Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT1
Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT1
Uploaded by
Nkemzi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageThe document discusses periodicity and periodic trends in the periodic table. It defines periodicity as the repetition of physical and chemical properties across periods of the periodic table. It also defines periodic trends as repeating patterns of properties across periods. It then provides examples of how properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and melting/boiling points change across periods and down groups in the periodic table.
Original Description:
NOTES
Original Title
14. Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses periodicity and periodic trends in the periodic table. It defines periodicity as the repetition of physical and chemical properties across periods of the periodic table. It also defines periodic trends as repeating patterns of properties across periods. It then provides examples of how properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and melting/boiling points change across periods and down groups in the periodic table.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pagePeriodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT1
Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT1
Uploaded by
NkemziThe document discusses periodicity and periodic trends in the periodic table. It defines periodicity as the repetition of physical and chemical properties across periods of the periodic table. It also defines periodic trends as repeating patterns of properties across periods. It then provides examples of how properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and melting/boiling points change across periods and down groups in the periodic table.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Page 1 of 1
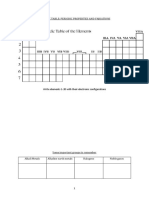
Periodicity
Groups I II III IV V VI VII VIII
Period 2 2s 2s 2s 2p 2s 2p 2s 2p 2s 2p 2s 2p 2s22p6
1 2 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 4 2 5
Period 3 3s1 3s2 3s23p1 3s23p2 3s23p3 3s23p4 3s23p5 3s23p6
Definition: Periodicity is the repetition of physical and chemical properties across periods
of the Periodic Table.
Definition: Periodic trends are repeating patterns of properties across periods of the
Periodic Table.
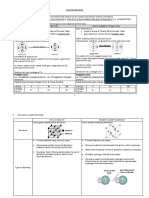
Period 2 Li Be B C N O F
Element Metal Metalloid Non-metal
type
Strong metallic Strong covalent bonds between atoms
Strong covalent bonds
Bonding bonds between and weak VDW forces between
between atoms
atoms molecules
Structure Giant metallic Giant covalent Simple molecular
Period 3 Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
Element
Metal Metalloid Non-metal
type
Strong
covalent Strong covalent bonds between atoms
Strong metallic bonds
Bonding bonds and weak VDW forces between
between atoms
between molecules
atoms
Structure Giant metallic Giant Simple molecular
covalent
14.2 Periodicity of physical properties within the Periodic Table
Properties such as atomic size (atomic radius), ionisation energy, melting and boiling points
etc change from one element to the other as one goes down a group or move across a period.
(a) Atomic radius: Atomic radius decreases across the period from left to right because
across the period from left to right, due to the fact that nuclear charge increases
progressively by one unit, additional electrons fill the same valence shell, shielding
effect to remain roughly constant. Therefore the pull of valence electrons towards the
nucleus by increasing effective nuclear charge results to a decrease in atomic size. From
group VII to group VIII, there is rather a drastic increase in atomic size because noble
gas atoms do not form covalent bonds with one another. So the radius measured for a
noble gas atom is a van der waals radius which bigger than a covalent radius. Atomic
size increases down the group due to increase in number of shells and shielding effect. A
graph of variation of atomic size across period 3 is shown below. F
Atomic Ar
size/nm Na
Cl
Mg
Al
Si
P S
Cl
Atomic number Br
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
Act: Sketch a graph to show the variation of atomic radius
(i) across period 2 and explain the shape of the graph.
(ii) Down group VIII and explain the shape of the graph.
THE NEN SERIES A-Level chemistry notes 2013-2014 school year prepared by Nkemzi E.N
You might also like
- Chatwal - College ChemistryDocument237 pagesChatwal - College ChemistryNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument25 pagesChemistry NotesEbuka AnwasiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A Star - WorksheetDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of A Star - WorksheetLNo ratings yet
- 01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsDocument9 pages01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Types of Solids POGIL - Student VersionDocument6 pagesTypes of Solids POGIL - Student VersionJesse SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mri PhysicsDocument16 pagesSummary of Mri Physicsshikha712100% (1)
- Physics Paper 1 TZ2 HL PDFDocument21 pagesPhysics Paper 1 TZ2 HL PDFdrive wahyudiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 303 Transition Metal Chemistry PDFDocument79 pagesCHEM 303 Transition Metal Chemistry PDFYoung Jay JacobNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument6 pagesPeriodicityHadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: Periodic TableDocument5 pagesPeriodicity: Periodic TableYamac SamaniNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument3 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- 04 - Periodic Table CORNELLDocument6 pages04 - Periodic Table CORNELLGeorge SolomouNo ratings yet
- 9 - The Periodic Table - Chemical PeriodicityDocument79 pages9 - The Periodic Table - Chemical PeriodicitySoma Chowdhury RosyNo ratings yet
- BS Chemistry MCQsDocument6 pagesBS Chemistry MCQsRamsha saeedNo ratings yet
- S and P Block Elements-1Document34 pagesS and P Block Elements-1Daniyal BeyNo ratings yet
- Asc0304 - Chapter 7 - Periodic TableDocument40 pagesAsc0304 - Chapter 7 - Periodic TableNURFASYA ATIKA BINTI ROSLI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Periodic Table - PeriodicityDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Periodic Table - Periodicitysitinur qahirahNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Inorganic Chemistry The Periodic Table: Chemical PeriodicityDocument22 pagesPioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Inorganic Chemistry The Periodic Table: Chemical PeriodicityTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Mme Unit. 1Document67 pagesMme Unit. 1Aanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Trends in Physical and Chemical-PropertiesDocument42 pagesLecture 2-Trends in Physical and Chemical-PropertiesFELIX ORATINo ratings yet
- CHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFDocument89 pagesCHM 122 - 2016 - grp1-4 PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDocument6 pages12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument51 pagesEngineering MaterialsSamer al sadikNo ratings yet
- L04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresDocument16 pagesL04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- L04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresDocument16 pagesL04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- L04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresDocument16 pagesL04 Secondary Bonding and Intro To Crystal StructuresVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (L-1) JLD 3.0Document69 pagesChemical Bonding (L-1) JLD 3.0Ayush BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Icse 10th - Periodic TableDocument5 pagesIcse 10th - Periodic TablePrutha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Periodicity: Learning OutcomesDocument16 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicity: Learning OutcomesAshley KuwodzaNo ratings yet
- CHM 122 - 2013 - 2014 PDFDocument27 pagesCHM 122 - 2013 - 2014 PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements - Quick Review: Chemistry - Cbse X Class Revision ProgrammeDocument25 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements - Quick Review: Chemistry - Cbse X Class Revision ProgrammeGurudhev KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument14 pagesTrends in The Periodic TableGoldenNo ratings yet
- DFFHMDocument9 pagesDFFHMyaswanthNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument29 pagesPeriodic Tablepraveen bukkaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT3Document2 pagesPeriodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT3NkemziNo ratings yet
- Chapter#1 Till HalidesDocument39 pagesChapter#1 Till HalidesMudassir JuttNo ratings yet
- Period 3 Na To ArDocument2 pagesPeriod 3 Na To Arjordangrierson12No ratings yet
- Periodic Table ArrangementDocument6 pagesPeriodic Table ArrangementAishani LakamsaniNo ratings yet
- 11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrDocument30 pages11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrÃrjït ShûklãNo ratings yet
- 06 CB Notes 2022Document6 pages06 CB Notes 2022Fitri armaya Jeffri (Greendaless)No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-1NotesDocument6 pages12th Chemistry CH-1NotesSaad JavedNo ratings yet
- Band Theory 2016Document25 pagesBand Theory 2016Mohd Ridz Zul WanNo ratings yet
- Thing To Remember D and F Block - 2022Document17 pagesThing To Remember D and F Block - 2022poornaNo ratings yet
- Across: Period 3Document8 pagesAcross: Period 3Nursyafiqa IdwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding One Shot Jee 29 - 11 - 2020Document142 pagesChemical Bonding One Shot Jee 29 - 11 - 2020Harshal KartikeyanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Chemical Bonding PDFDocument26 pagesCH 2 Chemical Bonding PDFTonald DrumpNo ratings yet
- Cfe Higher Chemistry - PeriodicityDocument34 pagesCfe Higher Chemistry - Periodicityiapm0708No ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic PropertiesDocument7 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic PropertiesHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument41 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsmacybnzNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument29 pagesTheoryRajesh JainNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument25 pagesIntroductionRaj vermaNo ratings yet
- Publication 1 1129 24Document14 pagesPublication 1 1129 24Marwan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Metals and Their Compounds Student VersionDocument23 pagesUnit 9 - Metals and Their Compounds Student VersionMalike ShamelNo ratings yet
- The D & F-Block ElementsDocument11 pagesThe D & F-Block Elementswify dihaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument4 pagesPeriodic TableKamal Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 PeriodicDocument4 pages1 PeriodicAneeshTandonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2aqsa zahidNo ratings yet
- S-EMM 3122-CH4-Solidification-2020Document30 pagesS-EMM 3122-CH4-Solidification-2020KHAIRUL NASHRAN BIN ANUAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- D - and F - Block Elements: Jatindranath Mandal PGT ChemistryDocument70 pagesD - and F - Block Elements: Jatindranath Mandal PGT ChemistryPrecisive OneNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Semiconductor Materials & PhysicsDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 1: Semiconductor Materials & PhysicsUma MaheswariNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Periodic Table-1Document57 pagesCH 2 Periodic Table-1BiahNo ratings yet
- Refractory Transition Metal Compounds: High Temperature CermetsFrom EverandRefractory Transition Metal Compounds: High Temperature CermetsNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT2Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT2NkemziNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT7Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT7NkemziNo ratings yet
- Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT3Document2 pagesPeriodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT3NkemziNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT3Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT3NkemziNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT4Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT4NkemziNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Shapes of Mole - CN - STDT3Document2 pagesBonding & Shapes of Mole - CN - STDT3NkemziNo ratings yet
- 13a. Intro To Inorg Chem - CN - STDT2Document1 page13a. Intro To Inorg Chem - CN - STDT2NkemziNo ratings yet
- Mathies 3Document10 pagesMathies 3ruskaNo ratings yet
- Max Planck and The Genesis of The Energy Quanta inDocument6 pagesMax Planck and The Genesis of The Energy Quanta inCatalin MeiuNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Nuclear Chemistry - 8Document7 pagesCoordination & Nuclear Chemistry - 8kumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Drill 1)Document4 pagesChemistry (Drill 1)Ellie PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds HandoutsDocument10 pagesNaming Compounds HandoutsNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- A Review on Uv Visible Spectroscopy_1 (4)Document8 pagesA Review on Uv Visible Spectroscopy_1 (4)Meladia SariNo ratings yet
- Physics SSC-II SolutionDocument9 pagesPhysics SSC-II SolutionFarhatullah Muhammad100% (1)
- Heterocyclic Chemistry and Spectroscopy C 22022/CHE 22022: Course Lecturer: Dr. Dinusha UdukalaDocument40 pagesHeterocyclic Chemistry and Spectroscopy C 22022/CHE 22022: Course Lecturer: Dr. Dinusha UdukalaDidula ThrimannaNo ratings yet
- Metallic and Ionic Solids (Autosaved)Document25 pagesMetallic and Ionic Solids (Autosaved)Asmaa HatemNo ratings yet
- Notes - Topic 11 Particle Physics - CAIE Physics A-LevelDocument7 pagesNotes - Topic 11 Particle Physics - CAIE Physics A-LevelHaydersNo ratings yet
- Basic Interaction Between X-Rays and MatterDocument62 pagesBasic Interaction Between X-Rays and MatterNazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Sigma Bond: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesSigma Bond: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMuhamad Hafifi AjwadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Explore..Document42 pagesChapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Explore..usercmdmcNo ratings yet
- 06 半導體能帶圖的說明與含意Document10 pages06 半導體能帶圖的說明與含意JingWu DongNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends WorksheetDocument5 pagesPeriodic Trends WorksheetChristy HuynhNo ratings yet
- IBSC 2018 Sample 8th std2Document11 pagesIBSC 2018 Sample 8th std2priyaamirthaNo ratings yet
- Make A Balloon Ecstatic Science For KidsDocument3 pagesMake A Balloon Ecstatic Science For KidsSarah MadukayilNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - 1 Grade 9Document4 pagesWork Sheet - 1 Grade 9SOLONo ratings yet
- Httpsauthors - Library.caltech - edu10520914TR000574 05 Chapter-5 PDFDocument41 pagesHttpsauthors - Library.caltech - edu10520914TR000574 05 Chapter-5 PDFKiệt LýNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 InorganicDocument20 pagesLecture 1 InorganicNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument20 pagesPreviewDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Using Mcphase To Calculate Magnetic Phase Diagrams of Rare Earth CompoundsDocument2 pagesUsing Mcphase To Calculate Magnetic Phase Diagrams of Rare Earth CompoundspovNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom - Exam - Part1Document1 pageStructure of The Atom - Exam - Part1zehra giyoriNo ratings yet
- 07-Chemical KineticsDocument5 pages07-Chemical KineticsMr XNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle InspectionDocument172 pagesMagnetic Particle InspectionRamesh RNo ratings yet
- MagnetismAndMatter CWDocument5 pagesMagnetismAndMatter CWAyesha AnjumNo ratings yet