Professional Documents
Culture Documents
List of Viceroy
Uploaded by
Malik GoharOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List of Viceroy
Uploaded by
Malik GoharCopyright:
Available Formats
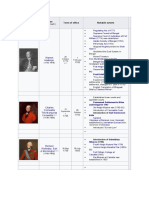
List of Governors-General
Name
Term of office Notable events Appointer
(Birth–Death)
Before 1773 Governor General of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal) was named as Governor of Bengal, which was in
existence since 1757 to 1772.
For the list of Governors of Bengal see List of governors of Bengal.
Governors General of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), 1773–1833
Regulating Act of 1773 East India
Supreme Council of Bengal Company
Supreme Court of Judicature at Fort William (1774) was
established
Asiatic Society of Bengal (1784)
Pitt's India Act (1784) (1773–
Stopped Mughal pension to Shah Alam II 1858)
Abolished the Dual System in Bengal (Which was
introduced by Robert Clive).[1]
Moved Treasury from Murshidabad to Calcutta
James Augustus Hicky's Bengal Gazette- First Indian
20 newspaper published (in 1780)
8
Warren Hastings October First Anglo-Maratha War (1775–82)
February
(1732–1818) 1773 Second Anglo-Mysore war (1780–84)
[nb 1] 1785
First Rohilla War of 1773–1774
Ring fence policy
Founded Calcutta Madrasa (Aliah University)
Creation of collector post
The first Governor General to be prosecuted for
impeachment. (As a consequence of his involvement
in First Rohilla War)[2]
Experimentation on land settlements. (1772-five years
settlement, changed to 1 year in 1776)
English Translation of Bhagwat Gita by Charles
Wilkins[3]
12
John Macpherson 8
Septemb
(acting) February
er
(1745–1821) 1785
1786
Established lower courts and appellate courts
Permanent Settlement in Bihar and Bengal in 1793
3rd Anglo-Mysore war (1790–92)
Charles Cornwallis 12
28 Introduction of Cornwallis Code
The Marquess Septembe
October Introduction of Civil Services in India
Cornwallis [nb 2] r
1793 Sanskrit Vidyalaya at Benares (now Varanasi)
(1738–1805) 1786
established by Johnathan Duncan(then Governor of
Bombay)
Introduced Sunset Law
Policy of Non-intervention
28 Charter Act of 1793
John Shore 18 March
October
(1751–1834) 1798 Second Rohilla War 1794
1793
Battle of Kharda between Nizam and Marathas (1795)
Alured Clarke
18 March 18 May
(acting)
1798 1798
(1744–1832)
Introduction of Subsidiary Alliance (1798)
Richard Fourth Anglo Mysore War 1799
Wellesley, Earl of 18 May 30 July
Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803–05)[4]
Mornington [nb 3] 1798 1805
Fort William College at Calcutta (1800)
(1760–1842)
Raj Bhavan at Calcutta was established in 1803
The Marquess
30 July 5 October
Cornwallis
1805 1805
(1738–1805)
Sepoy mutiny at Vellore (The prelude to the First
Sir George Barlow, Bt 10 War of Independence of India)
31 July
(acting) October
1807 Bank of Calcutta (1806) established (later Imperial Bank
(1762–1847) 1805
of India, now State Bank of India)
The Lord Minto 31 July 4 October Charter Act of 1813
(1751–1814) 1807 1813 Treaty of Amritsar, 1809 with Maharaja Ranjit Singh
Francis Rawdon- 4 October 9 January Ended the policy of Non-intervention
Hastings, 1813 1823 Third Anglo-Maratha War (1816–1818)
1st Marquess of
Treaty of Sugauli (1816)
Creation of Bombay Presidency in 1818
Establishment of Ryotwari System in Madras (1820)
Establishment of Mahalwari System in Northern India
(1822)
Hastings [nb 4]
Hindu College (now Presidency University)
(1754–1826)
at Calcutta in 1817
The Pindari War (1817–1818) (Complete Destruction of
the Pindari Clan of India)
General Committee of Public Instruction was formed in
1823
John Adam Licensing Regulations
9 January 1 August
(acting) Calcutta Unitarian Committee established by Raja Ram
1823 1823
(1779–1825) Mohan Roy
First Anglo-Burmese War (1824–26) (East India
Company defeats Burmese King Bagyidaw and
annexes Assam, Manipur, Arakan and Tenasserim)
The Lord Amherst[nb 5] 1 August 13 March
Establishment of Sanskrit College at Calcutta (1824)
(1773–1857) 1823 1828
Treaty of Yandabo, 1826 (East India Company
humiliates and extracts 1 million Pounds from
the Burmese King Bagyidaw)
William Butterworth
Bayley 13 March 4 July
(acting) 1828 1828
(1782–1860)
Governors-General of India, 1833–1858
First Governor General of India East India
Bengal Sati Regulation, 1829 Company
Mahalwari System in Central India, Punjab And
Western UP.
Saint Helena Act 1833 or Charter Act 1833 (Christian
Lord William Bentinck 4 July 20 March
Missionaries get Exclusive rights to (1773–
(1774–1839) 1828 1835
spread Christianity in British India which included 1858)
the present day Pakistan)
Kol Rebellion in 1831
English Education Act 1835
Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata (1835)
Repealed 1823 Licensing Regulations
Charles Metcalfe, Bt
20 March 4 March Known as Liberator of India Press
(acting)
1835 1836 Establishment of Calcutta Public Library in
(1785–1846)
1836 (currently known as National Library of India)
Tripartite Treaty in 1838 between British, Shah Shuja (a
cruel Afghan traitor) and Maharaja Ranjit
Singh against Dost Muhammad Khan.
The First Anglo Afghan War(1840–1842) (British
Army massacred by the strong Afghan army and militia
The Lord Auckland[nb 28 during the 1842 Retreat from Kabul-worst British Military
6] 4 March disaster)
February
1836
(1784–1849) 1842 Bank of Bombay (1840) established (later Imperial Bank
of India, now State Bank of India)
First Bengali daily newspaper Sambad Prabhakar was
published in 1839
Tattwabodhini Sabha was formed by Debendranath
Tagore in 1839
The Lord 28 Gwalior War (1843) (British defeat Marathas)
June
Ellenborough February Bank of Madras (1843) established (later Imperial Bank
1844
(1790–1871) 1842 of India, now State Bank of India)
William Wilberforce
Bird June 23 July
(acting) 1844 1844
(1784–1857)
The First Anglo-Sikh War (1845–46) (British
Empire defeats the Sikh Empire and confiscate major
12 portion of its territory)
Henry Hardinge[nb 7] 23 July
January Treaty of Lahore(1846) (British confiscate Kashmir from
(1785–1856) 1844
1848 the Sikhs and sell it to Raja of Jammu for 75 lakh
rupees)
Establishment of Roorkee Engineering College (1847)[5]
The Earl of 12 28 Doctrine of Lapse in 1848
Dalhousie[nb 8] January February Bethune Collegiate School (1849) (was also known
(1812–1860) 1848 1856 as Calcutta Female School) was established by John
Elliot Drinkwater Bethune
Charles Wood Despatch (1854)
Establishment of summer capital at Shimla
Second Anglo-Burmese War (1852) (The sole aim of
Dalhousie was to humiliate and annex more of Burmese
Territories. Burma was attacked unprovoked)
First Passenger train between Bombay and Thane
(1853)
First telegraph Line was laid between Diamond Harbour
to Calcutta. (1851)
Post Office Act, 1854
Established Public Works Department (1854)
The Second Anglo-Sikh War (1848–1849) (The British
totally defeats the Sikh Empire)
Santhal Rebellion (1855) (15,000 Santhals were killed
by the British Army during the rebellion. Elephants were
used to destroy Santhal Dwellings)
Hindu Widows' Remarriage Act, 1856
The Viscount 28 31
Indian Rebellion of 1857
Canning[nb 9] February October
University of Calcutta, University of Bombay,
(1812–1862) 1856 1858
and University of Madras were set up in 1857
Governors-General and Viceroys of India, 1858–1947
The Government of India Act, 1858 Victoria
1 System of Budget introduced
The Viscount Formation of Imperial Civil Services
Novembe 21 March
Canning[nb 9]
r 1862 Indigo Revolt in Bengal in 1859–60
(1812–1862)
1858 Enactment of Indian Penal Code in 1860
(1837–
Establishment of Archaeological Survey of India 1901)
20
Establishment of Calcutta High Court (2 July), Bombay
The Earl of Elgin 21 March Novembe
High Court (14 August) and Madras High Court (15
(1811–1863) 1862 r
August) in 1862
1863
21 2
Robert Napier
Novembe Decembe
(acting)
r r
(1810–1890)
1863 1863
2
William Denison 12
Decembe
(acting) January
r
(1804–1871) 1864
1863
Bhutan War (1864–65) (The British defeated an
undefended Bhutan and
annexed Assam and Bengal Duars)
Sir John Lawrence, 12 12 Establishment of Shimla as India's summer capital in
Bt January January 1863
(1811–1879) 1864 1869
The Tabernacle of New Dispensation, a new Church
established by Keshub Chandra Sen
Establishment of Allahabad High Court in 1866
Assassinated by a Pathan Sher Ali Afridi
Started the Census.
Opening of Rajkumar college in Rajkot and Mayo
12 8 College at Ajmer for political training of Indian Princes
The Earl of Mayo
January February Started Financial decentralization
(1822–1872)
1869 1872 Enacted IPC amendment-Sedition Act 1870 to tackle
Wahabi Movement
Keshub Chandra Sen establishes Indian Reform
Association
Sir John Strachey 9 23
(acting) February February
(1823–1907) 1872 1872
The Lord Napier 24
3 May
(acting) February
1872
(1819–1898) 1872
Jyotiba Phule launches The Satyashodhak
The Lord Northbrook 3 May 12 April Samaj in Maharashtra in 1873 against the caste
(1826–1904) 1872 1876 system and Untouchability.
Dramatic Performances Act, 1876
Great Famine of 1876–1878
Vernacular Press Act, 1878
The Lord Lytton 12 April 8 June
Second Anglo-Afghan War, (1878–80)
(1831–1891) 1876 1880
1st Delhi Durbar out of 3
Queen Victoria assuming the title of 'Empress of India'
The Marquess of 8 June 13 First Factory Act (1881)
Ripon 1880 Decembe Negotiable Instruments Act (1881)
(1827–1909) r Repeal of the Vernacular Press Act (1882)
1884 Ilbert Bill (1883)
Government resolution on local self-government (1882)
Appointment of Education Commission under Sir
William Hunter
First complete Census
13 10
The Earl of Dufferin Decembe Decembe Formation of Indian National Congress (1885)
(1826–1902) r r Third Anglo-Burmese War (1885)
1884 1888
10 Indian Council Act 1892
The Marquess of 11
Decembe Factory Act 1891
Lansdowne October
r Setting up of Durand Commission in 1893 (India-
(1845–1927) 1894
1888 Afghanistan)
11 Indian famine of 1896–97
The Earl of 6 January
October Establishment of Ramkrishna Mission by Swami
Elgin (1849–1917) 1899
1894 Vivekananda at Belur Math in 1897
Indian famine of 1899–1900
Partition of Bengal (1905)
Official Secrets Act 1904 to curb free press
2st Delhi Durbar out of 3 (1903)
Appointment of Police Commission under Sir Andrew
Frazer
18 Appointment of Raleigh University Commission (1902)
The Lord Curzon of
6 January Novembe Passing of Indian Universities Act 1904
Kedleston[nb 10]
1899 r 2nd Swadeshi Movement (1905–1911) against Partition
(1859–1925)
1905 of Bengal by Lal-Bal-Pal-Aurbindo Ghosh)
Benaras Hindu Girl's School was established by Annie
Besant in 1904
He said, "India is the pivot of our Empire.... If the Empire
loses any other part of its Dominion we can survive, but
if we lose India, the sun of our Empire will have set."
[6]
Morley-Minto Reforms 1909 or The Indian Councils Act Edward
1909 VII
18 23 Split in Congress in 1907
The Earl of Minto Novembe Novembe Seditious meetings (prohibition) Act 1907 to curb
(1845–1914) r r extremist movement
1905 1910 Establishment of Muslim League by Aga Khan III (1906)
Indian Press Act, 1910 (1901–
Jamsetji Tata established TISCO in 1907 1910)
Third Delhi Durbar (1911)
23 Transfer of capital from Calcutta to Delhi (1911)
The Lord Hardinge of
Novembe 4 April Partition of Bengal to form Bihar province (1912)
Penshurst
r 1916 McMahon border line was created between India and
(1858–1944)
1910 China in 1914
Ghadar Mutiny (1915)
Formation of Indian Home Rule Movement (1916)
Lucknow Pact (1916)
Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms (1919)
The Lord Chelmsford 4 April 2 April Government of India Act 1919
(1868–1933) 1916 1921 Rowlatt Act (1919)
Jallianwalla Bagh Massacre (1919)
Imperial Bank of India (now State Bank of
India established in 1921)
Malabar rebellion (also known as Moplah Rebellion),
first Ethnic Rebellion (1921)
The Earl of Reading 2 April 3 April Non-cooperation movement (1921–22)
(1860–1935) 1921 1926 Rabindranath Tagore founded Visva-Bharati George V
University in 1921
Chauri Chaura incident (1922)
Simon Commission (1928)
Nehru Report (1928) (1910–
Death of Lala Lajpat Rai (1928) 1936)
Fourteen Points of Jinnah (1929)
Purna Swaraj declaration (1929)
Salt March (1930)
The Lord Irwin 3 April 18 April
Dharasana Satyagraha (1930)
(1881–1959) 1926 1931
First Round Table Conferences (1930)
Allahabad Address (1930)
Chittagong armoury raid in 1930
Gandhi–Irwin Pact (1931)
Execution of Bhagat Singh, Shivaram Rajguru,
and Sukhdev Thapar (1931)
Poona Pact between Mahatma Gandhi and B. R.
Ambedkar in 1932
The Earl of Pakistan Declaration (1933)
18 April 18 April
Willingdon Government of India Act 1935
1931 1936
(1866–1941) Reserve Bank of India established by passing The
Reserve Bank of India Act 1934.
Foundation of Congress Socialist Party in 1934
Indian provincial elections (1937)
Indian entry into World War II (1939) Edward
Day of Deliverance (1939) VIII
The Marquess of Lahore Resolution (1940)
18 April 1 October
Linlithgow Cripps Mission (1942)
1936 1943
(1887–1952) Formation of Indian Legion (1942)
Quit India movement (1942)
Formation of Indian National Army (1942) (1936)
Bengal famine (1943)
C. R. formula (1944)
Simla Conference (1945)
21 Cabinet Mission (1946) George VI
The Viscount Wavell 1 October
February
(1883–1950) 1943 Interim Government was formed in 1946
1947
Direct Action Day (1946)
Royal Indian Navy mutiny (1946)
The Viscount (1936–
21 1952)
Mountbatten of 15 August
February Indian Independence Act 1947
Burma 1947
1947
(1900–1979)
Governors-General of the Dominion of India, 1947–1950
The Viscount George
Mountbatten of 15 August 21 June VIDominio
First Governor-General of Independent India
Burma[nb 11] 1947 1948 n of India
(1900–1979)
Chakravarti 26
21 June Last Governor-General of India, before the office was
Rajagopalachari January
1948 permanently abolished in 1950 (1936–
(1878–1972) 1950
1952)
You might also like
- List of Governor General & Viceroys of IndiaDocument9 pagesList of Governor General & Viceroys of IndiaSarthak Yadav100% (2)
- The Laws 43Document40 pagesThe Laws 43Melita BezjakNo ratings yet
- Family Code Complete Set of Digested Cases BedaDocument222 pagesFamily Code Complete Set of Digested Cases BedaRyan Heynrich Misa100% (1)
- Template - Change Management ProcessDocument10 pagesTemplate - Change Management ProcessGryswolfNo ratings yet
- Quick Indian History For Compet - Disha ExpertsDocument23 pagesQuick Indian History For Compet - Disha ExpertsNakuL KaliA100% (1)
- Furniture of The Olden Time (1917) PDFDocument508 pagesFurniture of The Olden Time (1917) PDFpatatitoNo ratings yet
- Recent Cases On Beneficial UseDocument13 pagesRecent Cases On Beneficial UseLeighNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals and ViceroysDocument14 pagesGovernor Generals and ViceroysGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- List of Governors-General of India - WikipediaDocument15 pagesList of Governors-General of India - WikipediaSaket Raj100% (1)
- List of Governors-GeneralDocument10 pagesList of Governors-GeneralKesto LoriakNo ratings yet
- Portrait Name Term of Office Notable Events: Warren HastingsDocument4 pagesPortrait Name Term of Office Notable Events: Warren HastingsGopa BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- GK For SSC CGL Upsc Pther State ExamsDocument10 pagesGK For SSC CGL Upsc Pther State ExamsYrt LuckyNo ratings yet
- Governors-General - ViceroyDocument5 pagesGovernors-General - ViceroySouvik SarkarNo ratings yet
- List of Governors General & Viceroys of India PDF For UPSC, Banking & SSC ExamsDocument7 pagesList of Governors General & Viceroys of India PDF For UPSC, Banking & SSC ExamsAditi MittalNo ratings yet
- List of Governors General & Viceroys of India PDF For UPSC, Banking & SSC ExamsDocument7 pagesList of Governors General & Viceroys of India PDF For UPSC, Banking & SSC ExamsGirithar M SundaramNo ratings yet
- Viceroys and GovernorsDocument6 pagesViceroys and GovernorsNeeraj Munda100% (1)
- Governor General ViceroysDocument10 pagesGovernor General Viceroysrahul singhNo ratings yet
- Modern History-Governor GeneralDocument5 pagesModern History-Governor GeneralHimanshu BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Governor General of IndiaDocument2 pagesGovernor General of Indiashakshamsachin1230No ratings yet
- List of GovernorsDocument2 pagesList of Governorsnewcontrol testNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals of Bengal (1757 1833)Document1 pageGovernor Generals of Bengal (1757 1833)sameer bakshiNo ratings yet
- List of Governor General & Viceroys of IndiaDocument9 pagesList of Governor General & Viceroys of IndiaSarthak YadavNo ratings yet
- List of Governors-General of India, First Governor-General of BengalDocument4 pagesList of Governors-General of India, First Governor-General of BengalsayaliNo ratings yet
- Governors General Viceroys OfindiaDocument6 pagesGovernors General Viceroys Ofindiabrain boosterNo ratings yet
- GG & Viceroys of British IndiaDocument8 pagesGG & Viceroys of British IndiaMuhammad AyazNo ratings yet
- List of Governor General of IndiaDocument3 pagesList of Governor General of Indiavickohli18No ratings yet
- List of British Governor Generals and ViceroysDocument7 pagesList of British Governor Generals and ViceroysShahid Imran100% (1)
- Governor Generals - British IndiaDocument5 pagesGovernor Generals - British IndiaSriSriNo ratings yet
- Modern History TimelineDocument29 pagesModern History TimelineNandu RajNo ratings yet
- List of Governors and Viceroys in British India: Name Tenure of Office Notable EventsDocument8 pagesList of Governors and Viceroys in British India: Name Tenure of Office Notable Events732000vcNo ratings yet
- Governor General of India Upsc Note 59Document25 pagesGovernor General of India Upsc Note 59Naeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals of IndiaDocument9 pagesGovernor Generals of IndiaSoujanya Venkat NNo ratings yet
- Governors and Governor GeneralsDocument18 pagesGovernors and Governor GeneralsKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Indian History-7 Modern Indian History and Freedom Strugle ADocument55 pagesIndian History-7 Modern Indian History and Freedom Strugle AkausaraNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals and Viceroys PDFDocument4 pagesGovernor Generals and Viceroys PDFKhushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Governor-General and ViceroysDocument4 pagesGovernor-General and ViceroysashuNo ratings yet
- The GovernorsDocument4 pagesThe GovernorsRagavanNo ratings yet
- Warren HastingsDocument16 pagesWarren HastingsDeepak kumar ChakravatyNo ratings yet
- 2-Modern IndiaDocument18 pages2-Modern IndiaRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- List of Prime Ministers of The United Kingdom - WDocument2 pagesList of Prime Ministers of The United Kingdom - WcomputerqwertyNo ratings yet
- List of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaDocument17 pagesList of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaRavi Kumar Agrahari100% (1)
- Governor GeneralDocument4 pagesGovernor GeneralkeerthihemaNo ratings yet
- British Viceroys and Governors of IndiaDocument46 pagesBritish Viceroys and Governors of IndiaShadow DrexNo ratings yet
- Governors of Bengal (1757 - 74) : Governor-Generals and ViceroysDocument5 pagesGovernors of Bengal (1757 - 74) : Governor-Generals and ViceroysHabib ManzerNo ratings yet
- NTSE Sheet 6 PDFDocument8 pagesNTSE Sheet 6 PDFVed bukhariyaNo ratings yet
- List of Governor GeneralsDocument10 pagesList of Governor GeneralsKamran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Warren Hastings (1732-1818) : Governors-General of The Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), 1773-1833Document21 pagesWarren Hastings (1732-1818) : Governors-General of The Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), 1773-1833Aishu HoneyNo ratings yet
- Governors ViceroysDocument14 pagesGovernors ViceroysNiyati AnandNo ratings yet
- Governor-Genera-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesGovernor-Genera-WPS OfficeRahul GurjarNo ratings yet
- Instapdf - in Governor General of India List 687Document14 pagesInstapdf - in Governor General of India List 687vivek30303No ratings yet
- Spectrum QuestionsDocument29 pagesSpectrum QuestionsuttamNo ratings yet
- Viceroy لجنرنررگوDocument40 pagesViceroy لجنرنررگوBaqirNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument34 pagesIndian PolityYusuf ShaanNo ratings yet
- British Governor Generals and ViceroysDocument3 pagesBritish Governor Generals and ViceroysDinesh KtNo ratings yet
- TNPSC PDFDocument20 pagesTNPSC PDFMalu SakthiNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals and ViceroysDocument6 pagesGovernor Generals and Viceroyskaushik.ghosh1111No ratings yet
- List of Viceroy in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Viceroy in Indiagopesh daga100% (1)
- Governor General and Viceroy of India 1 5 14Document22 pagesGovernor General and Viceroy of India 1 5 14RaviNo ratings yet
- Governor General of BengalDocument13 pagesGovernor General of BengalRahul Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Indian States Before 1947 A-JDocument37 pagesIndian States Before 1947 A-JHitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- British-Governors & ViceroyDocument13 pagesBritish-Governors & ViceroyAashiqKhajaNo ratings yet
- Modern India PDFDocument16 pagesModern India PDFSE Works-IINo ratings yet
- Modern India PDFDocument16 pagesModern India PDFAsrarNo ratings yet
- One Leg: The Life and Letters of Henry Wiliiam Paget, First Marquess of Anglesey, K.G. 1768–1854From EverandOne Leg: The Life and Letters of Henry Wiliiam Paget, First Marquess of Anglesey, K.G. 1768–1854No ratings yet
- SE Assignment 2Document4 pagesSE Assignment 2Malik GoharNo ratings yet
- DSM PresentationDocument18 pagesDSM PresentationMalik GoharNo ratings yet
- DSM ReportDocument60 pagesDSM ReportMalik GoharNo ratings yet
- Final TermDocument6 pagesFinal TermMalik GoharNo ratings yet
- DSM Assignment 1Document15 pagesDSM Assignment 1Malik GoharNo ratings yet
- Network SecurityDocument91 pagesNetwork SecurityMalik GoharNo ratings yet
- Web Service SecurityDocument25 pagesWeb Service SecurityMalik GoharNo ratings yet
- SIS Limited Annual Report 2022-23Document165 pagesSIS Limited Annual Report 2022-23Hemantha Kumar T RNo ratings yet
- The Fire Safety ACT 2021Document23 pagesThe Fire Safety ACT 2021FRConsultantsLtd123No ratings yet
- My AnsDocument25 pagesMy AnsNIHARIKA SIROHINo ratings yet
- Water ConservationDocument4 pagesWater Conservationmnt6176No ratings yet
- Women Rights SyllausDocument7 pagesWomen Rights Syllaussekar_smrNo ratings yet
- Road Map For Interview PreprationDocument9 pagesRoad Map For Interview PreprationMadara UchihaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Performance Analysis of Life Insurance Companies EditedDocument85 pagesComparative Performance Analysis of Life Insurance Companies EditedSumana Sadhukhan0% (1)
- Persian Sources For Reconstructing History of Delhi SultanateDocument6 pagesPersian Sources For Reconstructing History of Delhi SultanateKundanNo ratings yet
- Calvert Calvert: County Times County TimesDocument24 pagesCalvert Calvert: County Times County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- Pirates //group 3: As B Known For C Had Been Known Would Board C Was BoardingDocument3 pagesPirates //group 3: As B Known For C Had Been Known Would Board C Was BoardingstellatenNo ratings yet
- 6.1. Sources of Technology: Unit 6 Technicallgical Environment and The BusinessDocument3 pages6.1. Sources of Technology: Unit 6 Technicallgical Environment and The BusinessDivine DanielNo ratings yet
- Find Someone Who Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 9018Document1 pageFind Someone Who Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 9018Gihan Al HawaryNo ratings yet
- Soon Heng (01.03-15.03.2023) Soa PDFDocument2 pagesSoon Heng (01.03-15.03.2023) Soa PDFSicklyangel LokeNo ratings yet
- Ventureshield™ Paint Protection Film 7510Cc/Cs-Ld: Technical Data Sheet April 2011Document2 pagesVentureshield™ Paint Protection Film 7510Cc/Cs-Ld: Technical Data Sheet April 2011Димитър ПетровNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary: Answer Key: Unit 1Document2 pagesGrammar Summary: Answer Key: Unit 1OhwayNo ratings yet
- Reclaiming Lalon and His Philosophy: Deho-Totto, Transcendentalism and Our AcademiaDocument71 pagesReclaiming Lalon and His Philosophy: Deho-Totto, Transcendentalism and Our AcademiaSubaNo ratings yet
- SymbolismDocument14 pagesSymbolismchampong05No ratings yet
- Disequilibrium in Balance of PaymentDocument6 pagesDisequilibrium in Balance of PaymentIshant MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Environmental Science Module 5 Lesson 1: MutualismDocument2 pagesAssignment - Environmental Science Module 5 Lesson 1: MutualismJhan RhayNo ratings yet
- Igc Approved FrsDocument9 pagesIgc Approved Frstolomeo10No ratings yet
- Pangasinan State UniversityDocument21 pagesPangasinan State UniversityCarla BaquirinNo ratings yet
- Ankit Kumar Varun - WPR 9Document6 pagesAnkit Kumar Varun - WPR 9ankit varunNo ratings yet
- Sandro BotticelliDocument5 pagesSandro BotticelliGraphic Designer (harshu)No ratings yet
- Del Rosario vs. CA GR No. 115106Document10 pagesDel Rosario vs. CA GR No. 115106Michelle Jude TinioNo ratings yet
- Job DescriptionsDocument6 pagesJob DescriptionsMukund KanojiaNo ratings yet