Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marie Curie
Uploaded by
Izmir CokajCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marie Curie
Uploaded by
Izmir CokajCopyright:
Available Formats
Marie Curie:
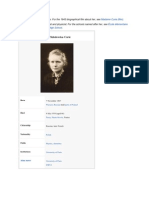
Marie Curie, born Maria Skłodowska on November 7, 1867, in Warsaw, Poland, was a
pioneering physicist and chemist. She is best known for her groundbreaking research on
radioactivity, a term she coined. Marie Curie's work led to the development of X-ray
machines for medical use and, more notably, the discovery of two radioactive elements,
polonium and radium.
In 1903, she became the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, sharing the prize in Physics
with her husband Pierre Curie and another scientist, Henri Becquerel, for their work on
radioactivity. Later, in 1911, she received a second Nobel Prize, this time in Chemistry,
for her isolation of radium and polonium. Marie Curie remains the only person to win
Nobel Prizes in two different scientific fields.
Despite her pioneering work, Marie Curie faced discrimination as a woman in the male-
dominated scientific community. She persevered and became a professor at the
Sorbonne, making her the first woman to hold that position.
Tragically, Marie Curie's extensive exposure to radiation during her research ultimately
led to her early death in 1934, but her legacy lives on. Her research not only advanced
our understanding of radioactivity but also paved the way for medical treatments such
as radiation therapy.
You might also like
- Marie Curie - Quotes Collection: Biography, Achievements And Life LessonsFrom EverandMarie Curie - Quotes Collection: Biography, Achievements And Life LessonsNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Unit 6Document5 pagesCritical Thinking Unit 6leongeladoNo ratings yet
- Discovery of RadioactivityDocument6 pagesDiscovery of RadioactivityJariza Daryl Tamang MejiaNo ratings yet
- Marie Skłodowska Curie (Salomea SkłodowskaDocument3 pagesMarie Skłodowska Curie (Salomea SkłodowskaYin XuanNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie: Pioneer in RadioactivityDocument4 pagesMarie Curie: Pioneer in RadioactivityNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Writing Task Marie CurieDocument1 pageWriting Task Marie CurieleongeladoNo ratings yet
- Madame CurieDocument5 pagesMadame CurieShaheer MujtabaNo ratings yet
- MARIE CURIE FyqDocument7 pagesMARIE CURIE FyqIrene Capel QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Script & Summary of Marie CurieDocument2 pagesScript & Summary of Marie CurieGrace Victoria Poo 1428041No ratings yet
- ,,maria Składowska - Curie''Document12 pages,,maria Składowska - Curie''AgiNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie Biography: SynopsisDocument4 pagesMarie Curie Biography: SynopsisVan Ly100% (1)
- Who Was Marie CurieDocument3 pagesWho Was Marie CurieDenisa DamianNo ratings yet
- The Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseDocument4 pagesThe Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseMarta HrynyovskaNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie: Early LifeDocument2 pagesMarie Curie: Early LifeKalaivani JsNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument2 pagesMarie CurieBhaskarNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument3 pagesMarie CurieAriva JasmineNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument3 pagesMarie Curiemay ehabNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie BiographyDocument5 pagesMarie Curie BiographyRenjie OliverosNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie's Life and DiscoveriesDocument2 pagesMarie Curie's Life and Discoveriesalexandra_6No ratings yet
- Marie Curie - BiographyDocument1 pageMarie Curie - BiographyFlores Velázquez MarianaNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie: Marie Salomea Skłodowska Curie (Born Maria Salomea Skłodowska 7 November 1867 - 4 JulyDocument1 pageMarie Curie: Marie Salomea Skłodowska Curie (Born Maria Salomea Skłodowska 7 November 1867 - 4 JulyAsher MsheliaNo ratings yet
- Early Life: Born: Died: Nationality: Famous For: AwardsDocument2 pagesEarly Life: Born: Died: Nationality: Famous For: AwardsNur Ayunni KhafizNo ratings yet
- Who Is She?: Marie Was A Famous Physician For Her Work On Radioactivity and She Won The Nobel Prize TwiceDocument11 pagesWho Is She?: Marie Was A Famous Physician For Her Work On Radioactivity and She Won The Nobel Prize TwiceLiss ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Marie SklodowskaDocument3 pagesMarie SklodowskaMa Michelle Nica DmNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument1 pageMarie CurieAnvi bNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument2 pagesMarie CurieSara Rodriguez RoseroNo ratings yet
- 11 XIA1 SKS Sasing Biografy Marie CurieDocument1 page11 XIA1 SKS Sasing Biografy Marie Curie11 HoganNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie's Groundbreaking Work on RadioactivityDocument5 pagesMarie Curie's Groundbreaking Work on RadioactivityThanh LiêmNo ratings yet
- Biography of Marie CurieDocument2 pagesBiography of Marie CurieSarah Don100% (1)
- Marie CurieDocument6 pagesMarie CurieGabriel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument4 pagesMarie CurieCherrisNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie (Polonia, 1867 - Francia, 1937) : Final Days SinopsisDocument2 pagesMarie Curie (Polonia, 1867 - Francia, 1937) : Final Days SinopsisEffrAa JerEddy PiÑaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Marie CurieDocument3 pagesPresentation - Marie CurieGiovanni MontàNo ratings yet
- MarieDocument9 pagesMarieapi-302661999No ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument5 pagesMarie CurieLucia BonalNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie Was A PolishDocument1 pageMarie Curie Was A PolishYugal KapurNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie Group-08Document5 pagesMarie Curie Group-08Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- Gehendra ShumsherDocument2 pagesGehendra ShumsherAmir MaharjanNo ratings yet
- English WorkDocument4 pagesEnglish WorkGabriela Maria OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie 1867-1934Document42 pagesMarie Curie 1867-1934zmeugaby89No ratings yet
- Crónica OkDocument2 pagesCrónica OkSALOMÉ MELENDEZ MUNOZNo ratings yet
- Sample PassageDocument4 pagesSample PassageAyushi S.No ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument12 pagesMarie CurieDivya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Madame CurieDocument5 pagesMadame CurieВладиславМартьяновNo ratings yet
- MARIA SKłODOWSKA CURIEDocument13 pagesMARIA SKłODOWSKA CURIEKasiaNo ratings yet
- 1.marie CurieDocument4 pages1.marie CurieEdgar Augusto Pedraza GomezNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie: Navigation SearchDocument3 pagesMarie Curie: Navigation SearchSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie by Morgan and OisinDocument7 pagesMarie Curie by Morgan and OisinMrGilmartinNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie BiographyDocument1 pageMarie Curie Biographykarol ceballos100% (1)
- Marie Salomea SkłodowskaDocument1 pageMarie Salomea SkłodowskaChatta NeeladeviNo ratings yet
- Marie Skłodowska Curie (Skłodowska : French: PolishDocument1 pageMarie Skłodowska Curie (Skłodowska : French: PolishAna KowalskaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Biolog I ADocument2 pagesTrabajo Biolog I Alol lolNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie, A Radioactive TaleDocument1 pageMarie Curie, A Radioactive Talearunkk1010No ratings yet
- Marie Curie ProjectDocument2 pagesMarie Curie ProjectMateiPaulNo ratings yet
- Marie Curie Was Born in Warsaw On November 7, 1867. Her Mother Was ADocument2 pagesMarie Curie Was Born in Warsaw On November 7, 1867. Her Mother Was AJames LambNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument6 pagesMarie Curieapi-242267718No ratings yet
- Unit Marie-CurieDocument10 pagesUnit Marie-CurieZara GL -Escritora-Ensayista. Asesora MarketingNo ratings yet
- MARIE CURIE Mas Que DefinitivaDocument7 pagesMARIE CURIE Mas Que DefinitivaIsabella Villanueva GallegoNo ratings yet
- Madame CurieDocument3 pagesMadame CurieUjwala GangaNo ratings yet
- Marie CurieDocument5 pagesMarie Curieapi-309791804No ratings yet