Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09 Co-Ordination Compound Final
Uploaded by
letscrackit676Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
09 Co-Ordination Compound Final
Uploaded by
letscrackit676Copyright:
Available Formats
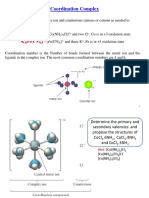
Co-ordination Compounds
Double Salt : Those compound which are stable in solid form but loose their identity in aqueous
solution are called double salt.
Eg.: FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O (Mohr’s salt) , KCl. MgCl2 6H2O (Carnalite) ,
K2SO4 .Al2 (SO4 )3 24H2O (Potash alum) etc.
Co-ordination Compound : Those compound which are stable in solid form also retain their
identity in aqueous solution are called co-ordination compound.
Eg.: K4[Fe(CN)6]
Werner’s Co-ordination theory :
i. In co-ordination compound, metal atom exhibit two types of valency, primary & secondary
valency.
ii. Primary valency is satisfied by anian by the formation of ionic bond whereas secondary valency
is satisfied by ligand by the formation of co-ordinate bond.
iii. Secondary valency is directional whereas primary valency is non-directonal.
iv. Primary valency is ionizable where as secondary valency is non ionizable.
v. Every metal atom has a fixed number of secondary valencies i.e., fixed co-ordination number.
vi. The metal atom tends to satisfy both its primary as well as secondary valencies.
Werner’s experiment :-
Compound Colour Moles of AgCl Formula
CoCl3.6NH3 Yellow 3 [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
CoCl3.5NH3 Purple 2 [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
CoCl3.4NH3 Green 1 [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl
CoCl3.3NH3 Red 0 [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
Q.1 How many moles of ion are present in the following complex.
i. [CoCl(NH3)5]Cl2 ii. [Ag(NH3)2]Cl iii. [PtCl3(NH3)3]Cl
Sol. i) [CoCl(NH3)5]Cl2 [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ + 2Cl–
3 ions
ii. [Ag(NH3)2]Cl [Ag(NH3)2]+ + Cl–
2 ions
iii. [PtCl3(NH3)3]Cl [PtCl3(NH3)3]+ + Cl–
2 ions
Q.2 On the basis of the following observation write the formula & calculate secondary valency of the
following.
Compound Moles of AgCl
CoCl3.4NH3 1
PdCl2. 4NH3 2
NiCl2.6H2O 2
PtCl4.2HCl 0
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 2
PtCl2.2NH3 0
Sol. i. [CoCl2.(NH3)4]cl Secondary valency = 6
ii. [Pd(NH3)4]Cl2 Secondary valency = 4
iii. [Ni(H2O)6]Cl2 Secondary valency = 6
iv. H2[PtCl6] Secondary valency = 6
v. [PtCl2(NH3)2] Secondary valency = 4
Some Important term :
Co-ordination Sphere
K4[Fe(CN)6]Cl2 Anian
Cation
Central Legand
Metal Co-ordination
number
i. Co-ordination sphere : The square bracket is called co-ordination sphere.
ii. Cation : The positive ion present outside of co-ordination sphere is called cation.
iii. Anian : The negative ion present outside of co-ordination sphere is called anian.
iv. Co-ordination number : The number of lone pair donated by ligand to central atom is called co-
ordination number.
v. Central atom : Atom which form co-ordinate bond with ligand.
vi. Ligand : Those species which can donate lone pair to the central metal is called ligand.
Classification of ligand on the basis of denticity :
Denticity : The ability of ligand to donate lone pair to central atom is called denticity.
i. Unidentate or monodentate ligands : Ligands which can coordinate to central metal through
only one donor atom is called unidentate or monodentate ligand.
Eg.: NH3, H2O, Cl– etc.
ii. Didentate or bidentate ligands : Ligands which have two donor atoms and therefore can co-
ordinate to the central atom from two donor atom is called Didentate or bidentate ligand.
Eg.: NH2 – CH2 – CH2 – NH2 (en)
Ethane – 1, 2- diamine
COO (OX )
|
COO
Oxalate ion
NH2 – CH2 – COO– (gly)
Glycinate ion
iii. Polydentate ligand : Ligand having move than two donor atoms present in the molecule are
called polydentate ligand.
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 3
–
OOCCH2 CH2COO–
N – CH2 – CH 2 – N
–
OOCCH2 CH2COO
–
EDTA denticity = 6
iv. Chelating ligand : When bidentate or polydentate ligand use it two or more donor atom to bind
with central metal and form a ring structure is called chelation and ligand is called chelating
ligand.
Eg.: NH2 CH2 CH2 NH2
v. Ambident ligand : The monondentate ligands which contain more than one lone pair donor
atom is called ambident ligand.
Eg.: NO2 , CN , SCN
vi. Homoleptic complex : Those complex in which metal is bonded with one type of ligand are
called homoleptic complex. Ex. K2[HgCl4]
vii. Heteroleptic complex : Those complex in which metal is bonded with more than one type of
ligand are called homoleptic complex. Ex. K[PtCl3(NH3)]
viii. Co-ordination polyhedron : Those structure which represent proper arrangement of ligand
which are attached to central metal is called co-ordination polyhedron.
IUPAC Naming of Co-ordinate compound :
Order of Naming :
6
K4[Fe(CN)6] Cl
Cl
1 5
4 3 2
1. Naming of cation : Write the name of cation without indicating its number.
2. Naming of co-ordination number :
For simple ligand For complex ligand
2 di 2 bis
3 tri 3 tris
4 tetra 4 tetrakis
5 penta
6 hexa
3. Naming of ligand :
i. Negative ligands : for negative ligand replace ‘e’ by ‘o’.
1. F– fluorido 9. NH 2 amido
2. Cl– chlorido 10. NH2– imido
3 NO 2 Nitrito-N 11. CNS thiocyanato
4. ONO– Nitrito-O 12. NCS isothiocyanato
5. SO 2
4
Sulphato 13. O 2 oxo
6. OH hydroxido 14. O 22 Peroxo
7. C2O42 (ox) oxalato 15. H– Hydrido
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 4
8. CN– Cyanido 16. CO32 Carbonato
ii. Neutral ligand :
1. H 2O aqua 5. NO nitrosyl
2. NH3 ammine 6. C6H5N Pyridine (Py)
3. CO Carbonyl 7. (C6H5)3P triphenylphosphine
(PPh3)
4. NH2CH2CH2NH2 ethane-1, 2- 8. CH3NH2 methylamine
diamine (en)
- If more than one different ligand are present then naming will be done in alphabetical order.
4. Naming of central metal :
Central metal naming is done on the basis of cation.
- If cation are present then a suffix ‘ate’ is added to central metal naming.
- If metal have latine name then suffix ‘ate’ is added to latine name.
Ex.:
Fe = Ferrate
Cu = Cuprate
Ag = Argentate
Au = Aurate
Sn = Stannate
Pb = Plumbate
- If cation is absent then suffix will not come & modern name of central metal will be used.
Note : After central metal name oxidation number will be added in roman number inside small
bracket.
5. Naming of anian : Simply write the name of anian without indicating its number.
6. Naming of charge : If compound have any charge then only write ion for it.
Naming of some co-ordination compound
1. K[Ag(CN)2] - potassium dicyanidoarygentate (I)
2. [PtCl(NO2)(NH3)4]SO4 - tetraammine chloridonitrito-N- platinum (IV) sulphate
3. K2[HgCl4] - potassium tetrachlorido mercurate (II)
4. [CoCl2(NO2)(NH3)3] - triammine dichloridonitrito-N-cobalt (III)
5. [CrCl2(H2O)4]NO3 - tetraaquadichloridochromium (III) nitrate
6. K[PtCl3(NH3)] - potassium amminetrichlorido platinate (II)
7. [Ni(H2O)2(NH3)4]SO4 - tetraammine diaquanickel (II) Sulphate
8. Na3[Co(NO2)6] - Sodium hexanitrito-N-cobaltate (III)
9. Na[Au(CN)2 - Sodium dicyanidoaurate (I)
10. K 3 [Fe(C2O4 )3 ] - Potassium trioxalato ferrate (III)
11. K 4 [Ni (CN )4 ] - Polassium tetracyanido nickelate (o)
12. [Cr (PPh3 )(CO )5 ] - pentacarbonyl triphenyl phosphine chromium (o)
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 5
13. [{(C6H5)3P}3 Rh]Cl - tris (triphenyl phosphine rhodium (1) chloride
14. [CoBr2(en)2]Cl - dibromidobis(ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt (III) chloride
15. K3[Cr(C2O4)3] - potassium trioxalato chromate (III)
16. [Ni(CO)4] - tetracarbonylnickel (o)
NH
17. [(en)2Co Co(en)2]3+- bis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)–µ-imido-µ-hydroxido
OH bis(ethane –1, 2-diamine)cobalt (III) ion
18. [Pt(NH3)4[PtCl4] - tetraammineplatinum (II), tetrachloridoplatinate (II)
19. [Co(CO)4] - Sodium tetracarbonylcobalt (0)
20. Li[AlH4] - lithium tetrahydridoaluminate (III)
NH2
21. (NH3) 4Co Co(NH 3)4 (NO3 )4 - Tetraamminecobalt(III)- -amido- -nitrito-N-
NO2
tetraamminecobalt(III)nitrate
OH
22. (H2O)4 Fe Fe(H2 O)4 (SO4 )2 - Tetraaquarion(III)- -dihydroxidotetraaquarion(III) sulphate.
OH
23. [(NH3)5 Cr–OH–Cr(NH3)5]Cl5 - pentaamminechromium(III)- -hydroxidopentaammine
chromium(III) chloride
24. [Cr(NCS)(NH3)5][ZnCl4] - pentaamminethiocyanato-N-chromium(III) tetrachloridozincate(II)
25. [Ag(NH3)2][Ag(CN)2] - diamminesilver(I) dicyanidoargentate(I)
26. [PtCl2(NH3)4][PtCl4] - tetraamminedichloridoplatinum(IV)tetrachloridoplatinate(II)
27. [CoCl2(NH3)4]3[Cr(CN)6] - tetraamminedichloridocobalt(III)hexacyanidochromate(III)
28. [Pt(py)4][PtCl4] - tetrapyridineplatinum(II) tetrachloridoplatinate(II)
ISOMERISM
Structural Isomerism Stereo isomerism
1. Ionisation isomerism 1. Geometrical isomerism
2. Hydrate isomerism 2. Optical isomerism
3. Linkage isomerism
4. Co-ordinate isomerism
1. Ionisation isomerism : Those compounds which are having some molecular formula but give
different ions in solution are called ionisation isomerism.
Ex.: i) [CoBr(NH3)5]SO4 & [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br
ii) [CoCl2(NH3)4]NO2 & [CoCl(NO2)(NH3)4]Cl
2. Hydrate or solvate isomerism : Those compounds which are having same molecular formula
but different number of solvent molecules present as ligands are called Hydrate or solvate
isomerism.
Ex.: i) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 & [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2.H2O
ii) [CoCl(en)2(H2O)]Cl2 & [CoCl2(en)2]Cl.H2O
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 6
3. Linkage isomerism : Those compounds which are having same molecular formula but different
linkage of ligand with central atom are called linkage isomerism.
Ex.: Ambident ligand cause linkage isomerism.
i) NO2 ONO ii) CN NC iii. SCN NCS
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 & [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2
4. Co-ordination isomerism : Those compounds which are having same molecular formula but
different ligand in cationic & anionic parts are called co-ordination isomerism.
Ex.: i) [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] & [Co(CN)6][Cr(NH3)6]
ii) [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4] & [PtCl(NH3)3][PtCl3(NH3)]
Geometrical isomerism :
For co-ordination number = 4
i. [MA2X2] or [MA2XY] type :-
A A A B
M M
B B B A
cis trans
Ex.:- [PtCl2(NH3)2]
Cl Cl NH 3 Cl
pt pt
NH 3 NH 3 Cl NH 3
cis trans
ii. [MABCD] type :
A D A B A B
M M M
C B D C C D
Ex.: [Pt(NO2)(Py) (NH2OH)(NH3)]+
NH2OH Py NH2OH NO2 NH2OH NO2
Pt Pt Pt
NH3 NO2 NH3 Py Py NH3
iii. [M(AB)2] type :
Ex.: [Pt(gly)2] where gly = NH2CH2COO–
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 7
NH2 NH2 NH2 O O
C
CH2 Pt CH2 CH2 Pt
CH2
C O O C C O NH2
O O O
cis trans
For co-ordination number = 6
i. [MA4X2] or [MA4XY] type :
x A
A A A x
M M
A A A x
x A
trans cis
Ex.: [CoCl2(NH3)4]+
ii. [MA3B3] type
B B
A A A B
M M
B A A B
B A
(meridinal (facial
isomer) isomer)
Ex.: [RhCl3(Py)3]
Cl Py
Py Py Cl Py
Rh Rh
Cl Py Cl Py
Cl Cl
(mer) (fac)
iii. [M(AA)2XY] type
X X
Y
AA M AA AA M
Y AA
(trans) (cis)
+
Ex.: [Co(en)2Cl2]
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 8
Optical Isomerism :
i. [M(AA)3] type :
AA AA
AA M M AA
AA AA
Ex.: [Co(en)3]3+
en 3+ en 3+
en Co Co en
en en
[Cr(ox)3]3–
ox 3– ox 3–
en Cr Co ox
ox ox
ii. [M(AA)2X2] or [M(AA)2XY] type
X 3– X
X X
AA M Co AA
AA AA
Ex.: [Co(en)2Cl2]+
Cl + Cl +
Cl Cl
en Co Co en
en en
Note : [M(AA)2X2] type is form is optically active but trans form is optically inactive.
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 9
Number of Possible Isomers for Specific Complexes
Formula Number of stereoisomers Pairs of Enantiomers
Ma4b2 2 0
Ma3b3 2 0
Ma4bc 2 0
Ma3bcd 5 1
Ma2bcde 15 6
Mabcdef 30 15
Ma2b2c2 6 1
Ma2b2cd 8 2
Ma3b2c 3 0
M(AA)(BC)de 10 5
M(AB)(AB)cd 11 5
M(AB)(CD)ef 20 10
M(AB)3 4 2
M is the metal ion and a, b, c, d, e and f represent monodentate ligands. AA is a bidentate
symmetrical ligand. AB is a bidentate unsymmetrical ligand.
Q.1 Draw the geometrical isomers of the following complex.
i. [CoCl2(NH3)4]+ ii. [Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]–
Sol.
Cl + Cl +
NH3 Cl NH3 NH3
Co Co
NH3 NH3 NH3 NH3
NH3 Cl
Cis trans
NH3 – NH3 –
CN NH3 CN NH3
Fe Fe
CN CN CN CN
CN NH3
Cis trans
Q.2 Write the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes :
i. [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 ii. [Co(en)3]3+ iii. [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6]
Sol. i. Ionisation isomerism
ii. Optical isomerism
iii. Co-ordination isomerism
Q.3 Write the following :
i. Ionisation isomer of [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4
ii. Linkage isomer of [Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2
iii. Co-ordination isomer of [Cu(NH3)4][PtCl4]
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 10
Sol.: (i) [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br
(ii) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2
(iii) [CuCl4][Pt(NH3)4]
Q.4 Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following :
i. [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] – [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6]
ii. [Co(ONO) (NH3)5]Cl2 – [Co(NO2)(NH3)5]Cl2
iii. [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br – [CoBr(NH3)5]SO4
iv. [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4] – [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4]
Sol. i) Co-ordination
ii) Linkage
iii) Ionisation
iv) Co-ordination
Q.5 Write the formula of following :
i. Linkage isomer of [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl2
ii. Co-ordination isomer of [Co(NH3)6][Cr(NO2)6]
iii. Ionization isomer of [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl
Sol. i) [CoCl(ONO)(en)2]Cl2
ii) [Cr(NH3)6].[Co(NO2)6]
iii) [CoCl2(en)2]NO2
:: Objective Questions ::
Q.1 The correct order of the stoichiometrices of AgCl formed when AgNO 3 in excess is treated with
the complexes : CoCl3.6NH3, CoCl3.5NH3, CoCl3.4NH3 respectively is [NEET-2017]
(a) 3AgCl, 1AgCl, 2AgCl (b) 3AgCl, 2AgCl, 1AgCl
(c) 2AgCl, 3AgCl, 2AgCl (d) 1AgCl, 3AgCl, 2AgCl
Q.2 Number of possible isomers for the complex [Co(en)2Cl2]Cl will be : (en = ethylenediamine)
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 2 (d) 1 [NEET-2015]
Q.3 The name of complex ion, [Fe(CN)6]3– is : [NEET-2015]
(a) Tricyanidoferrate (III) ion (b) Hexacyanidoferrate (III) ion
(c) Hexacyanidoiron (III) ion (d) Hexacyanidoferrate (II) ion
Q.4 Which of the following complexes is used to be as an anticancer agent ? [NEET-2014]
(a) mer-[Co(NH3)3Cl3] (b) cis-[PtCl2(NH3)2
(c) cis-K2[PtCl2Br2] (d) NaCoCl4
Q.5 The sum of coordination number and oxidation number of the metal M in the complex
[M(en)2 (C2O4)]Cl (where en is ethylenediamine) is : [NEET-2015]
(a) 7 (b) 8 (c) 9 (d) 6
Q.6 The complex that can show fac-and mer-isomers is : [JEE-2020]
(a) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (b) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ (c) [Co(NH3)3(NO2)3 (d) [CoCl2(en)2]
Q.7 The IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl is : [JEE-2020]
(a) Diammine (methanamine) chloride platinum (II) chloride
(b) Bisammine (methanamine) chloridoplatinum (II) chloride
(c) Diamminechlorido (aminomethane) platinum (II) chloride
(d) Diamminechlorido (methanamine) platinum (II) chloride
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 11
Q.8 The species that can have a trans-isomer is : (en = ethane-1, 2-diamine, ox – oxalate)
[JEE-2019]
(a) [Pt(en)Cl2] (b) [Cr(en)2(ox)]+ (c) [Zn(en)Cl2] (d) [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+
Q.9 The number of isomers possible for [Pt(en)(NO2)2] is : [JEE-2020]
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Q.10 Among (A) – (D), the complexes that can display geometrical isomerism are : [JEE-2020]
(a) Pt(NH3)3 Cl]+ (b) [Pt(NH3)Cl5]– (c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] (d) [Pt(NH3)4ClBr)]2+
ANSWER KEY
1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (c)
6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (d) 9. (c) 10.(d)
Valence Bond Theory :
The main assumption of this theory are :
i) The central metal ion makes available a number of empty orbitals for the formation of co-
ordination bonds with suitable ligands.
ii) The atomic orbital of the central metal hybridize to give orbitals of definite geometry.
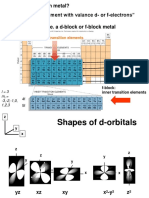
Co-ordination no. Hybridisation Geometry Type of d-orbitals
2 sp Linear
4 sp3 Tetrahedral
4 dsp2 Square planar dx 2 y2
4 d3s Tetrahedral dxy , dyz , dxz
5 sp3d Trigonal bipyramidal dz 2
5 dsp3 Square pyramidal dx 2 y2
6 sp3d2 Octahedral dx 2 y2
, dz 2
6 d2sp3 Octahedral dx 2 y2
, dz 2
iii) The d-orbital involved in hybridization may be either inner d-orbital i.e., (n – 1)d or outer d-
orbital i.e. nd.
iv) Each ligand has at least one orbital containing a lone pair of electron.
v) The empty hybrid orbitals of metal overlap with the filled orbitals of the ligands to form
coordinate bond.
Limitation of valence bond theory (VBT) :
i. It involves a number of assumption.
ii. It gives only the qualitative explanation for complex.
iii. It does not explain magnetic properties.
iv. It does not explain spectral properties.
v. It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands.
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) : It was given by H.Bethe & V.Bleck.
According to this theory the intraction between central metal ion & ligand is electrostatic. When
ligand approach to central metal ion it repel the electron of d-orbital of metal.
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 12
Due to repulsion degenerated d-orbital of central metal ion split into two sets of orbitals i.e., t2g
& eg this is called crystal field splitting.
The energy difference between t2g & eg orbitals are called crystal field splitting energy.
i) For octahedral geometry : For octahedral geometry ligand approach along the axis towards
central metal due to which degenerated d-orbital split into two sets of orbitals t2g & eg in which
eg having more energy & t2g having less energy.
+3
eg
5
d-orbital in –2
5
presence of ligand
t2g
d-orbital in
absence of ligand
Crystal field stabilizing energy in octahedral field (CFSE) :
CFSE = [–0.4 nt2g + 0.6 n e g ] o xP
nt2g = no. of e– in t2g
n e g = no. of e– in eg
o = Crystal field splitting energy of octahedral
x = no. of e– pair
p = pairing energy
ii) For tetrahedral geometry : For tetrahedral geometry ligand approach in between the axis toward
central metal due to which de-generated d-orbital split into two sets.
+2 t2g
5
t
d-orbital in –3
5
presence of ligand
eg
d-orbital in
absence of ligand
Crystal Field stabilizing energy in tetrahedral field (CFSE) :
CFSE = 0.6neg 0.4nt2 g t xP
4
Note t = o
9
Q.1 Among the following complexes the one which show zero crystal field stabilizing energy (CFSE)
is :
(a) [Mn(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ (c) [Co(H2O)6]2+ (d) [Co(H2O)6]3+
Sol. (b) Fe3+ = 3d5, 4So = t2g3, eg2
CFSE = (–0.4 nt2g + 0.6 n eg ) o xP
= (–0.4 × 3 + 0.6 × 2) o 0.P
= 0
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 13
Ligand Field Theory (LFT) :
According to LFT when a strong ligand approach to central metal it cause pairing of electron.
Ligand which can cause pairing of electron :
CO CN NO2 en NH 3
Condition of pairing of electron :
i) Ligand should be strong ligand i.e, CO CN NO2 en NH 3
ii) For octahedral geometry central metal should contain more than 3 electron in d-orbital and
for tetrahedral geometry central metal should contain more than 2 electron in d-orbital .
Note : i) Strong field ligand cause pairing of electron according to requirement not unnecessarily.
Exception :
i. In case of Co3+ even weak field ligand behave as a strong field ligand except F .
ii. NH3 act as a weak field ligand for Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ & Co2+ due to bad effective nuclear charge.
iii. O donor molecule act as a strong filed ligand for Co3+ & Cu2+.
iv. All ligand act as a strong field ligand for 4d, 5d series and +4 cation.
Q.1 Write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in a octahedral field when :
i) o P ii) o P
Sol. i) When, o P then pairing will occurs,
4
t 2g , eg
ii) When o P , then pairing will not occurs,
3 1
t 2g , eg
Q.2 CO is a stronger ligand than NH3 why ?
Sol. CO contain vacant orbital which overlap with central metal to form back bonding therefore
CO form & co-ordinate bond with metal but NH3 only form co-ordinate bond therefore
CO is strong ligand.
Q.3 CN− is a stronger ligand why ?
Sol. CN− contain vacant orbital which overlap with central metal to form back bonding
−
and CN act as psudohalide therefore it is a strong ligand.
Spectro-Chemical Series : The arrangement of ligands in the increasing order of crystal field
splitting is called spectro-chemical series.
I Br SCN Cl F OH OX 2 O2
H 2O NCS PY NH 3 en NO2 CN CO
Q.1 Write the name, stereochemistry and magnetic behaviour of the following :
(Atomic no. Fe = 26, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
i) K2[Ni(CN)4] ii. [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 iii. K3[Fe(H2O)6]6+
Sol. i) Name = Potassium tetracyanidonickelate (II)
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 14
Ni 2 3d 8 ,4S
Ni 2 in ground state,
3d8 4s° 4p°
Ni 2 in excited state,
3d8 4s° 4p°
dsp2
- hybridization = dsp2
- stereochemistry = square plannar
- Magnetic properties = Diamagnetic
- Type of Complex = inner orbital complex
- Spin = Low spin
- Magnetic momentum = n (n 2)
n = no. of unpaired e–
= 0(0 2) = 0 B.M.
ii. Name – Pentaammine chloride cobalt (III) chloride
Co3+ = 3d6, 4S°
Co3+ in ground state
6
3d 4s° 4p°
Co3+ in excited state,
6
3d 4s° 4p°
d2sp3
- Hybridisation = d2sp3
- Stereochemistry = octahedral
- Magnetic behaviour = diamagnetic
- Type of complex = Inner orbital complex
- Spin = low Spin
- Magnetic momentum = 0(0 2) = 0 BM
iii) Name – Potassium hexaaqua iron (III) ion
Fe3+ = 3d5, 4s°
Fe3+ in G.S.
5
3d 4s° 4p°
Fe3+ in E.S.
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 15
5
3d 4s° 4p°
d2sp3
- Hybridisation = sp3d2
- Stereochemistry = octahedral
- Magnetic behaviour = paramagnetic
- Type of complex = Outer orbital complex
- Spin = High spin
- Magnetic momentum = n (n 2)
= 5(5 2)
= 35 B.M.
Q.2 Write the stereochemistry & magnetic behaviour of the following :
i. K4[Mn(CN)6] ii. [Cr(NH3)6]3+ iii. [CoF6]3– iv. [Ni(CN)4]2–
v. [NiCl4]2–
Sol. i. d2sp3, octahedral, paramagnetic
ii. d2sp3, octahedral, paramagnetic
iii. sp3d2, octahedral, paramagnetic
iv. dsp2, square plannar, diamagnetic
v. sp3, tetrahedral, paramagnetic
Q.3 Co2+ is easily oxidized to Co3+ in the presence of a strong ligand why ?
Sol. In presence of strong ligand the configuration of Co 2+ is t2g6, eg1 and Co3+ is t2g6, eg° therefore
Co2+ easily oxidize to Co3.
:: Objective Questions ::
Q.1 Which of the following is the correct order of increasing field strength of ligands to form
coordinations compounds ? [NEET-2020]
(a) F SCN C2O24 CN (b) CN C2O24 SCN F
(c) SCN F C2O24 CN (d) SCN F CN C2O24
Q.2 What is the correct electronic configuration of the central atom in K 4[Fe(CN)6] based on
crystal field theory ? [NEET-2019]
4 2
(a) t2g eg (b) t62g e0g (c) e3 t 32 (d) e 4 t 22
Q.3 Pick out the correct statement with respect to [Mn(CN)6]3– : [NEET-2017]
(a) It is sp3d2 hybridised and tetrahedral
(b) It is d2sp3 hybridised and octahedral
(c) It is dsp2 hybridised and square planar
(d) It is sp3d2 hybridised and octahedral
Q.4 The hybridisation involved in complex [Ni(CN)4]2– is : (At. No. of Ni = 28) [NEET-2015]
(a) d2sp2 (b) d2sp3 (c) dsp2 (d) sp3
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 16
Q.5 Among the following complexes the one which shows zero crystal field stabilization energy
(CFSE) is : [NEET-2014]
(a) [Mn(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ (c) [Co(H2O)6]2+ (d) [Co(H2O)6]3+
Q.6 The Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) of [CoF3(H2O)3]( 0 P ) is : [JEE-2020]
(a) 0.40 (b) 0.80
(c) 0.40 P (d) 0.80 2P
Q.7 The pair in which both the species have the same magnetic moment (spin only) is :
[JEE-2020]
(a) [Cr(H2O)6]2+ and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ (b) [Co(OH)4]2– and [Fe(NH3)6]2+
(c) [Cr(H2O)6]2+ and [CoCl4]2– (d) [Mn(H2O)6]2+ and [Cr(H2O)6]2+
Q.8 For a d4 metal ion in an octahedral field, the correct electronic configuration is :
[JEE-2020]
4 0
(a) t2g eg when 0 P (b) t32g e1g when 0 P
(c) t32g e1g when 0 P (d) e2g t2g
2
when 0 P
Q.9 The calculated spin-only magnetic moments (BM) of the anionic and cationic species of
[Fe(H2O)6]2[Fe(CN)6], respectively, are : [JEE-2019]
(a) 4.9 and 0 (b) 2.84 and 5.92
(c) 0 and 4.9 (d) 0 and 5.92
Q.10 The degenerate orbitals of [Cr(H2O)6]3+ are : [JEE-2019]
(a) d yz and d z2 (b) d z2 and d xz
(c) d xz and d yz (d) d x2 y2
and d xy
ANSWER KEY
1. (c) 2. (b) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (a)
6. (c) 7. (a) 8. (c) 9. (c) 10.(c)
Colour Wheel :
V, B, G, Y, O, R
absorb
red
V
R B
O G
Y appear
green
If a co-ordinate compound absorb Red colour then it will emit green colour and vice-versa.
Generally co-ordination compounds are coloured due to d-d transition.
Stepwise stability of co-ordination compound :
Let us consider a general reaction,
M + 4L ML4
The stability constant for reaction,
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 17
[ML4 ]
K …….(1)
[M ][L ]4
If the reaction would occurs stepwise then,
M+L ML
[ML ]
K1 = ……. (2)
[M ][L ]
ML + L ML2
[ML2 ]
K2 ….. (3)
[ML ][L ]
ML2 + L ML3
[ML3 ]
K3 ….. (4)
[ML2 ][L ]
ML3 + L ML4
[ML4 ]
K4 …… (5)
[ML3 ][L ]
Eq. (2) × Eq. (3) × Eq. (4) × Eq. (5)
[ML ] [ML2 ] [ML3 ] [ML4 ]
K1 K 2 K3 K4
[M ][L ] [ML ][L ] [ML2 ][L ] [ML3 ][L ]
[ML4 ]
K1 K 2 K3 K4
[M ][L ]4
Form eq. 1
K1 K 2 K3 K4 K
K1, K2, K3 & K4 are stepwise stability constant K is overall stability constant.
Taking log on both side
log K log K1 log K 2 log K 3 log K 4
Factors affecting stability of complex :
i. Charge on central metal ion : greater the charge on central metal ion greater is the stability of
complex.
ii. EAN : if effective atomic number (EAN) is equal to nobel gases then complex is stable.
Effective atomic number (EAN or SIDWICK Theory)
EAN = Atomic number – oxidation no. + 2 × coordination number
i. [Co(NH3)6]3+
EAN = 27 – 3 + 2 × 6
= 27 – 3 + 12 = 36
ii. [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
EAN = 29 – 2 + 2 × 4 = 35
iii. [Ni(CO)4]
EAN = 28 – 0 + 2 × 4 = 36
iv. K3[Fe(C2O4)3]
EAN = 26 – 3 + 2 × 6 = 35
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 18
v. [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
EAN = 47 – 1 + 2 × 2 = 50
vi. K2[HgI4]
EAN = 80 – 2 + 2 × 4 = 86
iii. Size of metal ion : Size of metal ion decreases the stability of the complex increases.
Therefore order of stability is, Mn 2 Fe 2 Co2 Ni 2 Cu2 Zn 2
This order is called Irving William’s order of stability.
iv. Basicity of ligand : Basic strength of ligand increases stability of complex increases.
v. Chelating effect : Chelating effect of ligand increases stability of complex increases.
Organometallic compound : Those compound which contain one or more metal-carbon bonds are
called organometallic compound.
Ti(OC 3H7)3
Ex.
Types of organometallic compound :
i. -bonded organometallics : The compound containing metal-carbon sigma bonds are called -
bonded organometallic compound.
Ex. R – Mg – X
ii. -bonded organometallics : The compound containing metal carbon pi bonds are called -
bonded organo metallic compound.
Ex. Zeise’s Salt K [Pt Cl3 (2 − C2H4 )] , Ferrocene [Fe(5 − C5H5 )2 ] , Dibenzene chromium [Cr(6 − C6H6 )]
Application of co-ordination compound :
i. Estimation of hardness of water.
ii. In qualitative and quantitative analysis.
iii. In electroplating.
iv. In water treatment.
v. In dyeing of cloths
John Tellers effect or John Tellers distortion: John tellers distortion occurs in a non linear
molecule that reduce its symmetry and energy. This distortion occurs in octahedral complex due to
which two axial bond become shorter or longer than equatorial bond.
- John teller effect found in octahedral geometry.
- John teller effect not found in half filled, full filled and combination of half filled and full filled
configuration i.e d3,d5,d6,d8,d10.
:: Previous Year NEET Questions ::
Q.1 Match the coordination number and type of hybridization with distribution of hybrid orbitals
in space based on Valence bond theory. [NEET-2020]
Coordination number and type of Distribution of hybrid
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 19
hybridization. orbitals in space
1. 4, sp3 i. trigonal bipyramidal
2. 4, dsp2 ii. octahedral
3. 5, sp3d iii. tetrahedral
4. 6, d2sp3 iv. square planar
(a) 1-ii, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-i (b) 1-iii, 2-iv, 3-i, 4-ii
(c) 1-iv, 2-i, 3-ii, 4-iii (d) 1-iii, 2-i, 3-iv, 4-ii
Q.2 Iron carbonyl, Fe(CO)5 is : [NEET-2018]
(a) tetranuclear (b) mononuclear
(c) trinuclear (d) dinuclear
Q.3 The geometry and magnetic behavior of the complex [Ni(CO)4] are [NEET-2018]
(a) square planar geometry and diamagnetic
(b) tetrahedral geometry and diamagnetic
(c) square planar geometry and paramagnetic
(d) tetrahedral geometry and paramagnetic
Q.4 Correct increasing order for the wavelength of absorption in the visible region for the
complexes of Co3+ is : [NEET-2017]
(a) [Co(H2O)6 ]3 , [Co(en) 3 ]3 , [Co(NH3 )6 ]3 (b) [Co(H2O)6 ]3 , [Co(NH3 )6 ]3 ,[Co(en) 3 ]3
(c) [Co(NH3 )6 ]3 ,[Co(en) 3 ]3 , [Co(H2O)6 ]3 (d) [Co(en) 3 ]3 , [Co(NH3 )6 ]3 , [Co(H2O)6 ]3
Q.5 An example of a sigma bonded organometallic compound is : [NEET-2017]
(a) Grignard reagent (b) Ferrocene (c) Cobaltocene (d) ruthenocene
Q.6 Jahn-Teller effect is not observed in high spin complexes of [NEET-2016]
(a) d7 (b) d8 (c) d4 (d) d9
Q.7 Which of the following has longest C – O bond length ? (Free C – O bond length in CO is
1.128Å) ? [NEET-2016]
(a) [Fe(CO)4]2– (b) [Mn(CO)6]+ (c) Ni(CO)4 (d) [Co(CO)4]–
Q.8 Which of these statements about [Co(CN)6]3– is true ? [NEET-2015]
(a) [Co(CN)6]3– has four unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configuration
(b) [Co(CN)6]3– has no unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configuration
(c) [Co(CN)6]3– has no unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration
(d) [Co(CN)6]3– has four unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration
Q.9 An excess of AgNO3 is added to 100 mL of a 0.01 M solution of tetraaquadichloridochromium
(III) chloride. The number of moles of AgCl precipitated would be : [NEET-2013]
(a) 0.003 (b) 0.01 (c) 0.001 (d) 0.002
Q.10 Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behavior ?
[NEET-2012]
(a) [Ni(NH3)6]2+ (b) [Zn(NH3)6]2+ (c) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ (d) [Co(NH3)6]3+
:: Previous Year JEE MAINS Questions ::
Q.1 The volume (in mL) of 0.125 M AgNO3 required to quantitatively precipitate chloride ions in
0.3 g of [Co(NH3)6]Cl2 is [JEE-2020]
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 20
(a) 26.9 (b) 34.2 (c) 22.3 (d) 23
Q.2 The oxidation states of iron atoms in compounds (A), (B) and (C), respectively, are x, y and z.
The sum of x, y and z. The sum of x, y and z is [JEE-2020]
(a) 6 (b) 5 (c) 3 (d) 2
Q.3 Considering that 0 P, the magnetic moment (in BM) of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ would be
(a) 0.0 (b) 1.2 (c) 2.3 (d) 3.1 [JEE-2020]
Q.4 Complex A has a composition of H12O6Cl3Cr. If the complex on treatment with conc. H2SO4
loses 13.5% of its original mass, the correct molecular formula of A is : [JEE-2020]
[Given : atomic mass of Cr = 52 amu and Cl = 35 amu]
(a) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (b) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O
(c) [Cr(H2O)3Cl3].3H2O (d) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O
Q.5 The d-electron configuration of [Ru(en)3]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2, respectively are : [JEE-2020]
(a) t62g e0g and t2g
4 2
eg 4 2
(b) t2g 4 2
eg and t2g eg
(c) t62g e0g and t62g e0g 4 2
(d) t2g 6 0
eg and t2g eg
Q.6 The electronic spectrum of [Ti(H2O)6]3+ shows a single broad peak with a maximum at 20,300
cm–1. The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) of the complex ion, in kJ mol –1, is : (1 kJ
mol–1 = 83.7 cm–1) [JEE-2020]
(a) 242.5 (b) 145.5 (c) 83.7 (d) 97
Q.7 Simplified absorption spectra of three complexes (i), (ii) and (iii) of M n+ ion are provided below.
Their max values are marked as A, B and C respectively. The correct match between the
complexes and their max values is : [JEE-2020]
(i) [M(NCS)6](–6 + n) ii. [MF6](–6 + n) iii. [M(NH3)6]n+
(a) A-i, B-ii, C-iii (b) A-ii, B-iii, C-i (c) A-ii, B-i, C-iii (d) A-iii, B-i, C-ii
Q.8 Consider that d6
metal ion (M2+)
forms a complex with aqua ligands, and the spin only
magnetic moment of the complex is 4.90 BM. The geometry and the crystal field stabilization
energy of the complex is : [JEE-2020]
(a) tetrahedral and 1.6t 1P (b) octahedral and 2.40 2P
(c) tetrahedral and 0.6t (d) octahedral and 1.60
Q.9 Complex X of composition Cr(H2O)6Cln has a spin only magnetic moment of 3.83 BM. It
reacts with AgNO3 and shows geometrical isomerism. The IUPAC nomenclature of X is :
[JEE-2020]
(a) Tetraaquadichlorido chromium(III) chloride dihydrate
(b) Hexaaqua chromium (III) chloride
(c) Dichloridotetraaqua chromium (IV) chloride dehydrate
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 21
(d) Tetraaquadichlorido chromium (IV) chloride dehydrate
Q.10 [Pd(F)(Cl)(Br)(I)]2– has ‘n’ number of geometrical isomers. Then, the spin-only magnetic
moment and crystal field stabilization energy [CFSE] of [Fe(CN)6]n–6, respectively, are : [Note :
Ignore the pairing energy] [JEE-2020]
(a) 2.84 BM and 1.60 (b) 1.73 BM and 2.00
(c) 0 BM and 2.40 (d) 5.92 BM and 0
Q.11 The correct order of the calculated spin-only magnetic moments of complexes (A) to (D) is :
A. Ni(CO)4 B. [Ni(H2O)6]Cl2 C. Na2[Ni(CN)4] D. PdCl2(PPh3)2 [JEE-2020]
(a) A C D B (b) A C B D (c) C < D < B < A (d) C D B A
Q.12 The number of possible optical isomers for the complexes MA2B2 with sp3 and dsp2 hybridised
metal atom, respectively, is : [JEE-2020]
(Note : A and B are unidentate neutral and unidentate monoanionic ligands, respectively)
(a) 0 and 0 (b) 0 and 2 (c) 0 and 1 (d) 2 and 2
Q.13 Among the statements (A) – (D), the incorrect ones are –
A. Octahedral Co(III) complexes with strong field ligands have very high magnetic moments.
4 2
B. When 0 P , the d-electron configuration of Co(III) in an octahedral complex is t2g eg .
C. Wavelength of light absorbed by [Co(en)3]3+ is lower than that of [CoF6]3–.
D. If the 0 for an octahedral complex of Co(III) is 18,000 cm –1, then t for its tetrahedral
complex with the same ligands will be 16,000 cm–1. [JEE-2020]
(a) A and B only (b) C and D only (c) B and C only (d) A and D only
Q.14 The correct order of the spin-only magnetic moment of metal ions in the following low-spin
complexes, [V(CN)6]4–, [Fe(CN)6]4– and [Ru(NH3)6]3+ and [Cr(NH3)6]2+ is : [JEE-2019]
(a) Cr2+ > Ru3+ > Fe2+ > V2+ (b) V2+ > Cr2+ > Ru3+ > Fe2+
(c) V2+ > Ru3+ > Cr2+ > Fe2+ (d) Cr2+ > V2+ > Ru3+ > Fe2+
Q.15 Two complexes [Cr(H2O)6Cl3 (A) and [Cr(NH3)6]Cl3 (B) are violet and yellow coloured,
respectively. The incorrect statement regarding them is : [JEE-2019]
(a) 0 value of (A) is less than that of (B)
(b) 0 value of (A) and (B) are calculated from the energies of violet and yellow light,
respectively
(c) Both absorb energies corresponding to their complementary colours
(d) Both are paramagnetic with three unpaired electrons
Q.16 Homoleptic octahedral complexes of a metal ion ‘M3+’with three monodentate ligands L1, L2,
L3 absorb wavelengths in the region of green, blue and red respectively. The increasing order
of the ligand strength is : [JEE-2019]
(a) L2 < L1 < L3 (b) L3 < L2 < L1 (c) L3 < L1 < L2 (d) L1 < L2 < L3
Q.17 Mn2(CO)10 is an organometallic compound due to the presence of : [JEE-2019]
(a) Mn – C bond (b) Mn – Mn bond (c) Mn – O bond (d) C – O bond
Q.18 The metal d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in K3[Co(CN)6] are : [JEE-2019]
(a) dxy, dxz and dyz (b) dxz, dyz and d z 2 (c) d x2 y2 and d z2 (d) d xy and d x2 y2
Q.19 The difference in the number of unpaired electrons of a metal ion in its high-spin and low-
spin octahedral complexes is two. The metal ion is : [JEE-2019]
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 22
(a) Fe2+ (b) Co2+ (c) Mn2+ (d) Ni2+
Q.20 Match the metals (Column I) with the coordination compound(s)/enzyme(s) (Column II)
Column-I Column-II [JEE-2019]
Metals Coordinates compound(s)/Enzyme(s)
A. Co i. Wilkinson catalyst
B. Zn ii. Chlorophyll
C. Rh iii. Vitamin B12
D. Mg iv. Carbonic anhydrase
(a) A-ii, B-i, C-iv, D-iii (b) A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
(c) A-iv, B-iii, C-i, D-ii (d) A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
ANSWER KEY
Previous Year NEET Questions
1. (b) 2. (b) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (a)
6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (c) 9. (c) 10. (a)
Previous Year JEE MAINS Questions
1. (a) 2. (a) 3. (a) 4. (b) 5. (a)
6. (d) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (a) 10. (b)
11. (a) 12. (a) 13. (d) 14.(b) 15. (b)
16. (c) 17. (a) 18. (c) 19. (b) 20. (b)
:: LATEST YEAR QUESTIONS (IIT-JEE/NEET) ::
Q.1 Ethylene diaminetetraacetate (EDTA) ion is : [NEET-2021]
(a) hexadenate ligand with four O and two N donor atoms
(b) unidentate ligand
(c) bidentate ligand with two N donor atoms
(d) tridentate ligand with three N donor atoms
Q.2 Match List-I with List-II : [NEET-2021]
List-I List-II
A. [Fe(CN)6]3– 1. 5.92 BM
B. [Fe(H2O)6]3+ 2. 0 BM
C. [Fe(CN)6]4– 3. 4.90 BM
D. [Fe(H2O)6]2+ 4. 1.73 BM
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3 (b) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
(c) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2 (d) A-2, B-1, C-2, D-3
Q.3 Spin only magnetic moment in BM of [Fe(CO)4(C2O4)]+ is : [JEE-2021]
(a) 5.92 (b) 0 (c) 1 (d) 1.73
Q.4 The denticity of an organic ligand, biuret is : [JEE-2021]
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 3 (d) 6
Q.5 The number of optical isomers possible for [Cr(C2O4)3]3– is …….. [JEE-2021]
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 23
Q.6 1 mol of an octahedral metal complex with formula MCl 3.2L on reaction with excess of AgNO3
gives 1 mol of AgCl. The density of ligand L is ……….. (Integer answer). [JEE-2021]
Q.7 3 moles of metal complex with formula Co(en) 2Cl3 gives 3 moles of silver chloride on
treatment with excess of silver nitrate. The secondary valency of Co in the complex is ……. .
(Round off to the nearest integer) [JEE-2021]
Q.8 Given below are two statements. [JEE-2021]
Statement-I : [Mn(CN)6]3–, [Fe(CN)6]3– and [Co(C2O4)3]3– are d2sp3 hybridised.
Statement-II : [MnCl6]3– and [FeF6]3– are paramagnetic and have 4 and 5 unpaired electrons,
respectively.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Statement I is true but statement II is false
(b) Both Statement I and statement II are false
(c) Statement I is false but statement II is true
(d) Both statement I and statement II are true
Q.9 The number of geometrical isomers possible in triamminitrocobalt (III) is X and in
trioxalatochromate (III) is Y. Then, the value of X + Y is ……… [JEE-2021]
Q.10 An organic compound is subjected to chlorination to get compound A using 5.0 g of chlorine.
When 0.5 g of compound A is reacted with AgNO3 [Carius method], the percentage of chlorine
in compound A is ……….…. When it forms 0.3849 g of AgCl. (Round off to the nearest
integer). [JEE-2021]
Q.11 The number of geometrical isomers found in the metal complexes [PtCl 2(NH3)2], [Ni(CO)4],
[Ru(H2O)3Cl3] and [CoCl2(NH3)4]+ respectively, are [JEE-2021]
(a) 1, 1, 1, 1 (b) 2, 1, 2, 2 (c) 2, 0, 2, 2 (d) 2, 1, 2, 1
Q.12 The type of hybridization and magnetic property of the complex [MnCl6]3–, respectively, are :
(a) sp3d2 and diamagnetic (b) d2sp3 and diamagnetic [JEE-2021]
(c) d2sp3 and paramagnetic (d) sp3d2 and paramagnetic
Q.13 Indicate the complex/complex ion which did not show any geometrical isomerism.
(a) [CoCl2(en)2] (b) [Co(CN)5(NC)]3– [JEE-2021]
(c) [Co(NH3)3(NO2)3] (d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
Q.14 Which one of the following metal complexes is most stable ? [JEE-2021]
(a) [Co(en)(NH3)4]Cl2 (b) [Co(en)3]Cl2
(c) [Co(en)2(NH3)2]Cl2 (d) [Co(NH3)6]Cl2
Q.15 Three moles of AgCl get precipitated when one mole of an octahedral co-ordination compound
with empirical formula CrCl3.3NH3.3H2O reacts with excess of silver nitrate. The number of
chloride ions satisfying the secondary valency of the metal ion is ………. . [JEE-2021]
Q.16 Which one of the following species responds to an external magnetic field ? [JEE-2021]
(a) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Ni(CN)4]2– (c) [Co(CN)6]3– (d) [Ni(CO)4]
Q.17 The total number of unpaired electrons present in [Co(NH3)6]Cl2 and [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 is …… .
[JEE-2021]
Q.18 The correct order of intensity of colors of the compound is : [JEE-2021]
(a) [Ni(CN)4]2– > [NiCl4]2– > [Ni(H2O)6]2+ (b) [Ni(H2O)6]2+ > [NiCl4]2– > [Ni(CN)4]2–
(c) [NiCl4]2– > [Ni(H2O)6]2+ > [Ni(CN)4]2– (d) [NiCl4]2– > [Ni(CN)4]2– > [Ni(H2O)6]2+
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 24
Q.19 According to the valence bond theory the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp 2 for
which one of the following compounds ? [JEE-2021]
(a) NiCl2.6H2O (b) K2[Ni(CN)4] (c) [Ni(CO)4] (d) Na2[NiCl4]
Q.20 The correct pair(s) of the ambident nucleophiles is(are) : [JEE-2021]
A. AgCN/KCN B. RCOOAg/RCOOK
C. AgNO2/KNO2 D. Agl/Kl
(a) B and C (b) Only A (c) A and C (d) Only B
Q.21 The equivalents of ethylene diamine required to replace the neutral ligands from the
coordination sphere of the trans-complex of CoCl3.4NH3 is …….. (Round off to the nearest
integer). [JEE-2021]
Q.22 The number of stereisomers possible for [Co(ox)2(Br)(NH3)]2– is ……. [ox = oxalate].
[JEE-2021]
Q.23 Given below are two statements. [JEE-2021]
Statement-I : The identification of Ni2+ is carried out by dimethyl glyoxime in the presence of
NH4OH.
Statement-II : The dimethyl glyoxime is a bidentate neutral ligand.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both statements I and II are true
(b) Both statements I and II are false
(c) Statement I is true but statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but statement II is true
Q.24 The potassium ferrocyanide solution gives a Prussian blue colour, when added to :
[JEE-2021]
(a) CoCl3 (b) FeCl2 (c) CoCl2 (d) FeCl3
Q.25 The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) and magnetic moment (spin-only) of an
octahedral aqua complex of a metal ion (M+) are −0.8 0 and 3.87 BM, respectively. Identify
(M2+). [JEE-2021]
(a) V3+ (b) Cr3+ (c) Mn4+ (d) Co2+
Q.26 The number of hydrogen bonded water molecule(s) associated with stoichiometry CuSO 4
.5H2O is/are. [JEE-2021]
Q.27 The overall stability constant of the complex ion [Cu(NH 3)4]2+ is 2.1 × 1013. The overall
dissociations constant is y × 10–14. Then, y is …….. .(Nearest integer) [JEE-2021]
Q.28 Which one of the following complexes is violet in colour ? [JEE-2021]
(a) [Fe(CN)6]4– (b) [Fe(SCN)6]4–
(c) Fe4[Fe)CN6)]3.H2O (d) [Fe(CN)5NOS]4–
Q.29 The spin only magnetic moment value for the complex [Co(CN)6]4– is ……… BM. [Atomic
number of Co = 27]. [JEE-2021]
Q.30 The total number of unpaired electrons present in the complex K3[Cr(oxalate)3] is …….. .
[JEE-2021]
LATEST PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS (IIT-JEE/NEET)
1. (a) 2. (d) 3. (d) 4. (a) 5. (2)
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
Co-ordination Compounds 25
6. (2) 7. (6) 8. (d) 9. (2) 10. (19)
11. (c) 12. (d) 13. (b) 14. (b) 15. (0)
16. (a) 17. (1) 18. (c) 19. (b) 20. (c)
21. (2) 22. (3) 23. (a) 24. (d) 25. (d)
26. (1) 27. (5) 28. (d) 29. (2) 30. (3)
Branch 1: Near Bank of Baroda lane, Tagore nagar, Raipur (C.G.)
Branch 2:ATM Chowk, Avanti Vihar, Raipur, Mob.: 9111999765
You might also like
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds_DTS 0 SolDocument10 pagesCoordination Compounds_DTS 0 SolRudra guptaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ix - CoordinationDocument18 pagesUnit Ix - CoordinationxyzNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chem 1 PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination Chem 1 PDFSundar SinghNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Coordination CompoundsDocument51 pagesInorganic Chemistry Coordination CompoundsasdfNo ratings yet
- Coordination CoDocument19 pagesCoordination CoHandugan Quinlog NoelNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Titration AnalysisDocument5 pagesComplexometric Titration AnalysisRaymond R. SantosNo ratings yet
- Cordination CompoundDocument22 pagesCordination CompoundAdyaNo ratings yet
- 4-Coordination Chemistry IDocument61 pages4-Coordination Chemistry Igunjan pratapNo ratings yet
- Theory EnglishDocument11 pagesTheory Englishd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- COORDINATION COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - JEE MindmapDocument22 pagesCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - JEE Mindmapadsaditya24No ratings yet
- Chap 9part1Document69 pagesChap 9part1Marie Kris NogaNo ratings yet
- Simplified Focus Area Notes Ii CorrDocument8 pagesSimplified Focus Area Notes Ii Corrwargod RAMZNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 4 Transition MetalsDocument14 pagesMod 5 Revision Guide 4 Transition Metalsjohn mNo ratings yet
- D-Block Metal Chemistry: General ConsiderationsDocument23 pagesD-Block Metal Chemistry: General ConsiderationsPrativa BeheraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Co Ordination CompoundsDocument46 pagesChapter 9 Co Ordination Compoundssukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- HW Bonding&NamingDocument11 pagesHW Bonding&NamingManish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 09: Coordination CompoundsDocument30 pagesChapter - 09: Coordination CompoundsTeju tejasNo ratings yet
- First Row Transition MetalsDocument4 pagesFirst Row Transition MetalsDanielle BelconNo ratings yet
- Double Salts Complex Salts: Chapter 2. Coordination Compounds (9 Marks)Document14 pagesDouble Salts Complex Salts: Chapter 2. Coordination Compounds (9 Marks)PRUTHVINo ratings yet
- Inorganic Paper III 2010Document47 pagesInorganic Paper III 2010ls1955100% (3)
- Chemistry BookletDocument10 pagesChemistry BookletAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry BasicsDocument16 pagesCoordination Chemistry BasicsShaurya BaghelNo ratings yet
- Aakash Modules 05Document263 pagesAakash Modules 05WeirdoNo ratings yet
- 5 3 1 Revision Guide Transition MetalsDocument6 pages5 3 1 Revision Guide Transition MetalsGarret GordonNo ratings yet
- Coordinate CompoundsDocument5 pagesCoordinate Compoundsmandhareneel06No ratings yet
- Coordination Game Changer 14 DecDocument123 pagesCoordination Game Changer 14 DecFURIAS FACTYNo ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry Revision Workshop NotesDocument31 pagesA2 Chemistry Revision Workshop NotesVesna NikolicNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination and Organometallic CompDocument85 pagesCo-Ordination and Organometallic CompDr. Dhondiba Vishwanath100% (1)
- 15 Transition Metals Edexcel PDFDocument13 pages15 Transition Metals Edexcel PDFGanna109No ratings yet
- 2.3 Formulae and EquationsDocument10 pages2.3 Formulae and EquationsJay DaviesNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument9 pagesNomenclatureBrooke OttumNo ratings yet
- 17-Transition-Metals-Iedxcel ReviseDocument13 pages17-Transition-Metals-Iedxcel ReviseFathmath ShereleenNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Chemistry CH 9 Coordination Compounds by SajeevDocument2 pagesHsslive Xii Chemistry CH 9 Coordination Compounds by SajeevrasalgafoorrvgNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound RevisedDocument14 pagesCo-Ordination Compound RevisedabdullahausafmalikNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Chemistry: ChaptDocument9 pagesCo-Ordination Chemistry: ChaptDHINESH HARIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Revision 2022Document2 pagesCoordination Compounds Revision 2022Dêêpák Sîñgh Ñîtwál100% (1)
- Unit-9 Coordination CompoundsDocument20 pagesUnit-9 Coordination Compoundsharshiths425No ratings yet
- Understanding Isomerism in Coordination ChemistryDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Isomerism in Coordination ChemistryRomanNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Co-Ordination CompoundsAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Xii - Cbse Coordination Chemistry Material (23.11.2022)Document15 pagesXii - Cbse Coordination Chemistry Material (23.11.2022)Sanjana MohanNo ratings yet
- Coordination ChemistryDocument14 pagesCoordination Chemistryjangidudit115No ratings yet
- Bonding in coordination compoundsDocument65 pagesBonding in coordination compoundsHitesh vadherNo ratings yet
- MLP - UNIT 9 - Coordination ChemistryDocument9 pagesMLP - UNIT 9 - Coordination ChemistryJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 3 PPT - Part 1 To PostDocument45 pagesCH 3 PPT - Part 1 To PostGrace FernandesNo ratings yet
- PDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLDocument10 pagesPDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLJames SimNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompundsDocument13 pagesCoordination CompundsSatwik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Scan 10 Feb 2022Document14 pagesScan 10 Feb 2022George ParetNo ratings yet
- IIT Main Chemistry Coordination Compounds BaseDocument65 pagesIIT Main Chemistry Coordination Compounds BasePdkNo ratings yet
- D-Block Elements: Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesD-Block Elements: Short Answer QuestionsMahesh Babu100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Transition Metals IntroductionDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Transition Metals Introductiontiahayes2801No ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry Jeemain - GuruDocument30 pagesCoordination Chemistry Jeemain - GuruJp PatidarNo ratings yet
- Isomer Dan Spektrokimia Ok 2017Document90 pagesIsomer Dan Spektrokimia Ok 2017joyoNo ratings yet
- Yvh Uh SB Ytv DI5 XBW Ma 8 DDocument6 pagesYvh Uh SB Ytv DI5 XBW Ma 8 DTushant RaoNo ratings yet
- Ms ChauhanDocument4 pagesMs ChauhanNikhil VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFDocument59 pagesCHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFEhaz100% (1)
- Ajai Kumar Coordination Chemistry-1Document18 pagesAjai Kumar Coordination Chemistry-1Sudipyo NaskarNo ratings yet
- Química de CoordinacionDocument107 pagesQuímica de CoordinacionEMMANUEL ALEJANDRO FERNANDEZ GAVIRIANo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument12 pagesCoordination Compoundsnadeemmessi30No ratings yet
- Metal Atom Nonmetal Ligands Hemoglobin Chlorophyll Dyes Pigments CatalystsDocument18 pagesMetal Atom Nonmetal Ligands Hemoglobin Chlorophyll Dyes Pigments CatalystsNasima akterNo ratings yet
- Determining Ligand Percentages in Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesDetermining Ligand Percentages in Coordination CompoundsFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- L2 - Coordination PDFDocument36 pagesL2 - Coordination PDFShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Making Cis and Trans-Potassium Dioxocatodiacuchromat (III)Document16 pagesUnit 6 Making Cis and Trans-Potassium Dioxocatodiacuchromat (III)Riika RahayuNo ratings yet
- 86 - Definition of Some Important Terms Pertaining To Coordination Compounds - 2Document4 pages86 - Definition of Some Important Terms Pertaining To Coordination Compounds - 2Syed HusamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Introduction To Inorganic Chemistry (SKT1013)Document3 pagesLaboratory Report Introduction To Inorganic Chemistry (SKT1013)muhammad syahmi33% (3)
- Mr. Deepak Pradhan: Asst. Prof. Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry Ggscop, YnrDocument41 pagesMr. Deepak Pradhan: Asst. Prof. Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry Ggscop, YnrDeepak Pradhan100% (2)
- Cocomp. (Repaired)Document20 pagesCocomp. (Repaired)Vinod ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Chelate and Macrocyclic EffectsDocument24 pagesChelate and Macrocyclic EffectsRahul Kumar Gautam100% (2)
- Complexometric TitrationDocument83 pagesComplexometric Titrationengg100% (1)
- FUll NOTES-Transition Metal ChemistryDocument9 pagesFUll NOTES-Transition Metal ChemistryRomario Dallaz HudsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry S6 SBDocument631 pagesChemistry S6 SBRoykin Mugisha93% (15)
- Chem Academy: AssignmentDocument3 pagesChem Academy: AssignmentShreyas YewaleNo ratings yet
- Coordination TheoryDocument38 pagesCoordination TheorySLEVINPJOY100% (11)
- RAJGAD DNYANPEETH’S ANANTRAO THOPTE COLLEGE CBCS CHEMISTRY COURSE COORDINATION COMPOUNDSDocument14 pagesRAJGAD DNYANPEETH’S ANANTRAO THOPTE COLLEGE CBCS CHEMISTRY COURSE COORDINATION COMPOUNDSJìbí MalkøfNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3Document124 pagesChemistry 3Tanay Dubey100% (1)
- 9.03 Nomenclature and LigandsDocument32 pages9.03 Nomenclature and LigandsDebopam RayNo ratings yet
- IC Quiz QuestionsDocument2 pagesIC Quiz Questionsrohan NathNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Coordination Compounds ExplainedDocument51 pagesChemistry of Coordination Compounds Explainedishika chauhanNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument60 pagesCoordination CompoundsKassandraNo ratings yet
- Complexation NotesDocument6 pagesComplexation NotesDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- CPP: Types of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesCPP: Types of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- 4-Coordination Chemistry IDocument61 pages4-Coordination Chemistry Igunjan pratapNo ratings yet
- Chem 324 Fall 2016 Problem Set 5: AnswersDocument13 pagesChem 324 Fall 2016 Problem Set 5: AnswersrafelNo ratings yet
- Chelate SDocument3 pagesChelate Srajasuleman335No ratings yet
- by Nvs Teacher Coordination CompoundsDocument138 pagesby Nvs Teacher Coordination CompoundsDarshan PatilNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Activity On Coordination CompoundsDocument5 pagesSelf-Learning Activity On Coordination CompoundsAbigail CalalangNo ratings yet
- ComplexesDocument20 pagesComplexespunt3yNo ratings yet
- 11 - Isomerism in TMCDocument18 pages11 - Isomerism in TMCMohit KambojNo ratings yet
- MCQ Pp-IiDocument6 pagesMCQ Pp-IidadadNo ratings yet
- SankalpBharat Capsule 30Document36 pagesSankalpBharat Capsule 30Brazil server passNo ratings yet