dealt with the problem.
3. Helps to understand collecting data in an organized and controlled manner
and analyze data appropriately which helps in to arrive at valid decisions.
Course Outcomes:
At the end of the course students are able to:
1. Formulate hypothesis to investigate issues in the rural business
environment
2. Prepare research proposals and reports
3. Use various sources of rural statistics to study rural business problems
4. Use Participatory Rural Appraisal tools and techniques in the rural
setting
Module I Introduction to Rural Research Design 10 hours
Meaning, scope and importance of Rural Business research; Types of research,
Basic, applied, Exploratory, conclusive, descriptive, the research process, problem
definition, formulation and preparation of research proposal.Review of literature,
use of Software (Ex. Zotero / MS Word).Research application – various functional
areas, Features of research study
Module II Sample Design and Sampling 10 Hours
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 10
Determining universe, sampling frame and sampling unit; determining sampling
method; non probability and probability methods; sample size determination
(statistical); sampling errors vs.non-sampling errors
Sampling: simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified random
sampling, cluster sampling -Non Probability Sampling – convenience sampling-
judgmental sampling, snowball sampling- quota sampling.
Module III Qualitative methods of data collection 12 Hours
Qualitative & quantitative data, Secondary: Internal, external, published,
electronic, uses &benefits of secondary data, drawbacks. Primary data: mail
survey, telephone survey and interviews and their evaluation; observations;
questionnaire preparation and administering, organizing fieldwork for a collecting
data. Questionnaire design (QD):-Steps in Q.D. with examples for each step.
Rating Scales, Juster, Likert, Semantic Differential, Thurston, Attitude Scales,
Scales for illiterate respondents
Module IV Data Processing and testing 14 Hours
Measurement scales, Tabulation (Coding Sheet) and analysis of data, Correlation
& regression, Parametric &Non-Parametric Tests.
Hypothesis: basic concepts, Type-I & Type II errors, hypothesis testing for means
and proportions for small and large samples.
Statistical calculations using SPSS: Creating a Data File, Defining Variables &
data, Frequencies, Crosstabs, Hypothesis Testing Reliability test (and above tests),
factor analysis, Chi square, test for goodness of fits and independence. T-Test, Z-
Test, F-Test, U-Test, Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney U Test, Wilcoxon,
Multivariate analysis ANOVA one way and two way classification,
Module V Report writing and presentation of results 10 Hours
Importance of report writing, types of research report, report structure, guidelines
for effective documentation, bibliography using MS Word /Zotero. Concepts of
plagiarism
Practicum (Assignment / Activities):
1. Preparing a Questionnaire
2. Conducting Field Surveys
3. Analysing and Testing the dummy data
4. Analysing the data through different test and Writing inferences
Text Book
1. Research Methods for Business, Uma Sekaran& Roger Bougie, 6th Edition,
Wiley, 2013
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 11
2. Marketing Research- Naresh K Malhotrs- 5th Edition, Pearson Education
/PHI 2007
Reference:
1. Gupta P and Hira. D.S (2003). Op. Cit, pp 709-753.
2. Kothari C.R.(2003). Quantitative Techniques, New Delhi: UBS Publishers
Distributions Ltd.,Chap 1, pp 6-11.
3. Sharma, Anand(2000). Quantitative Techniques for Decision Making,
Mumbai: HimalayaPublishing House, Chap.122, pp.3-13.
4. Boyd H W & Westfall: Marketing Research text and cases Richard Irwin Inc
5. Lucki D J Wales H G Etal: Marketing Research Prentice Hall.
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 12
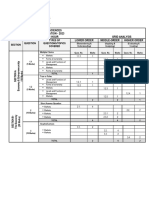
Advanced Skills in Agriculture and Allied Activities
Sub. Code:FAA 2.1 Total Marks (I+E) =20+30 =50
Credits:2 Total Hours = 30
Hours Per Week (T + P) = 0 + 2(4) =
4
Course Objectives:
1. To gain field exposure in real-time scenarios by students in Agriculture
and Allied Activities.
2. To implement lab to land and land to lab concept in students.
Course Outcome:
At the end of the course students are able to:
1. Hand holds exposure on agriculture -allied sectors like Diary,
Apiculture, Fishery, Poultry science etc.
2. Disseminate recent agricultural technologies through extension
activities.
Practical Titles of Practical Mode of
practical
Practical 1 Soil sampling and Testing Field
Practical 2 Seed treatment Lab and Field
Methods of Fertilizer Application and Fertilizer
Practical 3 Lab and Field
Calculation
Identification of nutrient deficiencies in plants
Practical 4 Lab and field
and Tissue Analysis
Packaging, Storage and Transportation of
Practical 5 Field
produce and cold storage of Farm Produce.
Visit to Poly house cultivation, Shade net
Practical 6 Field
Cultivation, etc.
Study of machines or equipment in rearing of
Practical 7 animals (Chaff Cutter, Milking Machine, Field
Lactometer and utensils.)
Value addition to Agriculture Produce (Fruits
Practical 8 Lab and Field
/Vegetable Processing)
Use of ICT in Agriculture (E commerce and M-
Practical 9 Computer Lab
Commerce)
Practical Visit to Tissue culture labs /popular nursery
Visit (Trip)
10 units.
Practical Visit to commercially viable labs/farms/firms/
Visit (Trip)
11 Agro-processing Unit
Practical
Visit to APMC and FPO’s Visit
12
Reference:
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 13
1. Agrawal, A. N., Indian Agriculture – problems, progress and prospects
2. Chinna,S.S, Agricultural Economics and Indian Agriculture.
3. Puttarudriah, M., 1983, A guide for cultivation and protection of important
crops
4. JalihalK.A ., and Veerabhadraiah V., 2007, Fundamentals of Extension
Education and Management in Extension. Concept Publ. Co.
5. Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India. 2004. State of Indian Farmer.
Vol V. Technology Generation and IPR Issues. Academic Foundation.
6. Jagadish Prasad, Principles and Practices of Dairy farm management.
Kalyani
7. Singh S. S., 2006. Principles and Practices of Agronomy. Kalyani.
8. Joshi M &Prabhakarasetty TK. 2005. Sustainability through Organic
Farming. Kalyani
9. Chadha KL. (Ed.). 2002. Hand Book of Horticulture. ICAR
10. Peter KV. 2008. (Ed.) Basics of Horticulture. New India Publ. Agency
KSRDPRU MBA (ABM&RM) Syllabus 2023 Onwards Page 14
You might also like
- CEMEX Case Study 2 v2Document16 pagesCEMEX Case Study 2 v2Sobina ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Atul Bisht Research Project ReportDocument71 pagesAtul Bisht Research Project ReportAtul BishtNo ratings yet
- Provisional Academic Transcript: S.No. Course Credit GradeDocument4 pagesProvisional Academic Transcript: S.No. Course Credit GradeNishant PrasadNo ratings yet
- MBA - (Complete Syllabus)Document225 pagesMBA - (Complete Syllabus)Swathi OjhaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument39 pagesSyllabusSrinivas DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- blr_mbaDocument232 pagesblr_mbaKriyaNo ratings yet
- NBKR Institute of Science & Technology:: VidyanagarDocument23 pagesNBKR Institute of Science & Technology:: VidyanagarrakeshNo ratings yet
- Sylabus MtechDocument86 pagesSylabus Mtechjyoti17 kammarNo ratings yet
- BBASyl56Sem UpdatedDocument47 pagesBBASyl56Sem UpdatedArjun PnNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledRosemaryfernandesNo ratings yet
- BBA FinalDocument4 pagesBBA FinalMP PooniaNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi.: Scheme of Teaching and Examinations and SyllabusDocument123 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi.: Scheme of Teaching and Examinations and SyllabusraghurockramNo ratings yet
- Ce PDFDocument45 pagesCe PDFFayum BirajdarNo ratings yet
- 85-CS Computer Science - TechnologyDocument5 pages85-CS Computer Science - TechnologyTOUHID ISLAMNo ratings yet
- VTU BE EEE Scheme 2018Document10 pagesVTU BE EEE Scheme 2018Vasavi VaasuNo ratings yet
- 5 6 Sem SyllabusDocument67 pages5 6 Sem Syllabusramizrhrr6786No ratings yet
- Bba V and Vi Sem Regular Nep SyllabusDocument52 pagesBba V and Vi Sem Regular Nep Syllabusamit.rajj199No ratings yet
- BE Mech 8th SEM Scheme - PDFDocument2 pagesBE Mech 8th SEM Scheme - PDFsiddeshsdNo ratings yet
- Civil 2nd, 4th & 6th Sem LoadDocument3 pagesCivil 2nd, 4th & 6th Sem LoadABHISHEK KUMAR MISHRANo ratings yet
- Elec SCHDocument11 pagesElec SCHCSE TCEGadagNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Scheme of Teaching and Examination and SyllabusDocument144 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Scheme of Teaching and Examination and SyllabusvidyaNo ratings yet
- ElecschDocument11 pagesElecschchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Visvesvaraya Technological University, BelagaviDocument1 pageArtificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Visvesvaraya Technological University, BelagavijrwtpfxkgsbdlconjvNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 5.35.32 PMDocument40 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 5.35.32 PMprathameshpawar7022No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument79 pagesSyllabuslucifer161103No ratings yet
- C 20 MY 3 4 SemDocument80 pagesC 20 MY 3 4 SemMatthew SmithNo ratings yet
- I Semester Scheme of Studies - Diploma in Electronics & Communications Engineering (C-20)Document2 pagesI Semester Scheme of Studies - Diploma in Electronics & Communications Engineering (C-20)Harsha Samagara100% (1)
- CseschDocument12 pagesCseschYtvancedNo ratings yet
- Btech Syllabus Electrical PDFDocument51 pagesBtech Syllabus Electrical PDFpranavmurthyNo ratings yet
- PG Mau SyllabusDocument71 pagesPG Mau SyllabusMaruthiNo ratings yet
- 70-Cs Mechanical TechnologyDocument5 pages70-Cs Mechanical Technologymdarifulislam234590No ratings yet
- Elec SCHDocument11 pagesElec SCHWell-balancedNo ratings yet
- Tentative scheme for Computer Science and Engineering and allied branches at Visvesvaraya Technological UniversityDocument12 pagesTentative scheme for Computer Science and Engineering and allied branches at Visvesvaraya Technological UniversitychaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Scheme of Teaching and Examination and SyllabusDocument10 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Scheme of Teaching and Examination and SyllabusRachnaNo ratings yet
- 335 - Download - Second Year B Tech Syllabus With Cove - 230126 - 123127Document25 pages335 - Download - Second Year B Tech Syllabus With Cove - 230126 - 123127shivampatel22098No ratings yet
- 357 - Download - Final Year B Tech Syllabus With Cover PageDocument108 pages357 - Download - Final Year B Tech Syllabus With Cover Pageshivampatel22098No ratings yet
- Feedback ReportDocument24 pagesFeedback ReportKirti LathiaNo ratings yet
- P Group Syllabus For 1st Sem CS ML DS September 2023Document34 pagesP Group Syllabus For 1st Sem CS ML DS September 2023Monisha RNo ratings yet
- BBSC Curriculum From 2021 Intake Onwards - 0Document170 pagesBBSC Curriculum From 2021 Intake Onwards - 0Nishantha FernandoNo ratings yet
- Vtu Cs SyllabusDocument12 pagesVtu Cs SyllabusShankha Suvro DuttaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Computer Science & Engineering: Scheme of Studies (C-20)Document55 pagesDiploma in Computer Science & Engineering: Scheme of Studies (C-20)P DeepikaNo ratings yet
- 64-CS Civil TechnologyDocument5 pages64-CS Civil TechnologyMonirul islam BadalNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviDocument139 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviPooja AshishNo ratings yet
- Electrical Electronics Engineering Tentative SCH PDFDocument9 pagesElectrical Electronics Engineering Tentative SCH PDFNabhisab NmNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviDocument148 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University BelagavichetanbvNo ratings yet
- VTU scheme of teaching and examination for III semesterDocument114 pagesVTU scheme of teaching and examination for III semesterIshwar ChandraNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi.: Scheme of Teaching and Examinations and SyllabusDocument53 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi.: Scheme of Teaching and Examinations and SyllabusSanjana CholkeNo ratings yet
- 63 - CS Chemical TechnologyDocument5 pages63 - CS Chemical TechnologyontumdfozlarabbiNo ratings yet
- MechschDocument11 pagesMechschTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- V & Vi Bcom Regular Syllabus Final Nep 17-9-2023 Bos ApprovedDocument48 pagesV & Vi Bcom Regular Syllabus Final Nep 17-9-2023 Bos ApprovedChethan MallikarjunNo ratings yet
- B.SC IT Scheme & Syllabus 4.5.2019Document74 pagesB.SC IT Scheme & Syllabus 4.5.2019Dr. Kaustubh JianNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 EMS Paper 2 ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK 2023 - END OF YEAR EXAMINATION - 085712Document2 pagesGRADE 8 EMS Paper 2 ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK 2023 - END OF YEAR EXAMINATION - 085712vutshilaashton52No ratings yet
- RGPV Scheme Cbgs Ec 6 SemDocument1 pageRGPV Scheme Cbgs Ec 6 SemAman Singh100% (1)
- Sapt - Social Science (Standard)Document2 pagesSapt - Social Science (Standard)Ahmadazams SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation and ControlDocument19 pagesPower System Operation and Controlsunitha vNo ratings yet
- 2020 21 Sem 2 PDFDocument25 pages2020 21 Sem 2 PDFHamza MallickNo ratings yet
- C20_3_4_sem_AEDocument92 pagesC20_3_4_sem_AEMohammed AyanNo ratings yet
- M.tech 1st Year SyllabusDocument13 pagesM.tech 1st Year SyllabusarshiNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument86 pagesSyllabustalawarraviNo ratings yet
- Structure-First YearDocument12 pagesStructure-First Yearioemk251No ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi Proudhyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal Scheme of Examination for B.Tech Computer Science and EngineeringDocument1 pageRajiv Gandhi Proudhyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal Scheme of Examination for B.Tech Computer Science and EngineeringShubham VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- BbafyDocument22 pagesBbafySanketNo ratings yet
- MANJU@874705Document7 pagesMANJU@874705Darshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit - 2Document13 pagesResearch Methodology Unit - 2Darshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- Fevicol FinalDocument12 pagesFevicol FinalDarshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- KotreshDocument9 pagesKotreshDarshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- Shakeera PPT HRMDocument9 pagesShakeera PPT HRMDarshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- Nipha VirusDocument21 pagesNipha VirusDarshan M BevoorNo ratings yet
- Financial MGTDocument179 pagesFinancial MGTyogeshjadhav333No ratings yet
- Strategic Service ManagementDocument312 pagesStrategic Service ManagementMarwaneEl-lamraniNo ratings yet
- Published MIHM306 Study Guide-Sem 2 2021Document33 pagesPublished MIHM306 Study Guide-Sem 2 2021Samir BhandariNo ratings yet
- Annualreport2003 2004Document64 pagesAnnualreport2003 2004Ryan ƁoŋŋęrNo ratings yet
- Department of Accountancy: Page - 1Document17 pagesDepartment of Accountancy: Page - 1NoroNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management of MAS PracticeDocument14 pagesOrganization and Management of MAS PracticeJohn AlbateraNo ratings yet
- Subjects Eligibility For Admission: Requirement of Minimum Marks Obtained in 10+2 Examination Calculation of Score For Merit List Gen B.A. HonoursDocument5 pagesSubjects Eligibility For Admission: Requirement of Minimum Marks Obtained in 10+2 Examination Calculation of Score For Merit List Gen B.A. HonoursRishikalpa SahaNo ratings yet
- #4 Assignment Description (Ch. 7-8)Document5 pages#4 Assignment Description (Ch. 7-8)Karan BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Strategy Consultant Ibm Job DescDocument4 pagesStrategy Consultant Ibm Job DescMax LeeNo ratings yet
- Kurt Lewins Change Model - Syed Talib Hussain 2016Document6 pagesKurt Lewins Change Model - Syed Talib Hussain 2016zailimiNo ratings yet
- 961 Beer Literatur 1Document49 pages961 Beer Literatur 1Budy s RaharjaNo ratings yet
- TANG Fu San BUSI2035 ASM1 PartB 1390993 1636330539Document1 pageTANG Fu San BUSI2035 ASM1 PartB 1390993 1636330539何子鋒No ratings yet
- BSBWRT411 Revised NewsletterDocument2 pagesBSBWRT411 Revised NewsletterUray FahreziNo ratings yet
- Career in ConsultingDocument4 pagesCareer in Consultinghugefan2018No ratings yet
- Tomas Del Rosario College Accountancy Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesTomas Del Rosario College Accountancy Course SyllabusVanessa L. VinluanNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Creation and Entrepreneurship - Seting BDocument2 pagesEnterprise Creation and Entrepreneurship - Seting BPelah Wowen Daniel100% (2)
- MSL884 ISS SyllabusDocument3 pagesMSL884 ISS SyllabusSureshNo ratings yet
- Mba Dissertation Topics Supply Chain ManagementDocument8 pagesMba Dissertation Topics Supply Chain ManagementWriteMyPaperCanadaNo ratings yet
- CV Tataru Andrada en AA DA NEWDocument4 pagesCV Tataru Andrada en AA DA NEWChuck NorrisNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/11Document4 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/11VenonNo ratings yet
- Highlighting Occupational Health and Safety (Ohs) Practices in Manufacturing Area: A Bibliography ReviewDocument13 pagesHighlighting Occupational Health and Safety (Ohs) Practices in Manufacturing Area: A Bibliography ReviewnursyahirahrosliNo ratings yet
- 109.jack R. KapoorDocument800 pages109.jack R. KapoorPriyanshuGuptaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship IntroductionDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurship IntroductionCHRIS MARLOWE YAMBAONo ratings yet
- Innovation and Design Thinking: I SemesterDocument4 pagesInnovation and Design Thinking: I Semestergreeshma100% (1)
- Case Study Topic PANASONICDocument6 pagesCase Study Topic PANASONICmayankagrawal549No ratings yet
- Impact of The Proposed CSR Mandate in The New Companies Bill On Indian CompaniesDocument17 pagesImpact of The Proposed CSR Mandate in The New Companies Bill On Indian CompaniesMayank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Business in A Changing WorldDocument47 pagesBusiness in A Changing WorldLaura BarusNo ratings yet
- Jack Stahl's Detailed Oriented LeadershipDocument2 pagesJack Stahl's Detailed Oriented LeadershipPrincess MagpatocNo ratings yet