Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCN Placenta Previa
Uploaded by
BSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCN Placenta Previa
Uploaded by
BSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciCopyright:
Available Formats
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING
LECTURE / NCM 109
PLACENTA PREVIA ASSESSMENT FINDINGS
1. PAINLESS VAGINAL BLEEDING
• Fresh, bright red and sudden
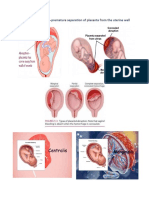
DEFINITION • Third trimester approximately week
• Abnormal / low implantation of the 30/7th month
placenta 2. UTERINE SOFT/FLACCID OR
o Nearing the cervical os INTERMITTENT HARDENING
• Accounts 20% of pregnancy bleeding • If in labor
• Painless bleeding 3. INTERMITTENT PAIN
• If it happens in labor secondary to
CAUSE
uterine contractions
• Unknown
4. SLIGHT / PROFUSED BLEEDING
DEGREES • Which may come after an activity,
A. LOW-LYING coitus or internal examination
• The implantation is lower rather than
ASSESSMENT FINDINGS (BLEEDING)
in the upper portion of the uterus
1. AOG / DURATION OF PREGNANCY
B. MARGINAL IMPLANTATION
2. TIME OF BLEEDING
• The placenta edge approaches the 3. ESTIMATED BLOOD AMOUNT
cervical os 4. ACCOMPANYING PAIN
C. PARTIAL 5. BLOOD COLOR
• Implantation of the placenta occludes 6. INTERVENTION USED FOR BLEEDING
a portion of the cervical os 7. PRIOR BLEEDING EPISODES
D. TOTAL 8. PRIOR CERVICAL SURGERY
• Implantation of the placenta totally 9. APT / KLEIHAUER-BETKE TEST
occludes of the cervical os 10. WEIGHT OF PERINEAL PADS
ASSOCIATED FACTORS • Before and after
1. INCREASED PARITY AND ADVANCED • Calculate by subtracting
MATERNAL AGE 11. INSPECT FOR BLEEDING & ESTIMATED
• Associated with the aging vasculature RATE OF BLOOD LOSS
of the uterus that leads to placental • To know how much blood is to be
hypertrophy replaced through BT
2. PAST CESAREAN BIRTHS
LABORATORY TESTS
• Because of uterine scarring d/t surgery 1. HEMOGLOBIN & HEMOCRIT
3. PAST UTERINE CURETTAGE 2. COAGULATION PROFILE
• d/t scarring • Prothrombin time & Partial
4. MULTIPLE PREGNANCY prothrombin time
• d/t a large placenta entering the o Use to determine clotting time
uterus o Normal value is 11-13 secs
INCIDENCE • Fibrinogen
• 5:1000 pregnancies • Platelet count
3. BLOOD TYPE & RH
OUTCOME 4. KLEIHAUER-BETKE TEST
• Increase in congenital fetal anomalies • Detects fetal blood in maternal
o d/t inadequate oxygenation and circulation
nutrition
RICCI D. CASTRO / BSN 2
1
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING
LECTURE / NCM 109
DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATIONS
• ULTRASONOGRAPHY A. HEMORRHAGE
o 95% accurate B. PREMATURITY
o Detects site of placental implantation / C. OBSTRUCTION OF BIRTH CANAL
position
o Determines fetal AOG NURSING IMPLEMENTATION
1. Maintain bedrest
o Detects possible malformations
• left lateral recumbent with a head
TREATMENT pillow
A. WATCHFUL WAITING (EXPECTANT 2. Do not perform an IE or vaginal
MANAGEMENT) examination
• Complete bed rest 3. Careful assessment
• No coitus • VS, bleeding, onset/progress of labor,
• No strenous activity FHT
• Keep hydrated 4. Prepare client for diagnostic
B. AMNIOTOMY ultrasonography
• Artificial rupture of the bag of waters 5. Institute shock measures as necessary.
• When AOG is full term Initially, bleeding in previa is rarely life-
• Sped-up descent of fetal head threatening but may become profuse with
C. DOUBLE SET UP internal examination
• One set for vaginal delivery and 6. Provide psycchological and physical
another for classical CS support
• Prepared for IE in suspected placenta 7. Prepare for conservative management,
previa double set-up, or a classical CS
Conditions 8. Observe for bleeding after delivery
• Term gestation • The lower uterine segment, the site of
• Mother in labor and progressing well placental detachement, is not a
contractile as the upper fundal portion
• Mother and fetus are stable
o If the woman is not in labor or in shock, 9. Administer IV fluids, blood products, &
and/or fetus is distressed, only one set-up medications
is to be prepared, an emergency 10. Have oxygen equipment incase of fetal
CLASSICAL cesarean section set up distress
D. DELIVERY
If conditions for watchful waiting are absent
• Vaginal delivery if birth canal is bot
obstructed
• Cesarean section if placental
placement prevents vaginal birth.
• In previa, CLASSICAL CS is indicated as
the lower uterine segment is occupied
by the placenta.
• Future pregnancies will be terminated
by another CS because the presence
of a CLASSICAL CS SCAR IS A
CONTRAINDICATION TO VAGINAL
DELIVERY
o leading the cause of UTERINE
RUPTURE.
RICCI D. CASTRO / BSN 2
2
You might also like
- Labor ReadinessDocument1 pageLabor ReadinessEvidence ChaibvaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery Nursing Knowledge & Skills ChecklistDocument4 pagesLabor and Delivery Nursing Knowledge & Skills Checklistnorthweststaffing100% (4)
- Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Ramon M. Gonzalez MD FPOGS Professor UST Faculty of Medicine and SurgeryDocument102 pagesUltrasound in Obstetrics: Ramon M. Gonzalez MD FPOGS Professor UST Faculty of Medicine and Surgeryaldeeray01No ratings yet
- Management Normal Labor 2021 SBOGDocument118 pagesManagement Normal Labor 2021 SBOGAHMED .KNo ratings yet
- Absolute Obstetric Anesthesia Review: The Complete Study Guide for Certification and RecertificationFrom EverandAbsolute Obstetric Anesthesia Review: The Complete Study Guide for Certification and RecertificationNo ratings yet
- High Risk Prenatal CareDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Prenatal CareKatherine Gayle GuiaNo ratings yet
- A Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 1 (Week 1-2)Document24 pagesA Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 1 (Week 1-2)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (3)
- Printable Pregnancy Journal PagesDocument11 pagesPrintable Pregnancy Journal PagesBudhi SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument6 pagesCephalopelvic DisproportionBaljinder kaurNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument74 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageApex College of Nursing100% (1)
- High Risk Labor and DeliveryDocument110 pagesHigh Risk Labor and DeliveryWilbert CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Nle - High-Risk PregnancyDocument113 pagesNle - High-Risk Pregnancytachycardia01No ratings yet
- NCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Document113 pagesNCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Maria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IINo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- High - Risk Labor and Delivery 2Document106 pagesHigh - Risk Labor and Delivery 2Charmaine Louie Macalanda Lopez-Soriano100% (2)
- Case Presentation Placenta PreviaDocument37 pagesCase Presentation Placenta PreviaJasmin Sabna100% (2)
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleDocument26 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleViktor InocNo ratings yet
- Fundic Height MeasurementDocument13 pagesFundic Height MeasurementGracy Morada Cu100% (1)
- Umbilical Cord AccidentsDocument16 pagesUmbilical Cord Accidentschebetnaomi945No ratings yet
- MCN Spontaneous MiscarriageDocument2 pagesMCN Spontaneous MiscarriageBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Accidents-1Document16 pagesUmbilical Cord Accidents-1chebetnaomi945No ratings yet
- Obstructed Labour FDocument53 pagesObstructed Labour FMax ZealNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa (OB)Document4 pagesPlacenta Previa (OB)Winj BudayNo ratings yet
- Late Pregnancy Bleeding (LPB) : Antepartum Hemorrhage (Aph) Dr. A. MutungiDocument3 pagesLate Pregnancy Bleeding (LPB) : Antepartum Hemorrhage (Aph) Dr. A. Mutungikhadzx100% (2)
- O Ultrasound FINAL 6-UpDocument7 pagesO Ultrasound FINAL 6-Uppiceng ismailNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse Final (Dr. P Garai)Document33 pagesCord Prolapse Final (Dr. P Garai)Akash ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CPD, Obstructed Labour, Ruptured UterusDocument47 pagesCPD, Obstructed Labour, Ruptured UterusMax ZealNo ratings yet
- 06 Placenta Previa Revised Feb 06 PDFDocument4 pages06 Placenta Previa Revised Feb 06 PDFrendyNo ratings yet
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentDocument43 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentkendrabooboooNo ratings yet
- PLACENTA PREVIA NewDocument38 pagesPLACENTA PREVIA NewJasmin SabnaNo ratings yet
- Educational Topic 32: Obstetric Procedures: U 2: O S C: PDocument4 pagesEducational Topic 32: Obstetric Procedures: U 2: O S C: PStetho LoveNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document6 pagesPresentation 1Sherylou Kumo SurioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDocument11 pages2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- Satuan Acara PenyuluhanDocument2 pagesSatuan Acara PenyuluhanNoni AlfridaNo ratings yet
- HIGH RISK AND SICK MOTHER 5PsDocument16 pagesHIGH RISK AND SICK MOTHER 5Psbaracream.exeNo ratings yet
- Rle Ncm109 Care of At-Risk / High Risk: Nursing Care of The Client During Labor and Delivery - Cesarean BirthDocument12 pagesRle Ncm109 Care of At-Risk / High Risk: Nursing Care of The Client During Labor and Delivery - Cesarean BirthHoping WinterNo ratings yet
- Interstitial PXDocument56 pagesInterstitial PXmenkir tegegneNo ratings yet
- 1st Trimester BleedingDocument3 pages1st Trimester BleedingdawnscribdNo ratings yet
- Problems Related To Gestational Weight NotesDocument11 pagesProblems Related To Gestational Weight NotesODESSA GALOLONo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument26 pagesMultiple PregnancyRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- OBGYN TransDocument6 pagesOBGYN TransanonymousNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Late PregnancyDocument44 pagesBleeding in Late Pregnancyratutev57No ratings yet
- Pathologic ObDocument8 pagesPathologic ObFvckin NonsenseNo ratings yet
- Wirausaha Bab 345Document6 pagesWirausaha Bab 345Bebby Siskiyawati GentiNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Previa AbruptioDocument28 pagesWeek 3 Previa Abruptiomico zarsadiazNo ratings yet
- OBST OPERATIONS - SMHS LogoDocument47 pagesOBST OPERATIONS - SMHS LogoMax ZealNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument8 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyDeniel Ivan MasangcayNo ratings yet
- Cs ObgDocument44 pagesCs ObghulwanvashaliNo ratings yet
- (OB2) Quiz 1 - Bleeding in 1st Half of Pregnancy (2020)Document5 pages(OB2) Quiz 1 - Bleeding in 1st Half of Pregnancy (2020)Jolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Maternity 2 Ante-Partum Haemorrhage (Aph) 26.3.2021Document29 pagesMaternity 2 Ante-Partum Haemorrhage (Aph) 26.3.2021Siti Nur Amalia FaizalNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room ProcedureDocument5 pagesDelivery Room ProcedureAparicio, Samantha Nicole D.No ratings yet
- Management of Uterine Inversion: Operative TechniquesDocument4 pagesManagement of Uterine Inversion: Operative TechniquesMuhammad AzkaNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Risks: Krizia Parrel Batch 9Document19 pagesPregnancy Risks: Krizia Parrel Batch 9krishanneNo ratings yet
- Nursing of Client With Highrisk Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesNursing of Client With Highrisk Labor and DeliveryshainakyllebarbonNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Student Activity SheetDocument7 pagesModule 8 Student Activity SheetJenny Agustin FabrosNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Maternal TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- MALPRESENTATIONDocument13 pagesMALPRESENTATIONLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Leong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument2 pagesLeong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- OSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisDocument82 pagesOSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisKahing LiNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Client Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipDocument2 pagesClient Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipLyssa Monique67% (3)
- Geriatrics - Developmental TaskDocument1 pageGeriatrics - Developmental TaskBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Research - Ethics of NSG ResearchDocument2 pagesResearch - Ethics of NSG ResearchBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Research - Intro To NSG ResearchDocument2 pagesResearch - Intro To NSG ResearchBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Rle - Perioperative NursingDocument11 pagesRle - Perioperative NursingBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Rle - Insulin InjectionDocument3 pagesRle - Insulin InjectionBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- MCN Rheumatic FeverDocument1 pageMCN Rheumatic FeverBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Nutridiet-Enteral and Parenteral FeedingDocument3 pagesNutridiet-Enteral and Parenteral FeedingBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues at The Beginning of LifeDocument37 pagesEthical Issues at The Beginning of LifeGeorgiana ButurăNo ratings yet
- NRG 204Document43 pagesNRG 204MICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- 7-Physiology of Normal PuerperiumDocument24 pages7-Physiology of Normal Puerperiumhade elNo ratings yet
- Maternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancyDocument62 pagesMaternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancySuad jakalatNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument32 pagesAmniotic FluidFahad KhanNo ratings yet
- VEAL CHOP With Interventions and OutcomesDocument1 pageVEAL CHOP With Interventions and Outcomesayngn13No ratings yet
- Case Scenario IDocument2 pagesCase Scenario IGynesis Lim RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Signs of LaborDocument5 pagesSigns of LaborweleyNo ratings yet
- Artificial Birth ControlDocument4 pagesArtificial Birth Controljessa tabanginNo ratings yet
- MCN 13157Document8 pagesMCN 13157Suis MionooNo ratings yet
- Health Educ Handout #11Document3 pagesHealth Educ Handout #11Ram AugustNo ratings yet
- Lo4 - Golingan Obstetric CalculationDocument4 pagesLo4 - Golingan Obstetric CalculationbabyboyNo ratings yet
- 9 Fetal Membranes-Dr - GosaiDocument22 pages9 Fetal Membranes-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Translational Research in Anatomy: James P. Nott, Elizabeth A. Bonney, James D. Pickering, Nigel A.B. SimpsonDocument7 pagesTranslational Research in Anatomy: James P. Nott, Elizabeth A. Bonney, James D. Pickering, Nigel A.B. Simpsonபாரதி ராஜாNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureDocument58 pagesBasic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- 2022 CFLGA - Data Capture FormDocument22 pages2022 CFLGA - Data Capture FormArnel AycoNo ratings yet
- Gender JusticeDocument105 pagesGender JusticeanuNo ratings yet
- Mid 3 QuizletDocument3 pagesMid 3 Quizletkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation During Postpartum HemorrhageDocument10 pagesEvaluation During Postpartum HemorrhageNilfacio PradoNo ratings yet
- T.P.U.W - Contraceptives Lecture (A4HI)Document35 pagesT.P.U.W - Contraceptives Lecture (A4HI)Osasere AiwansobaNo ratings yet
- Position Paper Teenage PregnancyDocument2 pagesPosition Paper Teenage PregnancyMark Joshua UyNo ratings yet
- Midterm109 QuestionDocument9 pagesMidterm109 Questionv6gv29sdv8No ratings yet
- PDCA Presentation - Barlekha UHCDocument16 pagesPDCA Presentation - Barlekha UHCMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Deomicah D. SolanoDocument42 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Deomicah D. SolanoJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Women in LabourDocument21 pagesPreparation of Women in LabourAbinaya RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Embryotransfer 160116150858Document18 pagesEmbryotransfer 160116150858Sol Gomez pacherreNo ratings yet