Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Presentation
Uploaded by
Anand Verma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Untitled presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views8 pagesUntitled Presentation
Uploaded by
Anand VermaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
DEPARTMENT OF
BIOCHEMISTRY
● NAME - ALOK KUMAR TIWARI
● ROLL NO. - 13
● TOPIC - STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION OF PROTEIN
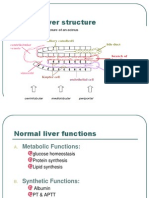
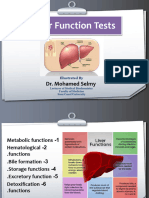
Enzyme profile in liver disease
Enzyme commonly studied for diagnosis of liver disease are:-
1. Alkaline aminotransferase (ALT)
2.Aspartate aminotransferase(AST)
3. Alkaline phosphate (ALP)
4. Nucleotide phosphate (NTP)
5.Gama glutamyl transferase(GGT)
1.Alkaline aminotransferase
● It was also called serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase(SGPT).
● the enzyme needed pyridoxal phosphate as coenzyme.
● Normal serum level for male is 13-35 U/L & for female is 10-30 U/L
● moderate increase of ALT may be seen in chronic liver disease such as
cirrhosis hepatitis C and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
2. Aspartate aminotransferase(AST)
● It was also called serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase(SGOT).
● AST needs pyridoxal phosphate as coenzyme.
● Normal serum level is- 8 to 20 U/L
● It is marker of liver injury & shows moderate to drastic increase in
parenchymal liver disease like hepatitis & malignancies of liver.
3. Alkaline phosphate (ALP)
● It is important enzyme to differentiate between hepatic disease & obstructive
pathology.
● it is an ectoenzyme- present on surface of biliary epithelium.
● some isoenzyme of ALP are:-
a).alpha-1
b).alpha-2 heat stable
c).alpha-2 heat labile
d).pre-beta
e).gamma
● In hepatic disease - ALP increases 2-3 times
● In obstructive disease - ALP increases 10-12 times
● obstruction to bile flow causes-irritates bile duct
epithelium--release of ALP from bile epithelium, which leads to
increase ALP level in serum
● In bone disease --upto 25 or more time increases.
4. Nucleotide phosphate (NTP)
● Normal in hepatitis
● increase in obstructive diseases
5. Gamma-glutamyl transferase
● Increases in alcoholic liver disease & obstructive liver disease.
You might also like
- PDF 20230919 013818 0000Document8 pagesPDF 20230919 013818 0000Anand VermaNo ratings yet
- Objective 6Document13 pagesObjective 6suyog raj gautamNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Function TestsDocument12 pagesHepatic Function TestsalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Pemeriksaan EnzimDocument25 pagesAplikasi Pemeriksaan EnzimBaiq NashaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test (LFT) OverviewDocument26 pagesLiver Function Test (LFT) Overviewanisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests ExplainedDocument20 pagesLiver Function Tests ExplainedALNAKINo ratings yet
- Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument40 pagesProfessor Dr. Najat A. HasanPeter MungaiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Document39 pages1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Syed ArefinNo ratings yet
- Measuring Enzyme Levels in Plasma for Disease Diagnosis and ManagementDocument27 pagesMeasuring Enzyme Levels in Plasma for Disease Diagnosis and ManagementharisNo ratings yet
- LFTSDocument34 pagesLFTSJoseline AliceNo ratings yet
- File NameDocument7 pagesFile NameHabib AbdurhmanNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Liver Function TestsDocument14 pagesInterpretation of Liver Function TestsNirav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDocument43 pages060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 pagesLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests ExplainedDocument14 pagesLiver Function Tests ExplainedRency ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Role of enzymes in metabolism, diagnosis and therapeuticsDocument19 pagesRole of enzymes in metabolism, diagnosis and therapeuticsMohamedErrmaliNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic enzymesDocument33 pagesDiagnostic enzymesDeepak DevaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Testssamdaman001No ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesMolecular BiologyMzwandile NyawoseNo ratings yet
- Transaminases or Aminotransferases: 1. ObjectiveDocument8 pagesTransaminases or Aminotransferases: 1. ObjectiveSeng HongNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document48 pagesWeek 2beltranayzellheartNo ratings yet
- Chem-Dr - Zainab-Liver Enzymes-Lab 3Document16 pagesChem-Dr - Zainab-Liver Enzymes-Lab 3gmpcbpzdysNo ratings yet
- Medical Use of EnzymesDocument13 pagesMedical Use of EnzymesSamhita ChitturiNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: Prepared By: Siti Norhaiza Binti HadzirDocument33 pagesLiver Function Test: Prepared By: Siti Norhaiza Binti Hadzirmhafiziab100% (1)
- Estimation of Sgot and SGPT - 113848Document32 pagesEstimation of Sgot and SGPT - 113848Become unique from otherNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Applications of EnzymesDocument40 pagesDiagnostic Applications of EnzymesmydadyNo ratings yet
- A Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsDocument5 pagesA Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsAbelantonNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Document16 pagesLiver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Shivansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Bio Section - Liver Function TestsDocument22 pagesBio Section - Liver Function Testsislam.o.walyNo ratings yet
- Plasma EnzymesDocument4 pagesPlasma EnzymesIbrahim ZorobNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TesDocument58 pagesLiver Function TesnoffrizalNo ratings yet
- 31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017Document59 pages31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument48 pagesLiver Function TestsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (12)
- Liver Function Tests LFTsDocument4 pagesLiver Function Tests LFTsDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- LFTs: Liver Function Tests ExplainedDocument3 pagesLFTs: Liver Function Tests ExplainedmahithNo ratings yet
- Standard LFT and It's Clinical SignificanceDocument28 pagesStandard LFT and It's Clinical SignificanceanimathzNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinDocument46 pagesAssessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinKomang YogatamaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: DescriptionDocument3 pagesLiver Function Test: DescriptionOkura JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Liver DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesLiver DiagnosticsTiny Briones-SallomanNo ratings yet
- Liver function test resultsDocument6 pagesLiver function test resultsSubhash Digambar VisalNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Group TwoDocument12 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Group TwoStanley KarugaNo ratings yet
- CC 2 Activity 2Document5 pagesCC 2 Activity 2Valdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Notes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Document6 pagesNotes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)Document51 pagesPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- LFTDocument12 pagesLFTRamchandra Satpute100% (1)
- ENZYMES OF CLINICAL IMPORTANCE ChapterDocument18 pagesENZYMES OF CLINICAL IMPORTANCE ChapterKeerthy VasanNo ratings yet
- Measuring SGOT and SGPT Levels in SerumDocument14 pagesMeasuring SGOT and SGPT Levels in SerumUmmul MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Clinical EnzymologyDocument25 pagesClinical Enzymologyaminata6No ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: AssignmentDocument6 pagesLiver Function Test: Assignmentsaud100% (2)
- Liver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsDocument14 pagesLiver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsshihochan100% (2)
- Objective 5Document9 pagesObjective 5suyog raj gautamNo ratings yet
- Liver (Hati) ZLDocument27 pagesLiver (Hati) ZLpafaniNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument90 pagesLiver Functionapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Assessment of Liver Function: HaeriaDocument16 pagesAssessment of Liver Function: Haeriaria_hai2359No ratings yet
- Abnormal LFTsDocument2 pagesAbnormal LFTsRenu RosyNo ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument22 pagesUrea CycleDawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument29 pagesLiver Function TestsJohnree A. EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Health Liver Interpretation and InterventionsDocument11 pagesHealth Liver Interpretation and InterventionsParas BansalNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and Their InterpretationDocument9 pagesLiver Function Tests and Their InterpretationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet