Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applied Economics Reviewer ST 1
Uploaded by
anastacio.althea.nieva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages1. Economics is the study of how scarce resources are allocated to meet unlimited human wants. It uses concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, and rational decision making to understand and predict economic behavior.
2. Key economic systems include free markets, where supply and demand dictate resource allocation, and command economies where the government controls resources. Most modern economies use a mixed system.
3. Applied economics uses tools like production possibility curves to illustrate concepts like opportunity cost and tradeoffs involved in allocating resources between alternatives.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Economics is the study of how scarce resources are allocated to meet unlimited human wants. It uses concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, and rational decision making to understand and predict economic behavior.
2. Key economic systems include free markets, where supply and demand dictate resource allocation, and command economies where the government controls resources. Most modern economies use a mixed system.
3. Applied economics uses tools like production possibility curves to illustrate concepts like opportunity cost and tradeoffs involved in allocating resources between alternatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesApplied Economics Reviewer ST 1
Uploaded by
anastacio.althea.nieva1. Economics is the study of how scarce resources are allocated to meet unlimited human wants. It uses concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, and rational decision making to understand and predict economic behavior.
2. Key economic systems include free markets, where supply and demand dictate resource allocation, and command economies where the government controls resources. Most modern economies use a mixed system.
3. Applied economics uses tools like production possibility curves to illustrate concepts like opportunity cost and tradeoffs involved in allocating resources between alternatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Economics Scarcity
CONCEPTS TO REMEMBER ECONOMIC
Study of social behavior guiding in the allocation of scarce QUESTIONS
resources to meet the unlimited needs and desires of the ● Requires people to make choices when choosing
society 1. Unlimited Human Wants 1. How to the resources that they wish to own or utilize
- ADAM SMITH and Needs (concept of Produce? ● Uses the concept of Rationality to predict the
● As Social Science scarcity) 2. What to actions or behavior of people
- How societies tackle the fundamental 2. Economic Resources and Produce?
Factors of Production: 3. For whom
challenge of balancing the insatiable Opportunity cost
Land(natural occurrence to
desires of individuals with the scarce resources), Labor (human produce? - Evident effect of scarcity
resource available inputs), Capital(man-made - What you sacrifice in return for something
factor of production), - Compelled to choose between 2 options
● As Applied Science Entrepreneurship(all things - represents the value of the next best alternative
- Applying economic theories, models. combined) that must be sacrificed when a choice is made
Principles, and concepts to understand and - often expressed in terms of the benefits, profits, or
predict outcomes ECONOMIC SYSTEMS value that could have been obtained if the
Scopes of Economics resources were used differently
● Demographics Free Market — TRADE OFF - the idea that in order to gain
● Labor -No Intervention from the government something, you must give up something else
● Agricultural - Individual resources, and answers 3 economic question
● History - wide variety of products available ASSUMPTIONS
● Monetary - Competition and self-interest work together to regulate the
● Development economy Rationality
● Education - that individuals, firms, or economic agents make
● Engineering Command Economic System decisions that maximize their overall well-being or
● Financial Health - Centrally planned economy utility
● Public - Government owns all resources and responsible - expected to weigh the costs and benefits of their
for allocating it decisions and choose the option that maximizes
- Everybody gets the same thing their satisfaction
Approaches in Applied Economics: Profit Maximization
- Use of econometrics Mixed Economic System - goal of maximizing the financial profit through
- Input-Output Analysis - Economic questions are both answered by the production & pricing
- Historical Analogy government and private entities in consideration of – Individuals :: maximize UTILITY
- Common-sense or Vernacular their mutual benefit (satisfaction)
– Firms :: maximize PROFIT (financial
gain)
Althea N. Anastacio REVIEWER ST 1 ECON
characteristics or behavior of individual COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE(LOWER OPP.COST)
PERFECT INFORMATION parts Ability of a country to produce goods/services for a lower
- Consumers have access to complete and accurate 4. Sweeping Generalization opportunity cost than other
market info. - overly general (simplified) statement about COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE (BETTER VALUE)
CETERIS PARIBUS a group, category, or situation based on refers to the unique strengths, attributes, or capabilities that
- Isolating the impact of one variable while assuming limited or insufficient evidence, presenting give a business or entity an edge over its competitors in the
all other relevant factors remain constant for it as a rule. marketplace
analysis ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE
- ALL THINGS BEING EQUAL UTILITY AND APPLICATION OF APPLIED ECONOMICS Anything a country does more efficiently than other
- used to isolate the effect of a single variable while TO ECONOMIC PROBLEMS/ ISSUES countries.
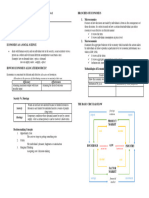
keeping other relevant factors unchanged ● Production Possibility Graph (PPG) - E.g. Countries that are blessed with Natural
- illustrate the concept of opportunity cost Resources/ abundance of resources or something
FALLACY and resource allocation innate to a business or country
Errors in judgment / conclusions due to faulty reasoning
1. Failure to hold thing constant under Ceteris ● Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
Paribus - the boundary of what an economy can
- occurs when someone makes a faulty produce with its existing resources and
argument by ignoring the principle of technology
ceteris paribus ● Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
- occurs when changes in one variable are - a graphical depiction of the PPF, showing
incorrectly attributed to another variable the trade-offs between two specific goods
without considering the influence of other or services
relevant factors that may have changed
simultaneously 4 KEY ASSUMPTIONS
2. Post Hoc (false cause) 1. Only Two Goods Can Be Produced: focusing on
- or post hoc ergo propter hoc, is a fallacy of two allows for a clear and illustrative analysis of
assuming that because one event occurred trade-offs and opportunity costs
after another, the first event must have 2. Full Employment of Resources: implies that all
caused the second. available resources, such as labor, capital, and
3. Fallacy of Composition land, are being used efficiently in the economy
- occurs when someone erroneously 3. Fixed Resources: the quantity and quality of
assumes that what is true for one part of a productive resources remain constant over the
whole must be true for the whole period of analysis
- involves making generalizations about an 4. Fixed Technology: technologies used for
entire group or system based on the production do not change during the analysis
Althea N. Anastacio REVIEWER ST 1 ECON
You might also like
- Brene Brown On VulnerabilityDocument6 pagesBrene Brown On Vulnerabilitymeili_siaw88% (8)
- Econ 100.1 - ReviewerDocument34 pagesEcon 100.1 - ReviewerLianne Angelico Depante100% (1)
- Prime Numbers and Primality TestsDocument23 pagesPrime Numbers and Primality TestsPritiJhaNo ratings yet
- IB Economics Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesIB Economics Chapter 1 NotesPauline OngchanNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Economics As A Social Science and As Applied ScienceDocument6 pagesApplied Economics: Economics As A Social Science and As Applied ScienceCRYSTAL CLAIRE PORRASNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument8 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerSharky RoxasNo ratings yet
- Salazar v. CFIDocument2 pagesSalazar v. CFILouie BruanNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerAevan Joseph100% (1)
- A Comparative Approach To Email Classification Using Naive Bayes Classifier and Hidden Markov ModelDocument6 pagesA Comparative Approach To Email Classification Using Naive Bayes Classifier and Hidden Markov ModeleswarlalmechNo ratings yet
- Economics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDocument11 pagesEconomics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDo KyungsoooooNo ratings yet
- Adam Smith - Basic Economic Concepts - o Needs - o Wants - : RENT - Payment For LandDocument5 pagesAdam Smith - Basic Economic Concepts - o Needs - o Wants - : RENT - Payment For LandBaluyut, Kenneth Christian O.No ratings yet
- What ECONOMICSDocument3 pagesWhat ECONOMICSLalisa ManobangsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MTPDocument5 pagesReviewer MTPMark Jason PinedaNo ratings yet
- PE NotebookDocument26 pagesPE NotebookNguyễn Hoàng ThơNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics IB HL Study GuideDocument41 pagesMicroeconomics IB HL Study GuideSara YokoyamaNo ratings yet
- Manecon NotesDocument78 pagesManecon Notesscholta00No ratings yet
- AP Chapter1 Less 2Document2 pagesAP Chapter1 Less 2Hannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- 1st CEC ReviewerDocument3 pages1st CEC ReviewerFeiNo ratings yet
- Economics ReviewerDocument7 pagesEconomics ReviewerLANANo ratings yet
- AP Chapter 1 Less 1Document4 pagesAP Chapter 1 Less 1Hannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Man Econ ReviewerDocument6 pagesMan Econ Reviewerruth san joseNo ratings yet
- Economics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsPatricia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Handout Economics 2018-EditionDocument12 pagesHandout Economics 2018-EditionClaide Vencent Arendain-Cantila DesiertoNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument11 pagesManagerial Economics423003597No ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument9 pagesApplied EconomicsAC Artiga ChristianNo ratings yet
- ECON 101 - EconomicsDocument6 pagesECON 101 - EconomicsAnne LunaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument13 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerKeiNo ratings yet
- Caie As Economics 9708 TheoryDocument15 pagesCaie As Economics 9708 TheoryMasimba MafukidzeNo ratings yet
- Employment Investment Income General Level of Prices/pricingDocument4 pagesEmployment Investment Income General Level of Prices/pricingKirstenNo ratings yet
- MANECONDocument13 pagesMANECONMae AsprecNo ratings yet
- Production and Distribution ACTIVITIES To Attain The Material Survival Stability and Growth of Any Society.Document2 pagesProduction and Distribution ACTIVITIES To Attain The Material Survival Stability and Growth of Any Society.mastery90210No ratings yet
- Micro 1to3 English ColourDocument13 pagesMicro 1to3 English Colourhanoonaa786No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Introduction To Microeconomics: Limits, Alternatives, and ChoicesDocument7 pagesManagerial Economics Introduction To Microeconomics: Limits, Alternatives, and ChoicesYsza Gian VispoNo ratings yet
- CIE As Economics Notes FinalDocument15 pagesCIE As Economics Notes Finalbeditanisha6No ratings yet
- Economic Systems Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesEconomic Systems Advantages and DisadvantagesKiano GrantNo ratings yet
- MGT1105 Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesMGT1105 Midterm ReviewerBlanche Carey AbonNo ratings yet
- Memory Aid in Management Advisory Services: EconomicsDocument10 pagesMemory Aid in Management Advisory Services: EconomicsAlbert MorenoNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesManagerial EconomicsIssabellaViktoriaMalezaLumantasNo ratings yet
- What Is ECONOMICS?: Chapter 1: Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceDocument3 pagesWhat Is ECONOMICS?: Chapter 1: Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceJeanne Grazielle PogataNo ratings yet
- Manecon ReviewerDocument12 pagesManecon ReviewerRIANE PADIERNOSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Microeconomics - Pcbet 22 302aDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Basic Microeconomics - Pcbet 22 302aAGONCILLO SOPIA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Mixed EconomyDocument2 pagesMixed EconomyJasmine Shane RoblesNo ratings yet
- ECO 415 CH 1 IntroDocument22 pagesECO 415 CH 1 IntroMohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Economics: Part I: Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesReviewer in Economics: Part I: Definition of TermsjenNo ratings yet
- BM101 Notes For PrelimDocument4 pagesBM101 Notes For PrelimEmily ResuentoNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Basic MicroDocument4 pagesLec1 Basic MicroNichole LabradorNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basic Concepts and PrinciplesDocument35 pages1 - Basic Concepts and Principlessanthosh sNo ratings yet
- (Reviewer For Prelims) Managerial EconomicsDocument14 pages(Reviewer For Prelims) Managerial EconomicsMicah Danielle S. TORMONNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - LessonDocument8 pagesManagerial Economics - LessonCrystal ApinesNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesManagerial Economics ReviewerDrieya KadiNo ratings yet
- Economics HandoutDocument18 pagesEconomics HandoutCarlos WebsterNo ratings yet
- Ev1CastilloAndrade 3aiDocument2 pagesEv1CastilloAndrade 3aiMariaNo ratings yet
- Eco ReviewerDocument35 pagesEco ReviewerNineteen AùgùstNo ratings yet
- SSM107 Lec 1Document3 pagesSSM107 Lec 1Ma. Krecia NicolNo ratings yet
- Economics - 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument4 pagesEconomics - 3rd Quarter ReviewerDRIFT KMGNo ratings yet
- Be 313 Week 1-3Document6 pagesBe 313 Week 1-3eri keiNo ratings yet
- Mic CH1 1Document11 pagesMic CH1 1Poona RasanNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity CostDocument4 pagesCircular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity Costadam_barrettoNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument3 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerEndeavorMakioNo ratings yet
- Econ System ModelDocument4 pagesEcon System ModelJhon Cristopher AngNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument154 pagesMicrobsdkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document1 pageLesson 1KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Hannah Lane SubongNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsFrom EverandThe Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Taped Interview With Corporal Al OteroDocument11 pagesTaped Interview With Corporal Al OterohsmathersNo ratings yet
- Spanish 2 Diagnostic Exam Answer Sheet: Me Llamo: - ClaseDocument2 pagesSpanish 2 Diagnostic Exam Answer Sheet: Me Llamo: - ClaseJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Women, Leadership, and Empowerment: UniversityDocument14 pagesWomen, Leadership, and Empowerment: Universityedo Tegar SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Capital Markets in IndiaDocument7 pagesEvolution of Capital Markets in Indiaanon_473668362100% (1)
- Cuuc70x To Nw740Document6 pagesCuuc70x To Nw740asomuncu1886No ratings yet
- Mary Parker Follett BiographyDocument1 pageMary Parker Follett Biographypankhil_maruNo ratings yet
- MUST TO KNOW CC RODRIGUEZ Flashcards - QuizletDocument32 pagesMUST TO KNOW CC RODRIGUEZ Flashcards - QuizletWho KnowsNo ratings yet
- Bulletin For 16th Sunday in Ordinary TimeDocument4 pagesBulletin For 16th Sunday in Ordinary TimeSt Patricks ChurchNo ratings yet
- E500 FD Rel11 Part1 OverviewDocument35 pagesE500 FD Rel11 Part1 OverviewЖорж КаназирскиNo ratings yet
- FCAT Mathematics Sample Questions: Grade 6Document16 pagesFCAT Mathematics Sample Questions: Grade 6David FournierNo ratings yet
- Acebedo - Optical - Co. - Inc. - v. - Court - of - AppealsDocument31 pagesAcebedo - Optical - Co. - Inc. - v. - Court - of - AppealsAtheena Marie PalomariaNo ratings yet
- QFD Applied To LibraryDocument15 pagesQFD Applied To LibraryUmesh VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Superlative Media: MusicDocument1 pageSuperlative Media: MusicRoberta AvatiNo ratings yet
- Press Release Hit and RunDocument2 pagesPress Release Hit and RunAnthony_Smith4792No ratings yet
- Listening ExercisesDocument4 pagesListening ExerciseslupsumetroNo ratings yet
- Syntel 10kDocument143 pagesSyntel 10kTara MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Involvement in SyphilisDocument6 pagesPulmonary Involvement in SyphilisVijayesh MokalNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan (Hypertension)Document1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan (Hypertension)octoberttwentythreeNo ratings yet
- 3.1st Year Main PDFDocument5 pages3.1st Year Main PDFSakibul Alom KhanNo ratings yet
- Prueba de Acceso A Estudios Universitarios (Logse) : Too Much TelevisionDocument2 pagesPrueba de Acceso A Estudios Universitarios (Logse) : Too Much TelevisionYvonne CarlileNo ratings yet
- Egkjk"V! VKJKSX Fokku Fo - Kihb) Ukf'AdDocument12 pagesEgkjk"V! VKJKSX Fokku Fo - Kihb) Ukf'AdunderwinefxNo ratings yet
- REVIEW - Solving The Social Dilemma TogetherDocument6 pagesREVIEW - Solving The Social Dilemma Togethermatthewjamesdennis12No ratings yet
- Crime and PunishmentDocument4 pagesCrime and PunishmentEliana GodoyNo ratings yet
- State of The Art in The Control of Inclusions During Steel Ingot CastingDocument29 pagesState of The Art in The Control of Inclusions During Steel Ingot Castinggaurav vermaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document12 pagesLesson 6Debayn OliquianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document62 pagesChapter 3Amira FawzyNo ratings yet