Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lewis Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Uploaded by
sachinkhandekar970Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lewis Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Uploaded by
sachinkhandekar970Copyright:
Available Formats
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Richard Alan Lewis M.D., M.S.,
PHARMACOLOGY FOPS PHARMACOKINETICS
OF Professor,
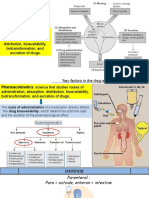
• The study of the absorption,
Departments of Ophthalmology,
OPHTHALMIC Medicine, Pediatrics, and Molecular distribution, metabolism,
AGENTS and Human Genetics and excretion of a drug or
and the National School of Tropical agent
Introduction and Review Medicine
Houston, Texas
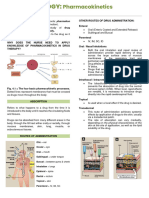
PHARMACOKINETICS Factors Affecting Drug Penetration Factors Affecting Drug Penetration
into Ocular Tissues into Ocular Tissues
• A drug can be delivered to ocular tissue:
– Locally: • Drug concentration and solubility: The higher
the concentration the better the penetration, • Surfactants: The preservatives in ocular
• Eye drop but limited by reflex tearing. preparations alter cell membrane in the cornea
• Ointment and increase drug permeability, e.g.,
• Viscosity: Addition of methylcellulose and benzalkonium and thiomersal
• Periocular injection polyvinyl alcohol increases drug penetration by
increasing the contact time with the cornea and • pH: The normal tear pH is 7.4; if the drug pH is
• Intraocular injection
altering corneal epithelium. much different, it will cause reflex tearing.
– Systemically: • Drug tonicity: When an alkaloid drug is put in
• Lipid solubility: Because of the lipid rich
• Orally environment of the epithelial cell membranes, relatively alkaloid medium, the proportion of
the higher lipid solubility, the more the the uncharged form will increase, thus more
• IM
penetration. penetration.
• IV
FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN
Chemistry Dosage
● C20H1205, brown crystal ● Adults: 500-750 mg IV
● M.W. 322.3 e.g., 3 cc 25% solution
● Peak absorption 485-500 nm. 5 cc 10% solution
● Children: 1.5-2.5 mg/kg IV
● Peak emission 520-530 nm.
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 1
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Needle Diameter Ideal Flow through a small
FLUORESCEIN
tube varies with the 4th power
Needle Outer Diameter Inner Diameter Side Effects
of the radius (r4)
Gauge mm mm
Gauge r r4
● Skin staining: 100% (6-12 hours)
18 1.270 0.838
20 0.3015 ~0.00826 ● Aqueous staining: 100% (8-24 hours)
20 0.908 0.603
● Urine staining: 100% (24-36 hours)
21 0.819 0.514
21 0.257 ~0.00436
23 0.641 0.337 0.00826/0.00436 = 1.895
25 0.514 0.260
FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN
Adverse Reactions Adverse Reactions Adverse Reactions
● Local Effects
Do not change with:
Reported with: - Extravascular
- Informed consent - Intravenous
● Topical phenylephrine
- NPO state - Intra-arterial
● Venipuncture
Systemic Effects
● Fundus photography
- Premedication ●
- Mild
- Dye concentration - Moderate
- Severe
FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN
Extravasation Extravasation Intravenous
● Think prevention ● Intense local pain
● Dull ache, ipsilateral extremity
● Warm, wet compress, - Duration: 20 - 45 minutes
Chemical thrombophlebitis
30 minutes Q.I.D. - Management: self-limited Duration: 3-10 days
● Examine site at 24°, 48° reassurance
Management: self-limited
cold pack
● If avascular, refer to plastic
● Dermal necrosis
surgeon
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 2
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY
Intra-arterial Mild Adverse Reactions Mild Adverse Reactions
● Immediate INTENSE stain of ● Nausea and vomiting < 5% ● Transient
distal extremity ● Extravasation ● Rapid and complete
● PAIN! resolution
● Sneezing
- Duration: 1-24 hours ● No treatment required
● Pruritus
- Management: Cold, Analgesia
FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY
Moderate Adverse Reactions Moderate Adverse Reactions Severe Adverse Reactions
● Transient ● Urticaria (1.2%) • Prolonged
Medical therapy required ● Syncope (0.3%)
●
Thrombophlebitis
• Intense therapy required
● Complete, if gradual, ●
resolution with no sequelae ● Local tissue necrosis • Threat to patient safety
● Nerve palsy • Variable recovery
Overall: 1.6%
FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY
Severe Adverse Reactions Toxicity Death
● Respiratory (1:3,800)
- Laryngeal stridor, edema
- Bronchospasm ● Phototoxicity to skin
- Anaphylaxis
● Cardiovascular
- Circulatory shock
(1:5,300) (Premature, jaundiced infant, Death rate: 1:220,000
- Myocardial infarction, arrest UV therapy: J Peds: 1985; 107)
● Neurological (1:13,900)
- Seizure
(Overall: 1:1,900)
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 3
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN FLUORESCEIN
Precautions Precautions Prophylaxis: Nausea
• Not approved for use in pregnancy
• No evidence for teratogenicity, • Does NOT cross-react with
embryocidicity iodinated contrast dyes Metoclopramide HCl
• Not approved for use in children • Avoid patients with prior
• Renal insufficiency prolongs serious reactions to fluorescein (Reglan) 20 mg IV
elimination
• Diabetics should not confuse color
• Avoid historically risky patients 5 min before F/A
with reactions for glucose
ADVERSE REACTIONS FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY MANAGEMENT
Management Screening
● Trained personnel ● Consent form, especially children
● Emergency equipment History of prior allergies, asthma
Not routinely conducted
●
- Airway (oral, AMBU) - A negative history is no
- O2 (mask, prongs cylinder) guarantee of impunity
- Parenteral fluids on pregnant subjects ● History of recent change in angina,
(I.V. stand, fluids, sets) uncontrolled hypertension,
- B/P cuff cardiac arrhythmia
- Drugs
FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY DRUGS for ANAPHYLACTOID
Most serious reactions
REACTIONS
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
occur within minutes of
25-50 mg p.o., i.m., i.v. injection. Severe
Informed Consent Tripelennamine (Pyribenzamine) anaphylactoid reactions
25-50 mg p.o. may develop as late as
Fexofenadine (Allegra)
one hour after injection.
180 mg. p.o.
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 4
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
INDOCYANINE GREEN INDOCYANINE GREEN
Therefore, if there is Description Formulation
any suspicion, the Tricarbocyanine dye with •Contains 5% Nal
patient should wait peak spectral •pH 5.5 - 6.5
and be absorption at 800-810 nm,
emission at 830-840 nm, •Unstable in
observed.
in blood. aqueous solution
INDOCYANINE GREEN INDOCYANINE GREEN INDOCYANINE GREEN
Chemistry Indications Dosage
● Ophthalmic angiography • 0.5 mg/kg (<2 mg/kg)
•C43H47N2NaO6S2 ● Cardiac output
• Adults: 40 mg in 2 ml
•M.W. 774.96 ● Hepatic function, blood flow solvent with 5 cc N.S.
flush
INDOCYANINE GREEN INDOCYANINE GREEN INDOCYANINE GREEN
Pharmacology Contraindications Adverse Reactions
• Anaphylaxis, urticaria
● Bound to plasma proteins ● Diluent contains Nal reported, without
(albumin, 95%) ● Avoid allergy to iodides
● Hepatic secretion to bile allergy to iodides
• 2 deaths reported
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 5
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Iodine/Iodide Allergy INDOCYANINE GREEN VERTEPORFIN
Pregnancy
• NO objective evidence • Trade Name: Visudyne
demonstrates cross- • Safety in pregnancy, • Formula: C41H42N4O8
reactivity between nursing not established
• No animal embryocidicity, • Isomers of benzoporphorin
allergy to shellfish and
teratogenicity studies • Molecular Weight: 718.8
iodine sensitivity!
J. Emerg. Med. 2010: 39 (5): 701-707
VERTEPORFIN VERTEPORFIN VERTEPORFIN
Indication Metabolism Adverse Reactions
●Skeletal: back pain, 2-15%
Light-activated drug for • Liver excretion into ● Skin: photosensitivity (5 days)
photodynamic therapy of bile, feces ● GI: nausea
various subretinal
• Half-life 5-6 hours ● CV: syncope, hypotension,
neovascularizations bradycardia
VERTEPORFIN VERTEPORFIN VERTEPORFIN
Contraindications Other Cautions Precautions
• Photosensitization,
• Porphyria • Pregnancy class C
~ 5 days
• Liver dysfunction • Rats: anophthalmia
• Avoid extravasation
• Known hypersensitivity • Avoid nursing
• Matched laser 689 nm.
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 6
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
VERTEPORFIN
Cautions PEGAPTANIB PEGAPTANIB
Macugen
● Avoid other photosensitizers
• Trade name: Macugen
(thiazides, sulfas, antidiabetics • Formula: • Mechanism of Action:
● 83 sec. treatment, exactly 15 C294H342F13N107Na28O188P28 Selective antagonist of
min. after 10 min. infusion [C2H4O]n, where n = ~900 Vascular Endothelial
• Molecular Wt: ~50 kD Growth Factor (VEGF)
PEGAPTANIB PEGAPTANIB PEGAPTANIB
Macugen Macugen Macugen
• Mechanism: An aptamer, • Dose: 0.3 mg intravitreous • Indication: ‘Wet’ macular
modified RNA oligonucleotide,
• Frequency: Every 6 weeks degeneration
that adopts the 3-dimensional
conformation to bind to • Half-life: ~ 10 days • Contraindications: ocular
extracellular VEGF165 inhibiting • Metabolism: Degraded by infections;
its binding to VEGF receptors. nucleases known sensitivity
PEGAPTANIB PEGAPTANIB RANIBIZUMAB
Macugen-Safety Macugen • Trade name: Lucentis
• Pregnancy: Not studied • Supplied: in a prefilled, • Formula: recombinant
• Nursing: Not studied single use, glass syringe, humanized IgG1 κ
• Children: Not studied with 0.3 mg Macugen, monoclonal antibody
• Safety or efficacy not packaged with 30 G x ½” fragment
proven beyond 2 years BD needle • Molecular wt.: 48 kD
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 7
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
RANIBIZUMAB RANIBIZUMAB
Lucentis Lucentis
• Indication: “Wet” • Dose: 0.5 mg intravitreous
macular degeneration • Frequency: q month x 4,
• Contraindications: then q 3 months
sensitivity; active • Half-life: 7 – 12 days
ocular infections
RANIBIZUMAB RANIBIZUMAB RANIBIZUMAB
Lucentis Lucentis Lucentis
• Mechanism of action: • Cautions: • Side Effects:
Binds to all receptor Transient elevation of subconjunctival
binding sites of VEGF-A, intraocular pressure; hemorrhage, pain,
preventing interaction of endophthalmitis; v. floaters, elevated IOP,
VEGF with its receptors. thromboembolic events (<4%) intraocular inflammation
BEVACIZUMAB BEVACIZUMAB BEVACIZUMAB
• Trade name: Avastin
Avastin Avastin
• Formula: complete • Dose: 1.25 – 2.5 mg.
intravitreous • Metabolism: ? Nucleases
humanized IgG
monoclonal antibody • Frequency: every 4 weeks • Excretion: ?
• Molecular wt.: 149 kD • Half-life: 20 days (11-50 d)
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 8
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
BEVACIZUMAB BEVACIZUMAB BEVACIZUMAB
Avastin Avastin Avastin
• Indications: OFF LABEL: • Side Effects: risk of
• Mechanism of Action:
“Wet” macular bleeding
Binds competitively to
degeneration; CNV, NVG, • Cost: among the most
VEGF receptors blocking
PDR, ROP, C/BRVO, expensive drugs in the
VEGF’s activity
diabetic macular edema world, widely marketed!
EYLEA: Aflibercept (EYLEA)
Mechanism Potential Risks
EYLEA
Schedule • Failure to control CNV
• Soluble
“decoy- • Endophthalmitis
receptor” of • Intravitreous injection • Retinal Detachment
both VEGF-A
and Placental • Q 4 weeks x 3; then • Transient elevation of IOP
Growth Factor • Q 8 weeks for ~1 year • ?Thromboembolism?
(PlGF)
Aflibercept (EYLEA) Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration:
• Pregnancy Class C Topical Topical - Drops
• Most ocular medications are
• Nursing mothers? delivered topically - maximizes
Factors affecting absorption:
• Pediatric population? anterior segment concentrations • Drug concentration (limited by
and minimizes systemic toxicity; tonicity) and solubility (aqueous
• Mutagenesis? • Drug gradient from tear reservoir to solution vs. suspension)
corneal and conjunctival epithelium • Viscosity (increased contact time)
• Carcinogenesis? forces passive absorption.
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 9
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration:
Topical - Drops Topical - Drops Topical - Drops
• Lipid solubility: lipid-rich epithelial Surfactants: preservatives are • Reflex tearing: Ocular irritation
cell membrane vs. water-rich and secondary tearing wash out
surface-active agents that alter of the drug reservoir in the tears
stroma
cell membranes in the cornea and reduce contact time with
• pH and ionic charge: Most eye
drops are weak bases, existing in
and bacteria, increasing drug cornea, especially when drops
both charged and uncharged permeability and preventing are not isotonic, have non-
forms, enhancing absorption. bacterial contamination. physiological pH, or contain
irritants.
Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration:
Topical - Drops Topical - Ungt. Topical - Ungt.
• Tissue binding: proteins in the tears • Increases contact time of drug with ocular
and on the ocular surface may surface; • Only drugs with high lipid
• Mixture of petrolatum and mineral oil;
bind drug making the drug solubility and some water
• Water-soluble drugs are insolvent in the
unavailable or creating a slow solubility will get into
ointment and are present as
release reservoir. This may affect
peak effect, duration of action,
microcrystals. both tears and corneal
• The surface microcrystals dissolve in the
and delayed local toxicity. tears; the rest are trapped until the
epithelium.
ointment melts.
Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration: Routes of Administration:
Peri-ocular Injections Intra-ocular Injections Systemic
• Subconjunctival, subTenon’s, • Allow instant drug delivery at • Extent of drug bound to plasma proteins
peribulbar, and retrobulbar; therapeutic concentrations to also effects access of drug into eye - only
• Allow drugs to bypass the unbound form can pass blood-ocular
target site;
barrier.
conjunctival/corneal epithelial • Intracameral, e.g., antibiotics, • Bolus administration exceeds the
barrier and reach therapeutic levels viscoelastics, miochol; capacity of a drug to bind to plasma
in the posterior segment; proteins and so leads to higher
• Intravitreous, e.g.,
• e.g., anesthetic agents, steroids triamcinolone, Avastin, Lucentis intraocular drug levels than with slow IV
drip
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 10
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Routes of Administration: Sustained Release Devices MYDRIASIS
Sustained Release • These devices deliver
an adequate supply
of medication at a
• Devices available for steady-state level
• e.g.,
delivery of steroids, – Ocusert delivering
pilocarpine
[G., μυδριασις]
gancyclovir within – Timoptic XE delivering
timolol Dilation of the pupil
– Ganciclovir sustained-
vitreous cavity release intraocular
device
– Collagen shields
Routes of Administration:
Topical - Drops Dilating Agents
• One drop = 50 µl • Dependent on iris
• Volume of conjunctival cul-de-sac 7-10 µl
pigmentation
• To increase drop absorption:
- wait 5-10 minutes between drops • Mechanism: Inhibition
- compress lacrimal sac of iris constrictor and
- keep lids closed for 5 minutes after ciliary muscles
instillation
MYDRIASIS CYCLOPLEGIC AGENTS
CYCLOPLEGIA
• Atropine (0.5%, 1%)
• Blockage of cholinergic [G. κυκλος = circle,
• Homatropine (1%, 5%)
stimulation to sphincter + πληγη = blow, stroke]
• Scopolamine (Hyoscine)
ms. of iris, ciliary body Paralysis of
• Cyclopentolate (0.5, 1, 2%)
• Stimulation of iris dilator accommodation
ms. • Tropicamide (0.5, 1%)
(ciliary ms.)
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 11
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
Parasympatholytic Drugs CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl
Chemistry
Mydriasis Cycloplegia Duration
• Available as
ATROPINE 30 min. 60 min. 10 – 14 days
- Cyclogyl • Anticholinergic,
- Ak-Pentolate, inter alia
• Parasympatholytic
HOMATROPINE 10 – 30 min. 30 – 90 min. 2 – 4 days
• 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.0% coll.
SCOPOLAMINE 40 min. 40 min. 2 – 6 days
CYCLO- 20 – 30 min. 15 – 45 min. 12 – 24 hrs
PENTOLATE
CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl
Action Toxicity Side Effects
• Mydriasis • Facial flushing
• Irritation with
- Onset: 15 – 30 minutes • Wandering, irrelevant speech
concentration
- Duration: 24 hours • Disorientation, hallucinations
• ↑ IOP in open angle
• Cycloplegia • Psychosis
glaucoma
- Onset: 15 – 45 minutes • Ataxia, restlessness
• Angle closure glaucoma
- Duration: 24 hours • Grand mal seizures
CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl CYCLOPENTOLATE HCl TROPICAMIDE
Allergy Guidelines Chemistry
• Use lowest concentration
• Irritation, injection
• Avoid repetition • Anticholinergic,
• Lacrimation,
mucoid discharge • Avoid seizure-prone • Parasympatholytic
infants, elderly
• Atopic dermatitis
• Use punctal occlusion
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 12
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
TROPICAMIDE TROPICAMIDE
TROPICAMIDE Action Side Effects
• Mydriasis
• Available as - Onset 15-30 min. ● Irritation on instillation
- Mydriacyl - Duration 4-6 hours ● ↑ IOP in open angle glaucoma
- Tropicacyl, inter alia • Cycloplegia ● Angle closure glaucoma
• 0.5%, 1.0% collyrium - Onset 20-30 min. ● Better mydriatic than cycloplegic
- Duration 4-6 hours
TROPICAMIDE PHENYLEPHRINE PHENYLEPHRINE
Toxicity • Chemistry: α1 adrenergic
● Available as stimulator, agonist
• Rare, due to brief action - NeoSynephrine (radial iris fibers)
• Cyanosis - Ak-Dilate • Action:
- Mydfrin - Mydriasis
• Muscle rigidity
- Efricel, inter alia Onset: 10-20 min.
• Vasomotor instability Duration: ~ 3°
● 2.5%, 10% collyria
- Vasoconstriction
PHENYLEPHRINE PHENYLEPHRINE PHENYLEPHRINE
Clinical Effects Side Effects
• Other Actions:
• Rapid onset
• Irritation on instillation - Reduced aqueous inflow
• Virtual absence of
- Reduced resistance to
cycloplegia • Angle closure glaucoma
outflow
• Accentuates effect of
- Stimulation of dilator ms.
mydriatic
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 13
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
PHENYLEPHRINE PHENYLEPHRINE PHENYLEPHRINE
Toxicity Toxicity Guidelines
• Use punctal occlusion
• 1 gtt. 10% coll. = 3.3-6.7 mg. • Sudden systemic hypertension • Do not use in patients on
(babies) MAO inhibitors or tricyclic
• Enhanced absorption in
• Ventricular arrhythmias antidepressants
inflamed eyes (e.g., Parnate, Tofranil, Elavil,
• Myocardial infarction
Sinequan).
PHENYLEPHRINE DAPIPRAZOLE
Guidelines DAPIPRAZOLE
Trade Name [Rev-Eyes]
• Use cautiously in hypertension,
cardiac disease, aneurysm
Rev-Eyes® • C19N27N5HCl
• Use 2.5% coll. in infants,
elderly • M.W. 361.93
• Approximately gtt.1/eye/hour
DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE
Description Pharmacology
Now available through
selected compounding • α-adrenergic smooth
α-adrenergic muscle blocker
pharmacies
(e.g., Leitner’s Pharmacy and
blocking agent • Induces miosis by
Compounding Center, San Jose, CA dilator muscles
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 14
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE
Pharmacology Indications Dosage
• Reconstituted as
• No action on ciliary ms. Iatrogenic mydriasis
0.5% collyrium
• Minimal effect on by adrenergic
(or parasympatholytic) • gtts ii O.U.;
sphincter ms.
agents repeat after 5 min.
DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE DAPIPRAZOLE
Pregnancy Pediatrics Contraindications
• Safety in pregnancy, • Hypersensitivity
nursing not established Safety and efficacy • Strong parasympatholytic
• Not embryocidal, not established agents
teratogenic in rats, • Use only once/week/pt.
rabbits
TOPICAL ANESTHETICS TOPICAL ANESTHETICS PROPARACAINE
• Proparacaine (Alcaine, ● Available as
• Mechanism of Action: Ophthetic, Fluoracaine, inter alia) - Ophthaine
- Reversible block, • Benoxinate (Fluress) - Aphthetic
competitive inhibition of ACh • Tetracaine - Ak-taine
- Decreased membrane
• Cocaine - Alcaine
permeability to Na+ flux
(1% - 4% as anesthetic) ● 0.5%
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 15
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
TOPICAL ANESTHETICS TOPICAL ANESTHETICS
TOPICAL ANESTHETICS Side Effects Maximum Effective Concentrations
• Onset: 5-30 sec. • Stinging on instillation Proparacaine 0.5%
• Duration:
• Suppression of reflex Tetracaine 1%
- Varies with concentration,
blinking Lidocaine 4%
frequency of instillation
• Increased corneal Cocaine 20%
- Generally, 20-30 min.
permeability to drugs Benoxinate 0.4%
TOPICAL ANESTHETICS TOPICAL ANESTHETICS
PROPARACAINE
Epithelial Toxicity Toxicity
Onset: 5-20 sec.
• Epithelial punctate keratopathy
Minimal: Lidocaine (2-4%) (ave. ~13 sec.)
• Retardation of epithelial healing
Maximal: Cocaine (4-20%) • Idiosyncrasy Duration : 15-25 min.
• Allergy: exfoliative dermatitis Irritation: minimal
PROPARACAINE PROPARACAINE Fluorescein – Topical
Allergy Toxicity • Available as drops or
strips
● Punctate epithelial keratopathy • Uses: stain corneal
• Rare; ● Stromal edema (after 5-10 min.)
defects and abrasions,
applanation tonometry,
● Suppression of reflex blink;
detecting wound leak,
• No cross-reaction with NLD obstruction
tetracaine, benoxinate drying • Caution:
• Stains soft contact lens
● Suppression of epithelial • Fluorescein drops can be
contaminated by
regeneration Pseudomonas sp.
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 16
Ophthalmic Pharmacology
ROSE BENGAL GLYCERIN, USP GLYCERIN
• Stains devitalized epithelium Glycerol
• Action: Osmotic agent
• Uses: Severe dry eye, • Chemistry: Trihydric Alcohol
herpetic keratitis - Hydroscopic
(CH2OHCHOCH2OH)
• Colorless viscous liquid
- Deturgesces
• Miscible with H2O, EtOH
corneal edema
• Used in 50-75% conc. (aqueous) • Onset: 1-2 min.
GLYCERIN GLYCERIN GLYCERIN
Side Effects Toxicity Advantages
• Burning pain on instillation • Inexpensive
Rare, topically • Use as gonioscopic
• Transient action (topical)
lubricant
Richard Alan Lewis, M.D., M.S. Nov 2013 17
You might also like
- Parenteral Products: The Preparation and Quality Control of Products for InjectionFrom EverandParenteral Products: The Preparation and Quality Control of Products for InjectionNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument23 pagesLecture 4 PDFosama05550666No ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Ocular Pharmacology - DR Fermin (2023)Document5 pagesOcular Pharmacology - DR Fermin (2023)Patricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Products for Topical Administration: Pharmaceutical MonographsFrom EverandPharmaceutical and Cosmetic Products for Topical Administration: Pharmaceutical MonographsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ocular Pharmacology-I: Dr. Ajai AgrawalDocument51 pagesOcular Pharmacology-I: Dr. Ajai AgrawalRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Microneedle-mediated Transdermal and Intradermal Drug DeliveryFrom EverandMicroneedle-mediated Transdermal and Intradermal Drug DeliveryNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Dosage FormsDocument40 pagesOphthalmic Dosage Formsabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal DrugsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal Drugskûrñï såñskrùthîNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic PDFDocument48 pagesOphthalmic PDFMichael Andre CorosNo ratings yet
- Local AnesthesiaDocument63 pagesLocal AnesthesiaReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Document75 pagesPediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Elamaaraeen MadhvanNo ratings yet
- Ocular Pharmacology - Dr. Fermin (2023)Document6 pagesOcular Pharmacology - Dr. Fermin (2023)Patricia Manalili100% (1)
- Formulasi Sediaan MataDocument73 pagesFormulasi Sediaan MataDwiNoviaNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics: Pharmacology and Toxicity: Dental Clinics of North America October 2010Document14 pagesLocal Anesthetics: Pharmacology and Toxicity: Dental Clinics of North America October 2010Afdol StoryNo ratings yet
- Route of Administration 2016Document71 pagesRoute of Administration 2016Movie Scene BankNo ratings yet
- Biopharm KineticsDocument27 pagesBiopharm KineticsJoslin Roz GalileaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Drug Delivery SystemDocument30 pagesOcular Drug Delivery SystemalijanmarwatNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lesson 2Document5 pagesPharma Lesson 2BabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics - PPT - Dr. Maulana Antian Empitu (Airlangga Medical Faculty)Document59 pagesPharmacology Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics - PPT - Dr. Maulana Antian Empitu (Airlangga Medical Faculty)rizkyyunitaa15No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document54 pagesUnit 3Shubh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 51 HR NddsDocument3 pages51 HR NddsJasna KNo ratings yet
- Ocular Drug PDFDocument4 pagesOcular Drug PDFPpa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument84 pagesAbsorptionDr. Bharat JainNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Development of Sublingual TabletDocument20 pagesFormulation and Development of Sublingual Tabletvedantyenge68No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Processes, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Individualized TherapyDocument50 pagesPharmacokinetics Processes, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Individualized TherapyIdris Balasa IdrisNo ratings yet
- NDDSDocument10 pagesNDDSJasna KNo ratings yet
- Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics: Ocular in Situ Gel: An OverviewDocument11 pagesJournal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics: Ocular in Situ Gel: An OverviewRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Synopsis New 22222Document18 pagesSynopsis New 22222pharma studentNo ratings yet
- Ocular Drug DeliveryDocument99 pagesOcular Drug DeliveryRishi ModyNo ratings yet
- Practical OphthalDocument35 pagesPractical OphthalShahzaib GouriNo ratings yet
- Nano DrugDocument72 pagesNano Drugjjdobariya11No ratings yet
- Development and in Vitro Characterization of Nanoemulsion Embedded Thermosensitive In-Situ Ocular Gel of Diclofenac Sodium For Sustained DeliveryDocument14 pagesDevelopment and in Vitro Characterization of Nanoemulsion Embedded Thermosensitive In-Situ Ocular Gel of Diclofenac Sodium For Sustained DeliveryVeaux NouNo ratings yet
- Teknologi Sediaan Steril: Pertemuan - 7Document26 pagesTeknologi Sediaan Steril: Pertemuan - 7Siska AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- PPH305 Lecture 1 9-10-2023Document49 pagesPPH305 Lecture 1 9-10-2023alihassan.ph40No ratings yet
- Preformbhav 101023234729 Phpapp02Document27 pagesPreformbhav 101023234729 Phpapp02adnanNo ratings yet
- Ocular Drug Delivery - 1638930129Document108 pagesOcular Drug Delivery - 1638930129PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of A Novel SmallDocument8 pagesPhysical Properties of A Novel SmallSheila BerbelzinhaNo ratings yet
- CC4A CC4B H Schneider - Why Are Therapeutic Drugs Ineffective in Some People and Toxic in OthersDocument12 pagesCC4A CC4B H Schneider - Why Are Therapeutic Drugs Ineffective in Some People and Toxic in OthersSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Reviewed - Ijgmp - Format-Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal PatchesDocument16 pagesReviewed - Ijgmp - Format-Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patchesiaset123No ratings yet
- Medicine (Pharmaceutical Chemistry)Document33 pagesMedicine (Pharmaceutical Chemistry)Crizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- 2404-Article Text-7186-1-10-20190315 PDFDocument7 pages2404-Article Text-7186-1-10-20190315 PDFnelisaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of General Pharmacology: at The End of This Session You Will Be Able To: Answer The Following QuestionDocument63 pagesObjectives of General Pharmacology: at The End of This Session You Will Be Able To: Answer The Following Questionkiran patilNo ratings yet
- BIOFAR 4 (Perjalanan Obat Dalam Tubuh-Parenteral)Document24 pagesBIOFAR 4 (Perjalanan Obat Dalam Tubuh-Parenteral)Sizura YuriNo ratings yet
- Eyes OutlineDocument7 pagesEyes OutlineNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Desak Ernawati., PHD., Apt Pharmacology and Therapeutics DepartmentDocument36 pagesDesak Ernawati., PHD., Apt Pharmacology and Therapeutics DepartmentpramelyNo ratings yet
- Parentrals: Advantages of ParentralDocument40 pagesParentrals: Advantages of Parentraltipu94100% (1)
- Department of Pediatrics and Preventive Dentistry.: Local Anasthesia in Pediatric DentistryDocument27 pagesDepartment of Pediatrics and Preventive Dentistry.: Local Anasthesia in Pediatric DentistrySudip ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic FormulationsDocument46 pagesOphthalmic FormulationsAzka FatimaNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument39 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationAditya AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Original Paper ForDocument15 pagesOriginal Paper ForDebopam RayNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Itraconazole Opthalmic in Situ GelsDocument8 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Itraconazole Opthalmic in Situ GelsiajpsNo ratings yet
- Absorption of DrugsDocument34 pagesAbsorption of Drugsalexpharm100% (1)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Introductionashwini wakadeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Block 1.4 - PharmacokineticsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Block 1.4 - Pharmacokineticsdaleng subNo ratings yet
- Formulasi Sediaan MataDocument70 pagesFormulasi Sediaan Matawida safitrNo ratings yet
- 577 704 1 PB PDFDocument9 pages577 704 1 PB PDFRianaNo ratings yet
- Oromucosal Drug Delivery 2015: DR Mine OrluDocument56 pagesOromucosal Drug Delivery 2015: DR Mine Orluchegu BusinessNo ratings yet
- Intra Canal Medication PDFDocument34 pagesIntra Canal Medication PDFKhalil El HalimyNo ratings yet
- Ointment Box OutlineDocument1 pageOintment Box OutlineDon Nestor Razon Jr.No ratings yet
- Laporan Penggunaan Maret 2020Document6 pagesLaporan Penggunaan Maret 2020siska thresiaNo ratings yet
- Nsaids BcqsDocument1 pageNsaids BcqsDR AbidNo ratings yet
- Questions From WorksheetDocument3 pagesQuestions From WorksheetosayomoreNo ratings yet
- Porphyria Unsafe Drugs - Extensive ListDocument23 pagesPorphyria Unsafe Drugs - Extensive ListDorisStinson100% (1)
- Persuasive Essay Final DraftDocument13 pagesPersuasive Essay Final Draftapi-3003748650% (1)
- Treatment ProtocolDocument3 pagesTreatment ProtocolFabio CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Medicines & Supplies: FebruaryDocument85 pagesMedicines & Supplies: FebruaryPharmacy DeamhiNo ratings yet
- Dispensary APTsDocument12 pagesDispensary APTsTewodros TafereNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology For AnesthetistsDocument586 pagesClinical Pharmacology For Anesthetistsagatakassa100% (2)
- Pantropazole DSDocument3 pagesPantropazole DSNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Bodybuilding Course BriefDocument1 pageBodybuilding Course BriefPNP76No ratings yet
- 2020 Complete Drug List FormularyDocument204 pages2020 Complete Drug List FormularyYvetal GardeNo ratings yet
- Second PrescriptionDocument4 pagesSecond PrescriptionSourabh Sharaf100% (2)
- M. Pharm Review NAPLEX38Document1 pageM. Pharm Review NAPLEX38JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Cough N Cold Medicine List PDFDocument7 pagesCough N Cold Medicine List PDFDonna DominnoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pharmacy Intervention To Patient With Polypharmacy - JournalDocument7 pagesEffect of Pharmacy Intervention To Patient With Polypharmacy - Journalanon_529380518No ratings yet
- Rational Prescribing of Antibiotics in Infections in ChildrenDocument43 pagesRational Prescribing of Antibiotics in Infections in ChildrenVictor UmbuNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookDocument7 pagesIntermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookRaniela MaeNo ratings yet
- MedicationsDocument13 pagesMedicationsReynaKatNo ratings yet
- Kefarmasian Klinik Ngudi WaluyoDocument234 pagesKefarmasian Klinik Ngudi Waluyoanaz caepNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Paten & GenerikDocument28 pagesLampiran Paten & GenerikSABRINA SAL SABILLANo ratings yet
- 16 Aug 2010 - Bupivacaine (Marcain®) and Reports of Lack of Efficacy - HSA - Health Sciences AuthorityDocument2 pages16 Aug 2010 - Bupivacaine (Marcain®) and Reports of Lack of Efficacy - HSA - Health Sciences AuthorityBarbara Sakura RiawanNo ratings yet
- Sedative & Hypnotics: Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Department Medical College King Saud UniversityDocument51 pagesSedative & Hypnotics: Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Department Medical College King Saud UniversityRose Ann Raquiza-PeranteNo ratings yet
- Passage I: Task 1. Answer and QuestionsDocument2 pagesPassage I: Task 1. Answer and QuestionsReynaldi SaifulNo ratings yet
- Analgesics Use in Dentistry: Armond DaciDocument32 pagesAnalgesics Use in Dentistry: Armond Daciyrkyrk0707No ratings yet
- D BL Promethazine Hydrochloride in JDocument10 pagesD BL Promethazine Hydrochloride in JarthurbaidoodouglasNo ratings yet
- Colibrí Wellness Center: Low Dose Naltrexone Patient InstructionsDocument4 pagesColibrí Wellness Center: Low Dose Naltrexone Patient InstructionsYannah ReonalNo ratings yet
- Serbian Association of Dermatovenereologists Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of PsoriasisDocument18 pagesSerbian Association of Dermatovenereologists Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of PsoriasisAndjela KosticNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Penyakit Paru Obstruksi Kronik (PPOK) : Tinjauan PustakaDocument10 pagesFarmakoterapi Penyakit Paru Obstruksi Kronik (PPOK) : Tinjauan PustakaLilisNo ratings yet