0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesMath Final Exam
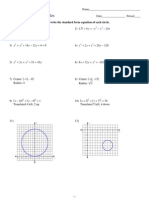
This document contains a 20 question multiple choice math test on solving quadratic equations. It covers determining the nature of roots based on the discriminant, finding the sum and product of roots, and solving quadratic equations through factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. It also contains true/false questions and inequality problems related to quadratic equations.
Uploaded by
Lean LeanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesMath Final Exam
This document contains a 20 question multiple choice math test on solving quadratic equations. It covers determining the nature of roots based on the discriminant, finding the sum and product of roots, and solving quadratic equations through factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. It also contains true/false questions and inequality problems related to quadratic equations.
Uploaded by
Lean LeanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd