Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impaired Gas Exchange NCP
Uploaded by
Romel Balili0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
137 views3 pagesImpaired Gas exchange nursing diagnosis. Nursing care plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentImpaired Gas exchange nursing diagnosis. Nursing care plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
137 views3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCP
Uploaded by
Romel BaliliImpaired Gas exchange nursing diagnosis. Nursing care plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.
P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
Name of Patient: Patient M. Date of Admission: 10/6/2022 Age: 26 Sex: Female Civil Status: N/A
Chief Complaint: 48-Hour history of progressive dyspnea, Generalized edema, and Left lower chest pain with non-productive cough
Attending Physician: Dr. Magallona
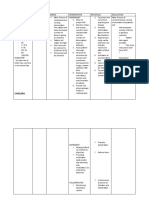
Date / Cues Nursing Goals & Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Time Diagnosis Objectives
October 6, Subjective/s: Impaired Gas Within 8 hours if INDEPENDENT: INDEPENDENT: GOAL MET
2022 - The patient exchange r/t nursing intervention, A. Assist the patient in A. To facilitate lung
@3:00 pm verbalized, accumulation of the patient will be finding a comfortable expansion and reduce After 8 hours of
fluid in pleural able to: position (e.g., semi- the work of breathing. nursing intervention
“I experienced space aeb Fowler's) that the patient able to:
fluid retention dyspnea, - Demonstrate optimizes lung
that went way elevated RR, improved gas expansion and - The patient's
beyond the o2sat of 92%, exchange as encourages deeper oxygen saturation
usual hormone and presence of evidenced by an breathing. has increased to
fluctuations or pleural effusion. increase in oxygen 95%
indulgence in saturation to ≥ 95%.
overly salty Scientific basis: B. Respiratory - The patient's
B. Encourage the exercises help in lung
food.” The nursing - The patient's respiratory rate has
patient to perform expansion, prevent
diagnosis of respiratory rate will decreased and
“I presented to "Impaired Gas decrease to within deep-breathing atelectasis (lung remained within the
the emergency Exchange" is the normal range exercises, coughing, collapse), and normal range (18
department supported by (e.g., 12-20 breaths and spirometry as promote the cpm)
with a 48-hour the scientific per minute) appropriate. clearance of
history of basis that - Reported
respiratory secretions.
progressive pleural effusion, - Report a reduction decreased in
dyspnea, characterized by in dyspnea and symptoms such as
generalized the increased comfort C. Educate the patient
and caregivers on the C. Educating the shortness of breath
edema and left accumulation of during breathing, and improved
lower chest fluid in the indicating improved importance of proper patient and caregivers comfort.
pain with a pleural space, gas exchange and positioning and offer on proper positioning
non-productive restricts lung lung function. guidance on activities and respiratory
cough.” expansion and that may improve gas techniques like
exchange such as
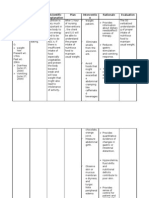
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
alters the diaphragmatic diaphragmatic and
Objectives: mechanics of breathing and pursed- pursed-lip breathing
- RR: 34 cpm respiration. This lip breathing can be helps optimize lung
- HR: 144 bpm leads to particularly helpful. mechanics, increase
- O2sat: 92% impaired
oxygenation, and
ventilation and
reduce the work of
ABG Result: gas exchange in
- Metabolic the alveoli, breathing, leading to
acidosis: causing reduced improved gas
pH: 7.134 oxygen uptake exchange and overall
HCO3: 6 and carbon respiratory function.
dioxide removal.
- (+) Pleural The
effusion compromised
lung function, DEPENDENT:
often associated A. Administer oxygen DEPENDENT:
with conditions @3L per minute via A. Helps raise the
such as heart nasal canulla patient's blood oxygen
failure or saturation levels (SpO2)
inflammatory to a normal range
diseases like (typically 95% or higher)
Systemic Lupus to ensure that cells
Erythematosus receive an adequate
(SLE), further supply of oxygen for
exacerbates the metabolism and organ
impairment, function.
ultimately
resulting in
decreased B. Administer
arterial Furosemide as per B. To treat the fluid
oxygenation accumulation in the
physician’s order.
levels pleural space of the
COLLABORATIVE:
(hypoxemia) patient.
A. Collaborate with a
and an elevated COLLABORATIVE:
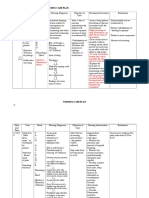
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
partial pressure physician or A. This procedure can
of carbon respiratory therapist help drain excess fluid
dioxide to perform from the pleural
(hypercapnia). thoracentesis or space, relieving
Consequently,
chest tube insertion pressure on the lungs
addressing the
as appropriate for and improving gas
effusion and
optimizing lung the patient's exchange.
function are condition.
essential to
alleviate
impaired gas
exchange in
affected
individuals.
https://
onlinelibrary.wil
ey.com/doi/
abs/
10.1002/978111
8702864.ch7
You might also like
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PrioritizationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan PrioritizationKASIA SyNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis 1Document2 pagesVasculitis 1PAMELA CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- NCP For DRDocument1 pageNCP For DRvalencia222No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- Managing Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaDocument3 pagesManaging Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabNo ratings yet
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDocument1 pageNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationgabbyNo ratings yet
- Assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation for Parkinson's patientDocument2 pagesAssessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation for Parkinson's patientBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Acute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansDocument2 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansJoannah Marie Juloya Kiat-ong100% (1)
- Sample CHN Teaching Learning GuideDocument3 pagesSample CHN Teaching Learning GuideSUREEN MAY ANG REGULARNo ratings yet
- Nursing Physical AssessmentDocument5 pagesNursing Physical AssessmentApril Louise PaluganNo ratings yet
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 pagesNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument3 pagesNCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisVencel Mae Famas Villahermosa50% (2)
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- Subjective Data: - To Know Base Line Information To Know Base Line InformationDocument8 pagesSubjective Data: - To Know Base Line Information To Know Base Line InformationRavinder BhagatNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Scientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsDocument4 pagesScientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisBondan PalestinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- ARDS Care Respiratory Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesARDS Care Respiratory Care Plan PDFeric parl0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Functional Urinary IncontinenceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Functional Urinary IncontinenceJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Fistula NCPDocument1 pageFistula NCPHasna LisnaNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationAyra PunzalanNo ratings yet
- NCP GCP FinalDocument15 pagesNCP GCP FinalssilvozaNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageFar Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationSarah CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneMartin Lєtmaku EspinaNo ratings yet
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument17 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Imbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument3 pagesImbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementselheezaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Managing Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and RestDocument2 pagesManaging Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and ResthaniehaehaeNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument16 pagesNCP FinalEuleen Tria PadrigoNo ratings yet
- 1 Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument11 pages1 Impaired Gas ExchangeKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy StatementDocument2 pagesPhilosophy Statementapi-547276829No ratings yet
- Complicated Grief Therapy For Clinicians: An Evidence Based Protocol For Mental Health PracticeDocument9 pagesComplicated Grief Therapy For Clinicians: An Evidence Based Protocol For Mental Health Practice110780No ratings yet
- Guven 11 Ci Sinif Buraxilis - 1Document3 pagesGuven 11 Ci Sinif Buraxilis - 1mmmdovasma09No ratings yet
- Disorders of Optic Nerve and Visual Pathways: Ipek MidiDocument24 pagesDisorders of Optic Nerve and Visual Pathways: Ipek MidiEcaterina ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Management of Traumatic Iridodialysis with HyphaemaDocument21 pagesManagement of Traumatic Iridodialysis with HyphaemaSyed NabilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patients With FractureDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patients With Fracture_cezca_89% (168)
- Worksheet 3 - 12Document3 pagesWorksheet 3 - 12Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Northern Samar Baseline Report Final 073018Document109 pagesNorthern Samar Baseline Report Final 073018janette borac100% (1)
- Legal Aspects of NursingDocument26 pagesLegal Aspects of NursingJasmin Jacob100% (1)
- Everyday Health Is ImportantDocument2 pagesEveryday Health Is ImportantEllen WrightNo ratings yet
- To Err Is Human A Case Study of Error Prevention in Process IsolationsDocument6 pagesTo Err Is Human A Case Study of Error Prevention in Process Isolationsairbuk doeingNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Dissertation Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesOccupational Therapy Dissertation Literature ReviewgjosukwgfNo ratings yet
- Cravings and Fad Diet WorkshopDocument19 pagesCravings and Fad Diet Workshopapi-487922974No ratings yet
- Posterior Uveitis HandoutDocument4 pagesPosterior Uveitis Handoutdanny wiryaNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit Planner Sample: Powering Your CurriculumDocument14 pagesMYP Unit Planner Sample: Powering Your CurriculumNigarNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior and The Social Environment I 1590508065Document1,310 pagesHuman Behavior and The Social Environment I 1590508065prim100% (1)
- Effects of Extra-Curricular Activities On The Academic Performance of BCAS Junior High School This S.Y 2017-2018Document51 pagesEffects of Extra-Curricular Activities On The Academic Performance of BCAS Junior High School This S.Y 2017-2018Maxine MarundanNo ratings yet
- Nature of Request No. of Cases Amount: Summary of Daily Cases Received Nueva Vizcaya Branch AUGUST 8, 2019Document25 pagesNature of Request No. of Cases Amount: Summary of Daily Cases Received Nueva Vizcaya Branch AUGUST 8, 2019Aileen EddubaNo ratings yet
- Brosur Zurich Travel Insurance English VersionDocument2 pagesBrosur Zurich Travel Insurance English VersionDhiany Nadya UtamiNo ratings yet
- Neurofeedback Technician Module 2 TrainingDocument25 pagesNeurofeedback Technician Module 2 TrainingborzupazhuhanNo ratings yet
- Cookbook ExcerptDocument0 pagesCookbook ExcerptchampakNo ratings yet
- OEC WorkbookDocument259 pagesOEC WorkbookAnonymous sWYHWOlbV100% (2)
- IELTS Academic Reading Practice #3Document7 pagesIELTS Academic Reading Practice #32057010349lamNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Health During Clear Aligners Treatment: A Systematic ReviewDocument5 pagesPeriodontal Health During Clear Aligners Treatment: A Systematic ReviewfaouziNo ratings yet
- Iodine SDSDocument8 pagesIodine SDSKike PadillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 HEALTH Q3 - LM - DiseaseDocument66 pagesGrade 8 HEALTH Q3 - LM - Diseaseleomille2100% (1)
- QBD Application For The Pharmaceutical Development ProcessDocument34 pagesQBD Application For The Pharmaceutical Development Processsooho32No ratings yet
- Causes of Hospital Admissions Among Diabetic Patients in BoholDocument81 pagesCauses of Hospital Admissions Among Diabetic Patients in BoholFrancis ButalNo ratings yet
- Negative: What Does It Mean To Have A Test Result?Document2 pagesNegative: What Does It Mean To Have A Test Result?Sophy SvecNo ratings yet
- Practical Raptor Nutrition Neil Forbes PDFDocument9 pagesPractical Raptor Nutrition Neil Forbes PDFWisnu JuliastitoNo ratings yet