Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Centella Asiatica 5% (Invivo For Moist)
Centella Asiatica 5% (Invivo For Moist)
Uploaded by
produksi roiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Centella Asiatica 5% (Invivo For Moist)
Centella Asiatica 5% (Invivo For Moist)
Uploaded by
produksi roiCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Paper
Moisturizing and Antiinflammatory Properties of
Cosmetic Formulations Containing Centella asiatica
Extract
A. RATZ-ŁYKO*, J. ARCT AND K. PYTKOWSKA
Department of Cosmetic Chemistry, Faculty of Cosmetology, Academy of Cosmetics and Health Care, 00-252 Warsaw,
Poland
Ratz-Łyko, et al.: Cosmetic Properties of Centella asiatica
Centella asiatica extract is a rich source of natural bioactive substances, triterpenoid saponins, flavonoids, phenolic
acids, triterpenic steroids, amino acids and sugars. Thus, many scavenging free radicals, exhibit antiinflammatory
activity and affect on the stratum corneum hydration and epidermal barrier function. The aim of the present study was
to evaluate the in vivo moisturizing and antiinflammatory properties of cosmetic formulations (oil-in-water emulsion
cream and hydrogel) containing different concentrations of Centella asiatica extract. The study was conducted
over four weeks on a group of 25 volunteers after twice a day application of cosmetic formulations with Centella
asiatica extract (2.5 and 5%, w/w) on their forearms. The measurement of basic skin parameters (stratum corneum
hydration and epidermal barrier function) was performed once a week. The in vivo antiinflammatory activity based
on the methyl nicotinate model of microinflammation in human skin was evaluated after four weeks application of
tested formulations. In vivo tests formulations containing 5% of Centella asiatica extract showed the best efficacy
in improving skin moisture by increase of skin surface hydration state and decrease in transepidermal water loss
as well as exhibited antiinflammatory properties based on the methyl nicotinate model of microinflammation in
human skin. Comparative tests conducted by corneometer, tewameter and chromameter showed that cosmetic
formulations containing Centella asiatica extract have the moisturizing and antiinflammatory properties.
Key words: Centella asiatica, stratum corneum hydration, epidermal barrier function, antiinflammatory properties
Centella asiatica (Linn.) Urban (also known by such as asiatic, centellic, madecassic and terminolic
common names as: Gotu kola, Indian pennywort acids [6,7]. Among the various chemicals the most
(ang.), Hydrocotyle asiatique (fr.) or Indischer important chemicals due to their dermatological
Wassernabel (ger.)) is a species belonging to the and pharmacological activity are, asiaticoside,
Apiaceae family (formerly Umbelliferae), genus madecasosside, asiatic acid and madecassic acid[8].
Centella (Linn.). Centella asiatica species is divided Centella asiatica also contains other components,
into three varieties, Centella asiatica var. typica, including flavonoids (quercetin and its glycoside,
Centella asiatica var. abyssinica, Centella asiatica rutin, kaempferol and its glycoside, catechin,
var. floridana, which growing in different regions, naringenin, apigenin, luteolin, astragalin glycoside
having different chemical composition and different and free form), phenolic acids (chlorogenic acid
morphology of leaves[1-4]. Centella asiatica is mainly and its isomers and derivatives), triterpenic steroids
found in India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, (stigmasterol, sitosterol), amino acids, sugars, vitamins
South Africa and Eastern Europe [5] . The most
important constituents isolated from C. asiatica are This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative
Commons Attribution‑NonCommercial‑ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows
primarily ursane- and oleanane-type pentacyclic others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non‑commercially, as long as the
triterpenoid saponins (up to 8%), also known as author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
centelloids[6]. These terpenoids include asiaticoside, For reprints contact: reprints@medknow.com
centelloside, madecassoside, moside, thankuniside,
Accepted 05 February 2016
sceffoleoside, centellose, as well as triterpenic acids Revised 17 November 2015
*Address for correspondence Received 11 December 2014
E-mail: anna.ratz-lyko@wszkipz.pl Indian J Pharm Sci 2016;78(1):27‑33
© 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences | Published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow 27
www.ijpsonline.com
and essential oils and other volatile constituents in for 24 h on a waterbath shaker with a frequency of
about 0.1%[9,10]. It has been known for a long time 200 cycles per min (Elpin-Plus, Lubawa, Poland). The
that Centella asiatica compounds exhibit a broad obtained extracts were filtrated through Whatman filter
spectrum of therapeutic activity. The most important paper (no. 1; GE Healthcare, Maidstone, UK). The
are antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antimicrobial and extracts were collected and used for preparation of
anticarcinogenic activity. In dermatology Centella cosmetic products.
asiatica is used in treatment of small wounds,
hypertrophic wounds as well as burns, psoriasis For evaluation of cosmetic properties of Centella
and scleroderma [8]. It was observed that Centella asiatica a simple recipes of cosmetic emulsion O/W
asiatica preparations can stimulate the fibroblast and hydrogel were developed (Tables 1 and 2). The
proliferation and activate the SMAD signaling concentration of the Centella asiatica extract in the
pathway therefore can increase the type I collagen tested cosmetics was 2.5 and 5%. The O/W emulsion
production as well as decrease in formation of stretch was prepared by heating separately the water and oily
marks and inflammatory reactions. Moreover, the phases (80°), followed by homogenization for 1.5 min
constituents isolated from C. asiatica can increase at 1500 rpm (Heidolph, Germany) and mixing by
the microcirculation of blood in the skin and prevent mechanic stirrer (IKA® RW16 Basic, Germany) to
excessive accumulation of fat in cells[11-14]. As for achieve a temperature of 30°. Then, the extract was
a cosmetic purpose, Centella asiatica is used as an added. The hydrogel was prepared by mixing carbomer
active compound in skin care preparations because with water and Centella asiatica extract. The bases
its antioxidant, antiinflammatory, anticellulite and (placebo) were prepared without extract. All samples
antiaging activity. Therefore Centella asiatica extract were freshly prepared and had the pH values of 5.5.
rich in triterpenes is a valuable raw material with a
broad spectrum of cosmetic action. The group of twenty five healthy volunteers between
18 and 55 years participated in the study after
The aim of this study was to evaluate the cosmetic giving written consent. Study was approved by
properties of Centella asiatica cream and hydrogel. ethics committee. Standardized 48 h patch test of
The researches included the impact of Centella the prepared cosmetics was carried out. The test
asiatica preparations on the skin surface hydration involves the application of the examined emulsion and
state, barrier function of the stratum corneum and
antiinflammatory properties based on the methyl
nicotinate model of microinflammation in human TABLE 1: THE EMULSION RECIPE
INCI name Producer Amount (%) Trade name
skin. In the present study, we used in vivo techniques
Glyceryl stearate Cognis 4 Cutina GSM
(corneometer, tewameter and chromameter) to evaluate Ceteareth ‑ 12 Cognis 1.5 Emulgin B1
the effects of cosmetic formulations containing Ceteareth ‑ 20 Cognis 1.5 Emulgin B2
different concentrations of Centella asiatica extract Caprylic/capric triglyceride Cognis 3 Myritol
(2.5 and 5%) on skin hydration, transepidermal water Octyldodecanol Cognis 3 Eutanol G
loss (TEWL) and microinflammation in human skin Cetyl alcohol Cognis 4 Speziol C
16 Pharma
after a four weeks period of double daily application.
Centella asiatica extract Cognis 3 Herbalia®
Centella
MATERIALS AND METHODS Phenoxyethanol, Lotioncrafter 0.25 LiquaPar
metyloparaben, ethylparaben, Optima
propylparaben, butylparaben
Dried extract of Centella asiatica (Herbalia® Aqua 79.75 Water
Centella) containing 10% active constituents
(madecassic acid, asiatic acid, asiaticoside) were TABLE 2: THE HYDROGEL RECIPE
purchased from Cognis Iberia s.l. (Spain). INCI name Producer Amount (%) Trade name
Carbomer Aqua Noveon 10 Carbopol
The dried Centella asiatica was extracted with ethanol Centella asiatica extract Cognis 3 Herbalia® Centella
Tea POCh q.s. Triethanoloamine
(70%, by volume). The extraction was performed
Aqua ‑ 96 Water
with a 10:1 solvent-raw material ratio (by volume INCI: International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients, q.s.: quantity
per mass) in 150-ml flasks at a temperature of 25° sufficient
28 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences January - February 2016
www.ijpsonline.com
hydrogel to the skin under adhesive tape, which was The measurements (by tewameter, pH-meter and
then left in place for 48 h. The results demonstrated chromameter) were performed at 5, 15, 30, 60, 90, and
that topical application of the emulsion and hydrogel 120 min after remove of the methyl nicotinate compress,
with Centella asiatica extract is not associated with respectively. All measurements were performed in
acute skin irritation or allergic sensitization. The controlled conditions at a temperature of 22-25o and
clinical investigator assessed that the volunteers with an average relative humidity 50%. Prior to the
were in good health and had no dermatological measurements, the volunteers were asked to stay in the
diseases. The in vivo studies for evaluation skin test room for at least 15 min before the measurements,
surface hydration state, barrier function of the stratum so the skin could acclimatize at room conditions. All
corneum and antiinflammatory properties (based on measurements were performed in triplicate.
the methyl nicotinate model of microinflammation in
human skin) of tested preparations were performed Statistical analysis:
over a period of four weeks. The first was the phase All results were presented as a mean±standard
consisting of the application of the o/w emulsion deviation of at least three independent experiments
and hydrogel with Centella asiatica extract and (each performed in triplicate). Statistical analysis was
placebo onto the skin areas twice a day for four performed by using Student’s t-test, ANOVA models
weeks. In order to minimize the errors during with Fisher-Snedecor test and Tukey post hoc test.
research the volunteers were asked not to apply any Differences were accepted as statistically significant
cosmetic cream in the tested area two weeks before at P<0.05.
the study was carried out and throughout the test
period. Additionally, solar exposure was forbidden. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The tested areas (3 cm×4 cm) were the forearms
of each volunteers: The inner surface of the left Effect of cosmetic formulations containing Centella
forearm was for emulsions with Centella asiatica asiatica extract in different concentrations on the
extract, the placebo (base cream) was also applied skin surface hydration state and barrier function of
on the inner surface of the left forearm, the inner the stratum corneum was using corneometer and
surface of the right forearm was for hydrogels with tewameter and the results of the long term study
Centella asiatica extract and placebo (hydrogel base), are shown in figs. 1 and 2. In the experiment there
the control areas were on the outer surface of the was observed a significant increase in hydration of
forearms, respectively. The cream and hydrogel were the stratum corneum after the first week application
applied in an uniform layer resulted from applying of tested preparations with 2.5 and 5% of Centella
of 0.1 ml of the tested products by a syringe. The asiatica extract. The best results were observed for
measurements of the skin surface hydration state cosmetic formulations with 5% of Centella asiatica
(Corneometer, Multiprobe MPA5 from Courage and extract. The comparison of emulsion with hydrogel
Khazaka Electronics GmbH, Cologne Germany) and revealed that emulsion with 5% Centella asiatica
barrier function of the stratum corneum (MPA 5 from extract increase in hydration of the stratum corneum
Courage and Khazaka Electronics GmbH, Cologne by 12%, followed by hydrogel with 5% Centella
Germany) were conducted before application the asiatica by 10% in comparison to the control area and
cosmetics and once a week (during 4 weeks). placebo (P<0.05). The average value of hydration of
the stratum corneum after four weeks application of
Additionally, after four weeks the treated and control tested emulsion and hydrogel increased significantly
areas were measured by tewameter (MPA 5 from in compared to baseline (control area) and placebo
Courage and Khazaka Electronics GmbH, Cologne (P<0.05). It was observed that emulsion with 5%
Germany) to assess barrier function of the stratum Centella asiatica extract effect on increase in skin
corneum, pH-meter (Mettler-Toledo Sp. z o.o.) for hydration by 25%, followed by hydrogel with 5%
determination of the skin pH after skin irritation by Centella asiatica extract by 22%. The experiment
methyl nicotynate and chromameter (Chroma Meter, realized on the basis of the analysis of variance
Konica Minolta, Osaka, Japan) for determination and statistically testing using Fisher’s-Snedecora
of the skin irritation after application of methyl test has found that (α=0.05) on the increase in skin
nicotynate. Then, an aqueous solution of the methyl hydration affected significantly the duration, extract
nicotinate (0.5%, m/v, Merck) was applied for 5 min. concentration and kind of the tested formulations.
January - February 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 29
www.ijpsonline.com
Fig. 2: Change of the transepidermal water loss.
Fig. 1: Hydration of stratum corneum. Change of the transepidermal water loss (TEWL [g/h/m2]) after
Hydration of stratum corneum after application of cosmetic application of cosmetic formulations containing different
formulations containing different concentrations of Centella asiatica concentrations of Centella asiatica extract and placebo. Data
extract and placebo. Data represent the mean values±standard represent the mean values±standard deviation. Student’s t-test:
deviation. Student’s t-test: P<0.05. Where: -●- control; -▲- placebo; P<0.05. Where: -●- control; -▲- placebo; -■- emulsion with 5% of
-■- emulsion with 5% of Centella asiatica extract; -*- emulsion with Centella asiaticaextract; -*- emulsion with 2.5% of Centella asiatica
2.5% of Centella asiatica extract; -♦- hydrogel with 5% of Centella extract; -♦- hydrogel with 5% of Centella asiatica extract; -×-hydrogel
asiatica extract; -×-hydrogel with 2.5% of Centella asiatica extract. with 2.5% of Centella asiatica extract.
The Tukey post hoc test (α=0.05) performed that four weeks the average value of TEWL was differ
the average rate of increase in skin hydration after significantly compared to baseline (control field)
application of moisturizing emulsion with 5% of and placebo. The decrease in transepidermal water
Centella asiatica extract was significantly differ in loss after application of emulsion and hydrogel with
comparison to the average value after the application Centella asiatica extract in different concentrations
of moisturizing emulsion without the extract. The was as followed. The emulsion and hydrogel with 5%
growth of hydration of the stratum corneum was of Centella asiatica extract showed 18 and 15%, the
stable. This is the evidenced that cosmetic with emulsion and hydrogel with 2.5% of Centella asiatica
Centella asiatica extract may affect significantly on extract have showed 10 and 8%, and placebo showed
the increase in hydration of the stratum corneum. 5% in comparison to the control area (P<0.05),
That is primarily bound to the presence in the respectively. The decrease in TEWL after application
Centella asiatica triterpene saponins a hydrophilic of the emulsions was mainly related to the presence
sugar chain (glycone) mainly glucose and rhamnose in the Centella asiatica extract the substances which
that have the ability to bind water within an occlusive can bind water on the stratum corneum surface
layer[1,15]. The increase in hydration in comparative by forming an occlusive hydrophilic film and can
tests conducted by corneometer was also observed by improve the state of the epidermal barrier, for
Morganti et al.[16] example sugars, saponins and polyphenols[1,9,10,15,17].
The effect of emulsion and hydrogel with Centella
The measurement of the epidermal barrier function asiatica extract on the epidermal barrier function and
was carried out on a group of 25 volounteers during hydration of the stratum corneum has not been widely
four weeks period of double daily applications of the studied. The present results indicate that the emulsion
emulsion and hydrogel with Centella asiatica extract with Centella asiatica extract has a significant impact
and placebo. The best results were observed for on the skin hydratation and epidermal barrier function,
cosmetic formulations with 5% of Centella asiatica especially on the epidermal barrier tightness, which is
extract. The results of tewameter mesurements in attributed to the presence of carbohydrates and natural
the long term study are shown in fig. 2. After the antioxidants such as saponins, flavonoids and phenolic
first week application of tested cosmetics there was compounds[1,17]. In in vivo studies the emulsion with
observed a significant decrease in transepidermal 5% of Centella asiatica extract showed the best
water loss, for emulsion with 5% of Centella asiatica effect on the skin hydration and the epidermal barrier
extract by 8%, followed by hydrogel with 5% of function. The effect of the emulsion with Centella
Centella asiatica extract 6%, emulsion with 2.5% of asiatica extract on the skin hydration and epidermal
Centella asiatica extract by 5%, hydrogel with 2.5% barrier function is significant and comparable with
of Centella asiatica extract by 4% and placebo by another plants[18]. Therefore, it can be concluded that
1% in comparison to the control area (P<0.05). After the cosmetics with Centella asiatica extract may
30 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences January - February 2016
www.ijpsonline.com
affect on the increase in hydration of the stratum (Table 3) in comparison to the control area and the
corneum and the improvement of the epidermal placebo. Moreover, the best results (decrease of
barrier function, and thus have potential application the a* parameter value, decrease in TEWL value
in moisturizing, protective and antiaging cosmetics[19]. and decrease in skin pH value) were observed after
the application of emulsion with 5% of Centella
The in vivo evaluation of antiinflammatory and asiatica extract, followed by hydrogel with 5%
antioxidant properties of cosmetic formulations of Centella asiatica extract (P<0.05). Thus, it has
containing Centella asiatica extract in different been hypothesized that the emulsion and hydrogel
concentrations were made based on the methyl with 5% of Centella asiatica extract significantly
nicotinate model of microinflammation in human influence on increase in the regenerative capacity
skin [20]. Methyl nicotinate is known to induce the of the epidermal barrier and alleviating the skin
release of prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) resulting in irritation (figs. 3 and 4). The results indicated that
localized erythema within 30 min after topical the tested cosmetic formulations demonstrate the
application to human skin, the release of nitric oxide antiinflammatory activity, which is associated with
from endothelial cells keratinocytes and human dermal the presence of the saponins. The antiinflammatory
microvascular as well as an increase in transepidermal properties of Centella asiatica extract are related
water loss (TEWL) and skin pH[21-23]. This method to the saponins especially asiaticoside ability to
based on the illumination of the skin surface by a inhibit of the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase
pulsed xenon lamp and analysis the skin color by activity and proinflammatoty cytokines inhibition
measuring the reflectance spectrophotometer using as well as saponins antioxidant activity [1,8,13]. The
the CIE L*a*b* colour space parameters. For the irritation after application of methyl nicotinate is
measurement of the skin redness (erythema) only the related to the activation of cyclooxygenase and
CIE a* component was observed[24]. prostaglandin synthesis D2, actuating in release of
the endoperoxydase and free radicals in the skin. This
The results of the in vivo studies showed that the cause a local erythema, release of the nitric oxide
emulsion and hydrogel with Centella asiatica extract from endothelial keratinocyte cells and human dermal
have a protective effect on the skin and may reduce microvascular as well as increased in transepidermal
its sensitivity to irritants. The results of tewameter water loss and skin pH value [21-24]. Therefore, the
and chromameter mesurements are shown in figs. 3-6. active substances contained in Centella asiatica
For the all applied cosmetics with Centella asiatica extract, especially saponins, flavonoids and phenolic
extract it was observed the statistically significant acid showing antioxidant and antiinflammatory
(α=0.05) reduction of erythema (decrease of the activity, could affect on the reduction of the
a* parameter value) (figs. 3 and 4) and decrease erythema and also help to improve the skin barrier
in TEWL value (figs. 5 and 6) and skin pH value function (decrease in TEWL and pH value), which
Fig. 3: Changes in the skin redness (erythema) by emulsion. Fig. 4: Changes in the skin redness (erythema) by hydrogel.
Change of the a* parameter - the skin redness (erythema) measured Change of the a* parameter - the skin redness (erythema) measured
by CIE L*a*b* colour space parameters (Chroma Meter, Konica by CIE L*a*b* colour space parameters (Chroma Meter, Konica
Minolta, Osaka, Japan) after topical application of methyl nicotynate, Minolta, Osaka, Japan) after topical application of methyl nicotynate,
emulsions containing different concentrations of Centella asiatica emulsions containing different concentrations of Centella asiatica
extract and placebo. Data represent the mean values±standard extract and placebo. Data represent the mean values±standard
deviation. Student’s t-test: P<0.05. Where: -♦- control; -▲- placebo; deviation. Student’s t-test: P<0.05. Where: -♦- control; -▲- placebo;
-■- methyl nicotynate; -●- emulsion with 2.5% of Centella asiatica -■- methyl nicotynate; -●- hydrogel with 2.5% of Centella asiatica
extract; -*-emulsion with 5% of Centella asiatica extract. extract; -*- hydrogel with 5% of Centella asiatica extract.
January - February 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 31
www.ijpsonline.com
TABLE 3. CHANGE OF THE SKIN PH AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF METHYL NICOTYNATE, EMULSION AND
HYDROGEL WITH CENTELLA ASIATICA EXTRACT AND PLACEBO
Formulation Before 5 min 15 min 30 min 60 min 90 min 120 min
Emulsion with 5% of Centella asiatica 5.53±0.30 11.65±0.80 10.50±0.75 8.50±0.55 7.85±0.65 6.65±0.55 5.65±0.50
Emulsion with 2.5% of Centella asiatica 5.50±0.25 11.70±0.25 11.35±0.70 9.25±0.55 8.50±0.55 7.45±0.45 6.50±0.75
Hydrogel with 5% of Centella asiatica 5.55±0.30 11.75±0.65 11.25±0.75 9.10±0.75 8.30±0.55 6.90±0.50 6.10±0.50
Hydrogel with 2.5% of Centella asiatica 5.50±0.25 11.65±0.25 11.45±0.70 9.35±0.55 8.60±0.55 7.35±0.45 6.80±0.75
Placebo 5.53±0.25 12.53±0.75 12.35±0.65 12.20±0.75 11.85±0.50 11.50±0.55 11.35±0.50
Control (area treated with MN only) 5.50±0.30 13.25±0.55 13.20±0.75 13.15±0.50 12.85±0.50 11.50±0.75 10.80±0.85
Control (not treated area) 5.55±0.30 5.55±0.25 5.45±0.25 5.55±0.25 5.50±0.35 5.50±0.25 5.53±0.25
MN: Methyl nicotinate
Fig. 5: Change of the transepidermal water loss by emulsion. Fig. 6: Change of the transepidermal water loss by hydrogel.
Change of the transepidermal water loss (TEWL [g/h/m2]) after Change of the transepidermal water loss (TEWL [g/h/m2]) after
topical application of methyl nicotynate, emulsions containing topical application of methyl nicotynate, emulsions containing
different concentrations of Centella asiatica extract and placebo. different concentrations of Centella asiatica extract and placebo.
Data represent the mean values±standard deviation. Student’s t-test: Data represent the mean values±standard deviation. Student’s t-test:
P<0.05. Where: -♦- control; -▲- placebo; -■- methyl nicotynate; -×- P<0.05. Where: -♦- control; -▲- placebo; -■- methyl nicotynate; -×-
emulsion with 2.5% of Centella asiatica extract; -●- emulsion with hydrogel with 2.5% of Centella asiatica extract; -●- hydrogel with
5% of Centella asiatica extract. 5% of Centella asiatica extract.
is associated with the fast skin return to homeostasis skin moisture by increase of skin surface hydration
after exposure on irritants. As previous in vitro studies state and decrease in transepidermal water loss
have shown saponins from Centella asiatica extract (TEWL) as well as antiinflammatory properties based
have the ability to chelate metal ions, this property on the methyl nicotinate model of microinflammation
is also associated with the ability of saponins to in human skin.
inhibit the activity of enzymes by the formation of
complexes with metals that present in the active On the basis of the obtained results it may be
centre and also by binding through sigma bonds concluded that cosmetic formulations containing
of the compounds that are cofactors for enzymes. Centella asiatica extract have the moisturizing
Also flavonoids and phenolic compounds from and antiinflammatory properties. Centella asiatica
Centella asiatica extract have been shown to possess extract is an effective ingredient not only in
antilipoxygenase and antioxidant activities[25]. antiaging cosmetics but also for improving skin
hydration. Therefore, Centella asiatica can be used
Therefore, the topical application of cosmetic in moisturizing cosmetic formulations and also to
formulations containing Centella asiatica extract can complement the treatment of dry and sensitive skin.
be suggested as a possible strategy to prevent and
modulate oxidative skin damages. The results showed Acknowledgements:
that the emulsion and hydrogel with Centella asiatica The research was funded from our own source.
extract was able to decrease, to a statistically significant
extent (P<0.05), the skin redness, TEWL and pH value Financial support and sponsorship:
in comparison to the control area and placebo. Nil.
Formulations containing different concentrations of Conflicts of interest:
Centella asiatica extract showed efficacy in improving There are no conflicts of interest.
32 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences January - February 2016
www.ijpsonline.com
REFERENCES 14. Flynn TC, Petros J, Clark RE, Viehman GE. Dry skin and moisturizers.
Clin Dermatol 2001;19:387-92.
15. Gioia F, Celleno L. The dynamics of transepidermal water loss (TEWL)
1. James JT, Dubery IA. Pentacyclic triterpenoids from the medicinal herb,
from hydrated skin. Skin Res Technol 2002;8:178-86.
Centella asiatica (L.) urban. Molecules 2009;14:3922-41.
16. Morganti P, Celleno L, Vasselli A. A new transdermal delivery cosmetic
2. Karting T. Clinical applications of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. In:
system to control the skin localized lipodystrophy. J Appl Cosmetol
Craker LE, Simon JE, editors. Herbs, Species, and Medicinal Plants:
1999;13:15-20.
Recent Advances in Botany, Horticulture, and Pharmacology. Vol. 3.
Phoenix, AZ: Oryx Press; 1988. p. 145-63. 17. Camargo Junior FB, Gaspar KR, Gonçalves PM, Campos M. Immediate
3. Sushma T, Sangeeta G, Gambir IS. Centella asiatica: A concise and long-term effects of polysaccharides-based formulations on human
drug review with probable clinical uses. J Stress Physiol Biochem skin. Braz J Pharm Sci 2012;48:547-50.
2011;7:39-44. 18. Dal’Belo SE, Gaspar LR, Maia Campos PM. Moisturizing effect
4. Jamil SS, Nizami Q, Salam M. Centella asiatica (Linn.) urban. A of cosmetic formulations containing Aloe vera extract in different
review. Nat Prod Radiance 2007;6:158-70. concentrations assessed by skin bioengineering techniques. Skin Res
5. Brinkhaus B, Lindner M, Schuppan D, Hahn EG. Chemical, Technol 2006;12:241-6.
pharmacological and clinical profile of the East Asian medical plant 19. Hashizume H. Skin aging and dry skin. J Dermatol 2004;31:603-9.
Centella asiatica. Phytomedicine 2000;7:427-48. 20. Vertuani S, Ziosi P, Solaroli N, Buzzoni V, Carli M, Lucchi E, et al.
6. James J, Dubery I. Identification and quantification of triterpenoid Determination of antioxidant efficacy of cosmetic formulations by non-
centelloids in Centella asiatica (L.) urban by densitometric TLC. J invasive measurements. Skin Res Technol 2003;9:245-53.
Planar Chromatogr 2011;24:82-7. 21. Duteil L, Queille C, Poncet M, Ortonne JP, Czernielewski J. Objective
7. Hashim P, Sidek H, Helan MH, Sabery A, Palanisamy UD, Ilham M. assessment of topical corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
Triterpene composition and bioactivities of Centella asiatica. Molecules drugs in methyl-nicotinate-induced skin inflammation. Clin Exp
2011;16:1310-22. Dermatol 1990;15:195-9.
8. Bylka W, Znajdek-Awizen P, Studzinska-Sroka E, 22. Treffel P, Gabard B. Feasibility of measuring the bioavailability of
Danczak-Pazdrowska A, Brzezinska M. Centella asiatica in topical ibuprofen in commercial formulations using drug content
dermatology: An overview. Phytother Res 2014;28:1117-24. in epidermis and a methyl nicotinate skin inflammation assay. Skin
9. Duke JA. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, Florida: Pharmacol Physiol 1993;6:268-75.
CRC Press; 2002. p. 344-6. 23. Yarosh DB, Galvin JW, Nay SL, Peña AV, Canning MT,
10. Mohd Zainol MK, Abdul-Hamid A, Abu Bakar F, Pak Dek S. Effect Brown DA. Anti-inflammatory activity in skin by biomimetic of
of different drying methods on the degradation of selected flavonoids Evodia rutaecarpa extract from traditional Chinese medicine. J Dermatol
in Centella asiatica. Int Food Res J 2009;16:531-7. Sci 2006;42:13-21.
11. Lee J, Jung E, Kim Y, Park J, Park J, Hong S, et al. Asiaticoside induces 24. Clarys P, Alewaeters K, Lambrecht R, Barel AO. Skin color
human collagen I synthesis through TGFbeta receptor I kinase (TbetaRI measurements: Comparison between three instruments: The
kinase)-independent Smad signaling. Planta Med 2006;72:324-8. Chromameter(R), the DermaSpectrometer(R) and the Mexameter(R).
12. Shukla A, Rasik AM, Dhawan BN. Asiaticoside-induced elevation of Skin Res Technol 2000;6:230-8.
antioxidant levels in healing wounds. Phytother Res 1999;13:50-4. 25. George M, Joseph L. Anti-allergic, anti-pruritic, and anti-inflammatory
13. Bylka W, Znajdek-Awizen P, Studzinska-Sroka E, Brzezinska M. Centella activities of Centella asiatica extracts. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern
asiatica in cosmetology. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2013;30:46-9. Med 2009;6:554-9.
January - February 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 33
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- NutraceuticalDocument17 pagesNutraceuticalDrFirdous DarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- IT Pharma CompaniesDocument12 pagesIT Pharma Companiesshriya shettiwarNo ratings yet
- Farmacos Agonistas y Antagonistas ColinergicosDocument31 pagesFarmacos Agonistas y Antagonistas ColinergicosAngel ES91% (11)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- POE 5 Expendio de Productos Farmacéuticos y Dispositivos Médicos.Document3 pagesPOE 5 Expendio de Productos Farmacéuticos y Dispositivos Médicos.Hurtado Gomez Abad86% (7)
- Debiopharm - Company-ProfileDocument42 pagesDebiopharm - Company-ProfileCarmen AdlerNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Proyecto de La Farmacia - CompletoDocument46 pagesProyecto de La Farmacia - CompletoRoxana Nuñez Ayala100% (1)
- Amgen Product Return PolicyDocument5 pagesAmgen Product Return PolicyGamer BuddyNo ratings yet
- Latex Template-SDIDocument5 pagesLatex Template-SDIEka LimNo ratings yet
- SebumDocument10 pagesSebumEka LimNo ratings yet
- Dermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesDermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaEka LimNo ratings yet
- Dermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesDermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaEka LimNo ratings yet
- Krim Anti AgingDocument106 pagesKrim Anti AgingEka LimNo ratings yet
- 276 467 1 SMDocument9 pages276 467 1 SMEka LimNo ratings yet
- Medication Errors: BY DR - Divya Ashok Kulkarni. Pharm DDocument68 pagesMedication Errors: BY DR - Divya Ashok Kulkarni. Pharm DShrenil LagadNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document4 pagesLab 2SHRUTI VERMANo ratings yet
- Price List DFMDocument12 pagesPrice List DFMHafiidha RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 10 - Integración PsicofarmacológicaDocument56 pages10 - Integración PsicofarmacológicaKaren CuencaNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Cdmo 14-01-2011Document4 pagesAdvertisement Cdmo 14-01-2011Deepak TiwariNo ratings yet
- 8 - DR S C Mathur.. Notes PDFDocument86 pages8 - DR S C Mathur.. Notes PDFAnkitTiwariNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacino 500 MGDocument3 pagesCiprofloxacino 500 MGRomina GalleguillosNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Agents: VbanetDocument26 pagesAnesthetic Agents: Vbanetdona0010100% (1)
- Adrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingDocument13 pagesAdrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- Preparados HomeopáticosDocument5 pagesPreparados HomeopáticosMarcela GomezNo ratings yet
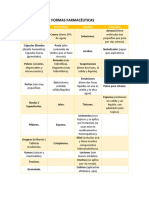
- Clasificación de Formas FarmacéuticasDocument2 pagesClasificación de Formas FarmacéuticasZúñiga EstherNo ratings yet
- Ivomec F Inyectable BovinosDocument3 pagesIvomec F Inyectable BovinosFernando Restrepo GalvisNo ratings yet
- Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitors and Inducers - UpToDateDocument2 pagesCytochrome P450 3A Inhibitors and Inducers - UpToDatemehrin.mahbodNo ratings yet
- Non-Depolarising Blockers Depolarising Blockers Botox: Anticholinesterase IMPORTANTDocument2 pagesNon-Depolarising Blockers Depolarising Blockers Botox: Anticholinesterase IMPORTANTjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- M VI FarmacologiaDocument19 pagesM VI Farmacologiarony condeñaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.-Vías de AdministraciónDocument16 pages3.1.-Vías de AdministraciónTheatronNo ratings yet
- Update On Management of BPSDDocument50 pagesUpdate On Management of BPSDMuhammad AfifuddinNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Business Management: Group 9Document25 pagesPharmaceutical Business Management: Group 9Dhanashree TeliNo ratings yet
- Examen FarmacoDocument4 pagesExamen FarmacoHuang Shan LinNo ratings yet
- 1397-Texto Del Artículo-3687-1-10-20140204Document14 pages1397-Texto Del Artículo-3687-1-10-20140204Katerin Rondo TolentinoNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem SyllabusDocument20 pages6th Sem SyllabusManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga HD Juni 2020Document34 pagesDaftar Harga HD Juni 2020Kean KhamidaaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument42 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentEman ElakkadNo ratings yet