Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L2 Drivenresponse RLRC
Uploaded by
Asj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views31 pagesOriginal Title
_'L2drivenresponseRLRC'
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views31 pagesL2 Drivenresponse RLRC
Uploaded by
AsjCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 31
A RECAP ON SOURCE-FREE RESPONSE: (natural response or zero input response)
Procedure to get natural response of RL, RC circuits
1. Find the equivalent circuit (simplify the circuit to Req and C or Req and L).
2. Find the initial conditions: initial current I0 through the equivalent inductor (or initial
voltage V0 across the equivalent capacitor).
3. Find the time constant of the circuit by the values of the equivalent R and L (or C)
4. Write the equation for the solution (iL(t) or vc(t)).
5. Other variables can then be computed based on the circuit connection
iL(t)= I0 e-t/τ where τ=L/Req.
(or vC(t)=V0 e-t/τ where τ=Req.C in an R-C circuit)
Driven or Forced response of RL and RC circuits
The source may be a Step function or a ramp or a
sinusoidal function of time.
The response of a given circuit depends on the type
of input. Here we consider zero initial conditions to
understand the forced or driven response alone,
with zero initial energy.
This response is also known as zero state response
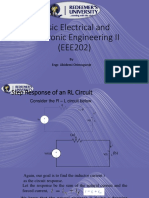
The Step Response of RL and RC Circuits
The Step reponse is the response of a circuit to the sudden
application of a constant voltage or current source, describing the
charging behavior of the circuit.
Step (charging) response and natural (discharging) response show
how the signal in a digital circuit switches between Low and High with
time.
Continuous-Time Unit Step Signal
The unit step signal which is defined for every instant of time is
known as continuous-time unit step signal. The continuous-time
unit step signal is denoted by u(t).
Mathematically, the continuous-time unit step signal u(t) is defined
as follows −
Other forms of unit step function
Driven response of a RC circuit with zero initial condition {Vc(0) is zero.}
Note: inductor voltage: a) 0 V, b)-40V, c) 0 V and d) -22V
31st May
You might also like
- RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesRL RC CircuitDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- RC and RL CircuitsDocument17 pagesRC and RL CircuitsManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Step Response LABDocument6 pagesStep Response LABGanesh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: First-Order CircuitsDocument22 pagesCircuit Theory: First-Order Circuitsmalek992No ratings yet
- RC and RL Circuits - FRDocument23 pagesRC and RL Circuits - FRIshtiyaq RafiqiNo ratings yet
- ENA ManualDocument60 pagesENA ManualAbdul Munim100% (1)
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- NA Exp6-RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesNA Exp6-RL RC CircuitakshithadharmasothNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis of CircuitsDocument31 pagesTransient Analysis of CircuitsvsasaankNo ratings yet
- Enginering AnalysisDocument11 pagesEnginering Analysisamr3repy4No ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Lecture Notes Unit 1: Transient AnalysisDocument36 pagesUNIT-1: Lecture Notes Unit 1: Transient AnalysisRamalingeswar JNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of First-Order RL & RC CircuitsDocument60 pagesFundamentals of First-Order RL & RC CircuitsPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Theory Lab Manual GuideDocument68 pagesElectric Circuit Theory Lab Manual GuideDeb Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhDocument40 pagesLecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhTran Quoc PhongNo ratings yet
- Saideep Mukhopadhyay ITDocument19 pagesSaideep Mukhopadhyay ITITSaideep MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronic Engineering II Step ResponseDocument12 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronic Engineering II Step ResponseALABI ABIODUNNo ratings yet
- IEEEDocument13 pagesIEEEMarc Anthony BañagaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument56 pagesElectric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsAlexander_Tir_91570% (1)
- Electric Circuit Analysis: Natural Response of RL CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis: Natural Response of RL CircuitsRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Understanding Natural Response of RC and RL CircuitsDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Natural Response of RC and RL CircuitsCraig PeriNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Exponential DecayDocument9 pagesRC Circuit Exponential DecayBulatovic NemanjaNo ratings yet
- RC, RL, and RLC Circuit TransientsDocument11 pagesRC, RL, and RLC Circuit TransientsEce KayaNo ratings yet
- 241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceDocument14 pages241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceWsma AmswNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Upto 12th MayDocument39 pagesChapter 7 Upto 12th Maycb.en.u4ece22010No ratings yet
- Transient in RC and RL CircuitsDocument10 pagesTransient in RC and RL CircuitsHenok BelaynehNo ratings yet
- First-Order Circuit ADocument42 pagesFirst-Order Circuit ARay Ann RamonNo ratings yet
- Transients DerivationsDocument18 pagesTransients DerivationsWendell NiveraNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 4 FisicaDocument15 pagesLaboratorio 4 FisicaAlejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument68 pagesBee LabwasimchaspraNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesCircuit AnalysisoffnruninNo ratings yet
- 120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab RecordDocument51 pages120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab Recordpappu singhNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady State Circuit Analysis Topic 3Document14 pagesSinusoidal Steady State Circuit Analysis Topic 3dsweetalker100% (1)
- LAB2Document4 pagesLAB2Anya SohailNo ratings yet
- R-L & R-C CircuitsDocument41 pagesR-L & R-C CircuitsAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Analysis NotesDocument111 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis NotesTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocument12 pagesRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- EE5251 Unit 1Document129 pagesEE5251 Unit 1SathyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1KESHAV JHANo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - First-Order CircuitsDocument37 pagesLecture 7 - First-Order CircuitsJalalAlRoumyNo ratings yet
- RL and RC Circuit Time Domain ResponseDocument21 pagesRL and RC Circuit Time Domain ResponseDharamNo ratings yet
- Manual EES451Document33 pagesManual EES451Saikat LayekNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringCharles SandersNo ratings yet
- RC and RL Circuit Time ConstantsDocument11 pagesRC and RL Circuit Time ConstantsMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- Kirchhoffs Rules RL RC NotesDocument4 pagesKirchhoffs Rules RL RC Notesniravgandhi93No ratings yet
- EMT 2334 - First Order cct-25 - 09 - 23Document13 pagesEMT 2334 - First Order cct-25 - 09 - 23Adan BagajaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document4 pagesLab 6JAGADISH TRIPATHYNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier and Smoothing FiltersDocument3 pagesDiode Rectifier and Smoothing Filtersppat2006No ratings yet
- Time Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument21 pagesTime Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsMOHSINALI MOMINNo ratings yet
- ECE 2201 Experiment 1 - 4Document13 pagesECE 2201 Experiment 1 - 4Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EdetedDocument69 pagesChapter 4 EdetedObsinet ObsinetNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)