Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wa0010.
Uploaded by
Krishnan 18Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wa0010.
Uploaded by
Krishnan 18Copyright:
Available Formats
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF AXIS BANK:
Financial ratios help you interpret any company's finances' raw data to get actionable inputs on
its overall performance. You can source the ratios from a company's financial statements to
evaluate its valuation, rates of return, profitability, growth, margins, leverage, liquidity, and more.
Investors and analysts employ ratio analysis to evaluate the financial health of companies by
scrutinizing past and current financial statements. Comparative data can demonstrate how a
company is performing over time and can be used to estimate likely future performance.
11.1 Ratio analysis:
Ratio analysis is the systematic use of the ratio to interpret the financial statements. Hence the
strengths and weaknesses of a firm, as well as its historical performance and current financial
condition can be determined. Ratio reflects a quantitative relationship that helps to form a
quantitative judgment.
11.1.1 Importance of Ratio Analysis:
• Aid to measure general efficiency
• Aid to measure financial solvency
• Helps in forecasting and planning
• Facilitate decision making
• Act as a good communication
• Evaluation of efficiency
• Analysis of Operational Efficiency of the Firms
• Helps in Understanding the Profitability of the Company
• To Compare the Performance of the Firms
11.2 Types of ratios interpreted below are:
11.2.1 Liquidity Ratios:
(a) Current Ratio
(b) Quick Ratio
11.2.2 Leverage Ratios:
(a) Debt to equity Ratio
(b) Fixed asset to long term funds Ratio
(c) Interest cover Ratio
11.2.3 Turnover Ratios:
(a) Inventory turnover Ratio
(b) Debtors turnover Ratio
(c) Creditors turnover Ratio.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
11.2.1 Liquidity Ratio :
Liquidity ratios measure the liquidity of a company. They provide insight into a company’s ability
to repay its debts and other liabilities out of its liquid assets. Liquidity includes all assets that can
be converted into cash quickly and cheaply.
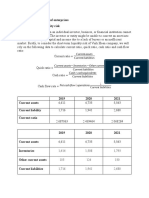
(a) Current Ratio:
Current ratio may be defined as the relationship between current assets and current liabilities.
This ratio also known as Working capital ratio is a measure of general liquidity and is most widely
used to make the analysis of a short-term financial position (or) liquidity of a firm. A current ratio
that is in line with the industry average or slightly higher is generally considered
acceptable. A current ratio that is lower than the industry average may indicate a higher
risk of distress or default. Similarly, if a company has a very high current ratio compared
with its peer group, it indicates that management may not be using its assets efficiently.
Current ratio = Current assets
Current Liabilities
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
CA& Loans and
advances 5,699.28 9,587.39 8,711.54 7,604.87 8,138.7
CL& provisions 4,973.51 4,370.12 7,811.18 12,255.16 5,674.04
Current Ratio 1.15:1 2.19:1 1.12:1 2.1:1 1.43:1
Table 11.2.1(a) Current Ratio
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.1(a) it is evident that the current ratio is higher in the year 2018-19
whereas it is lowest during the year 2019-20. The ideal Capital Ratio is 2.1, The company has failed
to meet it. Hence its short term financial position need to be improve .
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Current Ratio
2.5
1.5
0.5
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Chart 11.2.1(a) Bar graph depicting Current Ratio from 2017 to 2022
(b) Quick Ratio
Quick ratio is a test of liquidity than the current ratio. The term liquidity refers to the ability of a
firm to pay its short-term obligations as &when they become due. Quick ratio may be defined as
the relationship between quick or liquid assets and current liabilities. An asset is said to be liquid
if it is converted into cash within a short period without loss of value.
Quick Ratio = _Quick Assets__
Current Liabilities
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
CA and Loans & Advances 3,727.56 7,757.65 7,100.40 5,925.21 6,618.12
minus inventories
CL & Provisions minus Bank 4,382.64 2,735.56 7,640.17 9,214.90 5,674.04
OD
Quick Liabilities Ratio 0.85:1 2.84:1 0.93:1 0.64:1 1.17:1
Table 11.2.1(b) Quick Ratio
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.1(b) the bank is having good liquidity position i.e.1.17 in the year of
2021 to 2022. The quick ratio of 1:1 indicates satisfactory position of the firm. The highest ratio
is 2.84 in 2018-19 and the lowest one is 0.64 in 2020-21.
Quick Ratio
3
2.5
1.5
0.5
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Chart 11.2.1(b) Bar graph depicting Quick Ratio from 2017 to 2022
11.2.2 Leverage Ratios : The term ‘leverage ratio’ refers to a set of ratios that highlight a business’s
financial leverage in terms of its assets, liabilities, and equity. They show how much of an
organization’s capital comes from debt — a solid indication of whether a business can make good
on its financial obligations. A financial leverage ratio of less than 1 is usually considered good by
industry standards.
(a) Debt to equity Ratio:
Debt-to-equity ratio is the key financial ratio and is used as a standard for judging bank’s financial
standing. It is also a measure of a bank’s ability to repay its obligations When examining the health
of a bank, it is critical to pay attention to the debt/equity ratio if the ratio is increasing, the bank
is being financed by creditors rather than from its own financial sources which may be a
dangerous trend. Lenders and investors usually prefer low debt-to-equity ratios because their
interests are better protected in the event of a business decline. Thus, companies with high debt-
to-equity ratios may not be able to attract additional lending capital.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Debt to equity ratio = Long-time debt
Shareholders fund
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Long time debt 500.00 166.90 289.83 289.83 1,733.74
Share holders
fund 3,707.84 2,832.68 2,849.88 2,338.69 3,184.15
Debt-Equity
0.045:1 0.177:1 0.059:1 0.124:1 0.544:1
Ratio
Table 11.2.2(a) Debt-Equity Ratio
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.2(a) if the debt-equity ratio is greater than 1, then the bank assets are
financed through debt or if the ratio is less than 1, its assets are primarily financed through equity.
From the above table bank ratio is less than 1, from the year of 2018 to 2022. Hence the bank
assets are financed trough equity.
debt-to-equity ratio
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
debt-to-equity ratio
Chart 11.2.1(a) Bar graph depicting Debt- Equity Ratio from 2017 to 2022
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
(b)Fixed asset to Long term funds Ratio:
A fixed asset to equity ratio measures the contribution of stockholders and the contribution of
debt sources in the fixed assets of the bank. It is computed by dividing the fixed assets by the
stockholders’ equity. Other names of this ratio are fixed assets to net worth ratio and fixed assets
to proprietors fund ratio.
Fixed asset to long term funds ratio = Fund assets
Long term assets
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Fixed Assets 5,546.86 7,999.88 4,705.11 4,652.63 3,577.92
Long term 166.09 500.00 166.09 289.83 1,733.92
funds
Fixed assets 33.23:1 16:1 28.19:1 16.05:1 2.06:1
to long term
funds Ratio
Table 11.2.2(b) Fixed assets to Long term funds Ratio
Interpretation:
Comparing this fixed-assets-to long term funds ratio against industry, high ratios can be
interpreted as liquidity problems, because it means the bank does not have immediate access to
cash. From the above table the bank can have an easy access to cash to meet financial obligations
in the year 20014-15, when compared to remaining years (2017-18,2018-19 2019-20 2020-22).
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Fixed asset to long term funds ratio
35
30
25
20
15
10
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Fixed asset to long term funds ratio
Chart 11.2.1(b) Bar graph depicting Fixed Assets to long term funds Ratio from 2017 to 2022
(c)Interest cover Ratio :
The interest coverage ratio (ICR) is a measure of a bank’s ability to meet its interest payments.
Interest coverage ratio is equal to earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) for a time period, often
one year, divided by interest expenses for the same time period The interest coverage ratio is a
measure of the number of times a bank could make the interest payments on its debt with its
EBIT It determines how easily a bank can pay interest expenses on outstanding debt. Interest
coverage ratio is also known as interest coverage, debt service ratio or debt service coverage ratio.
Interest cover ratio =PBIDT
Interest
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
PBIT 1772.58 0334.09 1487.85 0594.85 2516.04
Interest 0286.09 0428.01 0704.44 0734.97 0637.54
Interest 6.18:1 0.78:1 2.11:1 0.81:1 3.95:1
Cover
Table 11.2.2(c) Interest Cover Ratio
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Interpretation:
In the years of 2017-18, 2019-20,2021-22 the interest expenses has incurred by bank is greater
than the earnings that bank have had to pay, but compare to remaining years However the bank
is easily able to meet the interest obligation from profits.
Interest cover Ratio
7
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Interest cover Ratio
Chart 11.2.1(c) Bar graph depicting Interest Cover Ratio from 2017 to 2022
11.2.3 Turnover Ratios: Turnover ratio is a measurement of efficiency, indicating the length of
time it takes a business to sell the goods that it has spent money up front to acquire. In a
company or industry, turnover ratio is the percentage of employees who leave within a
year.
(a) Inventory turnover ratio:
Inventory turnover is a measure of the number of times inventory is sold or used in a given time
period such as one year. It is a good indicator of inventory quality (whether the inventory is
obsolete or not), efficient buying practices, and inventory management. This ratio is important
because gross profit is earned each time inventory is turned over it is also called as stock turnover.
Inventory turnover ratio= Cost of goods sold
Average inventory
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Cost of goods 13693.650 15012.49 16426.22 19097.99 23281.47
sold
Average 563.905 501.96 417.845 322.025 365.68
Inventory
Inventory 24.28:1 29.91:1 39.31:1 59.31:1 63.67:1
turnover
ratio
Table 11.2.3(a) Inventory Turnover Ratio
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.2(b) the Inventory Turnover Ratio of the bank is satisfactory because the
ratio on increasing year by year from 2017-2018 to 2021-2022.the ideal inventory turnover ratio
will be between 5 and 10
Inventory Turnover Ratio
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Inventory Turnover Ratio
Chart 11.2.3(a) Bar graph depicting Inventory Turnover Ratio from 2017 to 2022
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
(b) Debtors turnover ratio:
The receivable turnover ratio (debtor’s turnover ratio, accounts receivable turnover ratio)
indicates the velocity of a bank’s debt collection, the number of times average receivables are
nummed over during a year. This ratio determines how quickly a bank collects outstanding cash
balances from its customers during an accounting period. It is an important indicator of a bank’s
financial and operational performance and can be used to determine if a bank is having difficulties
collecting sales made on credit.
Debtor’s turnover ratio= Credit sales
Average debtors
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Credit Sales 19104.87 19625.18 22356.35 24078.27 30664.18
Average 02937.07 04513.68 05813.3 5358.805 4946.355
Debtors
Debtors 6.5:1 4.35:1 3.85:1 4.49:1 6.2:1
Turnover
Ratio
Table 11.2.3(b) Debtors Turnover Ratio
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.3(b) the Debtors turnover ratio increases in the year 2017-18 is at 6.50, which
decreases to 6.20 in the year 2021-22. But in the year 2018-19 to 2020-21, it decreases to 4.35,
3.85,4.49 It indicates that debts are being collected more promptly.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Debtors Turnover Ratio
7
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Debtors Turnover Ratio
Chart 11.2.3(b) Bar graph depicting Debtors Turnover Ratio from 2017 to 2022
(c) Creditor’s turnover ratio:
This ratio is similar to the debtor’s turnover ratio. It compares creditors with the total credit
purchases. It signifies the credit period enjoyed by the firm in paying creditors. Accounts payable
include both sundry creditors and bills payable. Same as debtor’s turnover ratio, creditor’s
turnover ratio can be calculated in two forms, creditors’ turnover ratio and average payment
period.
Creditor’s turnover ratio = Credit purchase
Average creditors
Particulars 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Credit 13979.91 14885.1 16374.43 18086.99 23273.03
Purchase
Average 3020.295 36240.9 5472.705 07226.37 4802.085
Creditors
Creditors 4.63:1 4.11:1 2.99:1 2.50:1 4.85:1
Turnover
Ratio
Table 11.2.3(c) Creditors Turnover Ratio
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Interpretation:
From the table 12.2.3(c) creditor’s turnover ratio is likely down in 2019-210 and 2020-21. It shows
the payment of creditor’s is slow compare with other years. A high ratio implies velocity of
payment to creditors and low the other side.
Creditors Turnover Ratio
6
0
2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22
Creditors Turnover Ratio
Chart 11.2.3(c) Bar graph depicting Creditors Turnover Ratio from 2017 to 2022
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
FINDINGS AND SUGGESTIONS:
12.1 Findings :
1. The current ratio has shown in a fluctuating trend from 2010-11 to 2014-15 (i.e.1.15,
2.19, 1.12, 0.62and1.43) of which indicates a continuous increase in both current
assets and current liabilities.
2. The quick ratio is also in a fluctuating trend throughout the period 2010-2015 resulting
as 0.85, 2.84, 0.93, 0.64and 1.17. The bank’s present liquidity position is satisfactory.
3. The working capital turnover ratio is increased in the year 2010-11 is at 24.52, and in
the year 2014-15 is at 17.83. But in the years of 2010-11, 2011-12 and 2012-13 it
decreases to 14.74, 7.31 and 6.60. But it is quite normal and it is negligible. This ratio
indicates that working capital has been effectively utilized.
4. The fixed asset turnover is too high i.e., 7.45, when compared to remaining years. So,
its shows that firm is likely operating over capacity and needs to either increase its
asset base (plant, property, equipment) to support its sales or reduce its capacity.
5. The net profit ratio is in fluctuation manner. It increased in the current year compared
with the previous year from 0.68 to 6.79.
6. The total asset turnover ratio is increased i.e. 2.85 (in the year of 2010-11), when
compared with remaining years. In the beginning the bank was good in using asset
efficiency, later it was quite normal and negligible.
7. The return on capital employed is greater or higher in the year of 2014-15 compared
to previous years. Hence ROCE can indicate that a bank can reinvest a greater portion
of its profits back into its operations, to the benefit of shareholders.
8. In the years of 2010-011,2012-13,2014-15 the interest expenses has incurred by bank
is greater or higher the earnings that bank have had to pay, but compare to remaining
years. However the bank is easily able to meet the interest obligation from profits.
9. The debt service coverage of the bank is in negative cash flow except in the year 2007-
08, when compared to remaining years because it is less than 1.
10. The creditor’s turnover ratio is likely down in 2013-14 to 2014-15.It shows the
payment of creditor’s is slow compare with other years. A high ratio implies velocity
of payment to creditors and low the other side.
12.2 Suggestions:
1. From the study it is found that there is lack of periodic review & analysis which is leading
to inefficient utilization of resources &its leads to loss when its compare to previous years
apart from current year. So the firm should conduct quarterly analysis. Hence the
problems can be amended in time.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
2. Liquidity refers to the ability of the concern to meet its current obligation as and when
these become due. The bank should improve its liquidity position.
3. After the analysis of Financial Statements, the bank status is better, because the Net
working capital of the bank is doubled from the last year’s position.
4.The bank profits are huge in the current year; it is better to declare the dividend to
shareholders.
5.The bank is utilizing the fixed assets, which majorly help to the growth of the
organization. The bank should maintain that perfectly
6. The bank fixed deposits are raised from the inception, it gives the other income i.e.,
Interest on fixed deposits.
7.Bank needs to have stringent credit policy, to reduce the funds required for working
capital.
8. The bank must do efficient utilization of shareholders fund to improve its ROI and ROE
to maintain its goodwill in investors mind. The bank can go for some debt borrowing to
increase E.P.S for shareholders.
12.3 CONCLUSION :
Finance is the life blood of every business. Without effective financial management a bank
cannot survive in this competitive world. A Prudent financial Manager has to measure the
working capital policy followed by the bank
The bank’s overall position is at a good position. Particularly the current year’s position is
well due to raise in the profit level from the last year position. It is better for the
organization to diversify the funds to different sectors in the present market scenario.
Higher demand for seating system can be expected in the next decade, once investments
in ports and port development have started to reach fruition. As India is hopeful of
competing with other established shipbuilding nations, the multinationals are likely to find
plentiful opportunity in India, given the compliance requirements imposed by effects of
international legislation on seating systems.
Also other segments are showing promising opportunities to grow. With these many
opportunities at hand along with the potential player who would be able to make use of
the situation well, researcher would rather start looking at a career in Axis. So from this
researcher can conclude that there is a better opportunities for investors to invest in this
bank.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
CAPSTONE PROJECT REPORT-2023
Ratio analysis of financial statement shows that bank’s current ratio is better than the
quick ratio and fixed/worth ratio. It means bank has invested more in current assets than
the fixed assets and liquid assets. The cash flow statement shows that net increase
in cash generated from operating and financing activities is much more than the
previous year but cash generated from investing activities is negative in both years.
Therefore analysis of cash flow statement shows that cash inflow is more than the cash
outflow in AXIS Bank.
Thus, the ratio analysis and trend analysis and analysis of cash flow statement show that
AXIS Bank’s financial position is good. Bank’s profitability is increasing but not at high rate.
Bank’s liquidity position is fair but not good because bank invests more in current assets
than the liquid assets. As we all know that AXIS Bank is on the first position among the
entire private sector bank of India in all areas but it should pay attention on its profitability
and liquidity. Bank’s position is stable.
SRI KRISHNA ARTSS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
You might also like
- Financial Ratio Analysis and Interpretation (Final)Document15 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis and Interpretation (Final)Vignesh Muthu kannanNo ratings yet
- Analyze liquidity ratios with the current, quick, and working capital ratiosDocument3 pagesAnalyze liquidity ratios with the current, quick, and working capital ratiosNational ProjectCentreNo ratings yet
- 712-Ratio AnalysisDocument13 pages712-Ratio AnalysisAnarNo ratings yet
- Solvency Position: 1. Debt-Equity RatioDocument5 pagesSolvency Position: 1. Debt-Equity RatioShilpiNo ratings yet
- 712 Financial Reporting and Controls: Submitted By: Akash Narvaria 687082453Document13 pages712 Financial Reporting and Controls: Submitted By: Akash Narvaria 687082453AnarNo ratings yet
- 3 CompaniesreportfinanceDocument45 pages3 CompaniesreportfinanceMarisha RizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document73 pagesChapter 421ACO56 RAM PRANAV T PNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of Microsoft: Rania Elhossary Abu Dhabi University, EmailDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Microsoft: Rania Elhossary Abu Dhabi University, EmailvaibhavNo ratings yet
- FM Hup Seng (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesFM Hup Seng (AutoRecovered)Otaku Hime96 (neem)No ratings yet
- Finance TermpaperDocument12 pagesFinance Termpaper21.Tamzid TapuNo ratings yet
- Financial performance analysis of Hup Seng IndustriesDocument24 pagesFinancial performance analysis of Hup Seng Industriesotaku hime100% (2)
- Classification, Analysis & Interpretation of RatiosDocument26 pagesClassification, Analysis & Interpretation of RatiosPayal MahajanNo ratings yet
- AccountsDocument24 pagesAccountsrahulNo ratings yet
- ACI Limited's Financial PerformanceDocument13 pagesACI Limited's Financial PerformanceTariqul Islam TanimNo ratings yet
- DBBL FinalDocument8 pagesDBBL Finalnaziba aliNo ratings yet
- Fsa Final InterpretationDocument42 pagesFsa Final InterpretationTakibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fin424 - Final Report - 19104153 - Maliha Tahsin Shafa - Sec-3Document8 pagesFin424 - Final Report - 19104153 - Maliha Tahsin Shafa - Sec-3maliha tahsinNo ratings yet
- Fama Project FinalDocument7 pagesFama Project FinalPrachi MishraNo ratings yet
- BBF201 041220233 Ca1Document9 pagesBBF201 041220233 Ca1SO CreativeNo ratings yet
- FPM Sa - Var22556240Document27 pagesFPM Sa - Var22556240soniyavarghese0107No ratings yet
- Accounts Specific Project 1Document28 pagesAccounts Specific Project 1sakshi pandey100% (1)
- Sesssion 5 17-Oct-2020Document44 pagesSesssion 5 17-Oct-2020Uzma UzmaNo ratings yet
- SailashreeChakraborty 13600921093 FM401Document12 pagesSailashreeChakraborty 13600921093 FM401Sailashree ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- City Union ResearchDocument38 pagesCity Union ResearchamitNo ratings yet
- Acid Test ROA InterpretationsDocument2 pagesAcid Test ROA InterpretationsMary Mia CenizaNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument56 pagesRatio Analysisvishi takhar80% (10)
- Comparing financial analysis of Vietnam Airlines and VinaGamesDocument16 pagesComparing financial analysis of Vietnam Airlines and VinaGamesLam TuyenNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors AnalysisDocument9 pagesTata Motors AnalysisrastehertaNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesFinancial ManagementNida YounusNo ratings yet
- Liquidity RatiosDocument5 pagesLiquidity RatiosPastel Rose CloudNo ratings yet
- Name: Hira Saqib Rehman Submitted To: Sir Nasir Rasool Section:03 Date: 11 December 2023 Subject: Financial Statement AnalysisDocument18 pagesName: Hira Saqib Rehman Submitted To: Sir Nasir Rasool Section:03 Date: 11 December 2023 Subject: Financial Statement Analysishira saqibNo ratings yet
- ACI Limited FMDocument13 pagesACI Limited FMTariqul Islam TanimNo ratings yet
- A Study On Credit Appraisal and Npa in Kancheepuramcooperative Urban BankDocument4 pagesA Study On Credit Appraisal and Npa in Kancheepuramcooperative Urban BankG SUNIL MBANo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Npa of Public and Private Sector BanksDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of Npa of Public and Private Sector Banksiaset123No ratings yet
- Fca B SiddharthDocument12 pagesFca B SiddharthSiddharth SangtaniNo ratings yet
- The Influence of CSR & Corporate Governance OnDocument16 pagesThe Influence of CSR & Corporate Governance OnTRIPPY入KR1No ratings yet
- Finance ProjectDocument36 pagesFinance ProjectLokesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Marico Ltd financial management assignmentDocument14 pagesMarico Ltd financial management assignmentAvijit DindaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Tata Motors: Submitted by Binni.M Semester-2 Mba-Ib ROLL - No-6Document19 pagesFinancial Analysis of Tata Motors: Submitted by Binni.M Semester-2 Mba-Ib ROLL - No-6binnivenus100% (1)
- Audited Financial Statements AnalysisDocument15 pagesAudited Financial Statements AnalysisAllyson Charissa AnsayNo ratings yet
- Group Financial Analysis of Dien Quang Lamp Joint Stock CompanyDocument8 pagesGroup Financial Analysis of Dien Quang Lamp Joint Stock CompanyBonBonNo ratings yet
- Zaini Zain (BAF2009012) Adv. Fin. Acc Group Assignment (UPDATED)Document23 pagesZaini Zain (BAF2009012) Adv. Fin. Acc Group Assignment (UPDATED)Zaini ZainNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of KFCDocument15 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of KFCPrasiddha PradhanNo ratings yet
- Square Pharmaceuticals-Financial AnalysisDocument17 pagesSquare Pharmaceuticals-Financial AnalysisShahid MahmudNo ratings yet
- Source of Fund StructureDocument6 pagesSource of Fund StructureNgọc LanNo ratings yet
- ITCDocument10 pagesITCAnugya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fin358 Group Assignment - Pantech Group Holdings Berhad (D1ba1195d) FinalizedDocument26 pagesFin358 Group Assignment - Pantech Group Holdings Berhad (D1ba1195d) FinalizedFatin SafwanaNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis and Interpretation Ratio AnalysisDocument9 pagesData Analysis and Interpretation Ratio AnalysisRythum GoyalNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 2023Document16 pagesPaper 1 2023Salman ArshadNo ratings yet
- The Financial Statement AnalysisDocument25 pagesThe Financial Statement Analysisgk37765No ratings yet
- A Study on Cash Management at Salzer Electronics LimitedDocument14 pagesA Study on Cash Management at Salzer Electronics Limitedgarvmehra40No ratings yet
- Thal LTDDocument8 pagesThal LTDZameer AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Gas PetronasDocument33 pagesGas PetronasNour FaizahNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Indian Oil CorporationDocument29 pagesFinancial Analysis of Indian Oil CorporationNikshith HegdeNo ratings yet
- Nufus Et Al., 2020) Grewatsch and Kleindienst, 2017) Musciotto Et Al., 2018)Document8 pagesNufus Et Al., 2020) Grewatsch and Kleindienst, 2017) Musciotto Et Al., 2018)Sheraz KhanNo ratings yet
- KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENTDocument32 pagesKATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENTShuvam DotelNo ratings yet
- Acc7Document5 pagesAcc7Mai AnhNo ratings yet
- PCTE Group of Institutes, Ludhiana: Presentation Synopsis TopicDocument8 pagesPCTE Group of Institutes, Ludhiana: Presentation Synopsis TopicManmeetNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Public Budgeting and Financial Management: A Handbook for Academics and PractitionersFrom EverandThe Basics of Public Budgeting and Financial Management: A Handbook for Academics and PractitionersNo ratings yet
- KPMG Cartaeconomicjuly09Document23 pagesKPMG Cartaeconomicjuly09BevStar Cover UpNo ratings yet
- DebtFreeSecrets+V1 1Document45 pagesDebtFreeSecrets+V1 1Raul Fraul100% (1)
- Consumer Protection ACT, 1986: Aanchal Dhingra Shaleen Porwal Mahima Arya Shobhit Garg Kiran KumarDocument42 pagesConsumer Protection ACT, 1986: Aanchal Dhingra Shaleen Porwal Mahima Arya Shobhit Garg Kiran KumarAanchal DhingraNo ratings yet
- Shield Funding Application2Document1 pageShield Funding Application2Operator RakyatNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Mortgagee Bank PDFDocument1 pageAffidavit Mortgagee Bank PDFRanie DelaventeNo ratings yet
- Metropolitan Fabrics Inc. and Enrique Ang vs. Prosperity Credit Resources Inc., Domingo Ang and Caleb AngDocument3 pagesMetropolitan Fabrics Inc. and Enrique Ang vs. Prosperity Credit Resources Inc., Domingo Ang and Caleb AngMacky CaballesNo ratings yet
- Bank GuaranteeDocument30 pagesBank GuaranteeKaruna ThatsitNo ratings yet
- 2022 Personal Finance Statistics: 34% Feel Financially Healthy as Costs RiseDocument15 pages2022 Personal Finance Statistics: 34% Feel Financially Healthy as Costs RiseMasab AsifNo ratings yet
- 9 +Artikel+9+Vol+1+No+3+2022+Document14 pages9 +Artikel+9+Vol+1+No+3+2022+ebensalim15No ratings yet
- Tizita ProposalDocument21 pagesTizita Proposalanwar jemalNo ratings yet
- Questions in Credit TransactionsDocument9 pagesQuestions in Credit TransactionsKaren Sheila B. Mangusan - DegayNo ratings yet
- Mortgage LawDocument9 pagesMortgage LawmirmoinulNo ratings yet
- Dmgt512 Financial Institutions and ServicesDocument265 pagesDmgt512 Financial Institutions and ServicesASIF100% (1)
- Credit Risk Management On Ethiopian Commercial Banks": Case of Selected Commercial Banks in Adama TownDocument36 pagesCredit Risk Management On Ethiopian Commercial Banks": Case of Selected Commercial Banks in Adama TownAbdii Dhufeera100% (2)
- Chapter 13Document17 pagesChapter 13runawayyyNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Business FinancingDocument27 pagesCH-6 Business FinancingNatiphotography01No ratings yet
- Unit - Vii: Money and Banking: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOP 1/6Document6 pagesUnit - Vii: Money and Banking: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOP 1/6Aasif NengrooNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Fundamentals and The Statement of Financial Position - The Balance SheetDocument43 pagesWeek 1 Fundamentals and The Statement of Financial Position - The Balance SheetJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Comparing Car Loan Options at Mumbai UniversityDocument83 pagesComparing Car Loan Options at Mumbai UniversityTanvi Devale100% (1)
- Chen, Y.-K., Shen, C.-H., Kao, L., & Yeh, C. Y. (2018) .Document40 pagesChen, Y.-K., Shen, C.-H., Kao, L., & Yeh, C. Y. (2018) .Vita NataliaNo ratings yet
- Interest Change Prepayment Repayment Schedule: Input Details Details 14396Document22 pagesInterest Change Prepayment Repayment Schedule: Input Details Details 14396bidyut_roy_1No ratings yet
- How To Get An Instant Loan From Quick Credit AppDocument2 pagesHow To Get An Instant Loan From Quick Credit AppQuickCredit100% (2)
- Partnership AccountsDocument15 pagesPartnership AccountsAbdul Sameeu MohamedNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control Lesson GuideDocument11 pagesBudgetary Control Lesson GuiderscjatNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 1 Unitary Sec. Cert. - Domestic CorporationDocument3 pagesExhibit 1 Unitary Sec. Cert. - Domestic CorporationJoseph Reuben Balamiento0% (1)
- BTLPDocument282 pagesBTLPSanjeev Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- CMA Joshi Marketing-1Document53 pagesCMA Joshi Marketing-1Satish TomerNo ratings yet
- Credit Score in VietnamDocument10 pagesCredit Score in VietnamNguyen Ha QuanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship CH 6Document27 pagesEntrepreneurship CH 6AYELENo ratings yet
- ICAI MaterialDocument15 pagesICAI MaterialJignaNo ratings yet