Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diseño de Ejes
Uploaded by
michellereyesbadillo10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Diseño de ejes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views10 pagesDiseño de Ejes
Uploaded by
michellereyesbadillo1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Diseño de ejes
Diseño de elementos mecanicos
▪ Mechanical elements of circular section
▪ They hold pieces that rotate jointly or around them
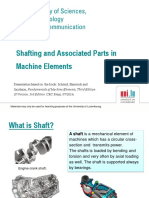
¿Whatare trees
▪ Tree or arrow: rotates transmitting power
and axes? ▪ Shaft: does not transmit power
▪ An axis (shaft) is a set of mechanical devices that
transmit rotary motion and power. It is part of any
mechanical system where power is transmitted from an
electric motor (or another) to other rotating parts of the
system.
▪ Material selection
▪ Construction design (geometric configuration) or
Shaftdesign ▪ Verification of resistance• Static•Fatigue• To dynamic
loads (for example peak loads)
stages ▪ Verification of stiffness•Torsion strain•Bending
deflection•Slope
▪ STEEL (the most used)
▪ Choose initially a carbon steel (low cost) or
▪ SAE 1020 to 1050, for example 1035, 1040, 1045
▪ If the strength criteria dominate the deformations:
select higher strength steels
Common ▪ SAE 3140, 4140 or 4340 alloy steels
materials ▪ Others: 3150, 5140, 1340, 1350 and 8650 Budynas and
Nabett, 2008)
▪ Cast or nodular iron (for parts integrated into the shaft)
▪ Bronzes and stainless steels (for corrosive
environments)
Geometric
configurationsand
details
▪ 1. Determine the speed of rotation of the shaft.
▪ 2. Calculate the torque or power that the shaft must
transmit.
▪ 3. Determine the design of the power transmissions and
specify the place of location.
Procedureto ▪ 4. Specify the location of the support elements (bearing,
bearings)
designa shaft ▪ 5. Propose the geometry for the axis considering the
form of axial position in which each element will be
maintained on the axis and how the power is
transmitted.
▪ .6. Determine the magnitude of the torque that develops
at each point on the axis.
▪ 7. Determine the forces acting on the shaft in the radial
and axial directions.
▪ 8. Resolve the radial forces into their vertical and
horizontal components.
▪ 9. Calculate the reactions in each plane on the supports
Procedureto (bearings).
designa shaft ▪ 10. Determine a design effort.
▪ 11. Analyze each critical point on the shaft to determine
the diameter.
▪ 12.Specify the final dimensions for each axis point
Proposedshaft
dimensions
▪ Gears, sprockets, pulleys, and other items that are
Forcesexertedby supported on a shaft exert forces on the shaft and cause
bending moment. In general, the principles of statics
machine elements and dynamics are used to calculate the forces on a
onshafts particular element.
You might also like
- Shaft DesignDocument37 pagesShaft DesignFarah HumaNo ratings yet
- Shaft DesignDocument73 pagesShaft Designmeenakumari05No ratings yet
- Shaft design procedure stepsDocument2 pagesShaft design procedure stepsPehr Hedström80% (5)
- Design of Shaft PDFDocument73 pagesDesign of Shaft PDFDhruv PancholiNo ratings yet
- ShaftsDocument33 pagesShafts20BME011 HARSHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- LM2.1 FinalDocument47 pagesLM2.1 FinalMADHESWARAN SNo ratings yet
- Machine Design PresentaionDocument24 pagesMachine Design PresentaionAwais RaoNo ratings yet
- Module 3ADocument35 pagesModule 3AShahzaib SalmanNo ratings yet
- Shafts & Couplings: Design and Types in 38 CharactersDocument13 pagesShafts & Couplings: Design and Types in 38 Characterschinnapa reddy reddyNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCBbUzWbifi3HUd2hlv2jClqW1h-MLkfgt7 ek4q4UNn-Lf6zxYt7xUcFMyudSogv6iFTQj76J0WFOChJEeD9Ls5XnmhkehuXoNULGMspr3hsaJCXlYtUi4dYD oMG3j3t1tYtdWZD7Jc2oDocument33 pagesACFrOgCBbUzWbifi3HUd2hlv2jClqW1h-MLkfgt7 ek4q4UNn-Lf6zxYt7xUcFMyudSogv6iFTQj76J0WFOChJEeD9Ls5XnmhkehuXoNULGMspr3hsaJCXlYtUi4dYD oMG3j3t1tYtdWZD7Jc2oShriparno deyNo ratings yet
- Shaft DesignDocument16 pagesShaft DesignOgunsina AdebayoNo ratings yet
- 7.shafts and Shaft ComponentsDocument90 pages7.shafts and Shaft ComponentsAekkasit SenaartNo ratings yet
- MEE342 - Shaft Design PrinciplesDocument27 pagesMEE342 - Shaft Design PrinciplesBrettNo ratings yet
- STTGP - Group 2 Part 2Document19 pagesSTTGP - Group 2 Part 2Achmad Luthfi MuzakkiNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia of Stepped ShaftsDocument11 pagesMoment of Inertia of Stepped ShaftsRakesh Nair A100% (2)
- Gearbox (An Overview)Document26 pagesGearbox (An Overview)Vũ Bùi TuấnNo ratings yet
- Shaft Components Design GuideDocument34 pagesShaft Components Design Guidesayyid alkahfiNo ratings yet
- Design of Shafts and Associated ComponentsDocument14 pagesDesign of Shafts and Associated ComponentsCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Combined Bending and Torsion in ShaftsDocument12 pagesCombined Bending and Torsion in ShaftsRenjin J BrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ShaftDocument21 pagesChapter 1 ShaftRayuth KEATNo ratings yet
- DME and CC Lecture #07 and 08Document20 pagesDME and CC Lecture #07 and 08Raising StarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Shaft Design With SolutionsDocument38 pagesLecture 5 Shaft Design With Solutionsgatoradeqazwsx100% (2)
- Shaft Design Procedure and AnalysisDocument36 pagesShaft Design Procedure and AnalysisashiyNo ratings yet
- LM2 2Document67 pagesLM2 2MADHESWARAN SNo ratings yet
- MACHINE DESIGN Part4Document32 pagesMACHINE DESIGN Part4MADHESWARAN SNo ratings yet
- Design of Shafts and CouplingsDocument10 pagesDesign of Shafts and CouplingsrenoldelsenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PP PDFDocument21 pagesAssignment 2 PP PDFjamesplanetearthNo ratings yet
- ShaftdesignlecDocument10 pagesShaftdesignlecTalha AbbasiNo ratings yet
- 2-Shaft Design ProcedureDocument24 pages2-Shaft Design ProcedureINDER SINGhNo ratings yet
- ME374 Module 2Document57 pagesME374 Module 2Christian Breth BurgosNo ratings yet
- Shaft 141118092812 Conversion Gate02Document14 pagesShaft 141118092812 Conversion Gate02Aso SerwanNo ratings yet
- FORCES ON SHAFTS FROM MACHINE ELEMENTSDocument13 pagesFORCES ON SHAFTS FROM MACHINE ELEMENTSTaha Elhasseen AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Machine Shaft Design GuideDocument48 pagesMachine Shaft Design GuideHammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Scriet (Agriculture Depatment), Ccsu Meerut: Machine Design (Unit 1, Shaft Lecture 1)Document2 pagesScriet (Agriculture Depatment), Ccsu Meerut: Machine Design (Unit 1, Shaft Lecture 1)Vivek MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 - Shaft NoteDocument65 pages1 - Shaft NoteShahir IsmailNo ratings yet
- Machine Design II Draft 3Document18 pagesMachine Design II Draft 3Solomon HassanNo ratings yet
- Modeling of A GyroscopeDocument9 pagesModeling of A GyroscopeIacob BogdanNo ratings yet
- MTE427 ShaftDocument29 pagesMTE427 ShaftRusydi RafiNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design Guide: Layout, Stresses, DeflectionDocument38 pagesShaft Design Guide: Layout, Stresses, DeflectionIan BytesNo ratings yet
- Rotordynamics Module V56!16!9Document57 pagesRotordynamics Module V56!16!9shubham patil100% (1)
- Shafts Part 2Document63 pagesShafts Part 2kghkhanNo ratings yet
- MACHINE DESIGN Part2Document16 pagesMACHINE DESIGN Part2MADHESWARAN SNo ratings yet
- 11.shafting and Associated Parts - V002Document64 pages11.shafting and Associated Parts - V002Policarpo AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Shaft Components and Design FactorsDocument25 pagesShaft Components and Design FactorsHüseyinYılmazNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Gear Manufacturing Process: Sprx1008 - Production Technology - IiDocument19 pagesUnit - Iii Gear Manufacturing Process: Sprx1008 - Production Technology - Iiramesh gondilNo ratings yet
- MECH2410 - Lecture 7 Shaft DesignDocument21 pagesMECH2410 - Lecture 7 Shaft Designaaarid1No ratings yet
- حسنين تقرير الشفتDocument6 pagesحسنين تقرير الشفتzamanNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design and Analysis GuideDocument11 pagesShaft Design and Analysis GuideJagadish Mogaveera BNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Spindle-Bearing and Machine Tool Systems For Virtual Simulation of Milling OperationsDocument9 pagesModeling of Spindle-Bearing and Machine Tool Systems For Virtual Simulation of Milling OperationsYak OubNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design and AnalysisDocument10 pagesShaft Design and Analysispenhameed100% (3)
- Unit 7 Shafts: StructureDocument23 pagesUnit 7 Shafts: StructureSabareesan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Machine Shaft Design FundamentalsDocument4 pagesMachine Shaft Design Fundamentalssanjay kushwahNo ratings yet
- Machine Design: Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy/ Industrial Engineering Branch/ Third StageDocument18 pagesMachine Design: Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy/ Industrial Engineering Branch/ Third Stageاحمد عبدالهادي ربيع سعيدNo ratings yet
- Bearings: A Tribology HandbookFrom EverandBearings: A Tribology HandbookM. J. NealeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (8)
- Machine Design Elements and AssembliesFrom EverandMachine Design Elements and AssembliesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsFrom EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersFrom EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Start Here Middle School Public Forum PREVIEWDocument5 pagesStart Here Middle School Public Forum PREVIEWi am henryNo ratings yet
- Linked PDFDocument337 pagesLinked PDFDmytro PichkurNo ratings yet
- The Validity of Beck Depression Inventory - Short Version in Depressed Patients Diagnosed According To ICD10Document11 pagesThe Validity of Beck Depression Inventory - Short Version in Depressed Patients Diagnosed According To ICD10sarhang talebaniNo ratings yet
- Belzona 1121: Product Specification SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 1121: Product Specification SheetQuy RomNo ratings yet
- Case Study:Iron Pillar Near Qutub Minar: Ji .'1, FJF,) .'1, (Document1 pageCase Study:Iron Pillar Near Qutub Minar: Ji .'1, FJF,) .'1, (Maina SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μDocument23 pages4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μTolesa F BegnaNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument24 pages1 SM PDFayu sekarNo ratings yet
- Tribological Performance Characterization of Brake Friction Materials: What Test? What Coefficient of Friction?Document13 pagesTribological Performance Characterization of Brake Friction Materials: What Test? What Coefficient of Friction?palash roy choudhuryNo ratings yet
- 9781315173078Document187 pages9781315173078John Leandro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muet Paper 3 (Reading) Trial 2019Document13 pagesMuet Paper 3 (Reading) Trial 2019PRAKASH100% (1)
- Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar: Notification No. B.Tech. (Mech. Engg.) (CBES) /-8th Semester/May-2019/1Document1 pageGuru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar: Notification No. B.Tech. (Mech. Engg.) (CBES) /-8th Semester/May-2019/1Nehal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Vernacular Design Principles of an Andhra Pradesh DwellingDocument9 pagesAnalyzing Vernacular Design Principles of an Andhra Pradesh DwellingtrishaNo ratings yet
- 1550-Article Text-4639-1-10-20190621Document15 pages1550-Article Text-4639-1-10-20190621Husnal Taufiq ZulkernainNo ratings yet
- SQL Plus UsersGuide and Quick ReferenceDocument432 pagesSQL Plus UsersGuide and Quick Referenceapi-25930603No ratings yet
- Manual - de - Bolso - Fanuc 16i 18i 21i MODEL BDocument988 pagesManual - de - Bolso - Fanuc 16i 18i 21i MODEL BJeffsouza2016100% (4)
- Stockhausen Cuatro Criterios de La Música ElectrónicaDocument44 pagesStockhausen Cuatro Criterios de La Música ElectrónicaFa SolisNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Metro Line 3: Cre Site Daily ReportDocument16 pagesMumbai Metro Line 3: Cre Site Daily Reportvansh chauhanNo ratings yet
- American Hospital Supply Corporation Case Study-Surojit SahaDocument6 pagesAmerican Hospital Supply Corporation Case Study-Surojit Sahasurojitsaha15094No ratings yet
- 11 Mindfuck Tactics Used by Abusers and Cult LeadersDocument3 pages11 Mindfuck Tactics Used by Abusers and Cult LeadersIgnotum Umbra100% (1)
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Mathematics (Quarter III - Week 6-7)Document13 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Mathematics (Quarter III - Week 6-7)Bai Shalimar PantaranNo ratings yet
- 76 Going To The Hairdresser CanDocument13 pages76 Going To The Hairdresser CanOlga AmyNo ratings yet
- 3x Anglais Ecran-4Document4 pages3x Anglais Ecran-4EMRE KAAN USTANo ratings yet
- Business Aptitude Test: BAT™ Module I - Academic AptitudeDocument18 pagesBusiness Aptitude Test: BAT™ Module I - Academic AptitudePriyam SaraogiNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE of Draft ASSIGNMENTDocument19 pagesEXAMPLE of Draft ASSIGNMENTOlivia RajatinNo ratings yet
- Eh TW5825Document2 pagesEh TW5825Lim Hendra Kurniawan Halim (Hendra)No ratings yet
- SAIL Catalogue: DownloadDocument16 pagesSAIL Catalogue: Downloadmishra usNo ratings yet
- Controller Tuning Methods for Process ControlDocument17 pagesController Tuning Methods for Process ControltrshaaaNo ratings yet
- Ergo PresentDocument7 pagesErgo PresentFan ZNo ratings yet
- Misubishi Engine S12R-PTADocument90 pagesMisubishi Engine S12R-PTAAnonymous uEt1sNhU7l100% (15)
- Digital Scent TechnologyDocument13 pagesDigital Scent TechnologyRahul Maravi0% (1)