Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preparation # 8 White Ointment
Uploaded by
Ivy Rose Orozco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageThis document discusses the preparation of a white ointment. It begins by defining ointments as semisolid preparations used externally on skin and mucous membranes that are smooth, homogenous and spreadable. It notes they should be free of grittiness and rancidity. The document then discusses the four types of ointment bases - oleaginous, absorption, water-removable and water-soluble bases. It provides examples such as petrolatum and lanolin for the oleaginous base used to prepare the white ointment.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the preparation of a white ointment. It begins by defining ointments as semisolid preparations used externally on skin and mucous membranes that are smooth, homogenous and spreadable. It notes they should be free of grittiness and rancidity. The document then discusses the four types of ointment bases - oleaginous, absorption, water-removable and water-soluble bases. It provides examples such as petrolatum and lanolin for the oleaginous base used to prepare the white ointment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pagePreparation # 8 White Ointment
Uploaded by
Ivy Rose OrozcoThis document discusses the preparation of a white ointment. It begins by defining ointments as semisolid preparations used externally on skin and mucous membranes that are smooth, homogenous and spreadable. It notes they should be free of grittiness and rancidity. The document then discusses the four types of ointment bases - oleaginous, absorption, water-removable and water-soluble bases. It provides examples such as petrolatum and lanolin for the oleaginous base used to prepare the white ointment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
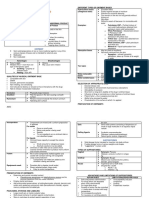
PHARMACEUTICS1L: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and
Medical Devices (Lab)
Ivy Rose C. Orozco, RPh
POST-LABORATORY DISCUSSION
PREPARATION #8
WHITE OINTMENT
Ointments – semisolid preparations used for external
applications on skin and mucous membrane; aka salve or
charisma; homogenous, smooth and free from grittiness
and should be spreadable
- Any sign of rancidity should be subject for
discontinuation
- Unmedicated oint. - Used as protectants, emollients
and lubricants
- Medicated ointment:
Used for topical
therapeutic effects.
Method of Preparation:
1. Mechanical
Incorporation –
levigation; trituration and slabbing with spatula
- Medication will be converted into
impalpable powder then incorporated into
base
2. Fusion – utilizes heat via water bath
Oint. Bases – vehicles for medicated ointments
Four Types of Ointment Bases:
Oleaginous base – non-water washable,
anhydrous and insoluble in water; do not have the
ability to absorb or contain water
Ex: Petrolatum,USP (Vaseline) – yellowish to light
amber unctuous feel; MP: 38-60 deg. C
White Petrolatum,USP (White Vaseline) – decolorized
Yellow Ointment, USP – 50g Yellow wax in 950g
Petrolatum; from honeycomb of Apis mallifera
Other examples: White ointment, lanolin, synthetic
Esther
Absorption base - non-water washable,
anhydrous and ability to absorb water; w/o
emulsions
Ex: petrolatum + wool fat (anhydrous lanolin) –
from the wool of the sheep called Ovis aries
Water-removable base – o/w bases and water
washable bases
Ex: hydrophilic ointment, USP
Water-soluble bases – water washable and
greaseless
Ex: Polyethylene glycol oint.
You might also like
- 7 Dispensing and Incompatibilities Part 2Document9 pages7 Dispensing and Incompatibilities Part 2MARY BERNADETTE EGANANo ratings yet
- C-10 Ointment 2Document90 pagesC-10 Ointment 2Mara Angelica100% (1)
- 10 04Midterm-Note SolutionsDocument9 pages10 04Midterm-Note SolutionsaddiramonaNo ratings yet
- Preparation # 7 Cold CreamDocument2 pagesPreparation # 7 Cold CreamIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- 15.shelke Usha Y. Mahajan Ashish A.Document23 pages15.shelke Usha Y. Mahajan Ashish A.Mahdhun ShiddiqNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide PasteDocument9 pagesZinc Oxide Pastekriss Wong100% (1)
- Dosage FormDocument48 pagesDosage FormbenreuNo ratings yet
- PHM Post Lab Finals PDFDocument39 pagesPHM Post Lab Finals PDFJannet Parica FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ointment: Presentation By: Ms. Krutika H. PardeshiDocument23 pagesOintment: Presentation By: Ms. Krutika H. PardeshiShumaila QadirNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument22 pagesDosage FormsMustafa ShahinNo ratings yet
- L-14 - Ointments, Pastes and JelliesDocument52 pagesL-14 - Ointments, Pastes and Jelliesf20231186No ratings yet
- Cold Cream USPDocument4 pagesCold Cream USPRon OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Topical Drug Delivery SystemsDocument56 pagesLecture 4 - Topical Drug Delivery Systemsapi-3707297100% (14)
- 1) Ointments and Creams .DispensingDocument63 pages1) Ointments and Creams .DispensingMeena Ali100% (1)
- Phardose Lab (Prep 6-10)Document3 pagesPhardose Lab (Prep 6-10)Jan Aira Almazan100% (1)
- 4 - Ointments PDFDocument29 pages4 - Ointments PDFremo s100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Lab Prep 6-18Document7 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Form Lab Prep 6-18Jana EncaboNo ratings yet
- Types of DFDocument48 pagesTypes of DFIdenyi Daniel EwaNo ratings yet
- Liquid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Mr. Naresh Rajgor, Assistant Professor, M.P. Patel College of Pharmacy, KapadwanjDocument39 pagesLiquid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Mr. Naresh Rajgor, Assistant Professor, M.P. Patel College of Pharmacy, KapadwanjatjaiNo ratings yet
- OintmentsDocument4 pagesOintmentsPrince EXENo ratings yet
- 10 04Midterm-Note SolutionsDocument9 pages10 04Midterm-Note SolutionsMoreen BayarcalNo ratings yet
- Liquid Dosage FormsDocument9 pagesLiquid Dosage FormsRama MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument39 pagesDosage FormsEyasuNo ratings yet
- Powders SuppositoriesDocument5 pagesPowders SuppositoriesSofiaRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial One: Routes of Drugs Administration&Dosage FormsDocument53 pagesTutorial One: Routes of Drugs Administration&Dosage FormsNarcissusNo ratings yet
- Liquid Dosage FormsDocument39 pagesLiquid Dosage Formsuma padmarajNo ratings yet
- PDDS Finals PostLabDocument54 pagesPDDS Finals PostLabjohnleedeguzman1230No ratings yet
- Dosages FormsDocument30 pagesDosages FormsDaksh KambojNo ratings yet
- A-Gaseous Dosage Forms:: AerosolsDocument16 pagesA-Gaseous Dosage Forms:: Aerosolsعلاوي البرشلوني100% (1)
- Activity 4 - White Ointment 2021Document3 pagesActivity 4 - White Ointment 2021MENDEZ ALYSSANo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Forms Deliv System 10 11Document42 pagesDrug Dosage Forms Deliv System 10 11Muhammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Assignment NEW1Document30 pagesPharma Assignment NEW1Amanuel TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage Form Part 1Document48 pagesSolid Dosage Form Part 1Claire Marie AlvaranNo ratings yet
- Semi-Solid Dosage Form: T. N. Saifullah S Laboratorium Teknologi Farmasi Fakultas Farmasi UGMDocument96 pagesSemi-Solid Dosage Form: T. N. Saifullah S Laboratorium Teknologi Farmasi Fakultas Farmasi UGMJuan LambeyNo ratings yet
- Types of Dosage Forms Lecture2,2Document34 pagesTypes of Dosage Forms Lecture2,2Bhuvana TejaNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Dr. Tara A. AbdullaDocument83 pagesSemisolid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Dr. Tara A. AbdullaEman Aziz100% (1)
- Pharmacology 0615 PDFDocument89 pagesPharmacology 0615 PDFWRONGHEARNo ratings yet
- Ointment Cream GelDocument13 pagesOintment Cream Gelprinceamit100% (1)
- Liniments-Tdmuv 1708132802570Document11 pagesLiniments-Tdmuv 1708132802570pearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- Ointments: Prodi Farmasi Universitas MalahayatiDocument35 pagesOintments: Prodi Farmasi Universitas MalahayatiAulia Fitri Handayani SiregarNo ratings yet
- Dosage Forms 2Document4 pagesDosage Forms 2Kawtar MenjraNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Various Cosmetic and Dental ProductDocument42 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Various Cosmetic and Dental ProductMarcelo Partes de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Topical Preparations Ointments Creams Pastes Gels Liniments and Lotions Suppositories and Pessaries Nasal Preparations Ear Preparations NoteskartsDocument5 pagesTopical Preparations Ointments Creams Pastes Gels Liniments and Lotions Suppositories and Pessaries Nasal Preparations Ear Preparations NoteskartsSalna Susan AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Ointments Creams and Gels PhardoseDocument8 pagesOintments Creams and Gels PhardoseAlec LimNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage Forms - Ointments, Pastes and JelliesDocument46 pagesSemisolid Dosage Forms - Ointments, Pastes and JelliesKhushbooNo ratings yet
- LINIMENTS ImmersionDocument6 pagesLINIMENTS ImmersionAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Semi-Solid Dosage Forms: OintmentDocument12 pagesSemi-Solid Dosage Forms: OintmentYanieNo ratings yet
- Oral Solution I.E SpiritDocument27 pagesOral Solution I.E SpiritQaswar aliNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage Forms: OintmentsDocument31 pagesSemisolid Dosage Forms: OintmentsHisham AlhirereNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous OintmentsDocument25 pagesHomogeneous OintmentsAh BoonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Cream Production SystemDocument48 pagesLiquid Cream Production SystemUMIE UMAIRA KM-PelajarNo ratings yet
- Semi-Solid Medicinal PreparationsDocument20 pagesSemi-Solid Medicinal Preparationsayushbhardwaj181820No ratings yet
- Unit OintmentDocument39 pagesUnit OintmentEE KMNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils For Dogs: Safe And Easy Aromatherapy Remedies For Fleas, Ticks, Internal Or External Troubles, Emotional Issues And Other Common Canine AilmentsFrom EverandEssential Oils For Dogs: Safe And Easy Aromatherapy Remedies For Fleas, Ticks, Internal Or External Troubles, Emotional Issues And Other Common Canine AilmentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Recipes: The Complete Guide, Health, Healing, Anti Aging, And Beauty Reference Over 700 Essential Oils Recipes Inclusive. (Essential Oils Recipes For Beginners....Aromatherapy Book)From EverandEssential Oil Recipes: The Complete Guide, Health, Healing, Anti Aging, And Beauty Reference Over 700 Essential Oils Recipes Inclusive. (Essential Oils Recipes For Beginners....Aromatherapy Book)No ratings yet
- Essential Oils for Dogs: Easy and Safe Essential Oil Recipes to Keep Your Dog Healthy and HappyFrom EverandEssential Oils for Dogs: Easy and Safe Essential Oil Recipes to Keep Your Dog Healthy and HappyNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils For Weight Loss: A Simple Guide and Introduction to Aromatherapy: Essential Aromatherapy Oils For Natural BeautyFrom EverandEssential Oils For Weight Loss: A Simple Guide and Introduction to Aromatherapy: Essential Aromatherapy Oils For Natural BeautyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- PHARCHEM4 Final ExamDocument4 pagesPHARCHEM4 Final ExamIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- PHARCHEM4 Midterm ExamDocument1 pagePHARCHEM4 Midterm ExamIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Tablet TrituratesDocument8 pagesActivity 8 Tablet TrituratesIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Unit III. Group Properties of ElementsDocument36 pagesUnit III. Group Properties of ElementsIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesAtomic TheoryIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Molded Solids: PillsDocument11 pagesActivity 9 Molded Solids: PillsIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Molded Solids: Troches and PastillesDocument18 pagesActivity 10 Molded Solids: Troches and PastillesIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 GranulationDocument18 pagesActivity 7 GranulationIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Midterms RHEOLOGY Learning PacketDocument3 pagesMidterms RHEOLOGY Learning PacketIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Preparation #1 Divided PowdersDocument23 pagesPreparation #1 Divided PowdersIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Preparation #3 Paracetamol TabletsDocument17 pagesPreparation #3 Paracetamol TabletsIvy Rose OrozcoNo ratings yet