Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ZZMethod (Beginner's Variation)
Uploaded by
bryanbsacCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ZZMethod (Beginner's Variation)
Uploaded by
bryanbsacCopyright:
Available Formats
ZZ Method Tutorial
Beginner’s Variation
Step 1 – EO + Line: Step 2 – F2L:
Theory: Blockbuilding: The strategy for solving pieces on a Rubik’s
An Oriented/Good edge does not require the use Cube that involves matching up individual pieces to form
of a F/B turn in order to become solved. small blocks that are combined with other small blocks to
An Unoriented/Bad edge requires the use of a F/B form bigger and bigger blocks. This will be used for solving
turn in order to become Oriented. F2L in the ZZ method.
F/B turns switch the Orientation of all edges in Types of Blocks:
that layer. Bad -> Good and vice versa. Buckle: An edge matched with a center
Cube Rotations affect edge orientation because Pair: A corner matched with an edge
the F/B layers change. Shield: a Buckle matched with a Pair
Recognizing Bad Edges: Wall: a Shield matched with one final Pair
Choose one position to be used throughout the F2L: a Wall built on each side of the EOLine.
entire solve (ex: Yellow in U, Green in F) Building Pairs:
Scanning order A Pair is comprised of any corner that is matched
1. U Layer up with an edge sharing two colors with the
2. D Layer corner. This is a highly intuitive step that is best
3. F Layer (2 edges in E slice) figured out on your own.
4. B Layer (2 edges in E slice) If you wish to see specific examples check out the
Rules: Bad edges either have a following links.
1. a R/L color (ex: Orange/Red) facing up o Conrad Rider’s ZZ F2L (Great! Specifically
OR for ZZ users)
2. a U/D color (ex: Yellow/White) on the side. http://cube.crider.co.uk/zz.php?p=f2l
Edge Orientation Strategy: o Speedsolving Wiki’s F2L (Watch out for
General Approach: Fill a F/B layer with four bad some cases that may change EO)
edges. Then F/B turn to eliminate/orient them. https://www.speedsolving.com/wiki/inde
Easy Cases x.php/F2L
o 4 Bad Edges: Fill either F/B with the 4 Strategies for Blockbuilding F2L:
edges, then turn that F/B layer to 1. Build one complete wall followed by the other.
eliminate them all. 2. Build a shield on each side of the line and expand
o 8 Bad Edges: Strategy for 4, twice. them into walls.
o 12 Bad Edges: Strategy for 4, three times.
Complex Cases
o 2 Bad Edges: Put one bad edge in F/B,
then turn that F/B layer to create three Note: This guide is intended as a supplement to Problem
new bad edges for a new total of 4. Solved’s ZZ Tutorial on YouTube, NOT as a standalone
Strategy for 4. tutorial. Congrats if you can use it as such though!
o 10 Bad Edges: Strategy for 8 followed by
strategy for 2. https://youtu.be/4Wrm2MGrRS8
o 6 Bad Edges: Either…
Strategy for 4 followed by strategy This guide was created by Problem Solved and may be
for 2. freely distributed in its current form.
Put three bad edges in F/B. Turn
that F/B layer to create one new The OLL and PLL diagrams are free to use and reproduce
bad edge for a new total of 4. (including for commercial purposes) without attribution.
Strategy for 4
Forming the Line: Largely intuitive. One strategy is to get
one line edge in the R Layer and the other in the L Layer.
Rotate R and L so both edges are in D. Turn D to form line.
goo.gl/v4VRzq
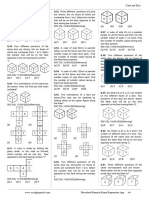
Step 3 - OLL: In this step you will create a solid face on the top of the cube. There are 7 cases as depicted below. Find the
one you have. Hold the cube in the same position as the diagram. Execute the algorithm to complete OLL.
Sune Double Headlights
Alg: R U R’ U R U2 R’ Alg: R U R’ U R (U’ R’ U R) U2 R’
This algorithm should be familiar This is the Sune, but with (four
from the beginner’s method. moves) added in.
Anti-Sune
Alg: L’ U’ L U’ L’ U2 L’ Pi/Bruno
This is Sune from the executed from Alg: R U2 R2' U' R2 U' R2' U2 R
the left side of the cube. No Comment. Just memorize it.
Headlights
Alg: R2 D’ R U2 R’ D R U2 R
Sidewinder
No Comment. Just memorize it.
Alg: l’ U R D’ R’ U’ R D
The lowercase “l” means grab two
layers when doing L.
Hammerhead
Alg: (r U r’ U’) (r’ F r F’)
The lowercase “r” means grab two
Note: This site has more algorithms for each case.
layers when doing R. https://www.speedsolving.com/wiki/index.php/OLL
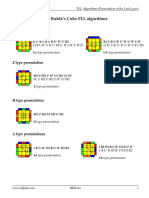
Step 4 - 2Look PLL: In this step you will permute (solve) the edges with one algorithm, then the corners with another
algorithm. There are 4 cases for edges and 3 cases for corners as depicted below. Find the one you have. Hold the cube in
the same position as the diagram. Execute the algorithm to complete OLL.
Edge Permutations:
H
Ua Alg: M2 U’ M2 U2 M2 U’ M2
Alg: R2 U' R' U' R U R U R U' R The M slice is the layer between R
No Comment. Just memorize it. and L
Ub Z
Alg: R' U R' U' R' U' R' U R U R2 Alg: M2 U’ M2 U’ M’ U2 M2 U2 M’
This is the inverse of Ua. Just Notation for the M slice matches L.
memorize it M’ goes the same direction as L’.
Corner Permutations:
Aa E
Alg: l' U R' D2 R U' R' D2 R2 Alg: (R U' R' D) (R U R' D') (R U R' D)
Remember “l” means grab two (R U' R' D')
layers when doing an L turn. I’ll let you figure out the pattern
Ab
Alg: r U’ L D2 L’ U L D2 L2
This is Aa executed from the left. Note: This site has more algorithms for each case.
Remember “r” grabs two layers https://www.speedsolving.com/wiki/index.php/PLL
You might also like
- RouxDocument8 pagesRouxzheroel100% (1)
- Rubik's Cube Solution - Useful LinksDocument48 pagesRubik's Cube Solution - Useful LinksYash Kumar100% (1)
- Giles Roux's Eponymous MethodDocument1 pageGiles Roux's Eponymous MethodBobik KobikNo ratings yet
- Blindfold Cube SolvingDocument9 pagesBlindfold Cube SolvingVani MuthukrishnanNo ratings yet
- ROUX Guide Rev4Document8 pagesROUX Guide Rev4LoSparviero100% (1)
- Orozco TutorialDocument7 pagesOrozco TutorialJeanNo ratings yet
- R 6x6x6 PDFDocument2 pagesR 6x6x6 PDFjavimm100% (1)
- 6 X 6 X 6Document2 pages6 X 6 X 6javimm100% (1)
- Rubik's Cube - Final Layer Algorithms (Printable Page)Document1 pageRubik's Cube - Final Layer Algorithms (Printable Page)jaymarNo ratings yet
- Rubik's Cube (HAW)Document60 pagesRubik's Cube (HAW)htotisumNo ratings yet
- Twenty-Two Moves Suffice For Rubik's Cube: Mathematical EntertainmentsDocument8 pagesTwenty-Two Moves Suffice For Rubik's Cube: Mathematical EntertainmentsCrisalcalaNo ratings yet
- Twenty-Five Moves Suffice For Rubik's CubeDocument10 pagesTwenty-Five Moves Suffice For Rubik's Cubes v k100% (2)
- 3x3 InstructionsDocument13 pages3x3 InstructionsBrad HylandNo ratings yet
- How To Solve A Rubik's Cube, Step by Step - WIREDDocument17 pagesHow To Solve A Rubik's Cube, Step by Step - WIREDAmv Bro100% (1)
- ScramblesDocument26 pagesScrambleseduardox11No ratings yet
- Beginners Method For Solving The 5x5 CubeDocument2 pagesBeginners Method For Solving The 5x5 CubeVikrant Parmar50% (2)
- Andy Klise 3op m2 Practice SolvesDocument2 pagesAndy Klise 3op m2 Practice Solvesరామకృష్ణ పాశలNo ratings yet
- Metodo PetrusDocument2 pagesMetodo Petruscgarcia16No ratings yet
- Beginners Method For Solving The 5x5 CubeDocument4 pagesBeginners Method For Solving The 5x5 CubeSilvanildo MacárioNo ratings yet
- Rubiks Cube or Magic Cube: The Solution To The Game/puzzleDocument6 pagesRubiks Cube or Magic Cube: The Solution To The Game/puzzleSubasi66No ratings yet
- The 2x2 RubikDocument7 pagesThe 2x2 Rubikapi-281945496No ratings yet
- Pretty Rubik S Cube Patterns With AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesPretty Rubik S Cube Patterns With AlgorithmsliangNo ratings yet
- M2/R2 Blindcubing Methods: Home Cube Corner BlindsolvingDocument7 pagesM2/R2 Blindcubing Methods: Home Cube Corner BlindsolvingKeith Ginoel GabineteNo ratings yet
- 4x4x4 Rubiks' Cube Reduction AlgorithmsDocument7 pages4x4x4 Rubiks' Cube Reduction Algorithms14nganhc1No ratings yet
- Rubik's Cube GuideDocument8 pagesRubik's Cube GuideJeremyUltraNo ratings yet
- How To Solve A Rubik'S Cube Advanced MethodDocument8 pagesHow To Solve A Rubik'S Cube Advanced MethodArnav PahalwanNo ratings yet
- Based On "The Beginner's Solution To The Rubik's Cube" by Jasmine LeeDocument20 pagesBased On "The Beginner's Solution To The Rubik's Cube" by Jasmine Leerk_gprkavi2011100% (1)
- Andy Klise 4x4x4 GuideDocument2 pagesAndy Klise 4x4x4 GuideVinay Goddemme100% (1)
- Petrus Method of Solving Rubiks CubesDocument2 pagesPetrus Method of Solving Rubiks CubesStuart 'Stu' Nofkee100% (2)
- Cube - 3x3x3 - OLL-PLL - 4-Look Version UpdatedDocument1 pageCube - 3x3x3 - OLL-PLL - 4-Look Version UpdatedBrasil America do sulNo ratings yet
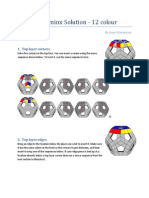
- Megaminx F2L S2LDocument3 pagesMegaminx F2L S2LngNo ratings yet
- Pll-Edges and CornersDocument17 pagesPll-Edges and CornersRichard Lorenzo BeloNo ratings yet
- Holey12sol PDFDocument8 pagesHoley12sol PDFrushi_007No ratings yet
- How To Solve The Latch CubeDocument19 pagesHow To Solve The Latch Cubemojohand100% (1)
- Solving A Rubik CubeDocument22 pagesSolving A Rubik Cubeaziz090No ratings yet
- Cube NotationDocument7 pagesCube NotationjNo ratings yet
- LMCF 3x3 Rubik's Cube Method (Revision 4.5) : Please Watch My LMCF Tutorial Video On My Youtube ChannelDocument43 pagesLMCF 3x3 Rubik's Cube Method (Revision 4.5) : Please Watch My LMCF Tutorial Video On My Youtube ChannelJohn Edward100% (2)
- Tutorial Penyelesaian Rubik CubeDocument9 pagesTutorial Penyelesaian Rubik CubenazzserilNo ratings yet
- Group Theory NotesDocument51 pagesGroup Theory NotesJan Hroch KošataNo ratings yet
- 4 Look Last LayerDocument4 pages4 Look Last LayerPCwizCube94% (17)
- Metodo Fridrich Full - RubikDocument7 pagesMetodo Fridrich Full - RubikManu319100% (1)
- Rubiks Cube or Magic Cube: The Solution To The Game/puzzleDocument6 pagesRubiks Cube or Magic Cube: The Solution To The Game/puzzle吴国豪No ratings yet
- Adams Rubiks Cube SolutionDocument11 pagesAdams Rubiks Cube SolutionArvin SinghNo ratings yet
- CFOPDocument3 pagesCFOPFranz Argandoña0% (1)
- Rubiks Cube SolverDocument10 pagesRubiks Cube Solverbrizmar07No ratings yet
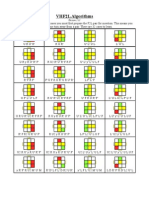
- VHF2L AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesVHF2L AlgorithmsHwangWalter100% (3)
- Optimising The Beginners MethodDocument1 pageOptimising The Beginners MethodAndré SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Rubik's Cube 3x3x3Document6 pagesRubik's Cube 3x3x3endangsubarnaNo ratings yet
- Beginner Rubik's CubeDocument4 pagesBeginner Rubik's CubePremjit DasNo ratings yet
- Oll y PLL PDFDocument4 pagesOll y PLL PDFpaul paulNo ratings yet
- How To Solve The Rubik's Cube?Document1 pageHow To Solve The Rubik's Cube?Elodie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- How To Solve The Rubik's Cube - Beginners MethodDocument1 pageHow To Solve The Rubik's Cube - Beginners Methodseppe.van.bogaertNo ratings yet
- 4 Top Layer EdgesDocument17 pages4 Top Layer Edgesapi-549171013No ratings yet
- 4x4 Edge PairingDocument15 pages4x4 Edge PairingSeeta GilbertNo ratings yet
- Minimum Formula For 3X3X3 Rubik Cube Solution Part 2 - Last Layer PermutationDocument13 pagesMinimum Formula For 3X3X3 Rubik Cube Solution Part 2 - Last Layer PermutationPuworkUtara OnScribd60% (5)
- Step 1 - Two Opposite Centers: Everything Is Taken Verbatim FromDocument2 pagesStep 1 - Two Opposite Centers: Everything Is Taken Verbatim Fromsoria_a721No ratings yet
- Fridrich (CFOP) - Stage 1Document9 pagesFridrich (CFOP) - Stage 1Master CloneNo ratings yet
- Rubiks Cube InstructionsDocument10 pagesRubiks Cube Instructionsapi-397660531No ratings yet
- Rubik 7 X 7 X 7 Solution JaapDocument3 pagesRubik 7 X 7 X 7 Solution JaapAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Blindfold Solving Rubik's CubeDocument10 pagesBlindfold Solving Rubik's Cubeanon_373981888No ratings yet
- Kapil Bhatt Cube: OLL Algorithms (Orientation of Last Layer)Document4 pagesKapil Bhatt Cube: OLL Algorithms (Orientation of Last Layer)Bibek PoudelNo ratings yet
- Rubik 4 X 4 X 4Document17 pagesRubik 4 X 4 X 4Mitch MateychukNo ratings yet
- Vulcano Professor Pyraminx 2010 Meffert SDocument25 pagesVulcano Professor Pyraminx 2010 Meffert SOrigami TutorialsNo ratings yet
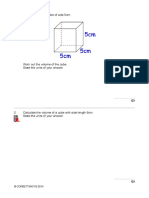
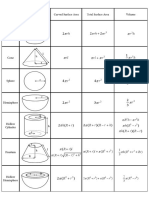
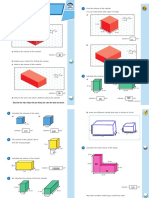
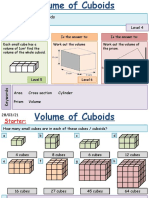
- Volume of A CuboidDocument8 pagesVolume of A CuboidAyeola RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formula Sheet - IGCSEDocument3 pagesMensuration Formula Sheet - IGCSEBeats79% (14)
- Rubik S Cube 3x3 Easy Solve Guide Tutorial May 2023Document7 pagesRubik S Cube 3x3 Easy Solve Guide Tutorial May 2023Muhammad Aslam .S100% (1)
- Kami Export - Destinee Yakubu - Student Worksheet - Volume of A CuboidDocument2 pagesKami Export - Destinee Yakubu - Student Worksheet - Volume of A CuboidDestineeNo ratings yet
- Up Science Year 2 Paper 1 - 2021Document9 pagesUp Science Year 2 Paper 1 - 2021masoryzaNo ratings yet
- Andy Klise Square-1 TutorialDocument1 pageAndy Klise Square-1 Tutorialvmq080812No ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument20 pagesRemote Sensinghakimhairi0% (1)
- XNXNXNXN Cube Algorithms Rubiks Revenge Parity AlgorithmsDocument17 pagesXNXNXNXN Cube Algorithms Rubiks Revenge Parity AlgorithmsAkashNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Science BDocument6 pagesYear 5 Science Bnorzila adanNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of A CuboidDocument8 pagesSurface Area of A CuboidFaizullah Faisal SyedNo ratings yet
- Rubiks Solution-Guide SlideDocument40 pagesRubiks Solution-Guide SlideCristovao Mendes RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Surface Area Cuboids PDFDocument2 pagesSurface Area Cuboids PDFihfurfure bdbbNo ratings yet
- Walt: Wilf:: Find The Volume of CuboidsDocument11 pagesWalt: Wilf:: Find The Volume of Cuboidsmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- LATIHAN ASAS - Congak 2Document1 pageLATIHAN ASAS - Congak 2zaini9009No ratings yet
- Answer - Surface Area - Cube, Cuboid & PrismDocument2 pagesAnswer - Surface Area - Cube, Cuboid & PrismtavizNo ratings yet
- Rubiks-Cube 3x3 PLLDocument4 pagesRubiks-Cube 3x3 PLLHarrey MaurealNo ratings yet
- 1LLLDocument89 pages1LLLDanyloHoncharenkoNo ratings yet
- Pages From 7200 Reasoning Chapter Wise Eng Extracted PagesDocument4 pagesPages From 7200 Reasoning Chapter Wise Eng Extracted PagesPrathmesh ThakareNo ratings yet
- Factor de Empaquetamiento de Las Celdas Unitarias BCC, FCC y HCPDocument3 pagesFactor de Empaquetamiento de Las Celdas Unitarias BCC, FCC y HCPrajel muñozNo ratings yet
- Word Problems Volume of Cube & CuboidsDocument2 pagesWord Problems Volume of Cube & CuboidsHardik ViraNo ratings yet
- Soal Pengayaan PTS 1 Grade 2Document5 pagesSoal Pengayaan PTS 1 Grade 2wardaniNo ratings yet
- 002 ContentsDocument6 pages002 ContentsMukul DasNo ratings yet
- N5 Applications of Maths With Solutions 4 PDFDocument59 pagesN5 Applications of Maths With Solutions 4 PDFThe Unique Game ChangerNo ratings yet
- Class Assignment On Cube and DiceDocument6 pagesClass Assignment On Cube and DiceAnmol AswalNo ratings yet
- Volume Problem Attic Flashcards Without Answer KeyDocument25 pagesVolume Problem Attic Flashcards Without Answer Keyapi-290509627No ratings yet
- Easy 1Document2 pagesEasy 1Malinee LimpipusanaNo ratings yet
- How To Speedsolve The Rubik's Cube - CFOP Method ExplainedDocument12 pagesHow To Speedsolve The Rubik's Cube - CFOP Method ExplainedRijal AbedinNo ratings yet