Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document
Uploaded by
Chonghua Tan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesDocument
Uploaded by
Chonghua TanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
In recent years, educational research has shown a growing interest
in exploring various teaching and learning strategies that can optimize
knowledge retention. One such approach that has gained considerable
attention is the implementation of peer-to-peer learning. Peer-to-peer
learning is a collaborative educational strategy that allows students to
actively engage with their peers, sharing knowledge, experiences, and
perspectives in an interactive and supportive environment.
In the context of computer system servicing, where the
rapid advancement of technology necessitates continuous
learning, the effectiveness of knowledge retention is of utmost
importance. By investigating the impact of peer-to-peer
learning in this specific domain, educators and researchers
can gain insights into the potential benefits and limitations of
this strategy and its influence on long-term knowledge
retention.
We chose this study because it deals with the potential
benefits of peer-to-peer learning in improving knowledge
retention, particularly in the field of computer system
servicing. This topic is essential because it explores an
alternate strategy for learning that has the potential to
improve what students learn in a practical and technical
setting. By studying the variety of aspects of peer-to-peer
learning, this study intends to provide beneficial insights into
the effectiveness of this strategy and its potential benefits for
individuals studying computer system service.
Peer-to-peer learning is a system where people share knowledge
and skills with one another, usually in an unorganized or decentralized
way. It involves peers or people with comparable degrees of experience
exchanging ideas, skills, and expertise Peer learning takes place among
group of individuals with the same status who interact one another
(Keerthirathne, 2020).
This learning often takes place outside of a formal educational
context and can be implemented through a variety of activities,
including group talks, study sessions, mentoring relationships, and team
projects. It places a focus on engaged involvement, teamwork, and the
sharing of various viewpoints and thoughts among peers. This approach
is useful when working with international students to develop their
independence as learners and to share their knowledge with their peers
(Williamson, 2018).
The primary objective of this research is to measure and evaluate
the effect of the peer-to-peer learning strategy on enhancing knowledge
retention in computer system servicing. This research aims to shed light
on whether peer-to-peer learning can effectively supplement traditional
instructional methods to improve the retention of technical knowledge
and skills. Additionally, the study will explore the factors that contribute
to the success of peer-to-peer learning in this context, such as
communication strategies, collaborative problem-solving, and student
engagement.
To achieve these objectives, this research will employ a mixed-
methods approach, integrating quantitative assessments and qualitative
feedback from participants. By combining these methods, a
comprehensive understanding of the impact of peer-to-peer learning on
knowledge retention can be obtained, encompassing both measurable
outcomes and subjective experiences.
Overall, this study aims to contribute to the existing body of
knowledge on effective educational strategies by examining the potential
of peer-to-peer learning in enhancing knowledge retention in computer
system servicing. The findings of this research have implications for
educational institutions, curriculum developers, and instructional
designers, providing evidence-based insights to improve pedagogical
practices and support students in their journey to becoming proficient
computer system servicing professionals.
You might also like
- UGC NET Psychology SyllabusDocument5 pagesUGC NET Psychology Syllabuskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To PsychologyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To PsychologyMel P. ManaloNo ratings yet
- Journal Article CritiqueDocument5 pagesJournal Article CritiqueMunira MusLiim75% (4)
- Master 1 - Final Oral Test - Type B - Teacher SDocument5 pagesMaster 1 - Final Oral Test - Type B - Teacher SAna Caroline santosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Grade 10 - Types of TextDocument4 pagesLesson Plan For Grade 10 - Types of TextMam Shiellan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Let ExamDocument4 pagesReviewer Let ExamMyca Ramos80% (5)
- Researc Title and IntroDocument12 pagesResearc Title and Introarchie A. EscasinasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VDocument11 pagesCHAPTER Vmanikandan swaminathanNo ratings yet
- Uma 1Document5 pagesUma 1PGP COENo ratings yet
- Learning Analytics For Student Success: Future of Education in Digital EraDocument9 pagesLearning Analytics For Student Success: Future of Education in Digital EraZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Digital GameDocument7 pagesEffects of Digital GameFirjaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Modular KitchenDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Modular Kitchenfvf2j8q0100% (1)
- Bolliger 2018Document17 pagesBolliger 2018Lê Thị Thảo Linh - Khoa Ngoại ngữ kinh tếNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis Methodological ApproachDocument10 pagesMaster Thesis Methodological Approachafbtbakvk100% (1)
- Uma MaheswariDocument4 pagesUma MaheswariPGP COENo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument6 pagesResearch Methodologyà S ÀdhìkãríNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cooperative Learning Model Type Group Investigation Assisted Phet To Students' Conceptual KnowledgeDocument6 pagesEffect of Cooperative Learning Model Type Group Investigation Assisted Phet To Students' Conceptual KnowledgeRAT CreatorNo ratings yet
- Thesis Synopsis ProformaDocument8 pagesThesis Synopsis Proformatayyaba_sNo ratings yet
- A Learning and Teaching Model Using Project-Based Learning (PBL) On The Web To Promote Cooperative LearningDocument9 pagesA Learning and Teaching Model Using Project-Based Learning (PBL) On The Web To Promote Cooperative LearningNenden Nur AeniNo ratings yet
- BS EducationDocument11 pagesBS EducationGhazanfar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Effective Teaching StrategiesDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Effective Teaching Strategiesfyswvx5b100% (1)
- Measuring Cognitive Load and Cognition: Metrics For Technology Enhanced LearningDocument36 pagesMeasuring Cognitive Load and Cognition: Metrics For Technology Enhanced LearningNaina SethNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Learning Improves Student Outcomes in Textile CourseDocument5 pagesHybrid Learning Improves Student Outcomes in Textile CourseRose Yan JiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Carla Bianca CuencoDocument10 pagesWorksheet 1 Carla Bianca CuencoCarla Bianca CuencoNo ratings yet
- Research 787878Document10 pagesResearch 787878onewayticketNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument18 pagesPractical ResearchSofia PatigdasNo ratings yet
- Natsis 2 K 18Document19 pagesNatsis 2 K 18Leah Erica VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Obenza FN TMA3Document7 pagesObenza FN TMA3Elsie PascualNo ratings yet
- Research CasimDocument7 pagesResearch CasimRemson B. AutilloNo ratings yet
- 10 1111@bjet 12212Document14 pages10 1111@bjet 12212DANY LOPEZ GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- PR - 2 - Chapter - 1 (1) - For MergeDocument7 pagesPR - 2 - Chapter - 1 (1) - For MergeLYNNEL GUIRITANNo ratings yet
- Tech For Personalized Learning & Better Student OutcomesDocument8 pagesTech For Personalized Learning & Better Student Outcomesplsse 2022No ratings yet
- IGI - Revised - Manuscript CleanCopy With TablesDocument40 pagesIGI - Revised - Manuscript CleanCopy With TablesFlorin CojocaruNo ratings yet
- Ej 1264408Document19 pagesEj 1264408api-581773260No ratings yet
- Supporting Participants in Web-Based Collaborative Learning Activities From A Holistic Point of View: A Tale of Seven Online and Blended CoursesDocument28 pagesSupporting Participants in Web-Based Collaborative Learning Activities From A Holistic Point of View: A Tale of Seven Online and Blended CoursesreymertaNo ratings yet
- IS20150 Critical Appraisal of ResearchDocument12 pagesIS20150 Critical Appraisal of Researchnosferatuwarrior4No ratings yet
- The Effect of Computer Mediated Conferencing and Computer Assisted Instruction On Student Learning OutcomesDocument22 pagesThe Effect of Computer Mediated Conferencing and Computer Assisted Instruction On Student Learning OutcomesYulia AstutiNo ratings yet
- 1154 3928 2 PBDocument14 pages1154 3928 2 PBAniMomentsNo ratings yet
- Final Nani Tehh Panabangi Final Mao Nani e PrintDocument35 pagesFinal Nani Tehh Panabangi Final Mao Nani e Printjuliana santosNo ratings yet
- Paper - Action Res.Document8 pagesPaper - Action Res.Jennyvi NapodNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Achievement: Traditional Instruction and Technology-Assisted Course Delivery Methods Robert Vilardi & Margaret L. Rice Troy University & The University of AlabamaDocument13 pagesMathematics Achievement: Traditional Instruction and Technology-Assisted Course Delivery Methods Robert Vilardi & Margaret L. Rice Troy University & The University of AlabamaHanzel DomensNo ratings yet
- PR 2 Chapter 1Document14 pagesPR 2 Chapter 1LYNNEL GUIRITANNo ratings yet
- EDTECH 504 - Annotated Bibliography AssignmentDocument11 pagesEDTECH 504 - Annotated Bibliography AssignmentThomas RobbNo ratings yet
- KainatDocument3 pagesKainatAsma YunusNo ratings yet
- Infedu 19 3 Infe2020 - 3 - 17Document38 pagesInfedu 19 3 Infe2020 - 3 - 17BarthoBarcelosNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Teaching-Learning Process in Online Education As Perceived by University Faculty and Instructional Technology ProfessionalsDocument11 pagesThe Effectiveness of Teaching-Learning Process in Online Education As Perceived by University Faculty and Instructional Technology ProfessionalsHenry James NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Blended Learning DesignDocument8 pagesLesson 6 Blended Learning DesignLou TraveroNo ratings yet
- Developing A Comprehensive Perspective On Educational Technology IntegrationDocument4 pagesDeveloping A Comprehensive Perspective On Educational Technology IntegrationLei Paghinayan. PoNo ratings yet
- Blended LearningDocument16 pagesBlended LearningKartik KumarNo ratings yet
- JPSP 2022 107Document8 pagesJPSP 2022 107connie batucanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Chat GPT On Learning MotivationDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Chat GPT On Learning Motivation1987 - Võ Thị Xuân Nhi - NCTNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Effectiveness ofDocument20 pagesAssessment of Effectiveness ofDr. M Nadarajan A/L Manickam IPGK KeningauNo ratings yet
- Computer Supported Collaborative LearningDocument2 pagesComputer Supported Collaborative LearningshahidNo ratings yet
- A Student Grouping Method For Massive Online CollaborativeDocument16 pagesA Student Grouping Method For Massive Online CollaborativeNi Nyoman ParwatiNo ratings yet
- Extended AbstractDocument4 pagesExtended AbstractAnneNo ratings yet
- Effects of Using Blended Learning in Relationship Between Student Characteristic, Design Features and OutcomesDocument4 pagesEffects of Using Blended Learning in Relationship Between Student Characteristic, Design Features and OutcomesNario Bedeser GemmaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography FinalDocument16 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Finalapi-488129500No ratings yet
- Teaching Techniques in Automobile IndustryDocument3 pagesTeaching Techniques in Automobile Industryindrajit1980No ratings yet
- Group Learning Strategies For Online Course: Lih-Juan Chanlin, & Kung-Chi ChanDocument5 pagesGroup Learning Strategies For Online Course: Lih-Juan Chanlin, & Kung-Chi ChaniwanhpNo ratings yet
- Learning Management Systems Annotated BibliographyDocument7 pagesLearning Management Systems Annotated BibliographyAshley Bonte100% (1)
- 2020 Malekgorji Edcation Article TP and CRSDocument17 pages2020 Malekgorji Edcation Article TP and CRStaher hatahetNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Blended Learning in Improving Students' Achievement in Third Grade's Science in Bani KenanaDocument8 pagesThe Effectiveness of Blended Learning in Improving Students' Achievement in Third Grade's Science in Bani KenanaAaron AsneNo ratings yet
- SR CSCLDocument7 pagesSR CSCLSahat MaruliNo ratings yet
- 34026-Texto Del Artículo-96950-6-10-20221215Document20 pages34026-Texto Del Artículo-96950-6-10-20221215Anonymous HUY0yRexYfNo ratings yet
- Using Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveFrom EverandUsing Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveNo ratings yet
- CBT Psychoeducation - GuideDocument9 pagesCBT Psychoeducation - Guideojasvikaul23No ratings yet
- 5late Childhood Development PowerPoint PresentationDocument13 pages5late Childhood Development PowerPoint PresentationDanilo BrutasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DesignDocument45 pagesCurriculum Designandrie sajarah salilamaNo ratings yet
- Sumara Gaspar - How To Study LanguagesDocument11 pagesSumara Gaspar - How To Study Languagesapi-572157085No ratings yet
- TEFL. Unit 4. AssignmentDocument7 pagesTEFL. Unit 4. AssignmentSiroj SuxrobovNo ratings yet
- 7 MandelaEffectDocument3 pages7 MandelaEffectagra hidayatNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Burgos GustavoDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Burgos GustavoVillar BurgosNo ratings yet
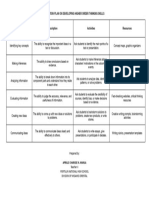
- Action Plan On Developing Higher Order Thinking SkillsDocument1 pageAction Plan On Developing Higher Order Thinking SkillsAprille Charisse ManlaNo ratings yet
- Airey, J. & Cedric Linder 2008 Bilingual Scientific Literacy The Use of English Inswedish University Science CoursesDocument18 pagesAirey, J. & Cedric Linder 2008 Bilingual Scientific Literacy The Use of English Inswedish University Science CoursesChristian XavierNo ratings yet
- Teaching Visually Impaired StudentsDocument3 pagesTeaching Visually Impaired StudentsEllen Mae Roldan GicoleNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Proficiency and Learning Engagement of Grade 11 Students in EnglishDocument106 pagesOral Communication Proficiency and Learning Engagement of Grade 11 Students in EnglishGeffrey S. QuilalaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Reading at Elsie Lund SchoolDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Reading at Elsie Lund SchoolLouise Mikylla LimNo ratings yet
- Template Tosia 2022 2023Document8 pagesTemplate Tosia 2022 2023Hanz paul IguironNo ratings yet
- Edu 259 p1 Prof Ed Edu 259 p1 Prof EdDocument92 pagesEdu 259 p1 Prof Ed Edu 259 p1 Prof EdkriztheiaaveriennenievesNo ratings yet
- Digitalcommons@Hamline Digitalcommons@HamlineDocument92 pagesDigitalcommons@Hamline Digitalcommons@HamlineMaría José CastroNo ratings yet
- KE QB Questions OnlyDocument7 pagesKE QB Questions OnlyJohnyNo ratings yet
- Child 390r Guidance Theory Worksheet-2 1Document4 pagesChild 390r Guidance Theory Worksheet-2 1api-709409044No ratings yet
- Memory QuestionnairesDocument55 pagesMemory QuestionnairesOsama ShreefNo ratings yet
- DLP TRENDS Week 9 Climate Change 2Document5 pagesDLP TRENDS Week 9 Climate Change 2Editha RobillosNo ratings yet
- Proponents of Professional Education (LET)Document2 pagesProponents of Professional Education (LET)Pau CortezNo ratings yet
- Parang High SchoolDocument14 pagesParang High SchoolIsidro, Benjamin Joseph A.No ratings yet
- GTD Workflow MapDocument1 pageGTD Workflow Maptfo13516No ratings yet
- 2 Self, Society, and Culture - UTSDocument18 pages2 Self, Society, and Culture - UTSAtalanta LeeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Service Teacher Performance THESIS2018Document63 pagesPre-Service Teacher Performance THESIS2018grasyatubongbanua03171988No ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Pagbibigay NG Komento o Reaksiyon Pagbibigay NG Komento o ReaksiyonDocument10 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Pagbibigay NG Komento o Reaksiyon Pagbibigay NG Komento o Reaksiyonmarife olmedoNo ratings yet