0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views2 pagesIB Physics Particle Practice Questions
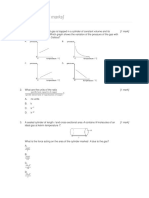
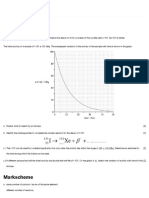
The document contains 4 practice questions about particle physics concepts. Question 1 asks about the spins of quarks in a proton and how they do not violate the Pauli exclusion principle. Question 2 asks about beta decay and virtual particles represented in a Feynman diagram. Question 3 asks about a pion reaction diagram and the possible charge and spin states of mesons. Question 4 asks about elementary particles, the class electrons belong to, and the exchange particle in neutron decay.
Uploaded by
Onur YavuzcetinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views2 pagesIB Physics Particle Practice Questions
The document contains 4 practice questions about particle physics concepts. Question 1 asks about the spins of quarks in a proton and how they do not violate the Pauli exclusion principle. Question 2 asks about beta decay and virtual particles represented in a Feynman diagram. Question 3 asks about a pion reaction diagram and the possible charge and spin states of mesons. Question 4 asks about elementary particles, the class electrons belong to, and the exchange particle in neutron decay.
Uploaded by
Onur YavuzcetinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd